浅谈Trie字典树
Trie字典树,又被称为前缀树,一种可以高效进行大量字符串的保存、统计、排序等的数据结构

基本原理
对于字典树而言,顾名思义其首先是一棵树。然后将每个字符串拆分为若干个字符依次存储到树的各节点中。其有三个特殊的性质:
根节点不包含字符,除根节点外每一个节点都只包含一个字符 从根节点到某一节点,将路径上经过的字符连接起来,就构成了一个字符串 每个节点的所有子节点包含的字符都不相同
假设存在hi、dog、da三个字符串,这里通过Trie树进行保存存储,则最终如下所示。可以看到Trie树的核心在于利用字符串的公共前缀减少查询时间
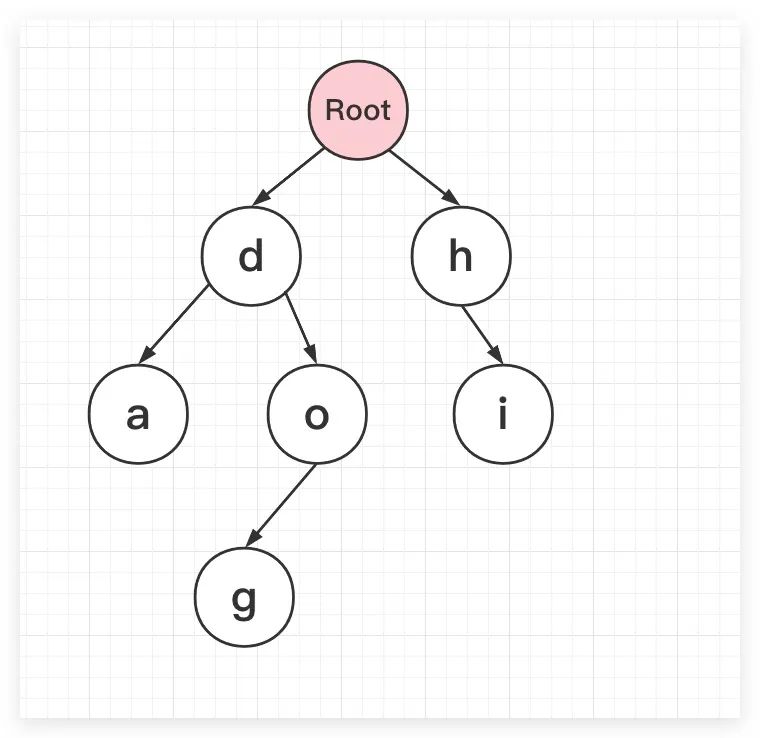
而在字典树的实现过程中,常见的功能包括向Trie树中插入一个字符串、判断Trie树中是否存在某字符串、判断Trie树中是否存在指定字符串前缀等,与此同时还可以提供统计、排序等高级功能
实践
实现Trie字典树
学习过程中要善于理论联系实际。故在介绍完Trie树的基本原理后,我们来实现一个Trie树。这里以LeetCode的第208题——实现Trie(前缀树)为例
请你实现 Trie 类:
Trie(): 初始化前缀树对象 void insert(String word): 向前缀树中插入字符串word boolean search(String word): 如果字符串word在前缀树中,返回true(即在检索之前已经插入);否则返回false boolean startsWith(String prefix): 如果之前已经插入的字符串word的前缀之一为prefix,返回true;否则返回 false Note: word 和 prefix 仅由小写英文字母组成
可以看到对于本题而言,由于仅存在26个小写英文字母。故对于子节点可以通过数组进行保存,其中0~25索引 对应于 a~z 字符。同时在节点增加一个标识endFlag,用于指示当前字符是否为字符串的最后一个字符。这样查询指定字符串时,如果其最后一个字符对应节点的endFlag为true,则表示该字符串查询成功。而对于查询字符串前缀而言,只要我们能够在Trie树中查询到相应的节点存在,即可判定为查询成功。Java实现如下所示
/**
* Trie字典树
*/
public class Trie {
/**
* 字典树的根节点
*/
private TrieNode root;
public Trie() {
root = new TrieNode();
}
/**
* 字典树中插入字符串 word
* @param word
*/
public void insert(String word) {
TrieNode current = root;
char[] chars = word.toCharArray();
for (int i=0; i char ch = chars[i];
int index = calcIndex(ch);
TrieNode[] childs = current.getChilds();
if( childs[index]==null ) {
childs[index] = new TrieNode();
}
current = childs[index];
}
current.setEndFlag( true );
}
/**
* 判断字符串是否存在于字典树
* @param word
* @return
*/
public boolean search(String word) {
TrieNode current = root;
char[] chars = word.toCharArray();
for(int i=0; i char ch = chars[i];
int index = calcIndex(ch);
TrieNode[] childs = current.getChilds();
if( childs[index]==null ) {
return false;
}
current = childs[index];
}
return current.isEndFlag();
}
/**
* 判断前缀是否存在于字典树中
* @param prefix
* @return
*/
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
TrieNode current = root;
char[] chars = prefix.toCharArray();
for(int i=0; i char ch = chars[i];
int index = calcIndex(ch);
TrieNode[] childs = current.getChilds();
if( childs[index] == null ) {
return false;
}
current = childs[index];
}
return true;
}
/**
* 根据字符计算索引
* 0~25索引 对应于 a~z 字符
* @param ch
* @return
*/
private static int calcIndex(char ch) {
return ch - 'a';
}
/**
* Trie字典树节点
*/
public static class TrieNode {
/**
* 子节点数组, 0~25索引 对应于 a~z 字符
*/
private TrieNode[] childs;
/**
* 当前字符是否为字符串的最后一个字符
*/
private boolean endFlag;
public TrieNode() {
childs = new TrieNode[26];
endFlag = false;
}
public TrieNode[] getChilds() {
return childs;
}
public boolean isEndFlag() {
return endFlag;
}
public void setEndFlag(boolean endFlag) {
this.endFlag = endFlag;
}
}
}
前K个高频单词
学习过程中要善于理论联系实际。这里以LeetCode的第692题——前K个高频单词为例
给定一个单词列表words和一个整数k,返回前k个出现次数最多的单词。返回的答案应该按单词出现频率由高到低排序;如果不同的单词有相同出现频率,按字典顺序排序
示例 1:
输入: words = ["i", "love", "leetcode", "i", "love", "coding"], k = 2
输出: ["i", "love"]
解析: "i" 和 "love" 为出现次数最多的两个单词,均为2次。注意,按字母顺序 "i" 在 "love" 之前
示例 2:
输入: ["the", "day", "is", "sunny", "the", "the", "the", "sunny", "is", "is"], k = 4
输出: ["the", "is", "sunny", "day"]
解析: "the", "is", "sunny" 和 "day" 是出现次数最多的四个单词,出现次数依次为 4, 3, 2 和 1 次
注意:
1 <= words.length <= 500 1 <= words[i] <= 10 words[i] 由小写英文字母组成 k 的取值范围是 [1, 不同 words[i] 的数量]
本题关键在于统计字符串的数量、获取Top K个字符串。前者可以先将字符串保存到字典树中,同时为了方便统计,我们对于树的节点增加完整字符串、计数值的字段。后者可以对字典树进行DFS深度优先遍历,并结合最小堆获取Top K个字符串。最后将最小堆中的元素进行输出即可。Java实现如下所示
public class Solution {
/**
* 获取字符串数组中Top K字符串列表
* @param words 字符串数组
* @param k
* @return
*/
public List topKFrequent(String[] words, int k) {
// 1. 遍历字符串存储到字典树中
Trie trie = new Trie();
for(String word : words) {
trie.insert(word);
}
// 2. 通过最小堆、DFS获取Top K个字符串
PriorityQueue minHeap = new PriorityQueue<>();
dfs(minHeap, k, trie.getRoot());
// 3. 将最小堆的元素按降序输出
LinkedList res = new LinkedList<>();
while( !minHeap.isEmpty() ) {
Trie.TrieNode min = minHeap.poll();
res.addFirst( min.getStr() );
}
return res;
}
/**
* DFS搜索字典树
* @param minHeap
* @param k
* @param current
*/
private void dfs(PriorityQueue minHeap, int k, Trie.TrieNode current) {
if( current==null) {
return;
}
// 字典树当前节点为完整的字符串
if( current.getStr()!=null ) {
// 最小堆中元素的数量未达到K, 则直接加入
if( minHeap.size() < k ) {
minHeap.offer( current );
} else if( current.compareTo( minHeap.peek() )>0 ) { // 当前节点比堆中最小的元素大, 则加入
// 将当前节点加入最小堆
minHeap.offer( current );
// 将堆中最小的元素移出堆, 保证堆中数量始终为K
minHeap.poll();
}
}
// DFS搜索字典树
for(int i=0; i<26; i++) {
Trie.TrieNode[] childs = current.getChilds();
dfs(minHeap, k, childs[i]);
}
}
}
/**
* Trie字典树
*/
class Trie {
/**
* 字典树的根节点
*/
private TrieNode root;
public Trie() {
root = new TrieNode();
}
public TrieNode getRoot() {
return root;
}
/**
* 字典树中插入字符串 word
* @param word
*/
public void insert(String word) {
TrieNode current = root;
char[] chars = word.toCharArray();
for (int i=0; i char ch = chars[i];
int index = calcIndex(ch);
TrieNode[] childs = current.childs;
if( childs[index]==null ) {
childs[index] = new TrieNode();
}
current = childs[index];
}
// 保存完整字符串信息
current.str = word;
// 计数值+1
current.count += 1;
}
/**
* 根据字符计算索引
* 0~25索引 对应于 a~z 字符
* @param ch
* @return
*/
private static int calcIndex(char ch) {
return ch - 'a';
}
/**
* Trie字典树节点
*/
public static class TrieNode implements Comparable<TrieNode> {
/**
* 子节点数组, 0~25索引 对应于 a~z 字符
*/
private TrieNode[] childs;
/**
* 字符串
*/
private String str;
/**
* 计数值
*/
private int count;
public TrieNode() {
childs = new TrieNode[26];
str = null;
count = 0;
}
public TrieNode[] getChilds() {
return childs;
}
public String getStr() {
return str;
}
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(TrieNode o) {
// 排序规则: 先比较字符串的频率
int res = this.count - o.count;
if( res!=0 ) {
return res;
}
// 排序规则: 频率相同, 按字典序排序
res = o.str.compareTo(this.str);
return res;
}
}
} 