多标签学习的新趋势(2020 Survey)
机器之心转载
这是2020 年多标签学习最新的 Survey。

Tsoumakas 的《Multi-label classification: An overview》(2007)
周志华老师的《A review on multi-label learning algorithms》(2013)
一篇比较小众的,Gibaja 《Multi‐label learning: a review of the state of the art and ongoing research》2014
关于单标签学习和多标签学习的区别,这里简单给个例子:传统的图片单标签分类考虑识别一张图片里的一个物体,例如 ImageNet、CIFAR10 等都是如此,但其实图片里往往不会只有一个物体,大家随手往自己的桌面拍一张照片,就会有多个物体,比如手机、电脑、笔、书籍等等。在这样的情况下,单标签学习的方法并不适用,因为输出的标签可能是结构化的、具有相关性的(比如键盘和鼠标经常同时出现),所以我们需要探索更强的多标签学习算法来提升学习性能。
Extreme Multi-Label Classification
Multi-Label with Limited Supervision
Deep Multi-Label Classification
Online Multi-Label Classification
Statistical Multi-Label Learning
New Applications


MLC with Noisy Labels (Noisy-MLC).
MLC with Unseen Labels. (Streaming Labels/Zero-Shot/Few-Shot Labels)
Multi-Label Active Learning (MLAL).
MLC with Multiple Instances (MIML).
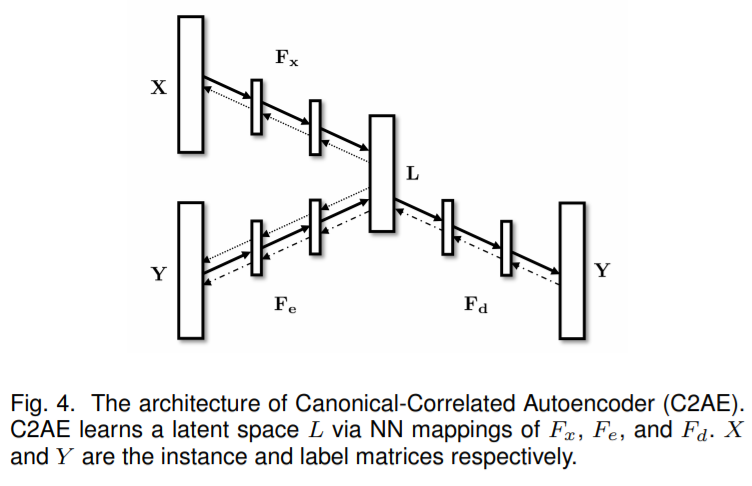
从架构上看,基于 Embedding、CNN-RNN、CNN-GNN 的三种架构受到较多的关注。
从任务上,在 XML、弱监督、零样本的问题上,DNN 大展拳脚。
从技术上,Attention、Transformer、GNN 在 MLC 上的应用可能会越来越多。
^Chang W C, Yu H F, Zhong K, et al. Taming Pretrained Transformers for Extreme Multi-label Text Classification[C]//Proceedings of the 26th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining. 2020: 3163-3171.
^abhttp://manikvarma.org/downloads/XC/XMLRepository.html
^abBhatia K, Jain H, Kar P, et al. Sparse local embeddings for extreme multi-label classification[C]//Advances in neural information processing systems. 2015: 730-738.
^Chu H M, Yeh C K, Frank Wang Y C. Deep generative models for weakly-supervised multi-label classification[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). 2018: 400-415.
^Zhang M L, Fang J P. Partial multi-label learning via credible label elicitation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020.
^Wang H, Liu W, Zhao Y, et al. Discriminative and Correlative Partial Multi-Label Learning[C]//IJCAI. 2019: 3691-3697.
^C. Yeh, W. Wu, W. Ko, and Y. F. Wang, “Learning deep latent space for multi-label classification,” in AAAI, 2017, pp. 2838–2844.
^X. Shen, W. Liu, Y. Luo, Y. Ong, and I. W. Tsang, “Deep discrete prototype multilabel learning,” in IJCAI, 2018, pp. 2675–2681.
^You R, Zhang Z, Wang Z, et al. Attentionxml: Label tree-based attention-aware deep model for high-performance extreme multi-label text classification[C]//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. 2019: 5820-5830.
^Chang W C, Yu H F, Zhong K, et al. Taming Pretrained Transformers for Extreme Multi-label Text Classification[C]//Proceedings of the 26th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining. 2020: 3163-3171.
^Durand T, Mehrasa N, Mori G. Learning a deep convnet for multi-label classification with partial labels[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2019: 647-657.
^Z. Wang, L. Liu, and D. Tao, “Deep streaming label learning,” in ICML, 2020.
^C. Lee, W. Fang, C. Yeh, and Y. F. Wang, “Multi-label zero-shot learning with structured knowledge graphs,” in CVPR, 2018, pp. 1576–1585.
^Wang J, Yang Y, Mao J, et al. Cnn-rnn: A unified framework for multi-label image classification[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2016: 2285-2294.
^Yazici V O, Gonzalez-Garcia A, Ramisa A, et al. Orderless Recurrent Models for Multi-label Classification[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2020: 13440-13449.
^Chen Z M, Wei X S, Wang P, et al. Multi-label image recognition with graph convolutional networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2019: 5177-5186.
^T. Chen, M. Xu, X. Hui, H. Wu, and L. Lin, “Learning semanticspecific graph representation for multi-label image recognition,” in ICCV, 2019, pp. 522–531.
^M. J. Er, R. Venkatesan, and N. Wang, “An online universal classifier for binary, multi-class and multi-label classification,” in IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 2016, pp. 3701–3706.
^H. Chu, K. Huang, and H. Lin, “Dynamic principal projection for cost-sensitive online multi-label classification,” Machine Learning, vol. 108, no. 8-9, pp. 1193–1230, 2019.
^S. Boulbazine, G. Cabanes, B. Matei, and Y. Bennani, “Online semi-supervised growing neural gas for multi-label data classification,” in IJCNN, 2018, pp. 1–8.
^H. Yu, P. Jain, P. Kar, and I. S. Dhillon, “Large-scale multilabel learning with missing labels,” in Proceedings of the 31th International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML 2014, Beijing, China, 21-26 June 2014, 2014, pp. 593–601.
^W. Gao and Z. Zhou, “On the consistency of multi-label learning,” Artificial Intelligence, vol. 199-200, pp. 22–44, 2013.
^W. Liu and X. Shen, “Sparse extreme multi-label learning with oracle property,” in ICML, 2019, pp. 4032–4041.
^X. Zhang, H. Shi, C. Li, and P. Li, “Multi-instance multi-label action recognition and localization based on spatio-temporal pretrimming for untrimmed videos,” in AAAI. AAAI Press, 2020, pp. 12 886–12 893.
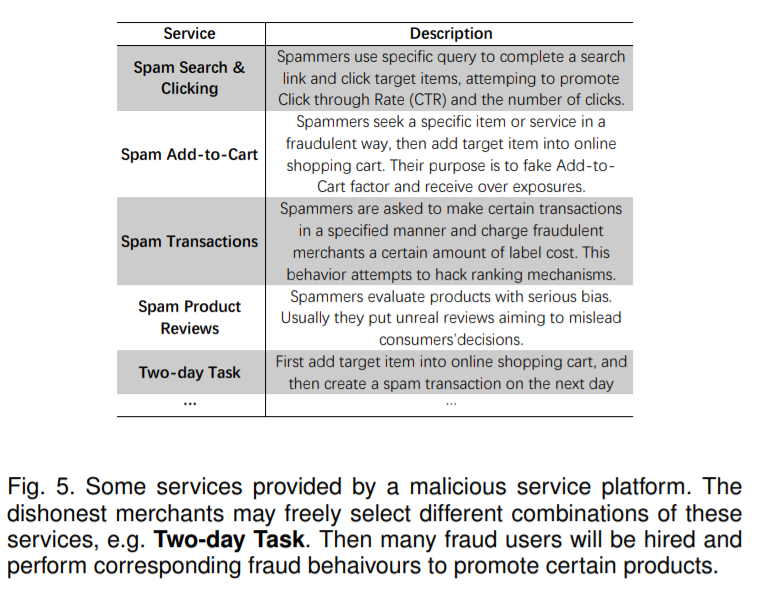
^H. Wang, Z. Li, J. Huang, P. Hui, W. Liu, T. Hu, and G. Chen, “Collaboration based multi-label propagation for fraud detection,” in IJCAI, 2020.
原文链接:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/266749365?utm_source=wechat_session&utm_medium=social&utm_oi=56560353017856&utm_campaign=shareopn
