实战:基于霍夫变换进行线检测
点击上方“AI算法与图像处理”,选择加"星标"或“置顶”
重磅干货,第一时间送达
霍夫变换算法线检测
一、目的
最近,我们发现自己不得不在应用程序中加入文档扫描功能。在做了一些研究之后,我们偶然发现了一篇熊英写的文章,他是Dropbox机器学习团队的成员。该文章介绍了如何Dropbox的的机器学习团队通过强调他们通过去的步骤,并在每个步骤使用的算法来实现他们的文档扫描仪。通过那篇文章,我们了解了一种称为霍夫变换的方法, 以及如何将其用于检测图像中的线条。因此,在本文中,我们想解释Hough变换算法,并提供该算法在Python中的“从头开始”的实现。
二、霍夫变换
Hough变换是Paul VC Hough专利的一种算法,最初是为了识别照片中的复杂线条而发明的(Hough,1962)。自从创建以来,该算法已进行了修改和增强,使其能够识别其他形状,例如特定类型的圆形和四边形。为了了解霍夫变换算法的工作原理,重要的是要了解四个概念:边缘图像,霍夫空间以及边缘点到霍夫空间的映射,表示线的替代方法以及如何检测线。
边缘图像

坎尼边缘检测算法
边缘图像是边缘检测算法的输出。边缘检测算法通过确定图像的亮度/强度急剧变化的位置来检测图像中的边缘(“边缘检测-使用Python进行图像处理”,2020年)。边缘检测算法的示例包括:Canny,Sobel,Laplacian等。对边缘图像进行二值化是很常见的,意味着其所有像素值均为1或0。根据你们的情况,为1或0可以表示边缘像素。
霍夫空间和边缘点到霍夫空间的映射
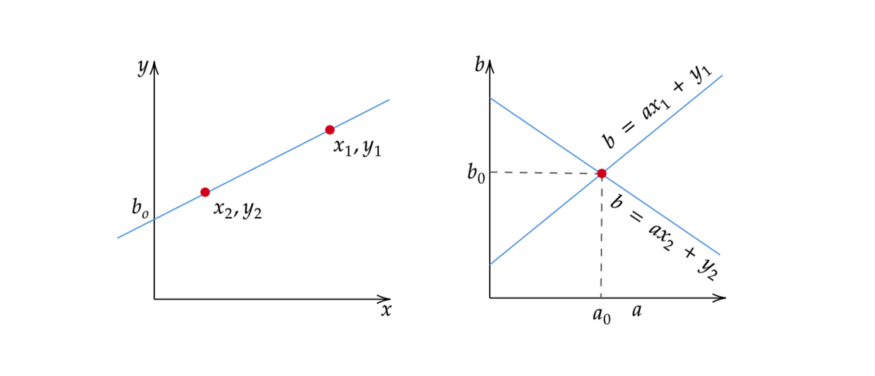
霍夫空间是2D平面,其水平轴表示坡度,而垂直轴表示边缘图像上直线的截距。边缘图像上的一条线以y = ax + b的形式表示(Hough,1962年)。边缘图像上的一条线在霍夫空间上产生一个点,因为一条线的特征在于其斜率a和截距b。另一方面,边缘图像上的边缘点(xᵢ,yᵢ)可以有无数的线通过。因此,边缘点在Hough空间中以b =axᵢ+yᵢ的形式生成一条线(Leavers,1992)。在霍夫变换算法中,霍夫空间用于确定边缘图像中是否存在线条。
表示线的另一种方法
用y = ax + b形式的直线 和带有斜率和截距的霍夫空间代表着一种缺陷。在这种形式下,该算法将无法检测垂直线,因为斜率a对于垂直线是不确定的/无穷大(Leavers,1992)。编程,这意味着,一个计算机将需要的存储器的无限量来表示的所有可能的值一个。为避免此问题,一条直线由一条称为法线的线表示,该线穿过原点并垂直于该直线。法线的形式为ρ = x cos( θ )+ y sin( θ ),其中ρ 是法线的长度,θ是法线与x轴之间的角度。
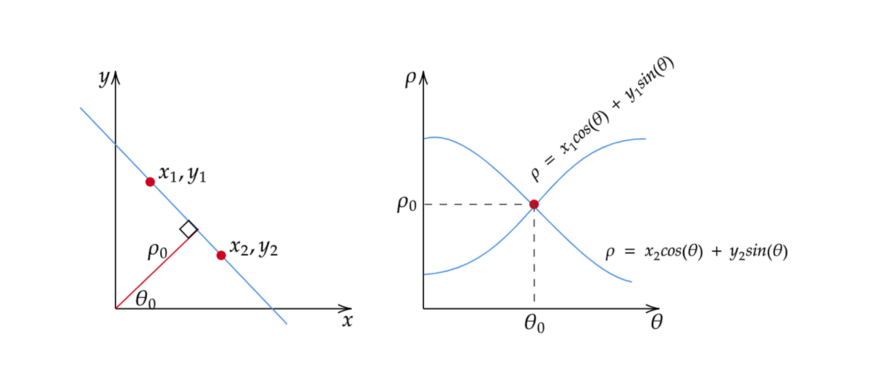
使用此方法,不再用坡度a和截距b表示霍夫空间,而是用ρ和θ表示,其中水平轴表示θ值,垂直轴表示ρ值。边缘点到霍夫空间的映射以类似的方式工作,除了边缘点(x,y)现在在霍夫空间中生成余弦曲线,而不是直线(Leavers,1992)。线的这种正常表示消除了在处理垂直线时出现的a的无限值的问题。
线检测
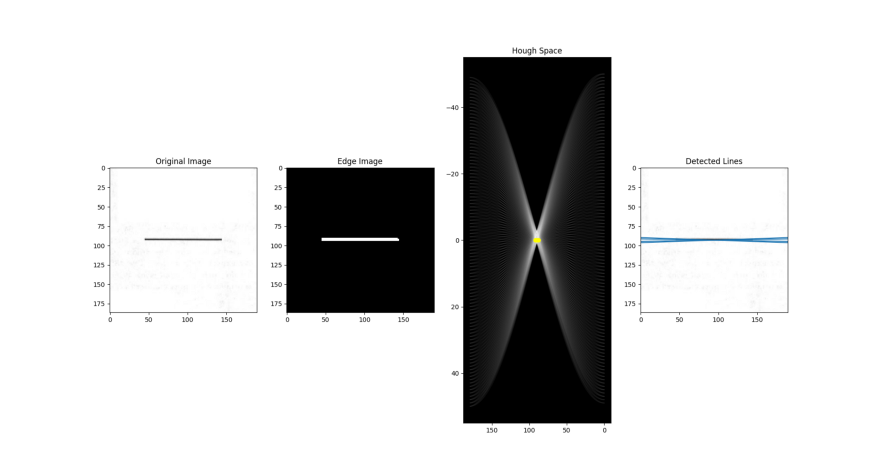
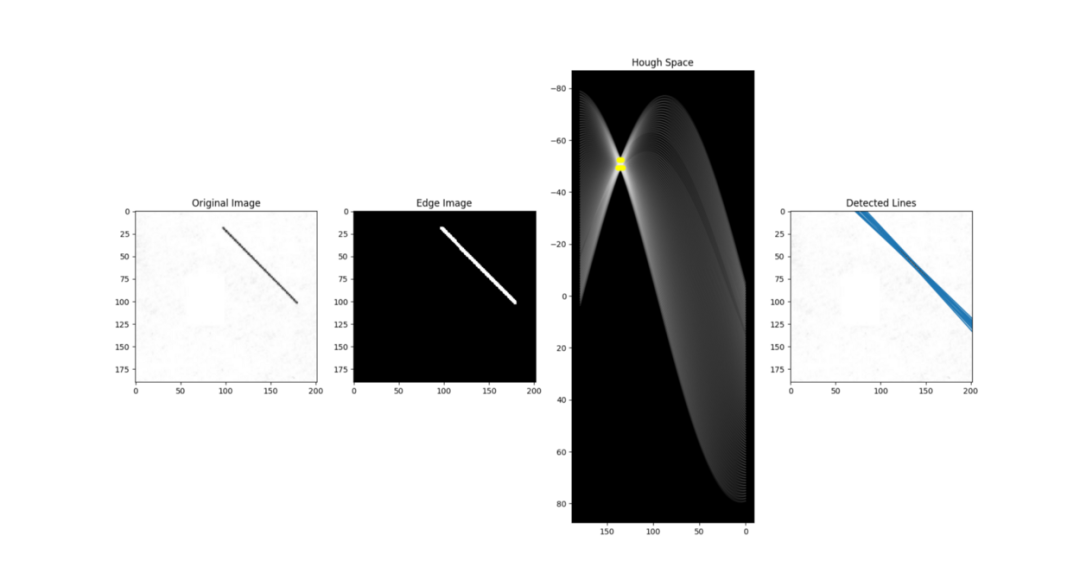
如前所述,边缘点在霍夫空间中产生余弦曲线。由此,如果我们将边缘图像中的所有边缘点映射到霍夫空间上,它将生成许多余弦曲线。如果两个边缘点位于同一条线上,则它们对应的余弦曲线将在特定的(ρ,θ)对上彼此相交。因此,霍夫变换算法通过找到交叉点数量大于某个阈值的(ρ,θ)对来检测线。值得注意的是,如果不对霍夫空间进行邻域抑制等预处理以去除边缘图像中的相似线条,这种阈值化方法可能不会总是产生最佳结果。
三、算法
确定ρ和θ的范围。通常,θ的范围是[0,180]度,而ρ是[ -d,d ],其中d是边缘图像对角线的长度。量化ρ和θ的范围很重要,这意味着应该有数量有限的可能值。
创建一个称为累加器的二维数组,该数组表示维度为(num_rhos,num_thetas)的霍夫空间,并将其所有值初始化为零。
对原始图像执行边缘检测。可以使用你们选择的任何边缘检测算法来完成。
对于边缘图像上的每个像素,请检查该像素是否为边缘像素。如果是边缘像素,则循环遍历所有可能的θ值,计算对应的ρ,在累加器中找到θ和ρ索引,并基于这些索引对递增累加器。
循环遍历累加器中的所有值。如果该值大于某个阈值,则获取ρ和θ索引,从索引对获取ρ和θ的值,然后可以将其转换回y = ax + b的形式。
四、代码
非向量化解决方案
import cv2import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport matplotlib.lines as mlinesdef line_detection_non_vectorized(image, edge_image, num_rhos=180, num_thetas=180, t_count=220):edge_width = edge_image.shape[:2]edge_width_half = edge_height / 2, edge_width / 2#d = np.sqrt(np.square(edge_height) + np.square(edge_width))dtheta = 180 / num_thetasdrho = (2 * d) / num_rhos#thetas = np.arange(0, 180, step=dtheta)rhos = np.arange(-d, d, step=drho)#cos_thetas = np.cos(np.deg2rad(thetas))sin_thetas = np.sin(np.deg2rad(thetas))#accumulator = np.zeros((len(rhos), len(rhos)))#figure = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 12))subplot1 = figure.add_subplot(1, 4, 1)subplot1.imshow(image)subplot2 = figure.add_subplot(1, 4, 2)cmap="gray")subplot3 = figure.add_subplot(1, 4, 3)0, 0))subplot4 = figure.add_subplot(1, 4, 4)subplot4.imshow(image)#for y in range(edge_height):for x in range(edge_width):if edge_image[y][x] != 0:edge_point = [y - edge_height_half, x - edge_width_half]xs = [], []for theta_idx in range(len(thetas)):rho = (edge_point[1] * cos_thetas[theta_idx]) + (edge_point[0] * sin_thetas[theta_idx])theta = thetas[theta_idx]rho_idx = np.argmin(np.abs(rhos - rho))+= 1ys.append(rho)xs.append(theta)ys, color="white", alpha=0.05)for y in range(accumulator.shape[0]):for x in range(accumulator.shape[1]):if accumulator[y][x] > t_count:rho = rhos[y]theta = thetas[x]a = np.cos(np.deg2rad(theta))b = np.sin(np.deg2rad(theta))x0 = (a * rho) + edge_width_halfy0 = (b * rho) + edge_height_halfx1 = int(x0 + 1000 * (-b))y1 = int(y0 + 1000 * (a))x2 = int(x0 - 1000 * (-b))y2 = int(y0 - 1000 * (a))[rho], marker='o', color="yellow")x2], [y1, y2]))subplot3.invert_yaxis()subplot3.invert_xaxis()Image")Image")Space")Lines")plt.show()return accumulator, rhos, thetasif __name__ == "__main__":for i in range(3):image = cv2.imread(f"sample-{i+1}.png")edge_image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)edge_image = cv2.GaussianBlur(edge_image, (3, 3), 1)edge_image = cv2.Canny(edge_image, 100, 200)edge_image = cv2.dilate(edge_image,(5, 5)),iterations=1)edge_image = cv2.erode(edge_image,(5, 5)),iterations=1)edge_image)
向量化解决方案
import cv2import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport matplotlib.lines as mlinesdef line_detection_vectorized(image, edge_image, num_rhos=180, num_thetas=180, t_count=220):edge_width = edge_image.shape[:2]edge_width_half = edge_height / 2, edge_width / 2#d = np.sqrt(np.square(edge_height) + np.square(edge_width))dtheta = 180 / num_thetasdrho = (2 * d) / num_rhos#thetas = np.arange(0, 180, step=dtheta)rhos = np.arange(-d, d, step=drho)#cos_thetas = np.cos(np.deg2rad(thetas))sin_thetas = np.sin(np.deg2rad(thetas))#accumulator = np.zeros((len(rhos), len(rhos)))#figure = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 12))subplot1 = figure.add_subplot(1, 4, 1)subplot1.imshow(image)subplot2 = figure.add_subplot(1, 4, 2)cmap="gray")subplot3 = figure.add_subplot(1, 4, 3)0, 0))subplot4 = figure.add_subplot(1, 4, 4)subplot4.imshow(image)#edge_points = np.argwhere(edge_image != 0)edge_points = edge_points - np.array([[edge_height_half, edge_width_half]])#rho_values = np.matmul(edge_points, np.array([sin_thetas, cos_thetas]))#theta_vals, rho_vals = np.histogram2d(rho_values.shape[0]),rho_values.ravel(),bins=[thetas, rhos])accumulator = np.transpose(accumulator)lines = np.argwhere(accumulator > t_count)theta_idxs = lines[:, 0], lines[:, 1]t = rhos[rho_idxs], thetas[theta_idxs]for ys in rho_values:ys, color="white", alpha=0.05)[r], color="yellow", marker='o')for line in lines:x = linerho = rhos[y]theta = thetas[x]a = np.cos(np.deg2rad(theta))b = np.sin(np.deg2rad(theta))x0 = (a * rho) + edge_width_halfy0 = (b * rho) + edge_height_halfx1 = int(x0 + 1000 * (-b))y1 = int(y0 + 1000 * (a))x2 = int(x0 - 1000 * (-b))y2 = int(y0 - 1000 * (a))[rho], marker='o', color="yellow")x2], [y1, y2]))subplot3.invert_yaxis()subplot3.invert_xaxis()Image")Image")Space")Lines")plt.show()return accumulator, rhos, thetasif __name__ == "__main__":for i in range(3):image = cv2.imread(f"sample-{i+1}.png")edge_image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)edge_image = cv2.GaussianBlur(edge_image, (3, 3), 1)edge_image = cv2.Canny(edge_image, 100, 200)edge_image = cv2.dilate(edge_image,(5, 5)),iterations=1)edge_image = cv2.erode(edge_image,(5, 5)),iterations=1)edge_image)
五、结论
综上所述,本文以最简单的形式展示了Hough变换算法,该算法可以扩展到检测直线以外。多年来,对该算法进行了许多改进,使其可以检测其他形状,例如圆形,三角形甚至特定形状的四边形。这导致了许多有用的现实世界应用,从文档扫描到自动驾驶汽车的车道检测。
个人微信(如果没有备注不拉群!)
请注明:地区+学校/企业+研究方向+昵称
下载1:何恺明顶会分享
在「AI算法与图像处理」公众号后台回复:何恺明,即可下载。总共有6份PDF,涉及 ResNet、Mask RCNN等经典工作的总结分析
下载2:终身受益的编程指南:Google编程风格指南
在「AI算法与图像处理」公众号后台回复:c++,即可下载。历经十年考验,最权威的编程规范!
下载3 CVPR2021
在「AI算法与图像处理」公众号后台回复:CVPR,即可下载1467篇CVPR 2020论文 和 CVPR 2021 最新论文
点亮  ,告诉大家你也在看
,告诉大家你也在看
