Transformer系列 | 更深、更强、更轻巧的Transformer,DeLighT(文末...
点击上方【AI人工智能初学者】,选择【星标】公众号
期待您我的相遇与进步

1 简介本文提出了一个更深更轻的Transformer,DeLighT,它的性能与Transformer相似,甚至更好,平均少了2到3倍的参数。
本文提出了一个更深更轻量的Transformer,DeLighT,DeLighT更有效地在每个Transformer Block中分配参数:
- 1)、使用DeLighT转换进行深度和轻量级的转换;
- 2)、使用Block-wise Scaling进行跨Block,允许在输入附近有较浅和较窄的DeLighT Block,以及在输出附近有较宽和较深的DeLighT Block。
总的来说,DeLighT网络的深度是标准Transformer的2.5到4倍,但参数和操作更少。在机器翻译和语言建模任务上的实验表明,DeLighT在提高了基准Transformer性能的基础上,平均减少了2到3倍的参数量。
2 相关工作2.1 Improving transformers
第1种研究研究解决了在长输入序列上计算Self-Attention的问题。这些方法可以与本文的架构相结合。
第2种研究侧重于解释多头注意力。研究表明增加Transformer Header的数量会导致冗余表示,使用带有预定义模式或综合注意矩阵的固定注意Header可以提高性能。
第3种研究重点是通过学习更好的表示来改进Transformer。这些工作旨在使用不同的变换来提高Transformer的表达性,例如,使用卷积、门控线性单元或多分支特征提取器。本文的工作属于这一类。与以前的工作不同,本文证明了使用DeLighT变换在块级和使用块尺度缩放操作在块级进行有效地分配参数是可能的。
2.2 Model scaling
Model scaling是提高序列模型性能的一种标准方法。模型的尺寸在宽度尺度上增加,同时在深度尺度上堆叠更多的Block。在这2种情况下(以及它们的组合),网络的每个Block内的参数都是相同的,这可能会导致次优解。为了进一步提高序列模型的性能,本文引入了块尺度缩放,允许设计可变大小的块和对网络中的参数进行有效的分配。
本文的研究结果表明:
- 1)、靠近输入的较浅且较窄的DeLighT Block,以及靠近输出的较深且较宽的DeLighT Block能够提供最好的性能;
- 2)、与单独使用模型缩放相比,基于块尺度缩放的模型能够获得更好的性能。
本文也注意到,卷积神经网络(CNNs)还可以学习靠近输入的较浅和较窄的表示,以及靠近输出的较深和较宽的表示。与CNN在每个卷积层执行固定数量的操作不同,建议的块缩放在每个层和块中使用可变数量的操作。
2.3 Improving sequence models
最近在改进序列模型的其他相关方法上也有重要的工作,包括(1)使用更好的标记级表示(例如使用BPE)、自适应输入和输出以及定义来提高准确性,以及(2)使用压缩、修剪和蒸馏来提高效率。
本文工作最接近的是定义转换,它也使用expand-reduce策略学习表示。DeFINE转换(图1c)和DeLighT转换(图1d)之间的关键区别是,DeLighT转换更有效地在扩展层和简化层中分配参数。
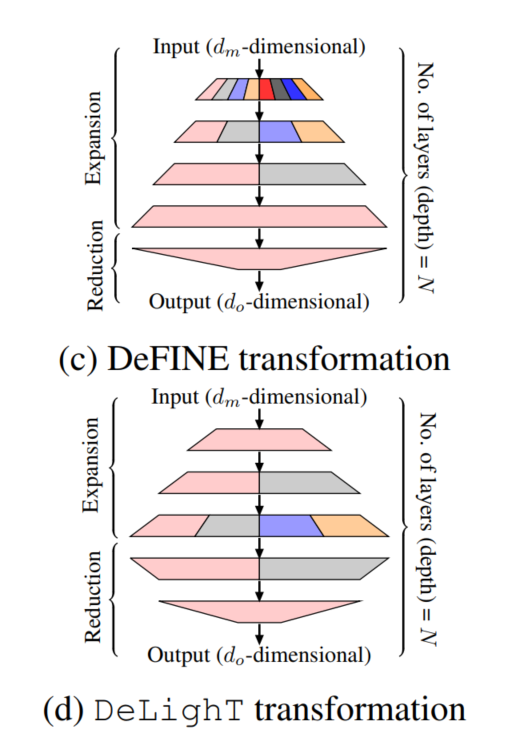
DeFINE在组线性变换中使用更少的组来学习更鲁棒的表征,与之不同的是,DeLighT transformation使用更多的组来学习更广泛的表示,且参数更少。DeLighT转换获得了与DeFINE转换相当的性能,但参数却少得多。
3 DeLight Transformer一个标准的Transformer Block如图1a所示:
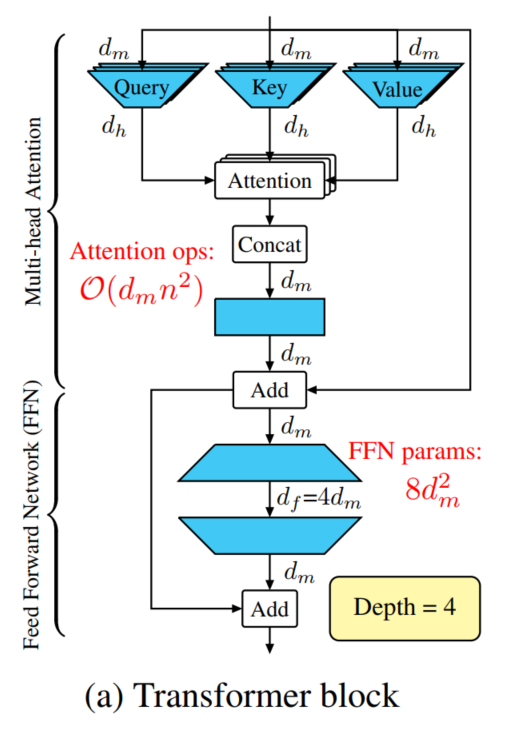
包括使用Query、Key、Value来建模序列Token之间的关系,以及使用一个前馈网络(FFN)来学习更广泛的表征。
多头注意通过对输入应用3个投影得到Query、Key、Value,每个投影由h个线性层(或头)组成,将维的输入映射到一个维的空间,其中是head维。
FFN由一下2个线性层操作完成:
- 第1步:扩展维度从到;
- 第2步:减少维度从到。
Transformer Block的深度是4,一般情况下,基于Transformer的网络设计均是按顺序堆叠Transformer Block,以增加网络容量和深度。
3.1 DeLight
DeLighT变换先将维度输入向量映射到高维空间(展开),然后利用N层群变换将其降为维度的输出向量(降阶),如图1d所示。
在expansion-reduction阶段,DeLighT变换使用组线性变换(GLTs),因为它们通过从输入的特定部分导出输出来学习局部表示,比线性变换更有效。为了学习全局表征,DeLighT变换使用特征变换在组线性变换的不同组之间共享信息,类似于卷积网络中的通道变换。
增加Transformer的表达能力和容量的一种标准方法是增加输入维数。然而,线性增加也会增加标准Transformer块中多线程注意力的复杂度(,其中是序列长度)。与此相反,为了增加DeLighT块的表现力和容量,本文使用扩展和缩小阶段来增加中间DeLighT转换的深度和宽度。这使DeLighT能够使用更小的维度和更少的操作来计算注意力。
DeLighT变换由5个配置参数控制:
- (1)GLT层数N,
- (2)宽度乘法器,
- (3)输入维数,
- (4)输出维数,
- (5)GLT中的最大组。
在expansion阶段,DeLighT transformation将维输入投影到高维空间,,线性层为N/2层;
在reduction阶段,DeLighT变换使用剩余的N−N/2 GLT层将维向量投影到维空间。
数学上定义GLT层l的输出Y为:
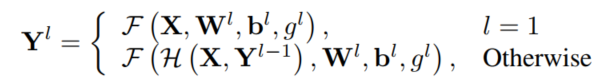
其中,和分别为liner的第l层组的变换函数F的权重和偏置项,简单地说,F函数输入X并分成个非重叠组,这样。函数F通过使用权重和偏差对每个进行线性变换,产生输出。
然后,将每组的输出cat起来,产生输出。函数H首先将每组的输出变换为Yl−1,然后通过Mehta等人的输入混频器连接将其与输入结合,以避免梯度消失问题。
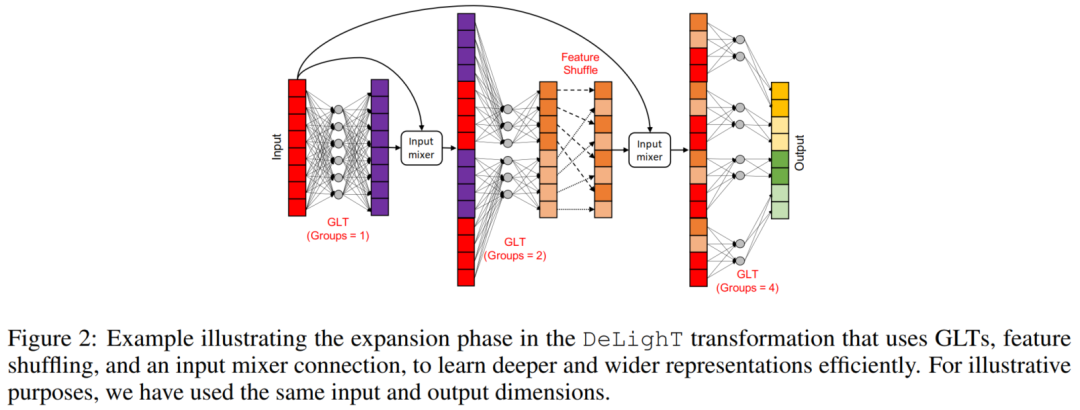
图2用组线性变换、特征变换和输入混频器连接来可视化了DeLighT变换的扩展阶段。在DeLighT变换中第l-th GLT处的组数计算如下:
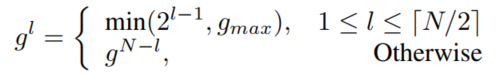
在实验中,作者使用,这样每组至少有32个输入元素。
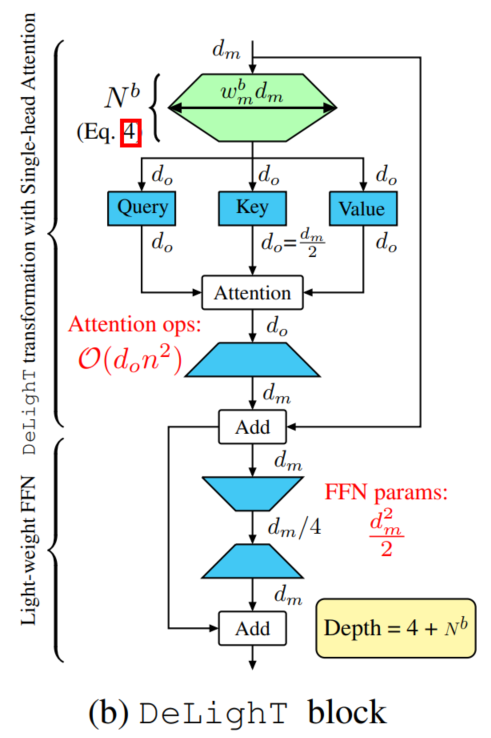
3.2 DeLighT Block
图1b显示了如何将DeLighT transformation集成到transformer块中以提高其效率。首先将维度的输入输入到DeLighT变换中,生成维度输出。然后将这些维度输出输入到一个单一的头部注意力中,然后是通过一个轻量级的FFN来建模它们的关系。
DeLighT layer和Single Head Attention
假设有一个由n个输入token组成的序列,每个token的维数都是。这些n个维的输入首先被输入到DeLighT变换中产生n个维的输出,其中。
然后使用3个线性层同时投影这n个维输出,以产生do维查询Q、键K和值v。然后,使用缩放点积注意对这n个token之间的上下文关系建模。为了使用剩余连接,这个注意操作的维输出被线性投影到维空间。
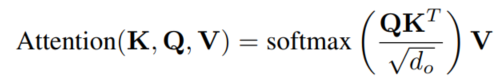
假设,DeLighT能够学习更广泛的表征,这使得可以用单头注意力取代多头注意力。标准transformer和DeLighT块中计算注意力的计算代价分别为和,其中;
因此,DeLighT块将计算注意力的成本降低了一个因子。在实验中,使用,因此需要的乘法-加法操作比transformer架构少2倍。
Light-weight FFN
与transformer中的ffn类似,这个块也由两个线性层组成。由于DeLighT块已经使用DeLighT转换合并了更广泛的表示,它允许在transformer中反转FFN层的功能。第1层将输入从降维到,第2层将输入从扩展到,其中为降维因子(见图1b)。轻量级FFN通过减少了参数和操作的数量。在标准transformer中,FFN的尺寸扩大了4.1倍。在实验中使用r=4。因此,轻量化的FFN将FFN中的参数数量减少了16倍。
Block depth
DeLighT块栈包括:
- 1)、1个有N个GLTs的DeLighT转换,
- 2)、3个平行的用于键、查询和值的线性层,
- 3)、一个投影层,
- 4)、轻量级FFN的2个线性层。
因此,DeLighT块的深度是N+4。与标准transformer(深度为4)相比,DeLighT块更深。
3.3 Block-Wise Scaling
改进序列模型性能的标准方法包括增加模型尺寸(宽度缩放),堆叠更多的块(深度缩放),或两者兼用。然而,这种尺度变换在小数据集上并不十分有效。
例如,在WMT'16 En-Ro语料上,当一个基于transformer(=512)的网络被替换为大型transformer(=1024)时,参数的数量增加了大约4倍,而性能没有明显变化(BLEU:34.28 vs.34.35)。假设这是因为缩放模型宽度和深度在块之间均匀分配参数,这可能导致学习冗余参数。为了创建更深和更广的网络,作者将模型扩展到块级别(参见下图3)。
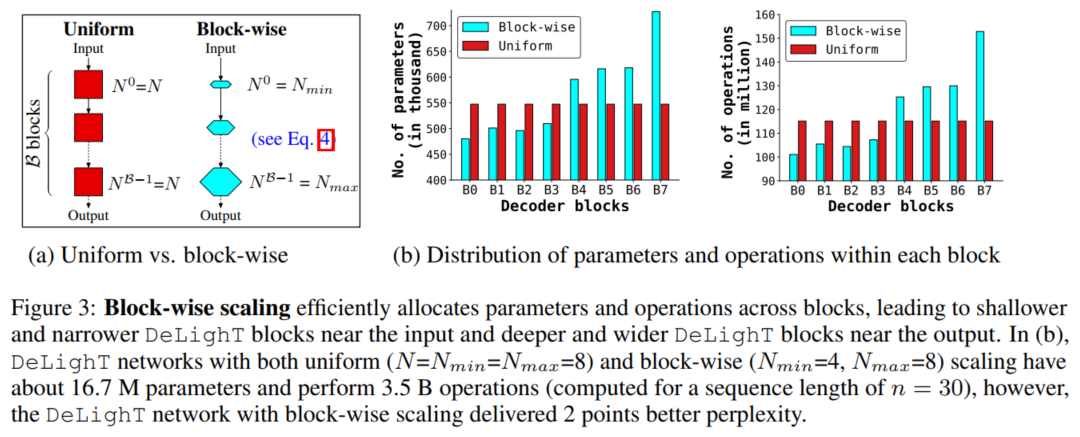
Scaling the DeLighT block
DeLighT块使用DeLighT变换学习深度和宽度表示,其深度和宽度分别由两个配置参数控制:GLT层数N和宽度乘法器(图3a)。这些配置参数允许增加DeLighT块内可学习参数的数量,独立于输入和输出维度。标准transformer组不可能进行这种校准,因为它们的表达能力和容量是输入的函数(输入维数=头维数)。
在这里,作者引入了按块缩放,它创建了一个具有可变大小的DeLighT块的网络,在输入附近分配较浅和较窄的DeLighT块,在输出附近分配较深和较宽的DeLighT块。
为此引入了2个网络范围的配置参数:DeLighT变换中的最小和最大数量。对于b-th DeLighT块使用线性缩放方法计算DeLighT变换中GLTs Nb的数目和宽度乘子。通过这种缩放,每个DeLighT块都有不同的深度和宽度(图3a)。
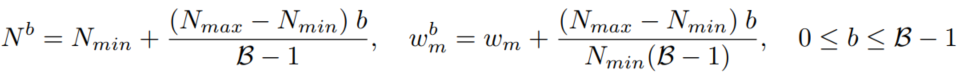
其中,B为网络中DeLighT块的数量。
Network depth
transformer组的深度固定,即depth=4。因此,先前的研究将基于transformer的网络的深度与transformer块的数量联系起来。而本文提供了一个不同的视角来学习更深层次的表示,其中每个块是不同大小的。为了计算网络深度使用了跨不同领域的标准定义,包括计算机视觉和理论机器学习。这些工作测量网络深度作为顺序可学习层的数量(例如,卷积,线性,或组线性)。同理,有B块的DeLighT和transformer网络的深度分别为和4B。
class DeLighTTransformerEncoderLayer(nn.Module):
"""DeLight Encoder layer
"""
def __init__(self, args, embed_dim, width_multiplier=DEFAULT_WIDTH_MULTIPLIER, dextra_depth=DEFAULT_MIN_DEXTRA_LAYERS,
dextra_proj=2):
super().__init__()
self.embed_dim = embed_dim
assert embed_dim % dextra_proj == 0
self.proj_dim = embed_dim // dextra_proj
self.dextra_layer = DExTraUnit(in_features=self.embed_dim,
in_proj_features=self.proj_dim,
out_features=self.proj_dim,
width_multiplier=width_multiplier,
dextra_depth=dextra_depth,
dextra_dropout=args.delight_dropout,
max_glt_groups=args.delight_enc_max_groups,
act_type=args.act_type,
use_bias=True,
norm_type=args.norm_type,
glt_shuffle=args.glt_shuffle,
is_iclr_version=args.define_iclr
)
self.self_attn = SingleHeadAttention(q_in_dim=self.proj_dim,
kv_in_dim=self.proj_dim,
proj_dim=self.proj_dim,
out_dim=self.embed_dim,
dropout=args.attention_dropout,
bias=True,
self_attention=True,
encoder_decoder_attention=False)
self.self_attn_layer_norm = get_norm_layer(name=args.norm_type, out_features=self.embed_dim)
self.dropout = args.dropout
self.norm_fn = args.norm_type
self.act_type = args.act_type
self.activation_fn = get_activation_layer(name=args.act_type)
self.activation_dropout = getattr(args, "activation_dropout", 0)
if self.activation_dropout == 0:
# for backwards compatibility with models that use args.relu_dropout
self.activation_dropout = getattr(args, "relu_dropout", 0)
self.normalize_before = args.encoder_normalize_before
# Light-weight FFN
self.ffn_dropout = args.ffn_dropout
ffn_red_factor = args.delight_enc_ffn_red
assert self.embed_dim % ffn_red_factor == 0, '{}/{} should be a perfect divisor'.format(self.embed_dim,
ffn_red_factor)
light_ffn_dim = self.embed_dim // ffn_red_factor
self.fc1 = get_weight_layer(name='linear',
in_features=self.embed_dim,
out_features=light_ffn_dim,
use_bias=True)
self.fc2 = get_weight_layer(name='linear',
in_features=light_ffn_dim,
out_features=self.embed_dim,
use_bias=True)
self.final_layer_norm = get_norm_layer(name=args.norm_type, out_features=self.embed_dim)
def __repr__(self):
s = '{name}(in_features={embed_dim}, out_features={embed_dim}, dropout={dropout},' \
'activation_dropout={activation_dropout}, ffn_dropout={ffn_dropout}, ' \
'activation_fn={act_type}, norm_fn={norm_fn})'
s += '\n \t Dextra Layer: \n \t \t {}'.format(self.dextra_layer)
s += '\n \t Self Attention: \n \t \t {}'.format(self.self_attn)
s += '\n \t Light-weight FFN: \n \t |---- {} \n \t |---- {}'.format(self.fc1, self.fc2)
return s.format(name=self.__class__.__name__, **self.__dict__)
def upgrade_state_dict_named(self, state_dict, name):
"""
Rename layer norm states from `...layer_norms.0.weight` to
`...self_attn_layer_norm.weight` and `...layer_norms.1.weight` to
`...final_layer_norm.weight`
"""
layer_norm_map = {"0": "self_attn_layer_norm", "1": "final_layer_norm"}
for old, new in layer_norm_map.items():
for m in ("weight", "bias"):
k = "{}.layer_norms.{}.{}".format(name, old, m)
if k in state_dict:
state_dict["{}.{}.{}".format(name, new, m)] = state_dict[k]
del state_dict[k]
def forward(self, x, encoder_padding_mask, attn_mask: Optional[Tensor] = None):
"""
Args:
x (Tensor): input to the layer of shape `(seq_len, batch, embed_dim)`
encoder_padding_mask (ByteTensor): binary ByteTensor of shape
`(batch, src_len)` where padding elements are indicated by ``1``.
attn_mask (ByteTensor): binary tensor of shape (T_tgt, T_src), where
T_tgt is the length of query, while T_src is the length of key,
though here both query and key is x here,
attn_mask[t_tgt, t_src] = 1 means when calculating embedding
for t_tgt, t_src is excluded (or masked out), =0 means it is
included in attention
Returns:
encoded output of shape `(seq_len, batch, embed_dim)`
"""
residual = x
if self.normalize_before:
x = self.self_attn_layer_norm(x)
if attn_mask is not None:
attn_mask = attn_mask.masked_fill(attn_mask.to(torch.bool), -1e8)
x = self.dextra_layer(x)
x, _ = self.self_attn(
query=x,
key_value=None,
key_padding_mask=encoder_padding_mask,
attn_mask=attn_mask
)
x = F.dropout(x, p=self.dropout, training=self.training)
x = residual + x
if not self.normalize_before:
x = self.self_attn_layer_norm(x)
# Light-weight FFN
residual = x
if self.normalize_before:
x = self.final_layer_norm(x)
x = self.activation_fn(self.fc1(x))
x = F.dropout(x, p=float(self.activation_dropout), training=self.training)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = F.dropout(x, p=self.ffn_dropout, training=self.training)
x = residual + x
if not self.normalize_before:
x = self.final_layer_norm(x)
return x
def compute_macs_params(self, S=1):
macs = 0
n_params = 0
macs_attn = 0
# Layer Norms
# MACS are zero for LayerNorm because they can be fused
n_params += sum([p.numel() for p in self.self_attn_layer_norm.parameters()])
# Dextra layer
dextra_layer = self.dextra_layer.compute_macs_params()
n_params += dextra_layer['params']
macs += (dextra_layer['macs'] * S)
# Attn
self_attn_layer = self.self_attn.compute_macs_params(T=S, S=S)
macs += self_attn_layer['macs']
n_params += self_attn_layer['params']
macs_attn += self_attn_layer['macs_attn']
# FFN
fc1_layer = self.fc1.compute_macs_params()
# scale MACS by S because S tokens can be processed in parallel
macs += (fc1_layer['macs'] * S)
n_params += fc1_layer['params']
fc2_layer = self.fc2.compute_macs_params()
# scale MACS by S because S tokens can be processed in parallel
macs += (fc2_layer['macs'] * S)
n_params += fc2_layer['params']
n_params += sum([p.numel() for p in self.final_layer_norm.parameters()])
return {
'name': self.__class__.__name__,
'macs': macs,
'params': n_params,
'macs_attn': macs_attn
}
class DeLighTTransformerDecoderLayer(nn.Module):
"""Delight Decoder layer
"""
def __init__(self, args, embed_dim, width_multiplier=DEFAULT_WIDTH_MULTIPLIER, dextra_depth=DEFAULT_MIN_DEXTRA_LAYERS,
no_encoder_attn=False, dextra_proj=2, *unused_args, **unused_kwargs):
super().__init__()
self.embed_dim = embed_dim
assert embed_dim % dextra_proj == 0
self.proj_dim = embed_dim // dextra_proj
self.norm_fn = args.norm_type
self.act_type = args.act_type
self.dextra_layer_sa = DExTraUnit(in_features=self.embed_dim,
in_proj_features=self.proj_dim,
out_features=self.proj_dim,
width_multiplier=width_multiplier,
dextra_depth=dextra_depth,
dextra_dropout=args.delight_dropout,
max_glt_groups=args.delight_dec_max_groups,
act_type=args.act_type,
use_bias=True,
norm_type=args.norm_type,
glt_shuffle=args.glt_shuffle,
is_iclr_version=args.define_iclr
)
self.self_attn = SingleHeadAttention(q_in_dim=self.proj_dim,
kv_in_dim=self.proj_dim,
proj_dim=self.proj_dim,
out_dim=self.embed_dim,
dropout=args.attention_dropout,
bias=True,
self_attention=True,
encoder_decoder_attention=False)
self.dropout = args.dropout
self.activation_fn = get_activation_layer(name=args.act_type)
self.activation_dropout = getattr(args, "activation_dropout", 0)
if self.activation_dropout == 0:
# for backwards compatibility with models that use args.relu_dropout
self.activation_dropout = getattr(args, "relu_dropout", 0)
self.normalize_before = args.decoder_normalize_before
self.self_attn_layer_norm = get_norm_layer(name=args.norm_type, out_features=self.embed_dim)
if no_encoder_attn:
self.encoder_attn = None
self.encoder_attn_layer_norm = None
else:
q_embed_dim = self.embed_dim
self.encoder_attn = SingleHeadAttention(q_in_dim=q_embed_dim,
kv_in_dim=self.embed_dim,
proj_dim=self.proj_dim,
out_dim=self.embed_dim,
dropout=args.attention_dropout,
bias=True,
encoder_decoder_attention=True,
self_attention=False)
self.encoder_attn_layer_norm = get_norm_layer(name=args.norm_type, out_features=self.embed_dim)
self.ffn_dropout = args.ffn_dropout
ffn_red_factor = args.delight_dec_ffn_red
assert self.embed_dim % ffn_red_factor == 0, '{}/{} should be a perfect divisor'.format(self.embed_dim,
ffn_red_factor)
# Feed forward network
light_ffn_dim = self.embed_dim // ffn_red_factor
self.fc1 = get_weight_layer(name='linear',
in_features=self.embed_dim,
out_features=light_ffn_dim,
use_bias=True)
self.fc2 = get_weight_layer(name='linear',
in_features=light_ffn_dim,
out_features=self.embed_dim,
use_bias=True)
self.final_layer_norm = get_norm_layer(name=args.norm_type, out_features=self.embed_dim)
self.need_attn = True
self.onnx_trace = False
def __repr__(self):
s = '{name}(in_features={embed_dim}, out_features={embed_dim}, dropout={dropout}, ' \
'activation_dropout={activation_dropout}, ffn_dropout={ffn_dropout}, ' \
'activation_fn={act_type}, norm_fn={norm_fn})'
s += '\n \t Dextra Layer (Query): \n \t \t {}'.format(self.dextra_layer_sa)
s += '\n \t Self Attention (Decoder): \n \t \t {}'.format(self.self_attn)
if self.encoder_attn is not None:
s += '\n \t Encoder-Decoder Attention: \n \t \t {}'.format(self.encoder_attn)
s += '\n \t Light-weight FFN: \n \t |---- {} \n \t |---- {}'.format(self.fc1, self.fc2)
return s.format(name=self.__class__.__name__, **self.__dict__)
def prepare_for_onnx_export_(self):
self.onnx_trace = True
def forward(
self,
x,
encoder_out: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
encoder_padding_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
incremental_state: Optional[Dict[str, Dict[str, Optional[Tensor]]]] = None,
prev_self_attn_state: Optional[List[torch.Tensor]] = None,
prev_attn_state: Optional[List[torch.Tensor]] = None,
self_attn_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
self_attn_padding_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
need_attn: bool = False,
need_head_weights: bool = False,
):
"""
Args:
x (Tensor): input to the layer of shape `(seq_len, batch, embed_dim)`
encoder_padding_mask (ByteTensor, optional): binary
ByteTensor of shape `(batch, src_len)` where padding
elements are indicated by ``1``.
need_attn (bool, optional): return attention weights
need_head_weights (bool, optional): return attention weights
for each head (default: return average over heads).
Returns:
encoded output of shape `(seq_len, batch, embed_dim)`
"""
if need_head_weights:
need_attn = True
residual = x
if self.normalize_before:
x = self.self_attn_layer_norm(x)
# apply dextra layer
x = self.dextra_layer_sa(x)
if prev_self_attn_state is not None:
prev_key, prev_value = prev_self_attn_state[:2]
saved_state: Dict[str, Optional[Tensor]] = {
"prev_key": prev_key,
"prev_value": prev_value,
}
if len(prev_self_attn_state) >= 3:
saved_state["prev_key_padding_mask"] = prev_self_attn_state[2]
assert incremental_state is not None
self.self_attn._set_input_buffer(incremental_state, saved_state)
x, attn = self.self_attn(
query=x,
key_value=None,
key_padding_mask=self_attn_padding_mask,
incremental_state=incremental_state,
need_weights=False,
attn_mask=self_attn_mask,
)
x = F.dropout(x, p=self.dropout, training=self.training)
x = residual + x
if not self.normalize_before:
x = self.self_attn_layer_norm(x)
if self.encoder_attn is not None:
residual = x
if self.normalize_before:
x = self.encoder_attn_layer_norm(x)
if prev_attn_state is not None:
prev_key, prev_value = prev_attn_state[:2]
saved_state: Dict[str, Optional[Tensor]] = {
"prev_key": prev_key,
"prev_value": prev_value,
}
if len(prev_attn_state) >= 3:
saved_state["prev_key_padding_mask"] = prev_attn_state[2]
assert incremental_state is not None
self.encoder_attn._set_input_buffer(incremental_state, saved_state)
x, attn = self.encoder_attn(
query=x,
key_value=encoder_out,
key_padding_mask=encoder_padding_mask,
incremental_state=incremental_state,
static_kv=True,
need_weights=need_attn or (not self.training and self.need_attn),
need_head_weights=need_head_weights,
)
x = F.dropout(x, p=self.dropout, training=self.training)
x = residual + x
if not self.normalize_before:
x = self.encoder_attn_layer_norm(x)
#Light-weight FFN
residual = x
if self.normalize_before:
x = self.final_layer_norm(x)
x = self.activation_fn(self.fc1(x))
x = F.dropout(x, p=float(self.activation_dropout), training=self.training)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = F.dropout(x, p=self.ffn_dropout, training=self.training)
x = residual + x
if not self.normalize_before:
x = self.final_layer_norm(x)
if self.onnx_trace and incremental_state is not None:
saved_state = self.self_attn._get_input_buffer(incremental_state)
assert saved_state is not None
if self_attn_padding_mask is not None:
self_attn_state = [
saved_state["prev_key"],
saved_state["prev_value"],
saved_state["prev_key_padding_mask"],
]
else:
self_attn_state = [saved_state["prev_key"], saved_state["prev_value"]]
return x, attn, self_attn_state
return x, attn, None
def make_generation_fast_(self, need_attn: bool = False, **kwargs):
self.need_attn = need_attn
def compute_macs_params(self, T=1, S=1):
macs = 0
n_params = 0
macs_attn = 0
# LayerNorm
n_params += sum([p.numel() for p in self.self_attn_layer_norm.parameters()])
# self attention
self_attn_layer = self.self_attn.compute_macs_params(T=T, S=T)
dextra_layer = self.dextra_layer_sa.compute_macs_params()
macs += self_attn_layer['macs'] + (dextra_layer['macs'] * T)
n_params += self_attn_layer['params'] + dextra_layer['params']
macs_attn += self_attn_layer['macs_attn']
# Encoder-decoder attn
if self.encoder_attn is not None:
# self attention scaled-dot-product Attn
n_params += sum([p.numel() for p in self.encoder_attn_layer_norm.parameters()])
enc_attn = self.encoder_attn.compute_macs_params(T=T, S=S)
macs += enc_attn['macs']
n_params += enc_attn['params']
macs_attn += enc_attn['macs_attn']
# FFN
fc1_layer = self.fc1.compute_macs_params()
macs += (fc1_layer['macs'] * T)
n_params += fc1_layer['params']
fc2_layer = self.fc2.compute_macs_params()
macs += (fc2_layer['macs'] * T)
n_params += fc2_layer['params']
n_params += sum([p.numel() for p in self.final_layer_norm.parameters()])
return {
'name': self.__class__.__name__,
'macs': macs,
'params': n_params,
'macs_attn': macs_attn
}
if __name__ == '__main__':
pass
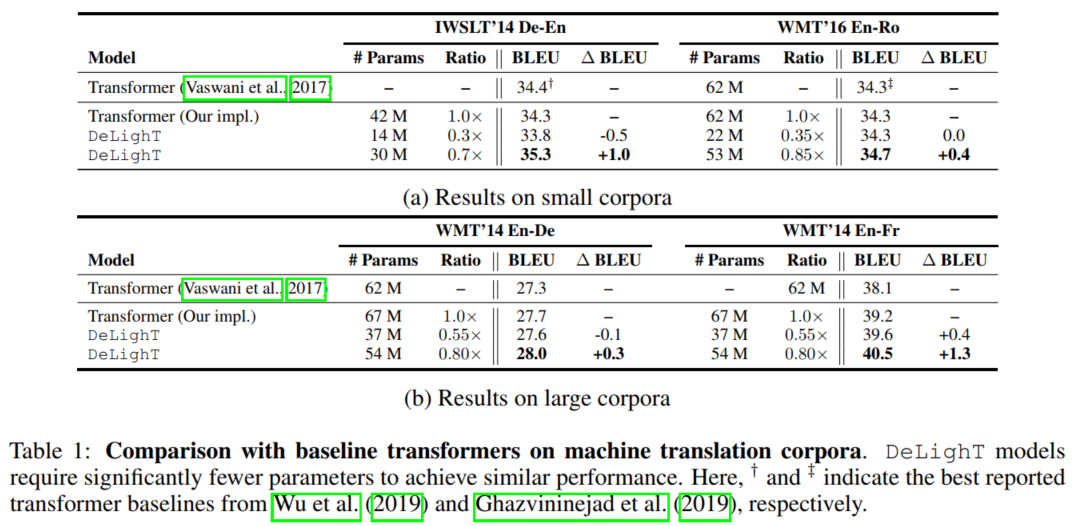
4.1 机器翻译实验

4.2 语言模型
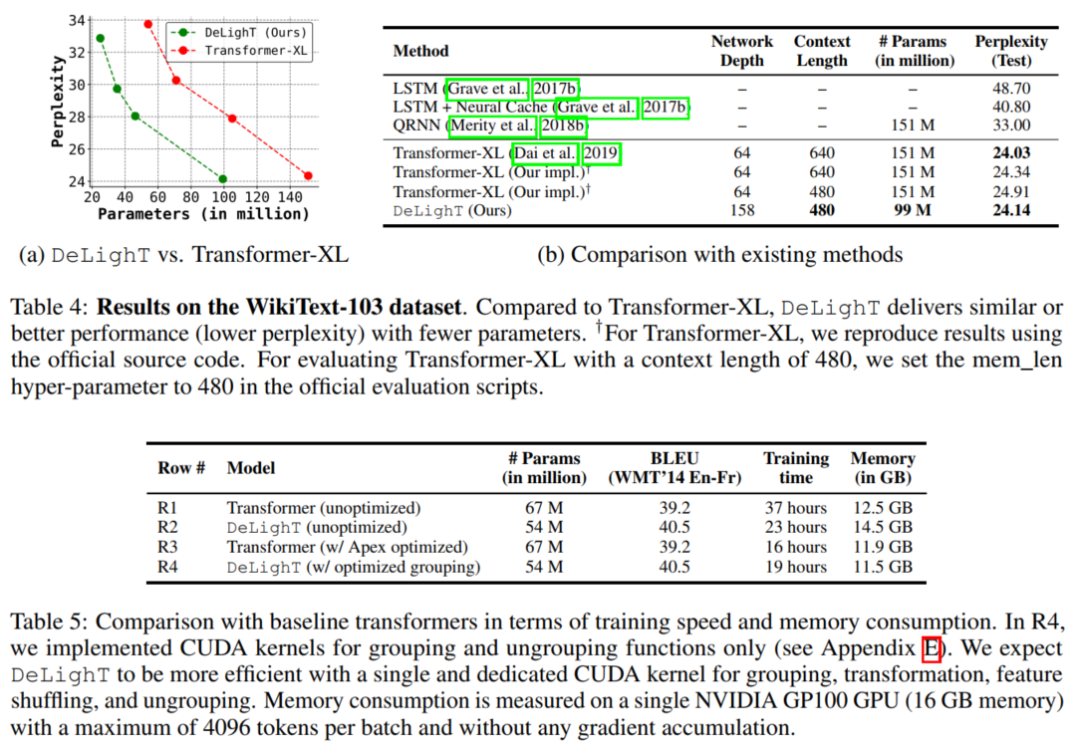
毫无疑问,更快更强!!!
5 参考[1].DELIGHT: DEEP AND LIGHT-WEIGHT TRANSFORMER
[2].https://github.com/sacmehta/delight
原文获取方式,扫描下方二维码
回复【DeLighT】即可获取论文与源码
声明:转载请说明出处
扫描下方二维码关注【AI人工智能初学者】公众号,获取更多实践项目源码和论文解读,非常期待你我的相遇,让我们以梦为马,砥砺前行!!!
点“在看”给我一朵小黄花呗![]()
