基于卷积神经网络的手写数字识别(附数据集+完整代码+操作说明)
配置环境
使用环境:python3.8 平台:Windows10 IDE:PyCharm
1.前言
手写数字识别,作为机器视觉入门项目,无论是基于传统的OpenCV方法还是基于目前火热的深度学习、神经网络的方法都有这不错的训练效果。当然,这个项目也常常被作为大学/研究生阶段的课程实验。可惜的是,目前网络上关于手写数字识别的项目代码很多,但是普遍不完整,对于初学者提出了不小的挑战。为此,博主撰写本文,无论你是希望借此完成课程实验或者学习机器视觉,本文或许对你都有帮助。
2.问题描述
本文针对的问题为:随机在黑板上写一个数字,通过调用电脑摄像头实时检测出数字是0-9哪个数字
3.解决方案
基于Python的深度学习方法: 检测流程如下:
检测流程如下: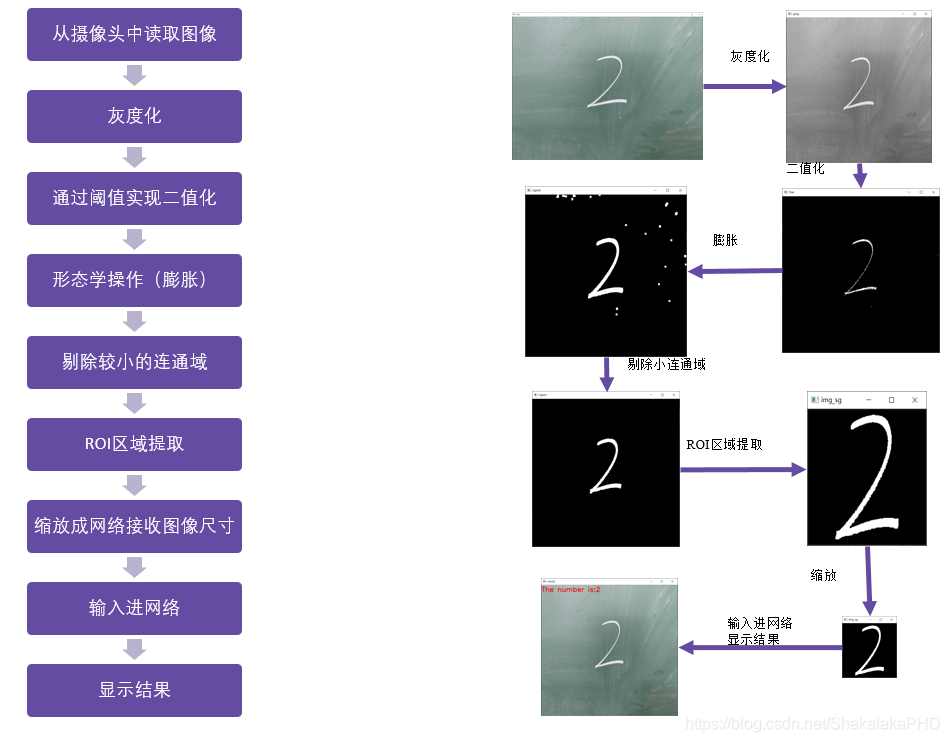
4.实现步骤
4.1数据集选择
手写数字识别经典数据集:本文数据集选择的FishionMint数据集中的t10k,共含有一万张28*28的手写图片(二值图片)  数据集下载地址见:
数据集下载地址见:
4.2构建网络
采用Resnt(残差网络),残差网络的优势在于:
更易捕捉模型细微波动- 更快的收敛速度 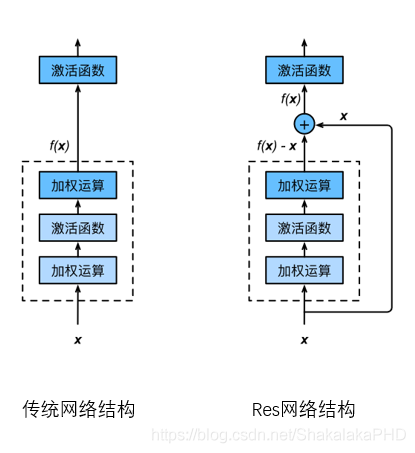 本文的网络结构如下图所示,代码见第五节:
本文的网络结构如下图所示,代码见第五节: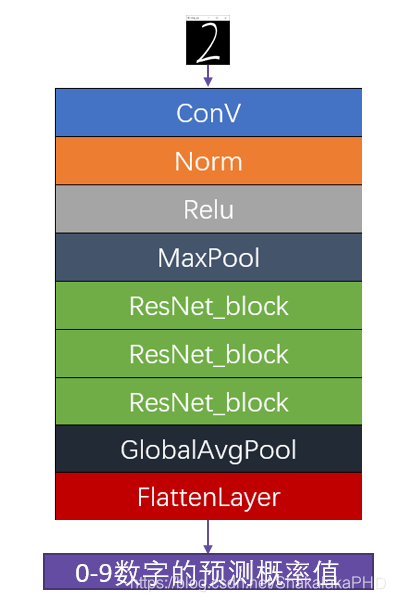
4.3训练网络
本文设置训练次数为100个循环,其实网络的训练过程是这样的:
给网络模型“喂”数据(图像+标签)- 网络根据“喂”来的数据不断自我修正权重- 本文一共“喂”100次1万张图像- RTX2070上耗时2h 训练结果如下: 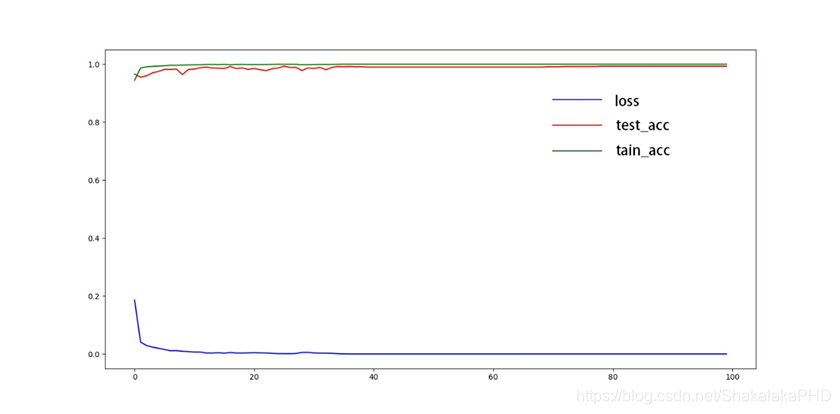
4.4测试网络
随机选取数据集中37张图片进行检测- 正确率为36/37- 选取其中6张进行展示 
4.5图像预处理
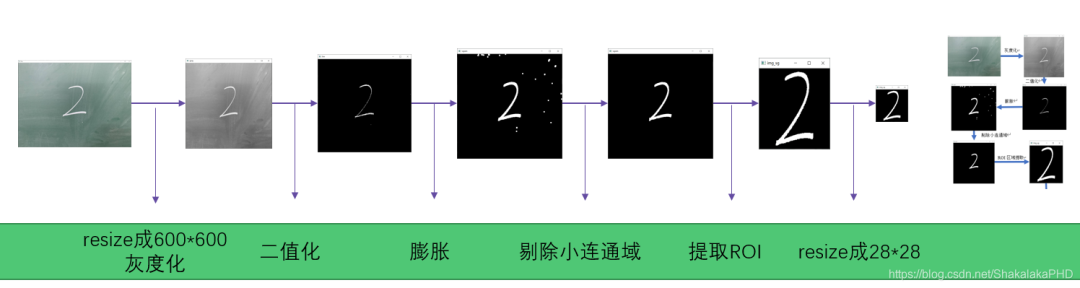
全部采取传统机器视觉的方法- 速度“飞快”,仅做以上操作处理速度高达200fps
4.6传入网络进行计算
手写0-9的数字除了3识别不了其余均能识别- 检测速度高达60fps 

5.代码实现
本文所有代码都已经上传至Github上
https://github.com/Hurri-cane/Hand_wrtten/tree/master
5.1文件说明
dataset文件夹存放的是训练数据集- logs文件夹为训练结束后权重文件所在- real_img、real_img_resize、test_imgs为用来测试的图片文件夹- 下面的py文件为本文代码
5.2使用方法
按照博主的环境配置自己的Python环境 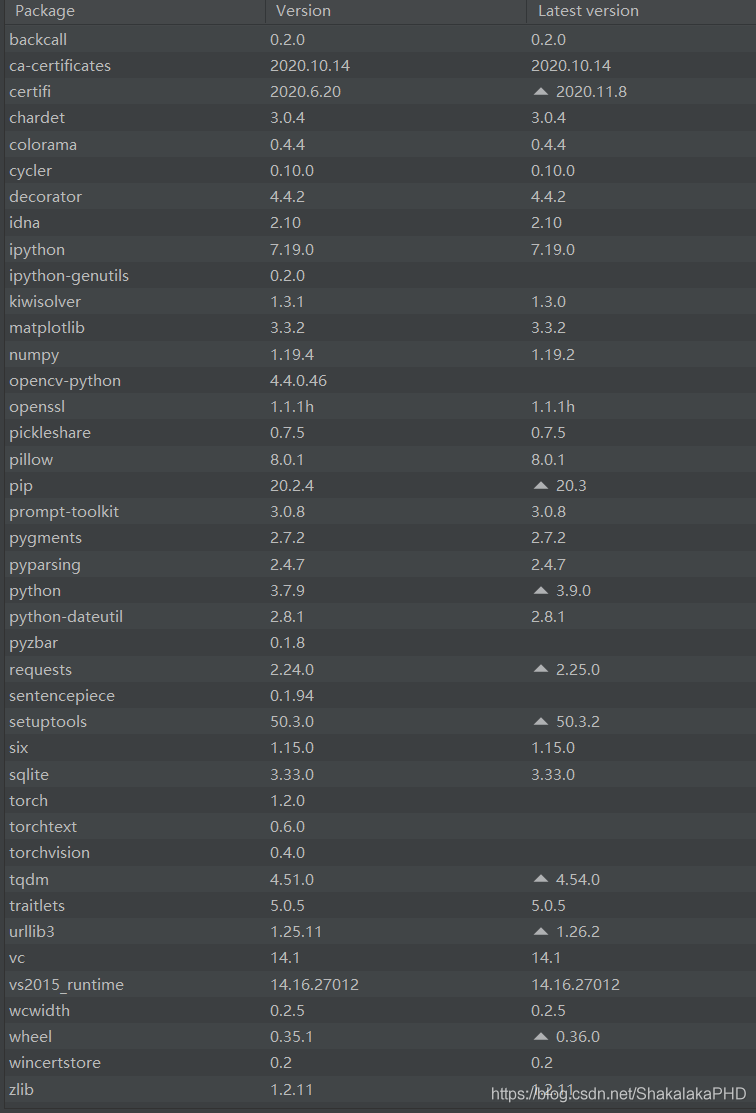 其中主要的包有:numpy、struct、matplotlib、OpenCV、Pytorch、torchvision、tqdm
其中主要的包有:numpy、struct、matplotlib、OpenCV、Pytorch、torchvision、tqdm
5.3 训练模型
本文提供了训练好的模型,大家可以直接调用,已经上传至GitHub,如果不想训练的话,可以跳过训练这一步骤  下面是训练的流程:
下面是训练的流程:
打开hand_wrtten_train.py文件,点击运行(博主使用的是PyCharm,大家根据自己喜好选择IDLE即可)  值得注意的是,数据集路径需要修改为自己的路径,即这一段
值得注意的是,数据集路径需要修改为自己的路径,即这一段 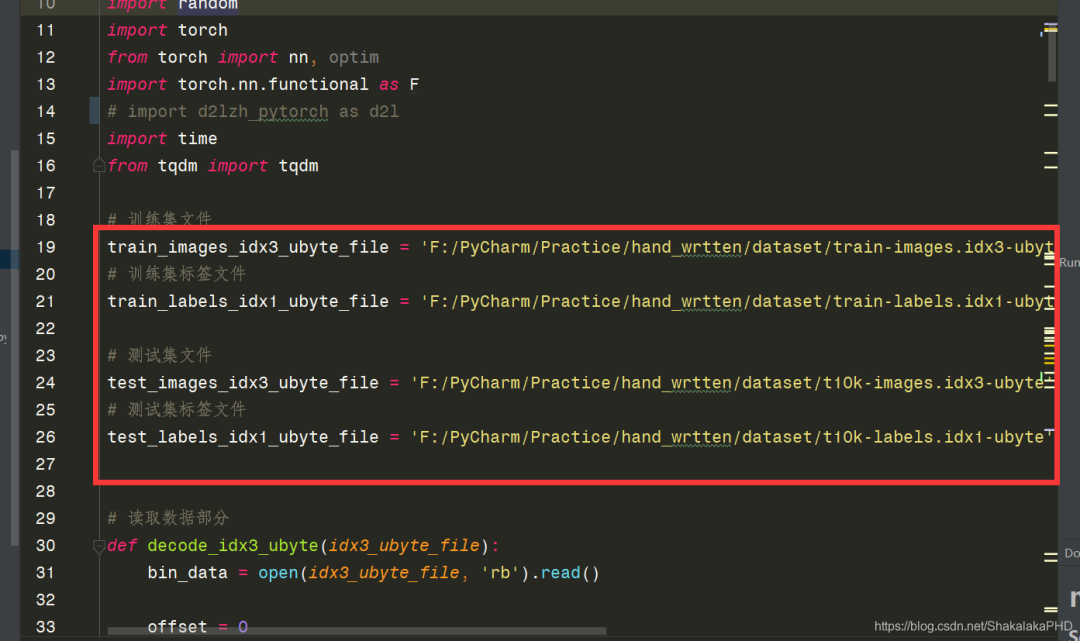 训练过程没报错会出现以下显示
训练过程没报错会出现以下显示 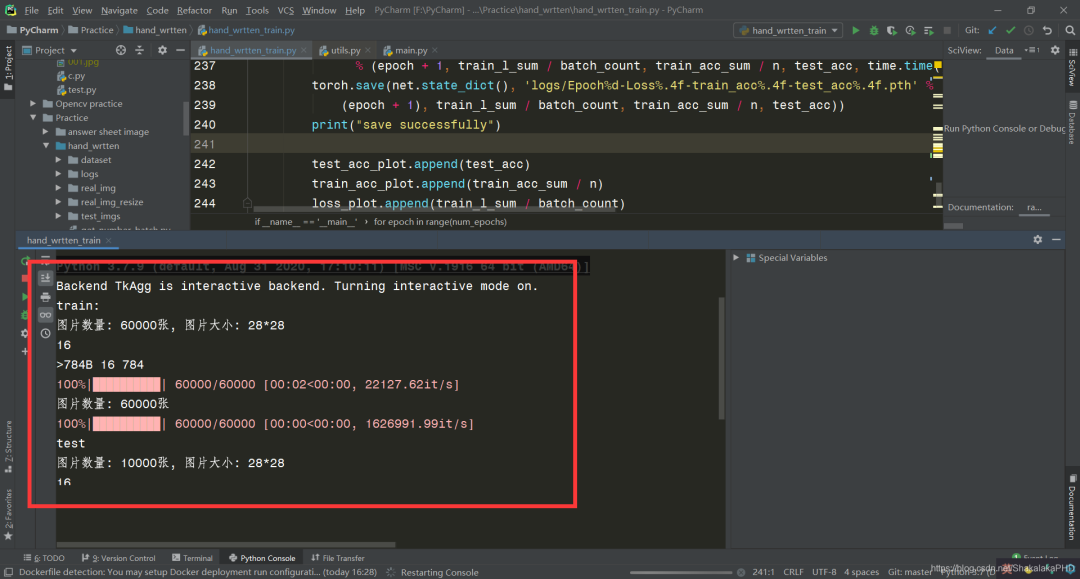
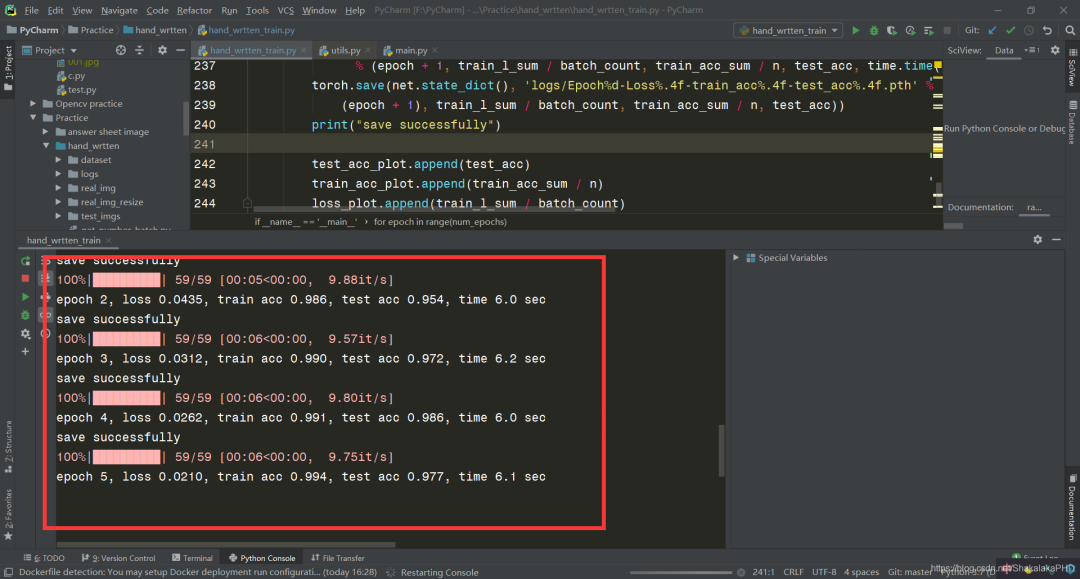 训练得到的权重会保存在logs文件夹下
训练得到的权重会保存在logs文件夹下 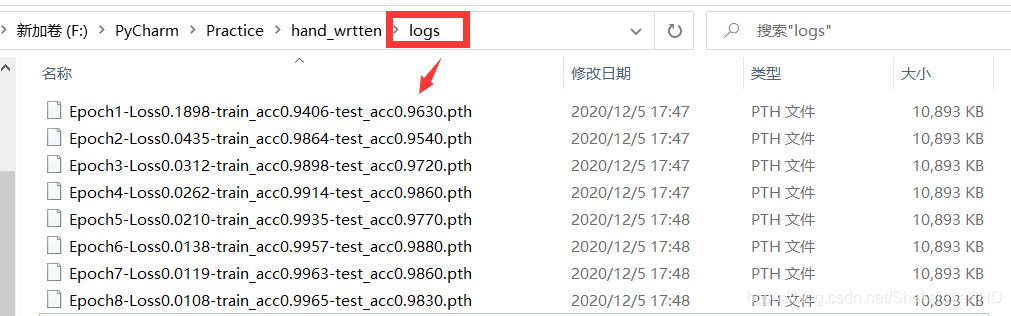 模型训练需要时间,此时等待训练结束即可(RTX2070上训练了1h左右)
模型训练需要时间,此时等待训练结束即可(RTX2070上训练了1h左右)
5.4使用训练好的模型测试网络
测试采用图片进行测试,代码见main_pthoto.py文件,使用方法与上面训练代码一直,代开后运行即可  同样值得注意的是,main_pthoto.py文件中图片路径需要修改为自己的路径,即这一段
同样值得注意的是,main_pthoto.py文件中图片路径需要修改为自己的路径,即这一段 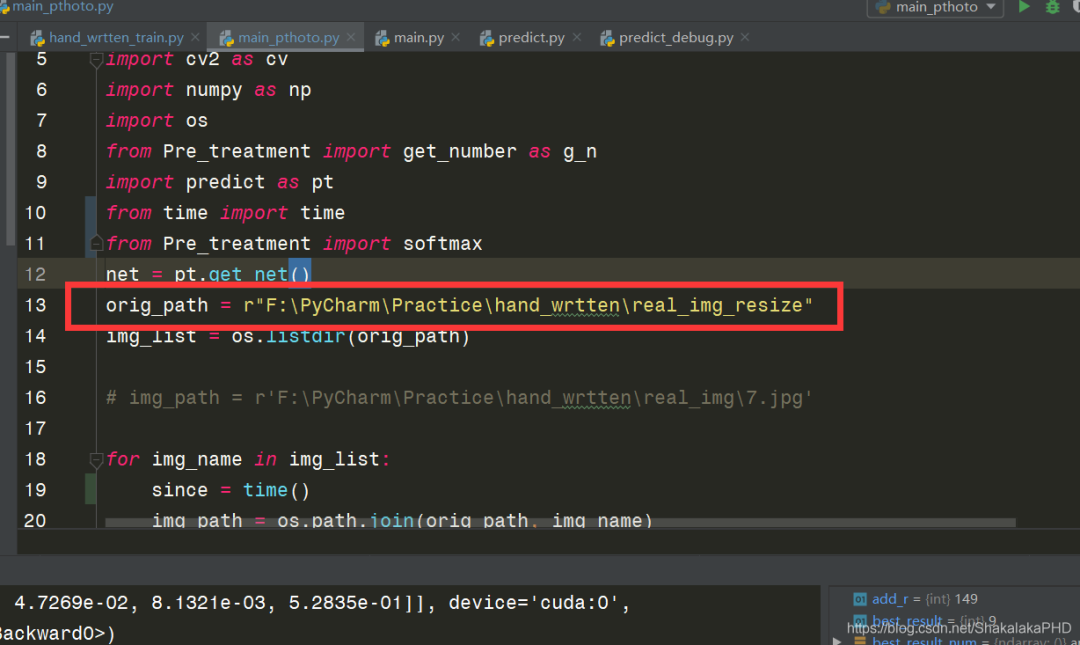 以及predict.py文件中权重片路径需要修改为自己在5.3步中训练得到的.pth文件路径,如图所示
以及predict.py文件中权重片路径需要修改为自己在5.3步中训练得到的.pth文件路径,如图所示 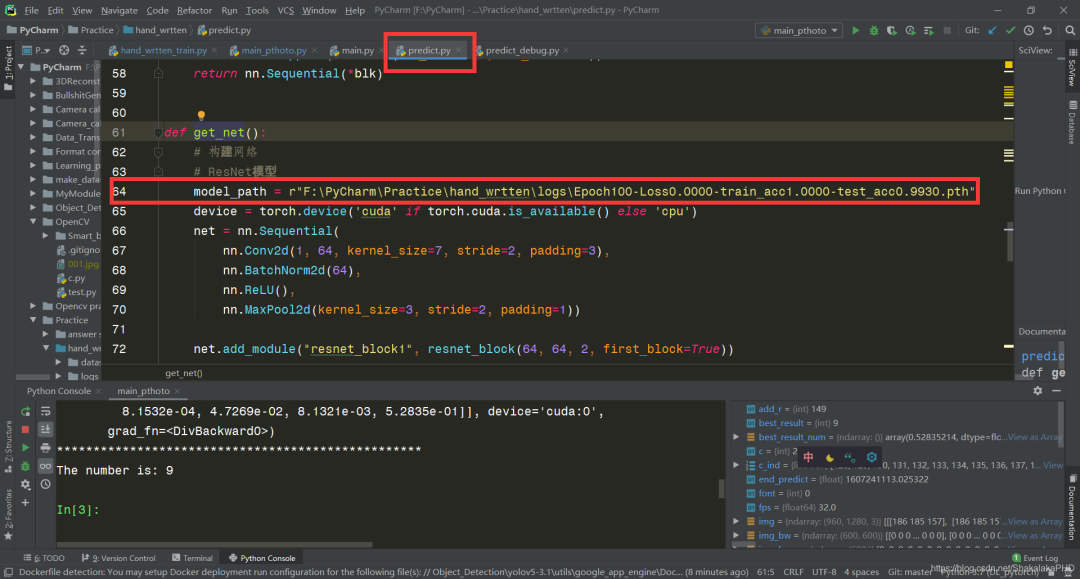 运行结果如下
运行结果如下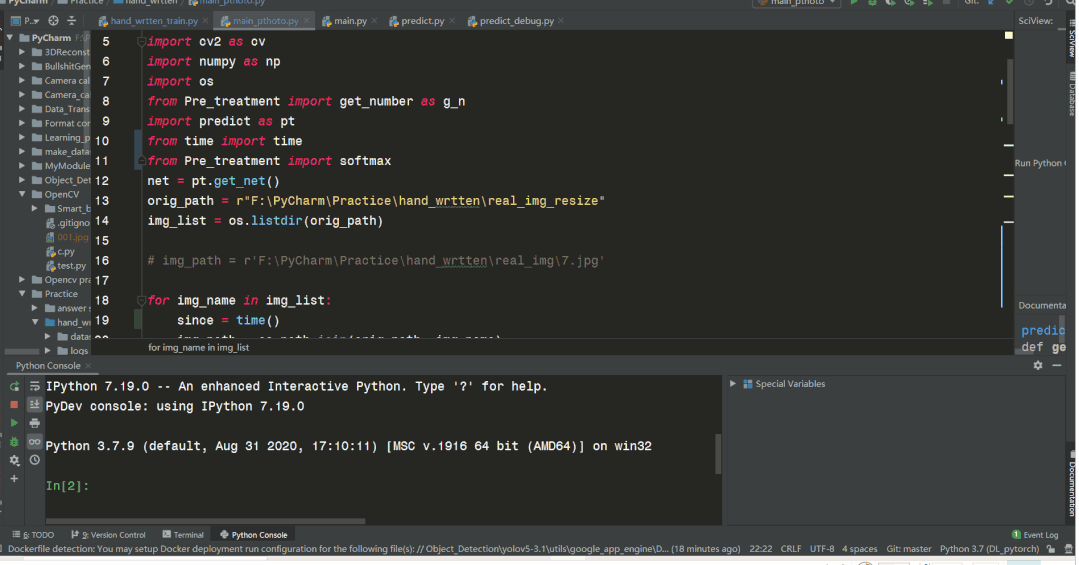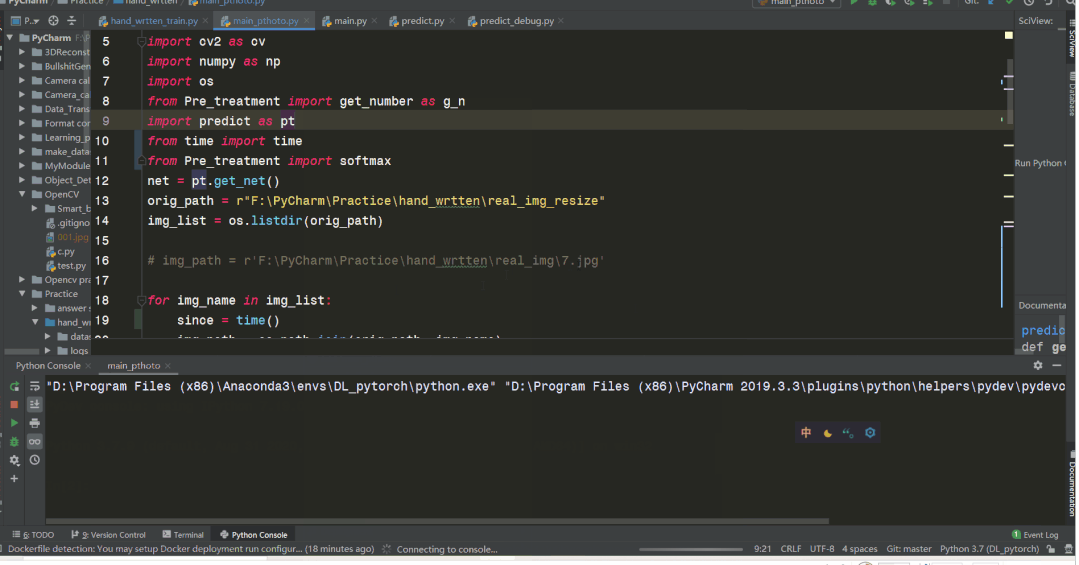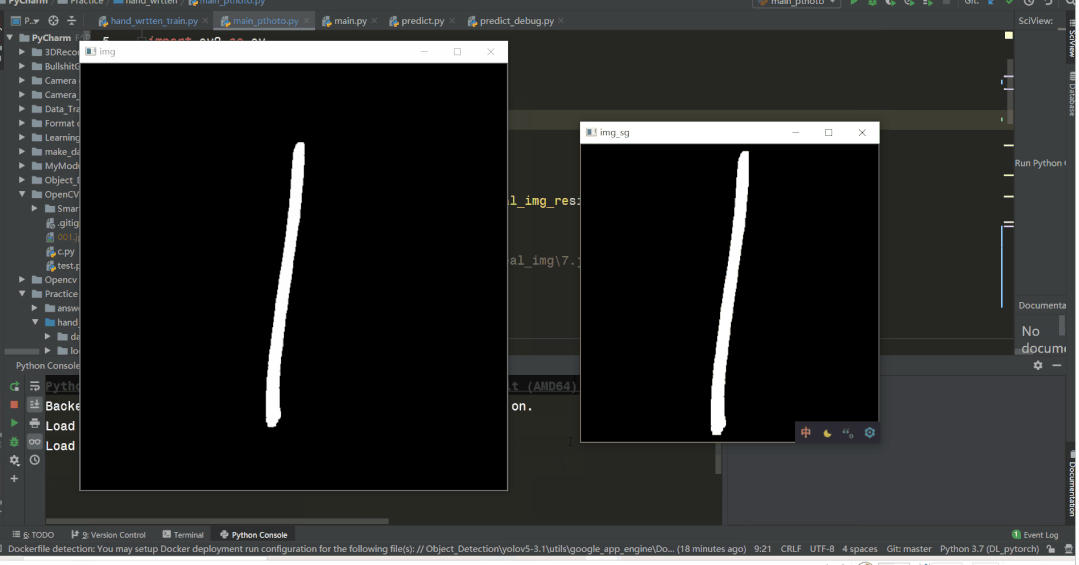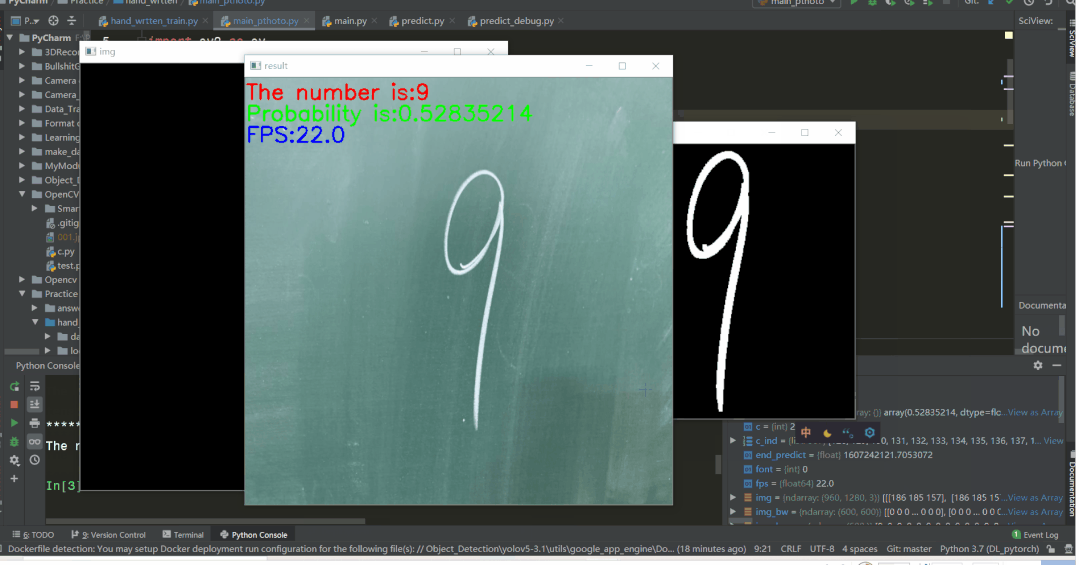
5.5调用摄像头实时检测
代码存在于main.py文件下,使用方法和5.4节图片检测一致,修改predict.py文件中权重片路径需要修改为自己在5.3步中训练得到的.pth文件路径,如图所示  再运行main.py文件即可,可以看到载入网络模型后开始调用摄像头,并开始检测
再运行main.py文件即可,可以看到载入网络模型后开始调用摄像头,并开始检测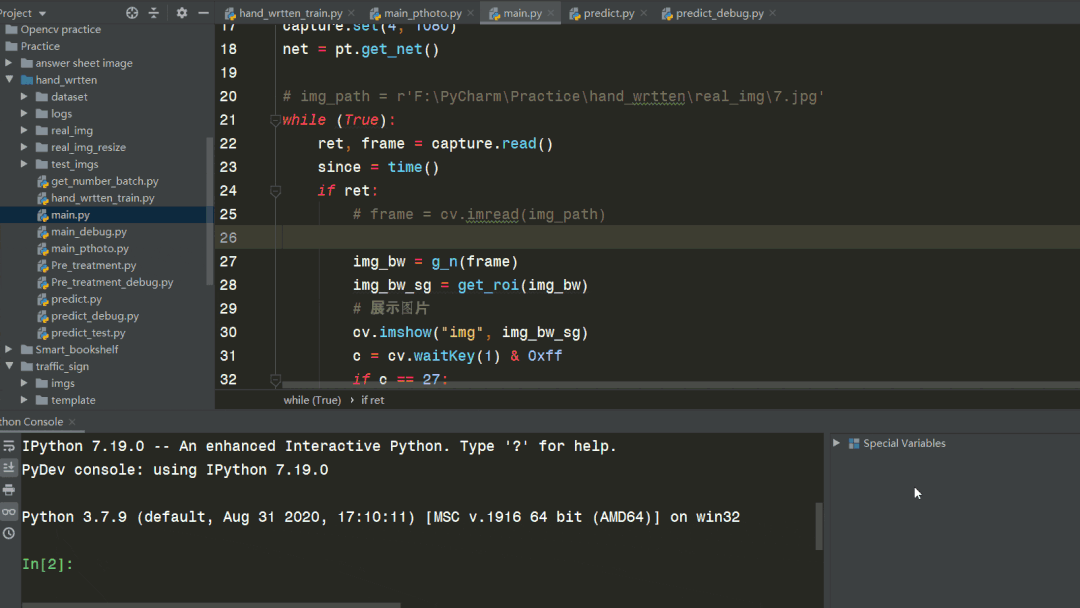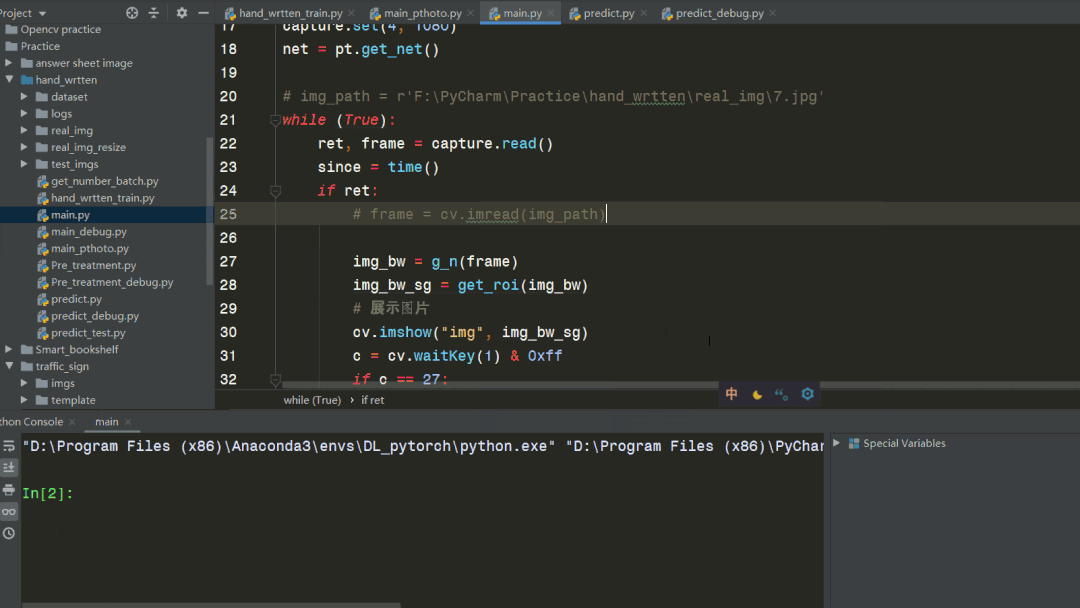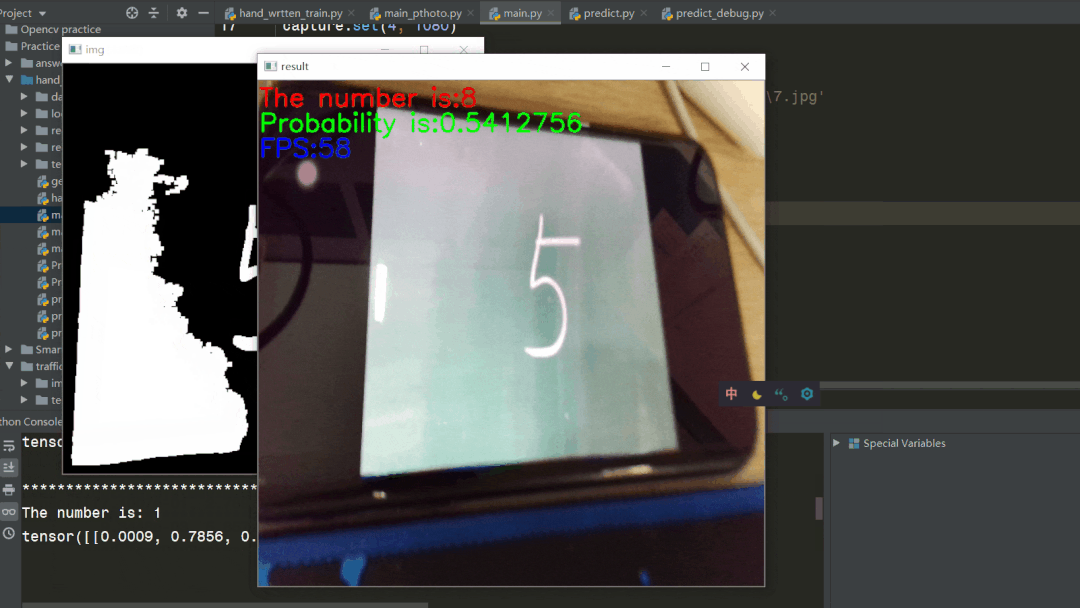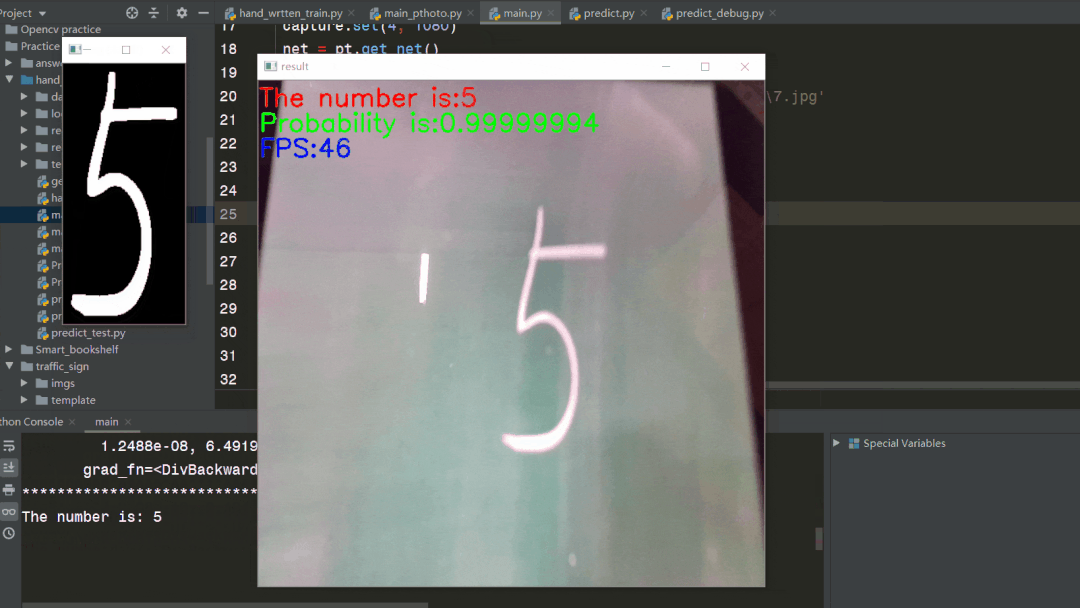
6.附录
在此附上本文核心代码:hand_wrtten_train.py
# author:Hurricane
# date: 2020/11/4
# E-mail:hurri_cane@qq.com
import numpy as np
import struct
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import cv2 as cv
import random
import torch
from torch import nn, optim
import torch.nn.functional as F
# import d2lzh_pytorch as d2l
import time
from tqdm import tqdm
# 训练集文件
train_images_idx3_ubyte_file = 'F:/PyCharm/Practice/hand_wrtten/dataset/train-images.idx3-ubyte'
# 训练集标签文件
train_labels_idx1_ubyte_file = 'F:/PyCharm/Practice/hand_wrtten/dataset/train-labels.idx1-ubyte'
# 测试集文件
test_images_idx3_ubyte_file = 'F:/PyCharm/Practice/hand_wrtten/dataset/t10k-images.idx3-ubyte'
# 测试集标签文件
test_labels_idx1_ubyte_file = 'F:/PyCharm/Practice/hand_wrtten/dataset/t10k-labels.idx1-ubyte'
# 读取数据部分
def decode_idx3_ubyte(idx3_ubyte_file):
bin_data = open(idx3_ubyte_file, 'rb').read()
offset = 0
fmt_header = '>iiii' # 因为数据结构中前4行的数据类型都是32位整型,所以采用i格式,但我们需要读取前4行数据,所以需要4个i。我们后面会看到标签集中,只使用2个ii。
magic_number, num_images, num_rows, num_cols = struct.unpack_from(fmt_header, bin_data, offset)
print('图片数量: %d张, 图片大小: %d*%d' % (num_images, num_rows, num_cols))
# 解析数据集
image_size = num_rows * num_cols
offset += struct.calcsize(fmt_header) # 获得数据在缓存中的指针位置,从前面介绍的数据结构可以看出,读取了前4行之后,指针位置(即偏移位置offset)指向0016。
print(offset)
fmt_image = '>' + str(
image_size) + 'B' # 图像数据像素值的类型为unsigned char型,对应的format格式为B。这里还有加上图像大小784,是为了读取784个B格式数据,如果没有则只会读取一个值(即一副图像中的一个像素值)
print(fmt_image, offset, struct.calcsize(fmt_image))
images = np.empty((num_images, 28, 28))
# plt.figure()
for i in tqdm(range(num_images)):
image = np.array(struct.unpack_from(fmt_image, bin_data, offset)).reshape((num_rows, num_cols)).astype(np.uint8)
# images[i] = cv.resize(image, (96, 96))
images[i] = image
# print(images[i])
offset += struct.calcsize(fmt_image)
return images
def decode_idx1_ubyte(idx1_ubyte_file):
bin_data = open(idx1_ubyte_file, 'rb').read()
offset = 0
fmt_header = '>ii'
magic_number, num_images = struct.unpack_from(fmt_header, bin_data, offset)
print('图片数量: %d张' % (num_images))
# 解析数据集
offset += struct.calcsize(fmt_header)
fmt_image = '>B'
labels = np.empty(num_images)
for i in tqdm(range(num_images)):
labels[i] = struct.unpack_from(fmt_image, bin_data, offset)[0]
offset += struct.calcsize(fmt_image)
return labels
def load_train_images(idx_ubyte_file=train_images_idx3_ubyte_file):
return decode_idx3_ubyte(idx_ubyte_file)
def load_train_labels(idx_ubyte_file=train_labels_idx1_ubyte_file):
return decode_idx1_ubyte(idx_ubyte_file)
def load_test_images(idx_ubyte_file=test_images_idx3_ubyte_file):
return decode_idx3_ubyte(idx_ubyte_file)
def load_test_labels(idx_ubyte_file=test_labels_idx1_ubyte_file):
return decode_idx1_ubyte(idx_ubyte_file)
# 构建网络部分
class Residual(nn.Module): # 本类已保存在d2lzh_pytorch包中方便以后使用
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, use_1x1conv=False, stride=1):
super(Residual, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=stride)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
if use_1x1conv:
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=stride)
else:
self.conv3 = None
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
def forward(self, X):
Y = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(X)))
Y = self.bn2(self.conv2(Y))
if self.conv3:
X = self.conv3(X)
return F.relu(Y + X)
class GlobalAvgPool2d(nn.Module):
# 全局平均池化层可通过将池化窗口形状设置成输入的高和宽实现
def __init__(self):
super(GlobalAvgPool2d, self).__init__()
def forward(self, x):
return F.avg_pool2d(x, kernel_size=x.size()[2:])
def resnet_block(in_channels, out_channels, num_residuals, first_block=False):
# num_residuals:残差数
if first_block:
assert in_channels == out_channels # 第一个模块的通道数同输入通道数一致
blk = []
for i in range(num_residuals):
if i == 0 and not first_block:
blk.append(Residual(in_channels, out_channels, use_1x1conv=True, stride=2))
else:
blk.append(Residual(out_channels, out_channels))
return nn.Sequential(*blk)
def evaluate_accuracy(img, label, net):
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
acc_sum, n = 0.0, 0
with torch.no_grad():
X = torch.unsqueeze(img, 1)
if isinstance(net, torch.nn.Module):
net.eval() # 评估模式, 这会关闭dropout
acc_sum += (net(X.to(device)).argmax(dim=1) == label.to(device)).float().sum().cpu().item()
net.train() # 改回训练模式
else: # 自定义的模型, 3.13节之后不会用到, 不考虑GPU
if ('is_training' in net.__code__.co_varnames): # 如果有is_training这个参数
# 将is_training设置成False
acc_sum += (net(X, is_training=False).argmax(dim=1) == label).float().sum().item()
else:
acc_sum += (net(X).argmax(dim=1) == label).float().sum().item()
n += label.shape[0]
return acc_sum / n
class FlattenLayer(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(FlattenLayer, self).__init__()
def forward(self, x): # x shape: (batch, *, *, ...)
return x.view(x.shape[0], -1)
if __name__ == '__main__':
print("train:")
train_images_org = load_train_images().astype(np.float32)
train_labels_org = load_train_labels().astype(np.int64)
print("test")
test_images = load_test_images().astype(np.float32)[0:1000]
test_labels = load_test_labels().astype(np.int64)[0:1000]
# 数据转换为Tensor
train_images = torch.from_numpy(train_images_org)
train_labels = torch.from_numpy(train_labels_org)
test_images = torch.from_numpy(test_images)
test_labels = torch.from_numpy(test_labels)
# test_images = load_test_images()
# test_labels = load_test_labels()
# 查看前十个数据及其标签以读取是否正确
for i in range(5):
j = random.randint(0, 60000)
print("now, show the number of image[{}]:".format(j), int(train_labels_org[j]))
img = train_images_org[j]
img = cv.resize(img, (600, 600))
cv.imshow("image", img)
cv.waitKey(0)
cv.destroyAllWindows()
print('all done!')
print("*" * 50)
# ResNet模型
net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1))
net.add_module("resnet_block1", resnet_block(64, 64, 2, first_block=True))
net.add_module("resnet_block2", resnet_block(64, 128, 2))
net.add_module("resnet_block3", resnet_block(128, 256, 2))
net.add_module("global_avg_pool", GlobalAvgPool2d()) # GlobalAvgPool2d的输出: (Batch, 512, 1, 1)
net.add_module("fc", nn.Sequential(FlattenLayer(), nn.Linear(256, 10)))
# 测试网络
X = torch.rand((1, 1, 28, 28))
for name, layer in net.named_children():
X = layer(X)
print(name, ' output shape:/t', X.shape)
# 训练
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
lr, num_epochs = 0.001, 100
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=lr)
batch_size = 1000
net = net.to(device)
print("training on ", device)
loss = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
loop_times = round(60000 / batch_size)
train_acc_plot = []
test_acc_plot = []
loss_plot = []
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
train_l_sum, train_acc_sum, n, batch_count, start = 0.0, 0.0, 0, 0, time.time()
for i in tqdm(range(1, loop_times)):
x = train_images[(i - 1) * batch_size:i * batch_size]
y = train_labels[(i - 1) * batch_size:i * batch_size]
x = torch.unsqueeze(x, 1) # 对齐维度
X = x.to(device)
y = y.to(device)
y_hat = net(X)
l = loss(y_hat, y)
optimizer.zero_grad()
l.backward()
optimizer.step()
train_l_sum += l.cpu().item()
train_acc_sum += (y_hat.argmax(dim=1) == y).sum().cpu().item()
n += y.shape[0]
batch_count += 1
test_acc = evaluate_accuracy(test_images, test_labels, net)
print('epoch %d, loss %.4f, train acc %.3f, test acc %.3f, time %.1f sec'
% (epoch + 1, train_l_sum / batch_count, train_acc_sum / n, test_acc, time.time() - start))
torch.save(net.state_dict(), 'logs/Epoch%d-Loss%.4f-train_acc%.4f-test_acc%.4f.pth' % (
(epoch + 1), train_l_sum / batch_count, train_acc_sum / n, test_acc))
print("save successfully")
test_acc_plot.append(test_acc)
train_acc_plot.append(train_acc_sum / n)
loss_plot.append(train_l_sum / batch_count)
x = range(0,100)
plt.plot(x,test_acc_plot,'r')
plt.plot(x, train_acc_plot, 'g')
plt.plot(x, loss_plot, 'b')
print("*" * 50)
main_pthoto.py
# author:Hurricane
# date: 2020/11/6
# E-mail:hurri_cane@qq.com
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
import os
from Pre_treatment import get_number as g_n
import predict as pt
from time import time
from Pre_treatment import softmax
net = pt.get_net()
orig_path = r"F:\PyCharm\Practice\hand_wrtten\real_img_resize"
img_list = os.listdir(orig_path)
# img_path = r'F:\PyCharm\Practice\hand_wrtten\real_img\7.jpg'
for img_name in img_list:
since = time()
img_path = os.path.join(orig_path, img_name)
img = cv.imread(img_path)
img_bw = g_n(img)
img_bw_c = img_bw.sum(axis=1) / 255
img_bw_r = img_bw.sum(axis=0) / 255
r_ind, c_ind = [], []
for k, r in enumerate(img_bw_r):
if r >= 5:
r_ind.append(k)
for k, c in enumerate(img_bw_c):
if c >= 5:
c_ind.append(k)
img_bw_sg = img_bw[ c_ind[0]:c_ind[-1],r_ind[0]:r_ind[-1]]
leng_c = len(c_ind)
leng_r = len(r_ind)
side_len = leng_c + 20
add_r = int((side_len-leng_r)/2)
img_bw_sg_bord = cv.copyMakeBorder(img_bw_sg,10,10,add_r,add_r,cv.BORDER_CONSTANT,value=[0,0,0])
# 展示图片
cv.imshow("img", img_bw)
cv.imshow("img_sg", img_bw_sg_bord)
c = cv.waitKey(1) & 0xff
img_in = cv.resize(img_bw_sg_bord, (28, 28))
result_org = pt.predict(img_in, net)
result = softmax(result_org)
best_result = result.argmax(dim=1).item()
best_result_num = max(max(result)).cpu().detach().numpy()
if best_result_num <= 0.5:
best_result = None
# 显示结果
img_show = cv.resize(img, (600, 600))
end_predict = time()
fps = np.ceil(1 / (end_predict - since))
font = cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX
cv.putText(img_show, "The number is:" + str(best_result), (1, 30), font, 1, (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv.putText(img_show, "Probability is:" + str(best_result_num), (1, 60), font, 1, (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv.putText(img_show, "FPS:" + str(fps), (1, 90), font, 1, (255, 0, 0), 2)
cv.imshow("result", img_show)
cv.waitKey(1)
print(result)
print("*" * 50)
print("The number is:", best_result)
main.py
# author:Hurricane
# date: 2020/11/6
# E-mail:hurri_cane@qq.com
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
import os
from Pre_treatment import get_number as g_n
from Pre_treatment import get_roi
import predict as pt
from time import time
from Pre_treatment import softmax
# 实时检测视频
capture = cv.VideoCapture(0,cv.CAP_DSHOW)
capture.set(3, 1920)
capture.set(4, 1080)
net = pt.get_net()
# img_path = r'F:\PyCharm\Practice\hand_wrtten\real_img\7.jpg'
while (True):
ret, frame = capture.read()
since = time()
if ret:
# frame = cv.imread(img_path)
img_bw = g_n(frame)
img_bw_sg = get_roi(img_bw)
# 展示图片
cv.imshow("img", img_bw_sg)
c = cv.waitKey(1) & 0xff
if c == 27:
capture.release()
break
img_in = cv.resize(img_bw_sg, (28, 28))
result_org = pt.predict(img_in, net)
result = softmax(result_org)
best_result = result.argmax(dim=1).item()
best_result_num = max(max(result)).cpu().detach().numpy()
if best_result_num <= 0.5:
best_result = None
# 显示结果
img_show = cv.resize(frame, (600, 600))
end_predict = time()
fps = round(1/(end_predict-since))
font = cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX
cv.putText(img_show, "The number is:" + str(best_result), (1, 30), font, 1, (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv.putText(img_show, "Probability is:" + str(best_result_num), (1, 60), font, 1, (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv.putText(img_show, "FPS:" + str(fps), (1, 90), font, 1, (255, 0, 0), 2)
cv.imshow("result", img_show)
cv.waitKey(1)
print(result)
print("*" * 50)
print("The number is:", best_result)
else:
print("please check camera!")
break
Pre_treatment.py
# author:Hurricane
# date: 2020/11/6
# E-mail:hurri_cane@qq.com
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
import os
def get_number(img):
img_gray = cv.cvtColor(img, cv.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
img_gray_resize = cv.resize(img_gray, (600, 600))
ret, img_bw = cv.threshold(img_gray_resize, 200, 255, cv.THRESH_BINARY)
kernel = np.ones((3, 3), np.uint8)
# img_open = cv.morphologyEx(img_bw,cv.MORPH_CLOSE,kernel)
img_open = cv.dilate(img_bw, kernel, iterations=2)
num_labels, labels, stats, centroids = \
cv.connectedComponentsWithStats(img_open, connectivity=8, ltype=None)
for sta in stats:
if sta[4] < 1000:
cv.rectangle(img_open, tuple(sta[0:2]), tuple(sta[0:2] + sta[2:4]), (0, 0, 255), thickness=-1)
return img_open
def get_roi(img_bw):
img_bw_c = img_bw.sum(axis=1) / 255
img_bw_r = img_bw.sum(axis=0) / 255
all_sum = img_bw_c.sum(axis=0)
if all_sum != 0:
r_ind, c_ind = [], []
for k, r in enumerate(img_bw_r):
if r >= 5:
r_ind.append(k)
for k, c in enumerate(img_bw_c):
if c >= 5:
c_ind.append(k)
img_bw_sg = img_bw[c_ind[0]:c_ind[-1], r_ind[0]:r_ind[-1]]
leng_c = len(c_ind)
leng_r = len(r_ind)
side_len = max(leng_c, leng_r) + 20
if leng_c == side_len:
add_r = int((side_len - leng_r) / 2)
add_c = 10
else:
add_r = 10
add_c = int((side_len - leng_c) / 2)
img_bw_sg_bord = cv.copyMakeBorder(img_bw_sg, add_c, add_c, add_r, add_r, cv.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=[0, 0, 0])
return img_bw_sg_bord
else:
return img_bw
def softmax(X):
X_exp = X.exp()
partition = X_exp.sum(dim=1, keepdim=True)
return X_exp / partition
predict.py
# author:Hurricane
# date: 2020/11/5
# E-mail:hurri_cane@qq.com
# -------------------------------------#
# 对单张图片进行预测
# -------------------------------------#
import numpy as np
import struct
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import cv2 as cv
import random
import torch
from torch import nn, optim
import torch.nn.functional as F
class Residual(nn.Module): # 本类已保存在d2lzh_pytorch包中方便以后使用
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, use_1x1conv=False, stride=1):
super(Residual, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=stride)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
if use_1x1conv:
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=stride)
else:
self.conv3 = None
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
def forward(self, X):
Y = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(X)))
Y = self.bn2(self.conv2(Y))
if self.conv3:
X = self.conv3(X)
return F.relu(Y + X)
class GlobalAvgPool2d(nn.Module):
# 全局平均池化层可通过将池化窗口形状设置成输入的高和宽实现
def __init__(self):
super(GlobalAvgPool2d, self).__init__()
def forward(self, x):
return F.avg_pool2d(x, kernel_size=x.size()[2:])
def resnet_block(in_channels, out_channels, num_residuals, first_block=False):
# num_residuals:残差数
if first_block:
assert in_channels == out_channels # 第一个模块的通道数同输入通道数一致
blk = []
for i in range(num_residuals):
if i == 0 and not first_block:
blk.append(Residual(in_channels, out_channels, use_1x1conv=True, stride=2))
else:
blk.append(Residual(out_channels, out_channels))
return nn.Sequential(*blk)
class FlattenLayer(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(FlattenLayer, self).__init__()
def forward(self, x): # x shape: (batch, *, *, ...)
return x.view(x.shape[0], -1)
def get_net():
# 构建网络
# ResNet模型
model_path = r"F:\PyCharm\Practice\hand_wrtten\logs\Epoch100-Loss0.0000-train_acc1.0000-test_acc0.9930.pth"
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1))
net.add_module("resnet_block1", resnet_block(64, 64, 2, first_block=True))
net.add_module("resnet_block2", resnet_block(64, 128, 2))
net.add_module("resnet_block3", resnet_block(128, 256, 2))
net.add_module("global_avg_pool", GlobalAvgPool2d()) # GlobalAvgPool2d的输出: (Batch, 512, 1, 1)
net.add_module("fc", nn.Sequential(FlattenLayer(), nn.Linear(256, 10)))
# 测试网络
# X = torch.rand((1, 1, 28, 28))
# for name, layer in net.named_children():
# X = layer(X)
# print(name, ' output shape:\t', X.shape)
# 加载网络模型
print("Load weight into state dict...")
stat_dict = torch.load(model_path, map_location=device)
net.load_state_dict(stat_dict)
net.to(device)
net.eval()
print("Load finish!")
return net
def predict(img, net):
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
img_in = torch.from_numpy(img)
img_in = torch.unsqueeze(img_in, 0)
img_in = torch.unsqueeze(img_in, 0).to(device)
img_in = img_in.float()
result_org = net(img_in)
return result_org
