(附论文)ICCV2021 | GUPNet:基于几何不确定性映射的单目3D检测网络
点击左上方蓝字关注我们

论文标题:Geometry Uncertainty Projection Network for Monocular 3D Object Detection
作者单位:The University of Sydney, SenseTime Computer Vision Group 等
论文:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2107.13774.pdf
一句话读论文:
利用几何关系衡量深度估计的不确定度。

Existing methods with the projection model usually estimate the height of 2D and 3D bounding box first and then infer the depth via the projection formular.
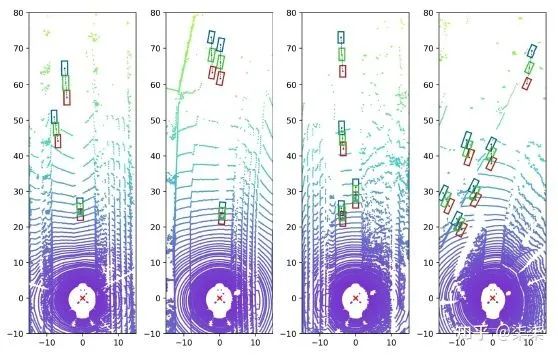
We can find that a slight bias (0.1m) of 3D heights could cause a significant shift (even 4m) in the projected depth.
The first problem is inference reliability. A small quality change in the 3D height estimation would cause a large change in the depth estimation quality. This makes the model cannot predict reliable uncertainty or confidence easily, leading to uncontrollable outputs.
Another problem is the instability of model training. In particular, at the beginning of the training phase, the estimation of 2D/3D height tends to be noisy, and the errors will be amplified and cause outrageous depth estimation. Consequently, the training process of the network will be misled, which will lead to the degradation of the final performance
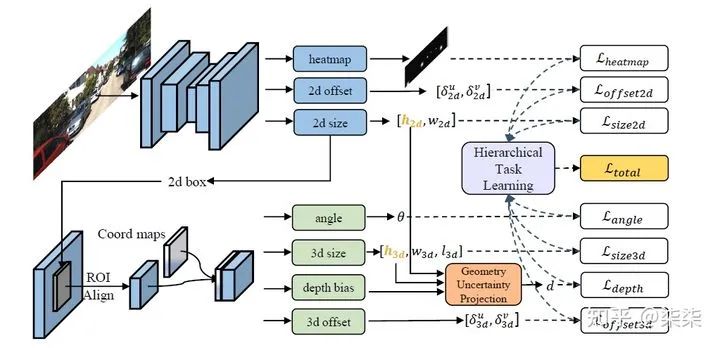
The overall module builds the projection process in the probability framework rather than single values so that the model can compute the theoretical uncertainty for the inferred depth, which can indicate the depth inference reliability and also be helpful for the depth learning.

To achieve this goal, we first assume the prediction of the 3D height for each object is a Laplace distribution. The distribution parameters are predicted by the 3D size streame in an end-to-end way. The average denotes the regression target output and the variation is the uncertainty of the inference
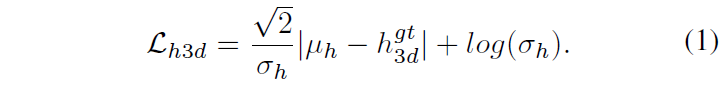
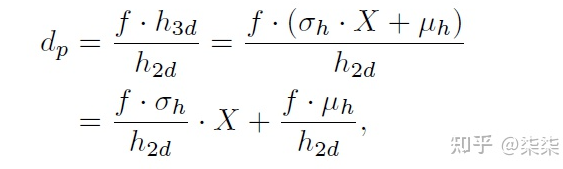
 。
。Based on the learned height distribution, the depth distribution of the projection output can be approximated as above, where X is the standard Laplace distribution.
We also assume that the learned bias is a Laplace distribution and independent with the projection one.
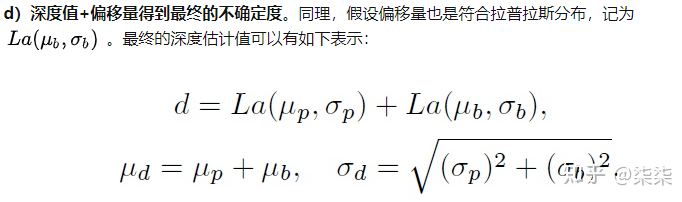
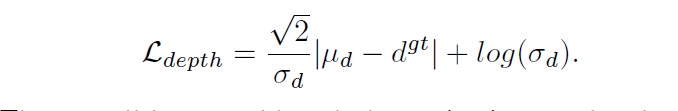
The overall loss would push the projection results close to the ground truth and the gradient would affect the depth bias, the 2D height and the 3D height simultaneously. Besides, the uncertainty of 3D height and depth bias is also trained in the optimization process.

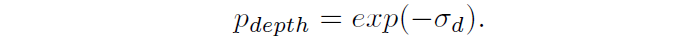
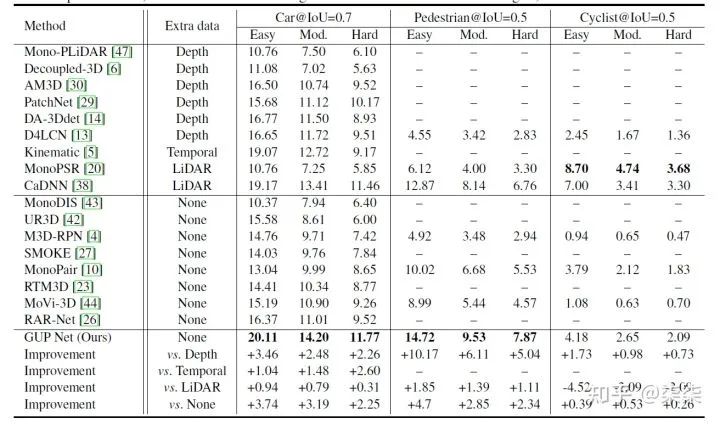
END
点赞三连,支持一下吧↓
评论
