卷,AAAI 2024 的投稿量接近14,000了!
导读

今天不经意间看到这么一个激动人心的数字,此刻只能用一个字表达内心的感受:"卷"!为此,小编默默打开尘封许久的 CMT 后台。。。
只能说要换成今年投稿,可能只有1篇能中,又或者全军覆没?国内这行情,现在无论是考公、考研、考教师编,亦或者送外卖、做网约车司机等,处处卷上天。可能这个时代最利好的人群便是整天“贩卖焦虑”转手又“卖服务”给你的那群人,把流量赚足了再顺便把你给收割了,留下一片绿油油的韭菜田子。。。
作为一名初入自媒体创作的新手,奶盖一直坚持利用工作学习之余的业余时间进行创作无私分享给大家,不求质量超群,只求问心无愧,做人还是要坚持底线。现在也慢慢察觉到,以前一些经常关注的技术号,现在几乎都沦陷成营销号了,实属可惜,可能这也是如今大内卷时代必然的产物。然而,笔者仍希望能在这个浮躁的社会风气下,保持初心,坚持创作。谁也不能预知未来会什么事情,可能某一天也停笔了,但人最重要的还是要活在当下,毕竟人生是一段旅程,在旅行中遇到的每一个人,做的每一件事,看过的每一个美丽景色,都有可能成为一生中难忘的回忆。
回到正文,投稿数量的激增会带来很多问题,显而易见的便是审稿人数量不足、工作量激增、部分审稿人资质不足等。当然,这不是我们应该考虑的问题,作为一名科(磕)研(盐)人(汪),我们首要掌握的核心秘诀便是——斐波那契投稿法。可以说,自从有了斐波那契投稿法,爸爸妈妈再也不用担心我们没有论文了。
斐波那契投稿法:
本次投稿的文章 = 上次被拒的文章 + 上上次被拒的文章
该法则得以成立的一个前提条件便是:“只要投出去的论文,总会在某一处被接收”。下面简单附上本届 AAAI 会议的相关信息以及往年的一些统计数据,希望大家都能有所收获。
会议信息
AAAI 2024: AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence
| 日期 | 事件 |
|---|---|
| 2023.07.04 | AAAI-24 网站开放作者注册 |
| 2023.07.11 | AAAI-24 网站开放论文提交 |
| 2023.08.08 | 截止日期:摘要提交(UTC-12 时区) |
| 2023.08.15 | 截止日期:完整论文提交(UTC-12 时区) |
| 2023.08.18 | 截止日期:补充材料和代码提交(UTC-12 时区) |
| 2023.09.25 | 截止日期:NeurIPS 快速通道提交的注册、摘要和完整论文(UTC-12 时区) |
| 2023.09.27 | 第一阶段拒绝通知 |
| 2023.09.28 | 截止日期:NeurIPS 快速通道提交的补充材料和代码(UTC-12 时区) |
| 2023.11.02-05 | 作者反馈窗口 |
| 2023.12.09 | 最终录取或拒绝通知 |
| 2023.12.19 | 提交论文预印本以包含在电子会议材料中 |
| 2024.02.20-27 | AAAI-24 会议 |
今年 AAAI 也对使用 LLM 做出了相应规定:
-
不允许提交包含如ChatGPT这类大型语言模型(LLM)生成的文本的论文,除非这些文本是作为论文实验分析的一部分。 -
但可以使用LLM进行文本的编辑或润色。 -
根据AAAI的政策,任何AI系统(包括Chat-GPT、BARD、DALL-E等生成模型)不满足AAAI论文的作者资格,也不能作为AAAI论文的可引用来源。作者需对内容承担全部责任,包括检查抄袭和文本的真实性
同往年一样,今年依旧采用双阶段评审:第一阶段两次评审,第一阶段未被拒绝的论文在第二阶段进行额外评审。仅第一阶段未被拒绝的论文在第二阶段后有作者回应。
录用率
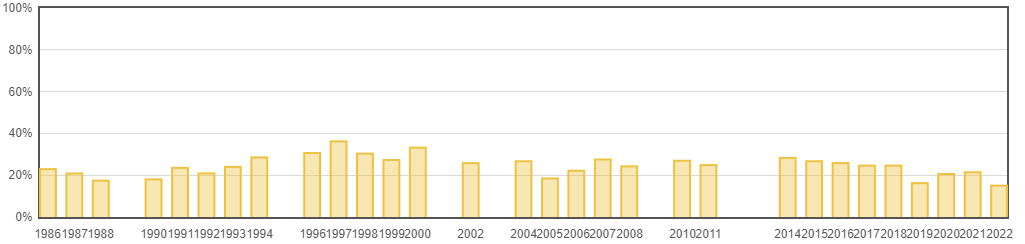
| 年份 | 提交数 | 录取数 | 录取率(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 | 9020 | 1349 | 15% |
| 2021 | 7911 | 1692 | 21.4% |
| 2020 | 7737 | 1591 | 20.6% |
| 2019 | 7095 | 1150 | 16.2% |
| 2018 | 3800 | 933 | 24.6% |
| 2017 | 2590 | 638 | 24.6% |
| 2016 | 2132 | 549 | 25.8% |
| 2015 | 1991 | 531 | 26.7% |
| 2014 | 1406 | 398 | 28.3% |
| 2011 | 975 | 242 | 24.8% |
| 2010 | 982 | 264 | 26.9% |
| 2008 | 937 | 227 | 24.2% |
| 2007 | 921 | 253 | 27.5% |
| 2006 | 774 | 171 | 22.1% |
| 2005 | 803 | 148 | 18.4% |
| 2004 | 453 | 121 | 26.7% |
| 2002 | 469 | 121 | 25.8% |
| 2000 | 431 | 143 | 33.2% |
| 1999 | 400 | 109 | 27.3% |
| 1998 | 475 | 144 | 30.3% |
| 1997 | 323 | 117 | 36.2% |
| 1996 | 643 | 197 | 30.6% |
| 1994 | 780 | 222 | 28.5% |
| 1993 | 524 | 126 | 24% |
| 1992 | 636 | 133 | 20.9% |
| 1991 | 603 | 142 | 23.5% |
| 1990 | 892 | 161 | 18% |
| 1988 | 850 | 148 | 17.4% |
| 1987 | 715 | 149 | 20.8% |
| 1986 | 817 | 187 | 22.9% |
往年最佳论文
| 年份 | 最佳论文 |
|---|---|
| 2022 | Online certification of preference-based fairness for personalized recommender systems |
| 2021 | Exploration-Exploitation in Multi-Agent Learning: Catastrophe Theory Meets Game Theory |
| 2021 | Informer: Beyond Efficient Transformer for Long Sequence Time-Series Forecasting |
| 2021 | Mitigating Political Bias in Language Models Through Reinforced Calibration |
| 2020 | A Distributed Multi-Sensor Machine Learning Approach to Earthquake Early Warning |
| 2020 | WinoGrande: An Adversarial Winograd Schema Challenge at Scale |
| 2020 | Fair Division of Mixed Divisible and Indivisible Goods |
| 2019 | Zero Shot Learning for Code Education: Rubric Sampling with Deep Learning Inference |
| 2019 | How to Combine Tree-Search Methods in Reinforcement Learning |
| 2018 | Counterfactual Multi-Agent Policy Gradients |
| 2018 | Memory-Augmented Monte Carlo Tree Search |
| 2017 | The Option-Critic Architecture |
| 2017 | Label-Free Supervision of Neural Networks with Physics and Domain Knowledge |
| 2016 | Toward a Taxonomy and Computational Models of Abnormalities in Images |
| 2016 | Bidirectional Search That Is Guaranteed to Meet in the Middle |
| 2015 | Surpassing Human-Level Face Verification Performance on LFW with GaussianFace |
| 2015 | From Non-Negative to General Operator Cost Partitioning |
| 2014 | Recovering from Selection Bias in Causal and Statistical Inference |
| 2013 | SMILe: Shuffled Multiple-Instance Learning |
| 2013 | HC-Search: Learning Heuristics and Cost Functions for Structured Prediction |
| 2012 | Learning SVM Classiiers with Indeinite Kernels |
| 2012 | Document Summarization Based on Data Reconstruction |
| 2011 | Complexity of and Algorithms for Borda Manipulation |
| 2011 | Dynamic Resource Allocation in Conservation Planning |
| 2010 | How Incomplete Is Your Semantic Web Reasoner? |
| 2010 | A Novel Transition Based Encoding Scheme for Planning as Satisfiability |
| 2008 | Optimal False-Name-Proof Voting Rules with Costly Voting |
| 2008 | How Good is Almost Perfect? |
| 2007 | PLOW: A Collaborative Task Learning Agent |
| 2007 | Thresholded Rewards: Acting Optimally in Timed, Zero-Sum Games |
| 2006 | Model Counting: A New Strategy for Obtaining Good Bounds |
| 2006 | Towards an Axiom System for Default Logic |
| 2005 | The Max K-Armed Bandit: A New Model of Exploration Applied to Search Heuristic Selection |
| 2004 | Learning and Inferring Transportation Routines |
| 2002 | On Computing all Abductive Explanations |
| 2000 | The Game of Hex: An Automatic Theorem Proving Approach to Game Programming |
| 1999 | PROVERB: The Probabilistic Cruciverbalist |
| 1998 | Acceleration Methods for Numeric CSPs |
| 1998 | The Interactive Museum Tour-Guide Robot |
| 1998 | Learning Evaluation Functions for Global Optimization and Boolean Satisfiability |
| 1997 | Statistical Parsing with a Context-Free Grammar and Word Statistics |
| 1997 | A Practical Algorithm for Finding Optimal Triangulations |
| 1997 | Building Concept Representations from Reusable Components |
| 1997 | Fast Context Switching in Real-Time Propositional Reasoning |
| 1996 | Verification of Knowledge Bases Based on Containment Checking |
| 1996 | A Novel Application of Theory Refinement to Student Modeling |
| 1996 | Pushing the Envelope: Planning, Propositional Logic and Stochastic Search |
| 1994 | A Prototype Reading Coach that Listens |
| 1993 | Equations for Part-of-Speech Tagging |
| 1992 | Hard and Easy Distributions of SAT Problems |
| 1991 | Improving Rule-Based Systems Through Case-Based Reasoning |
| 1988 | Qualitative Results Concerning the Utility of Explanation-Based Learning |
| 1988 | Approach to Qualitative Algebraic Reasoning |
| 1987 | An Approach to Default Reasoning Based on a First-Order Conditional Logic |
| 1987 | PROMPT: An Innovative Design Tool |
| 1987 | Curing Anomalous Extensions |
| 1987 | Non-Deterministic Lisp with Dependency-directed Backtracking |
| 1987 | Defining Operationality for Explanation-based Learning |
| 1987 | Word-Order Variation in Natural Language Generation |
| 1987 | Energy Constraints on Deformable Models: Recovering Shape and Non-Rigid Motion |
| 1987 | Incremental Causal Reasoning |
| 1986 | Default Reasoning, Nonmonotonic Logics, and the Frame Problem |
| 1986 | Generating Tests by Exploiting Designed Behavior |
| 1984 | The Tractability of Subsumption in Frame-Based Description Languages |
| 1984 | Choices without Backtracking |
| 1984 | A Logic of Implicit and Explicit Belief |
| 1984 | Shading into Texture |
未完,待续。
来源:CVHub
