Flink SQL空闲状态保留时间实现原理

前言
如果要列举Flink SQL新手有可能犯的错误,笔者认为其中之一就是忘记设置空闲状态保留时间导致状态爆炸。
为什么要设置
如果我们在数据流上进行分组查询,分组处理产生的结果(不仅仅是聚合结果)会作为中间状态存储下来。随着分组key的不断增加,状态自然也会不断膨胀。但是这些状态数据基本都有时效性,不必永久保留。例如,使用Top-N语法进行去重,重复数据的出现一般都位于特定区间内(例如一小时或一天内),过了这段时间之后,对应的状态就不再需要了。Flink SQL提供的idle state retention time特性可以保证当状态中某个key对应的数据未更新的时间达到阈值时,该条状态被自动清理。设置方法是:
stenv.getConfig().setIdleStateRetentionTime(Time.hours(24), Time.hours(36))
注意setIdleStateRetentionTime()方法需要传入两个参数:状态的最小保留时间minRetentionTime和最大保留时间maxRetentionTime(根据实际业务决定),且两者至少相差5分钟。为什么会有这种限制呢?看一下源码就知道了。
如何实现的
idle state retention time特性在底层以o.a.f.table.runtime.functions.CleanupState接口来表示,代码如下。
public interface CleanupState {
default void registerProcessingCleanupTimer(
ValueState<Long> cleanupTimeState,
long currentTime,
long minRetentionTime,
long maxRetentionTime,
TimerService timerService)
throws Exception {
// last registered timer
Long curCleanupTime = cleanupTimeState.value();
// check if a cleanup timer is registered and
// that the current cleanup timer won't delete state we need to keep
if (curCleanupTime == null || (currentTime + minRetentionTime) > curCleanupTime) {
// we need to register a new (later) timer
long cleanupTime = currentTime + maxRetentionTime;
// register timer and remember clean-up time
timerService.registerProcessingTimeTimer(cleanupTime);
// delete expired timer
if (curCleanupTime != null) {
timerService.deleteProcessingTimeTimer(curCleanupTime);
}
cleanupTimeState.update(cleanupTime);
}
}
}
由上可知,每个key对应的最近状态清理时间会单独维护在ValueState中。如果满足以下两条件之一:
ValueState为空(即这个key是第一次出现)
或者当前时间加上minRetentionTime已经超过了最近清理的时间
就用当前时间加上maxRetentionTime注册新的Timer,并将其时间戳存入ValueState,用于触发下一次清理。如果有已经过期了的Timer,则一并删除之。可见,如果minRetentionTime和maxRetentionTime的间隔设置太小,就会比较频繁地产生Timer与更新ValueState,维护Timer的成本会变大(参见之前笔者写的Timer原理文章),所以一般建议设置间隔比较长的清理区间。
CleanupState接口的继承关系如下图所示。
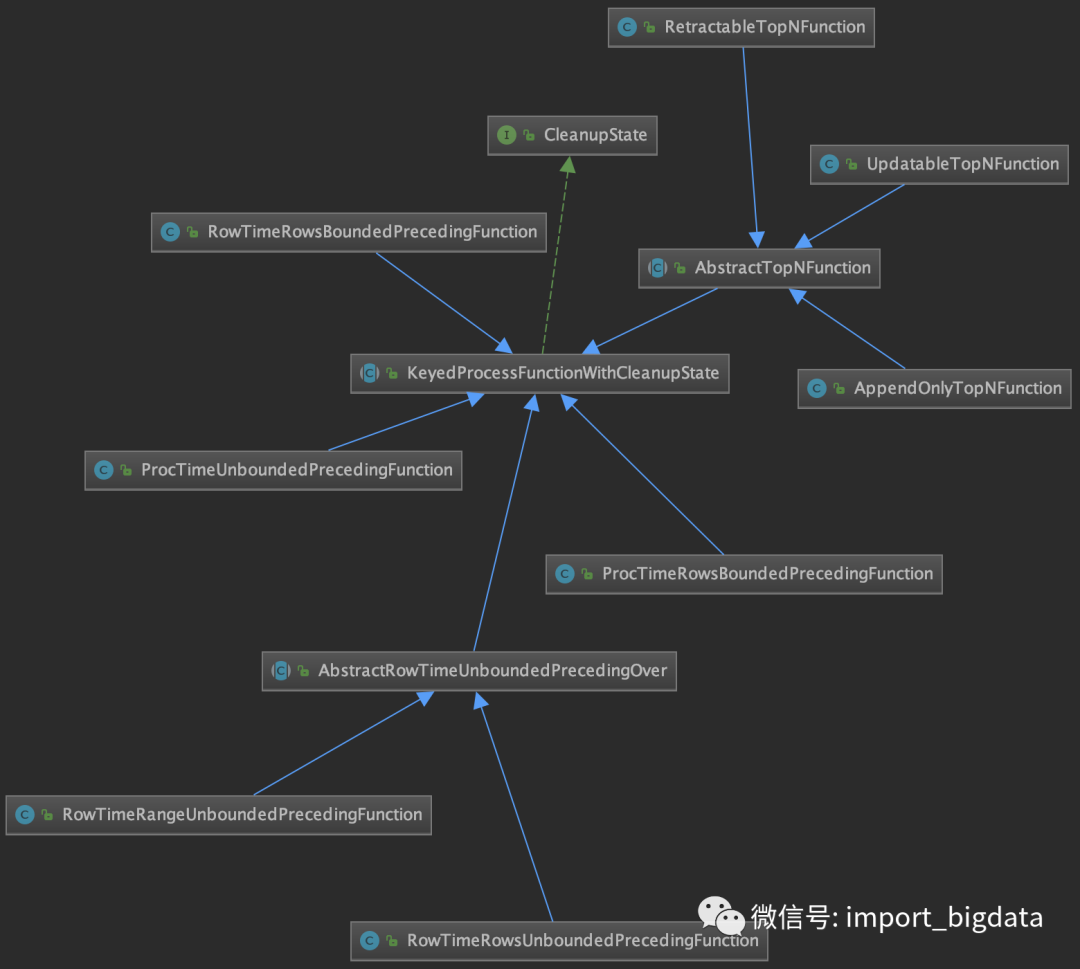
可见支持空闲状态清理的Function很多,但基类都是KeyedProcessFunctionWithCleanupState抽象类。它的源码如下。
public abstract class KeyedProcessFunctionWithCleanupState<K, IN, OUT>
extends KeyedProcessFunction<K, IN, OUT> implements CleanupState {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2084560869233898457L;
private final long minRetentionTime;
private final long maxRetentionTime;
protected final boolean stateCleaningEnabled;
// holds the latest registered cleanup timer
private ValueState<Long> cleanupTimeState;
public KeyedProcessFunctionWithCleanupState(long minRetentionTime, long maxRetentionTime) {
this.minRetentionTime = minRetentionTime;
this.maxRetentionTime = maxRetentionTime;
this.stateCleaningEnabled = minRetentionTime > 1;
}
protected void initCleanupTimeState(String stateName) {
if (stateCleaningEnabled) {
ValueStateDescriptor<Long> inputCntDescriptor =
new ValueStateDescriptor<>(stateName, Types.LONG);
cleanupTimeState = getRuntimeContext().getState(inputCntDescriptor);
}
}
protected void registerProcessingCleanupTimer(Context ctx, long currentTime) throws Exception {
if (stateCleaningEnabled) {
registerProcessingCleanupTimer(
cleanupTimeState,
currentTime,
minRetentionTime,
maxRetentionTime,
ctx.timerService());
}
}
protected boolean isProcessingTimeTimer(OnTimerContext ctx) {
return ctx.timeDomain() == TimeDomain.PROCESSING_TIME;
}
protected void cleanupState(State... states) {
for (State state : states) {
state.clear();
}
this.cleanupTimeState.clear();
}
protected Boolean needToCleanupState(Long timestamp) throws IOException {
if (stateCleaningEnabled) {
Long cleanupTime = cleanupTimeState.value();
// check that the triggered timer is the last registered processing time timer.
return timestamp.equals(cleanupTime);
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
可以发现,空闲状态保留时间目前仍然只支持processing time语义,并且minRetentionTime只有设为大于0的值才会生效。
KeyedProcessFunctionWithCleanupState只是提供了一些helper方法,具体发挥作用需要到实现类中去找。以计算Top-N的AppendOnlyTopNFunction为例,它的processElement()方法中会对到来的每个元素注册清理Timer:
@Override
public void processElement(RowData input, Context context, Collector<RowData> out) throws Exception {
long currentTime = context.timerService().currentProcessingTime();
// register state-cleanup timer
registerProcessingCleanupTimer(context, currentTime);
// ......
}
而一旦Timer触发,在onTimer()方法中调用基类的cleanupState()方法来实际清理:
@Override
public void onTimer(
long timestamp,
OnTimerContext ctx,
Collector<RowData> out) throws Exception {
if (stateCleaningEnabled) {
// cleanup cache
kvSortedMap.remove(keyContext.getCurrentKey());
cleanupState(dataState);
}
}
空闲状态保留的逻辑并不仅应用在上述Function中。在Table/SQL模块中还有一个内置的触发器StateCleaningCountTrigger,它可以对窗口中的元素进行计数,并按照计数阈值或者空闲状态保留的时间阈值来清理(即FIRE_AND_PURGE)。看官可自行参考对应的源码。

