可以迭代大部分数据类型的 for…of 为什么不能遍历普通对象?
加入我们一起学习,天天进步
for…of 及其使用
for...of的语法:
for (variable of iterable) {// statement}// variable:每个迭代的属性值被分配给该变量。// iterable:一个具有可枚举属性并且可以迭代的对象。
常用用法
{// 迭代字符串const iterable = 'ES6';for (const value of iterable) {console.log(value);}// Output:// "E"// "S"// "6"}{// 迭代数组const iterable = ['a', 'b'];for (const value of iterable) {console.log(value);}// Output:// a// b}{// 迭代Set(集合)const iterable = new Set([1, 2, 2, 1]);for (const value of iterable) {console.log(value);}// Output:// 1// 2}{// 迭代Mapconst iterable = new Map([["a", 1], ["b", 2], ["c", 3]]);for (const entry of iterable) {console.log(entry);}// Output:// ["a", 1]// ["b", 2]// ["c", 3]for (const [key, value] of iterable) {console.log(value);}// Output:// 1// 2// 3}{// 迭代Arguments Object(参数对象)function args() {for (const arg of arguments) {console.log(arg);}}args('a', 'b');// Output:// a// b}{// 迭代生成器function* foo(){yield 1;yield 2;yield 3;};for (let o of foo()) {console.log(o);}// Output:// 1// 2// 3}
Uncaught TypeError: obj is not iterable
// 普通对象const obj = {foo: 'value1',bar: 'value2'}for(const item of obj){console.log(item)}// Uncaught TypeError: obj is not iterable
如何用for...of迭代普通对象
const obj = {foo: 'value1',bar: 'value2'}// 打印由value组成的数组console.log(Object.values(obj)) // ["value1", "value2"]// 打印由key组成的数组console.log(Object.keys(obj)) // ["foo", "bar"]// 打印由[key, value]组成的二维数组// copy(Object.entries(obj))可以把输出结果直接拷贝到剪贴板,然后黏贴console.log(Object.entries(obj)) // [["foo","value1"],["bar","value2"]]
const obj = {foo: 'value1',bar: 'value2'}// 方法一:使用for of迭代Object.entries(obj)形成的二维数组,利用解构赋值得到valuefor(const [, value] of Object.entries(obj)){console.log(value) // value1, value2}// 方法二:Map// 普通对象转Map// Map 可以接受一个数组作为参数。该数组的成员是一个个表示键值对的数组console.log(new Map(Object.entries(obj)))// 遍历普通对象生成的Mapfor(const [, value] of new Map(Object.entries(obj))){console.log(value) // value1, value2}// 方法三:继续使用for infor(const key in obj){console.log(obj[key]) // value1, value2}{// 方法四:将【类数组(array-like)对象】转换为数组// 该对象需具有一个 length 属性,且其元素必须可以被索引。const obj = {length: 3, // length是必须的,否则什么也不会打印0: 'foo',1: 'bar',2: 'baz',a: 12 // 非数字属性是不会打印的};const array = Array.from(obj); // ["foo", "bar", "baz"]for (const value of array) {console.log(value);}// Output: foo bar baz}{// 方法五:给【类数组】部署数组的[Symbol.iterator]方法【对普通字符串属性对象无效】const iterable = {0: 'a',1: 'b',2: 'c',length: 3,[Symbol.iterator]: Array.prototype[Symbol.iterator]};for (let item of iterable) {console.log(item); // 'a', 'b', 'c'}}
注意事项
const obj = {foo: 'value1',bar: 'value2',baz: 'value3'}for(const [, value] of Object.entries(obj)){if (value === 'value2') break // 不会再执行下次迭代console.log(value) // value1};[1,2].forEach(item => {if(item == 1) break // Uncaught SyntaxError: Illegal break statementconsole.log(item)});[1,2].forEach(item => {if(item == 1) continue // Uncaught SyntaxError: Illegal continue statement: no surrounding iteration statementconsole.log(item)});[1,2].forEach(item => {if(item == 1) return // 仍然会继续执行下一次循环,打印2console.log(item) // 2})
Array.prototype.newArr = () => {};Array.prototype.anotherNewArr = () => {};const array = ['foo', 'bar', 'baz'];for (const value in array) {console.log(value); // 0 1 2 newArr anotherNewArr}for (const value of array) {console.log(value); // 'foo', 'bar', 'baz'}
普通对象为何不能被 for of 迭代
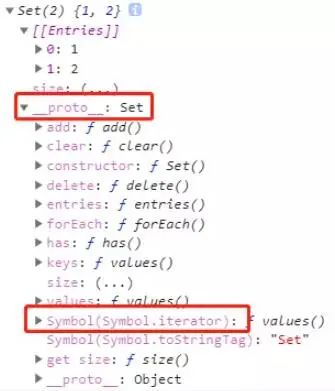
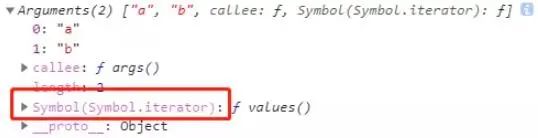
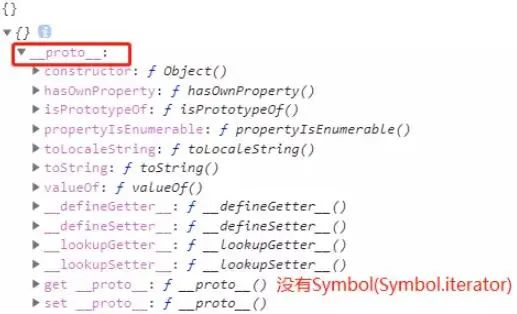
Iterator(遍历器)
关于Iterator(遍历器),可以参照阮一峰老师写的《ECMAScript 6 入门教程—异步遍历器》教程。
如何实现Symbol.iterator方法,使普通对象可被 for of 迭代
const arr = [1,2,3];const iterator = arr[Symbol.iterator]();console.log(iterator.next()); // {value: 1, done: false}console.log(iterator.next()); // {value: 2, done: false}console.log(iterator.next()); // {value: 3, done: false}console.log(iterator.next()); // {value: undefined, done: true}
// 普通对象const obj = {foo: 'value1',bar: 'value2',[Symbol.iterator]() {// 这里Object.keys不会获取到Symbol.iterator属性,原因见下文const keys = Object.keys(obj);let index = 0;return {next: () => {if (index < keys.length) {// 迭代结果 未结束return {value: this[keys[index++]],done: false};} else {// 迭代结果 结束return { value: undefined, done: true };}}};}}for (const value of obj) {console.log(value); // value1 value2};
console.log([...obj]); // ["value1", "value2"]console.log([...{}]); // console.log is not iterable (cannot read property Symbol(Symbol.iterator))
迭代器模式
const obj = {// 数据结构调整data: ['value1', 'value2'],[Symbol.iterator]() {let index = 0;return {next: () => {if (index < this.data.length) {// 迭代结果 未结束return {value: this.data[index++],done: false};} else {// 迭代结果 结束return { value: undefined, done: true };}}};}}// 外部调用for (const value of obj) {console.log(value); // value1 value2}
const obj1 = {data: ['value1', 'value2']}const obj2 = {data: [1, 2]}// 遍历方法consoleEachData = (obj) => {obj[Symbol.iterator] = () => {let index = 0;return {next: () => {if (index < obj.data.length) {return {value: obj.data[index++],done: false};} else {return { value: undefined, done: true };}}};}for (const value of obj) {console.log(value);}}consoleEachData(obj1); // value1 value2consoleEachData(obj2); // 1 2
一点补充
let aClone = { ...a };// 等同于let aClone = Object.assign({}, a);
❤️爱心三连击 1.看到这里了就点个在看支持下吧,你的「点赞,在看」是我创作的动力。
2.关注公众号
程序员成长指北,回复「1」加入Node进阶交流群!「在这里有好多 Node 开发者,会讨论 Node 知识,互相学习」!3.也可添加微信【ikoala520】,一起成长。
“在看转发”是最大的支持
评论
