21 句话入门机器学习!
对于程序员来说,机器学习的重要性毋庸赘言。也许你还没有开始,也许曾经失败过,都没有关系,你将在这里找到或者重拾自信。只要粗通Python,略知NumPy,认真读完这21句话,逐行敲完示例代码,就可以由此进入自由的AI王国。
分类是对个体样本做出定性判定,回归是对个体样本做出定量判定,二者同属于有监督的学习,都是基于经验的。举个例子:有经验的老师预测某学生考试及格或不及格,这是分类;预测某学生能考多少分,这是回归;不管是预测是否及格还是预测考多少分,老师的经验数据和思考方法是相同的,只是最后的表述不同而已。
4
numpy as npmembers = np.array([['男', '25', 185, 80, '程序员', 35, 200, 30],['女', '23', 170, 55, '公务员', 15, 0, 80],['男', '30', 180, 82, '律师', 60, 260, 300],['女', '27', 168, 52, '记者', 20, 180, 150]])
6
> security = np.float32((members[:,-1])) # 提取有价证券特征列数据> securityarray([ 30., 80., 300., 150.], dtype=float32)> (security - security.mean())/security.std() # 减去均值再除以标准差array([-1.081241, -0.5897678, 1.5727142, 0.09829464], dtype=float32)
9
归一化是对样本集的每个特征列减去该特征列的最小值进行中心化,再除以极差(最大值最小值之差)进行缩放。
> security = np.float32((members[:,-1])) # 提取有价证券特征列数据> securityarray([ 30., 80., 300., 150.], dtype=float32)> (security - security.min())/(security.max() - security.min()) # 减去最小值再除以极差array([0., 0.18518518, 1., 0.44444445], dtype=float32)
> from sklearn import preprocessing as pp> X = [['男', '程序员'],['女', '公务员'],['男', '律师', ],['女', '记者', ]]> ohe = pp.OneHotEncoder().fit(X)> ohe.transform(X).toarray()array([[0., 1., 0., 0., 1., 0.],[1., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0.],[0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 0.],[1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1.]])
11
datasets.load_boston([return_X_y]) :加载波士顿房价数据集datasets.load_breast_cancer([return_X_y]) :加载威斯康星州乳腺癌数据集datasets.load_diabetes([return_X_y]) :加载糖尿病数据集datasets.load_digits([n_class, return_X_y]) :加载数字数据集datasets.load_iris([return_X_y]) :加载鸢尾花数据集。datasets.load_linnerud([return_X_y]) :加载体能训练数据集datasets.load_wine([return_X_y]) :加载葡萄酒数据集datasets.fetch_20newsgroups([data_home, …]) :加载新闻文本分类数据集datasets.fetch_20newsgroups_vectorized([…]) :加载新闻文本向量化数据集datasets.fetch_california_housing([…]) :加载加利福尼亚住房数据集datasets.fetch_covtype([data_home, …]) :加载森林植被数据集datasets.fetch_kddcup99([subset, data_home, …]) :加载网络入侵检测数据集datasets.fetch_lfw_pairs([subset, …]) :加载人脸(成对)数据集datasets.fetch_lfw_people([data_home, …]) :加载人脸(带标签)数据集datasets.fetch_olivetti_faces([data_home, …]) :加载 Olivetti 人脸数据集datasets.fetch_rcv1([data_home, subset, …]):加载路透社英文新闻文本分类数据集datasets.fetch_species_distributions([…]) :加载物种分布数据集
>>> from sklearn.datasets import load_iris>>> X, y = load_iris(return_X_y=True)>>> X.shape # 数据集X有150个样本,4个特征列(150, 4)>>> y.shape # 标签集y的每一个标签和数据集X的每一个样本一一对应(150,)>>> X[0], y[0](array([5.1, 3.5, 1.4, 0.2]), 0)
> iris = load_iris()> iris.target_names # 查看标签的名字array(['setosa', 'versicolor', 'virginica'], dtype='<U10')> X = iris.data> y = iris.target
>>> from sklearn.datasets import load_iris>>> from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split as tsplit>>> X, y = load_iris(return_X_y=True)>>> X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = tsplit(X, y, test_size=0.1)>>> X_train.shape, X_test.shape((135, 4), (15, 4))>>> y_train.shape, y_test.shape((135,), (15,))
> from sklearn.datasets import load_iris> from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split as tsplit> from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier # 导入k-近邻分类模型> X, y = load_iris(return_X_y=True) # 获取鸢尾花数据集,返回样本集和标签集> X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = tsplit(X, y, test_size=0.1) # 拆分为训练集和测试集> m = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=10) # 模型实例化,n_neighbors参数指定k值,默认k=5> m.fit(X_train, y_train) # 模型训练KNeighborsClassifier()> m.predict(X_test) # 对测试集分类array([2, 1, 2, 2, 1, 2, 1, 2, 2, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 2])> y_test # 这是实际的分类情况,上面的预测只错了一个array([2, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 1, 2, 2, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 2])> m.score(X_test, y_test) # 模型测试精度(介于0~1)0.9333333333333333
> from sklearn.datasets import load_boston> from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split as tsplit> from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsRegressor> X, y = load_boston(return_X_y=True) # 加载波士顿房价数据集> X.shape, y.shape, y.dtype # 该数据集共有506个样本,13个特征列,标签集为浮点型,适用于回归模型((506, 13), (506,), dtype('float64'))> X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = tsplit(X, y, test_size=0.01) # 拆分为训练集和测试集> m = KNeighborsRegressor(n_neighbors=10) # 模型实例化,n_neighbors参数指定k值,默认k=5> m.fit(X_train, y_train) # 模型训练KNeighborsRegressor(n_neighbors=10)> m.predict(X_test) # 预测6个测试样本的房价array([27.15, 31.97, 12.68, 28.52, 20.59, 21.47])> y_test # 这是测试样本的实际价格,除了第2个(索引为1)样本偏差较大,其他样本偏差还算差强人意array([29.1, 50. , 12.7, 22.8, 20.4, 21.5])
> from sklearn import metrics> y_pred = m.predict(X_test)> metrics.mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred) # 均方误差60.27319999999995> metrics.median_absolute_error(y_test, y_pred) # 中位数绝对误差1.0700000000000003> metrics.r2_score(y_test, y_pred) # 复相关系数0.5612816401629652
> from sklearn.datasets import load_boston> from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split as tsplit> from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor> X, y = load_boston(return_X_y=True) # 加载波士顿房价数据集> X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = tsplit(X, y, test_size=0.01) # 拆分为训练集和测试集> m = DecisionTreeRegressor(max_depth=10) # 实例化模型,决策树深度为10> m.fit(X, y) # 训练DecisionTreeRegressor(max_depth=10)> y_pred = m.predict(X_test) # 预测> y_test # 这是测试样本的实际价格,除了第2个(索引为1)样本偏差略大,其他样本偏差较小array([20.4, 21.9, 13.8, 22.4, 13.1, 7. ])> y_pred # 这是6个测试样本的预测房价,非常接近实际价格array([20.14, 22.33, 14.34, 22.4, 14.62, 7. ])> metrics.r2_score(y_test, y_pred) # 复相关系数0.9848774474870712> metrics.mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred) # 均方误差0.4744784865112032> metrics.median_absolute_error(y_test, y_pred) # 中位数绝对误差0.3462962962962983
> from sklearn.datasets import load_diabetes> from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split as tsplit> from sklearn.svm import SVR> from sklearn import metrics> X, y = load_diabetes(return_X_y=True)> X.shape, y.shape, y.dtype((442, 10), (442,), dtype('float64'))> X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = tsplit(X, y, test_size=0.02)> svr_1 = SVR(kernel='rbf', C=0.1) # 实例化SVR模型,rbf核函数,C=0.1> svr_2 = SVR(kernel='rbf', C=100) # 实例化SVR模型,rbf核函数,C=100> svr_1.fit(X_train, y_train) # 模型训练SVR(C=0.1)> svr_2.fit(X_train, y_train) # 模型训练SVR(C=100)> z_1 = svr_1.predict(X_test) # 模型预测> z_2 = svr_2.predict(X_test) # 模型预测> y_test # 这是测试集的实际值array([ 49., 317., 84., 181., 281., 198., 84., 52., 129.])> z_1 # 这是C=0.1的预测值,偏差很大array([138.10720127, 142.1545034 , 141.25165838, 142.28652449,143.19648143, 143.24670732, 137.57932272, 140.51891989,143.24486911])> z_2 # 这是C=100的预测值,偏差明显变小array([ 54.38891948, 264.1433666 , 169.71195204, 177.28782561,283.65199575, 196.53405477, 61.31486045, 199.30275061,184.94923477])> metrics.mean_squared_error(y_test, z_1) # C=0.01的均方误差8464.946517460194> metrics.mean_squared_error(y_test, z_2) # C=100的均方误差3948.37754995066> metrics.r2_score(y_test, z_1) # C=0.01的复相关系数0.013199351909129464> metrics.r2_score(y_test, z_2) # C=100的复相关系数0.5397181166871942> metrics.median_absolute_error(y_test, z_1) # C=0.01的中位数绝对误差57.25165837797314> metrics.median_absolute_error(y_test, z_2) # C=100的中位数绝对误差22.68513954888364
>>> from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer # 导入数据加载函数>>> from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier # 导入随机树>>> from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier # 导入随机森林>>> from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score # 导入交叉验证>>> ds = load_breast_cancer() # 加载威斯康星州乳腺癌数据集>>> ds.data.shape # 569个乳腺癌样本,每个样本包含30个特征(569, 30)>>> dtc = DecisionTreeClassifier() # 实例化决策树分类模型>>> rfc = RandomForestClassifier() # 实例化随机森林分类模型>>> dtc_scroe = cross_val_score(dtc, ds.data, ds.target, cv=10) # 交叉验证>>> dtc_scroe # 决策树分类模型交叉验证10次的结果array([0.92982456, 0.85964912, 0.92982456, 0.89473684, 0.92982456,0.89473684, 0.87719298, 0.94736842, 0.92982456, 0.92857143])>>> dtc_scroe.mean() # 决策树分类模型交叉验证10次的平均精度0.9121553884711779>>> rfc_scroe = cross_val_score(rfc, ds.data, ds.target, cv=10) # 交叉验证>>> rfc_scroe # 随机森林分类模型交叉验证10次的结果array([0.98245614, 0.89473684, 0.94736842, 0.94736842, 0.98245614,0.98245614, 0.94736842, 0.98245614, 0.94736842, 1. ])>>> rfc_scroe.mean()# 随机森林分类模型交叉验证10次的平均精度0.9614035087719298
> from sklearn import datasets as dss # 导入样本生成器
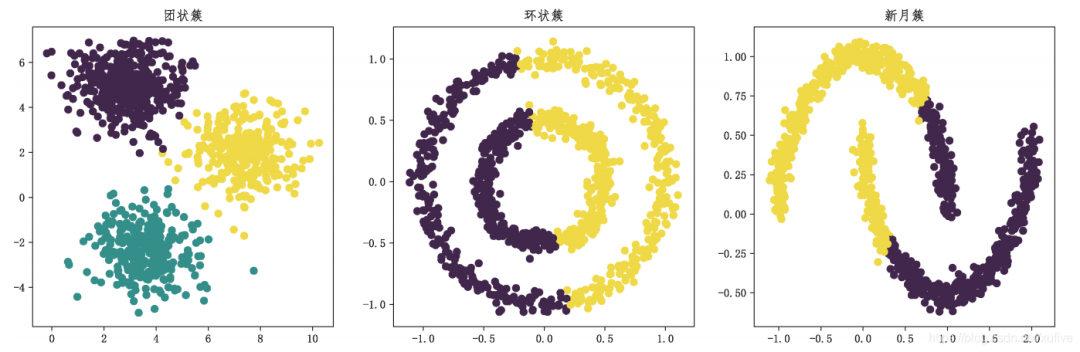
> from sklearn.cluster import KMeans # 从聚类子模块导入聚类模型> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt> plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['FangSong']> plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False> X_blob, y_blob = dss.make_blobs(n_samples=[300,400,300], n_features=2)> X_circle, y_circle = dss.make_circles(n_samples=1000, noise=0.05, factor=0.5)> X_moon, y_moon = dss.make_moons(n_samples=1000, noise=0.05)> y_blob_pred = KMeans(init='k-means++', n_clusters=3).fit_predict(X_blob)> y_circle_pred = KMeans(init='k-means++', n_clusters=2).fit_predict(X_circle)> y_moon_pred = KMeans(init='k-means++', n_clusters=2).fit_predict(X_moon)> plt.subplot(131)<matplotlib.axes._subplots.AxesSubplot object at 0x00000180AFDECB88>> plt.title('团状簇')Text(0.5, 1.0, '团状簇')> plt.scatter(X_blob[:,0], X_blob[:,1], c=y_blob_pred)<matplotlib.collections.PathCollection object at 0x00000180C495DF08>> plt.subplot(132)<matplotlib.axes._subplots.AxesSubplot object at 0x00000180C493FA08>> plt.title('环状簇')Text(0.5, 1.0, '环状簇')> plt.scatter(X_circle[:,0], X_circle[:,1], c=y_circle_pred)<matplotlib.collections.PathCollection object at 0x00000180C499B888>> plt.subplot(133)<matplotlib.axes._subplots.AxesSubplot object at 0x00000180C4981188>> plt.title('新月簇')Text(0.5, 1.0, '新月簇')> plt.scatter(X_moon[:,0], X_moon[:,1], c=y_moon_pred)<matplotlib.collections.PathCollection object at 0x00000180C49DD1C8>> plt.show()
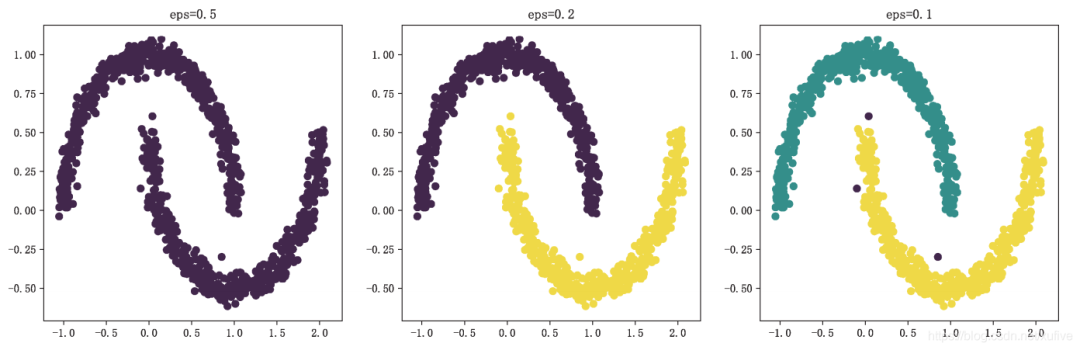
> from sklearn import datasets as dss> from sklearn.cluster import DBSCAN> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt> plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['FangSong']> plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False> X, y = dss.make_moons(n_samples=1000, noise=0.05)> dbs_1 = DBSCAN() # 默认核心样本半径0.5,核心样本邻居5个> dbs_2 = DBSCAN(eps=0.2) # 核心样本半径0.2,核心样本邻居5个> dbs_3 = DBSCAN(eps=0.1) # 核心样本半径0.1,核心样本邻居5个> dbs_1.fit(X)DBSCAN(algorithm='auto', eps=0.5, leaf_size=30, metric='euclidean',metric_params=None, min_samples=5, n_jobs=None, p=None)> dbs_2.fit(X)DBSCAN(algorithm='auto', eps=0.2, leaf_size=30, metric='euclidean',metric_params=None, min_samples=5, n_jobs=None, p=None)> dbs_3.fit(X)DBSCAN(algorithm='auto', eps=0.1, leaf_size=30, metric='euclidean',metric_params=None, min_samples=5, n_jobs=None, p=None)> plt.subplot(131)<matplotlib.axes._subplots.AxesSubplot object at 0x00000180C4C5D708>> plt.title('eps=0.5')Text(0.5, 1.0, 'eps=0.5')> plt.scatter(X[:,0], X[:,1], c=dbs_1.labels_)<matplotlib.collections.PathCollection object at 0x00000180C4C46348>> plt.subplot(132)<matplotlib.axes._subplots.AxesSubplot object at 0x00000180C4C462C8>> plt.title('eps=0.2')Text(0.5, 1.0, 'eps=0.2')> plt.scatter(X[:,0], X[:,1], c=dbs_2.labels_)<matplotlib.collections.PathCollection object at 0x00000180C49FC8C8>> plt.subplot(133)<matplotlib.axes._subplots.AxesSubplot object at 0x00000180C49FCC08>> plt.title('eps=0.1')Text(0.5, 1.0, 'eps=0.1')> plt.scatter(X[:,0], X[:,1], c=dbs_3.labels_)<matplotlib.collections.PathCollection object at 0x00000180C49FC4C8>> plt.show()
sklearn import datasets as dsssklearn.decomposition import PCAds = dss.load_iris()ds.data.shape # 150个样本,4个特征维(150, 4)m = PCA() # 使用默认参数实例化PCA类,n_components=Nonem.fit(ds.data)PCA(copy=True, iterated_power='auto', n_components=None, random_state=None,svd_solver='auto', tol=0.0, whiten=False)m.explained_variance_ # 正交变换后各成分的方差值array([4.22824171, 0.24267075, 0.0782095 , 0.02383509])m.explained_variance_ratio_ # 正交变换后各成分的方差值占总方差值的比例array([0.92461872, 0.05306648, 0.01710261, 0.00521218])
对鸢尾花数据集的主成分分析结果显示:存在一个明显的成分,其方差值占总方差值的比例超过92% ;存在一个方差值很小的成分,其方差值占总方差值的比例只有0.52% ;前两个成分贡献的方差占比超过97.7%,数据集特征列可以从4个降至2个而不至于损失太多有效信息。
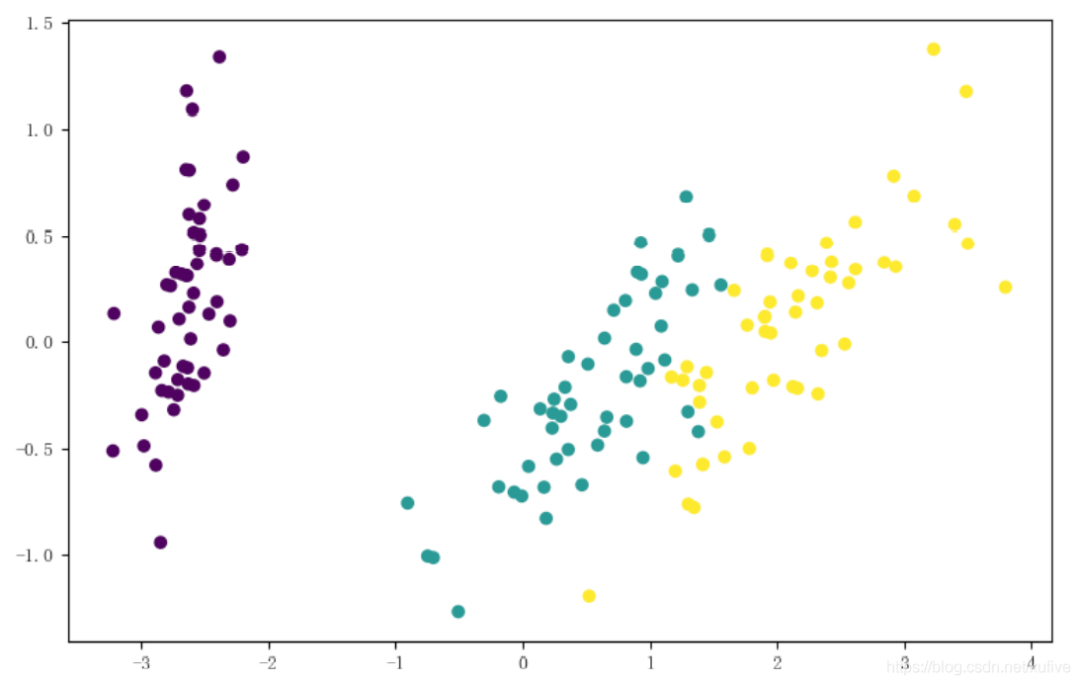
> m = PCA(n_components=0.97)> m.fit(ds.data)PCA(copy=True, iterated_power='auto', n_components=0.97, random_state=None,svd_solver='auto', tol=0.0, whiten=False)> m.explained_variance_array([4.22824171, 0.24267075])> m.explained_variance_ratio_array([0.92461872, 0.05306648])> d = m.transform(ds.data)> d.shape(150, 2)
> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt> plt.scatter(d[:,0], d[:,1], c=ds.target)<matplotlib.collections.PathCollection object at 0x0000016FBF243CC8>> plt.show()
可能是全网最全的速查表:Python机器学习ChatGPT线性代数微积分概率统计
评论
