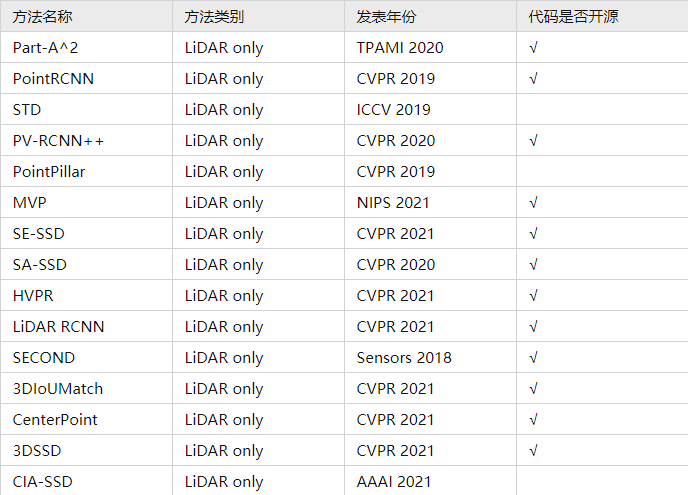
基于激光雷达点云的3D检测方法汇总(LiDAR only)
点击下方卡片,关注“新机器视觉”公众号
视觉/图像重磅干货,第一时间送达
前段时间比较忙,鸽了挺久,近期应该会恢复更新。
这篇文章主要是梳理一下近期3D Detection的进展,分类列举出一些我认为的比较重要的、有代表性的工作。
论文总结(一)主要讲解基于激光雷达点云的3D检测方法(LiDAR only),欢迎补充指正。
一、论文分类汇总
1. 基于激光雷达点云的3D检测方法(LiDAR only)
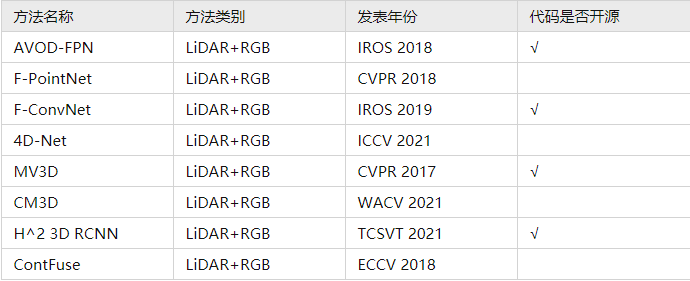
2. 基于多模态融合的3D检测方法(LiDAR+RGB)
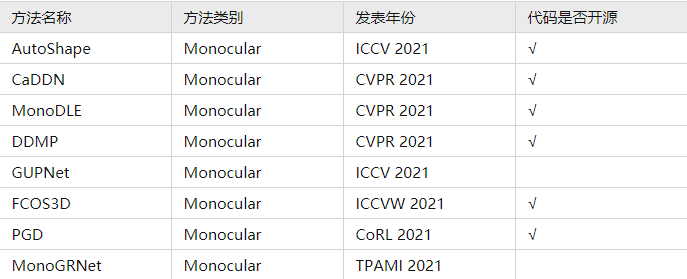
3. 基于单目图像的3D检测方法(Monocular)
4. 基于双目图像的3D检测方法(Stereo)

5. 基于视角特征提取的3D检测方法
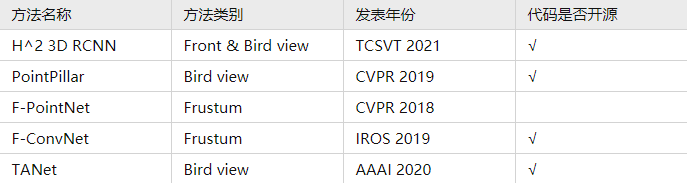
6. 基于特征补充/伪点云生成的3D检测方法(pseudo augment)
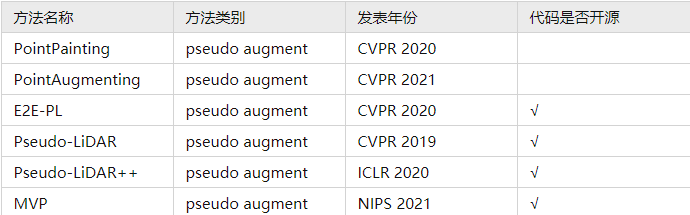
7. 基于transformer的3D检测方法 (Transformer)
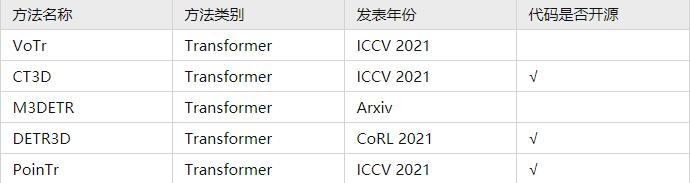
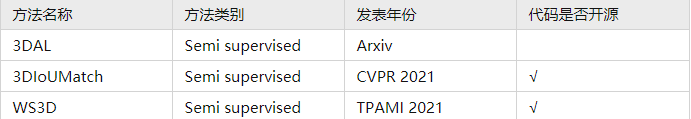
8. 基于半监督学习的3D检测方法(Semi supervised)
二、论文分类解读
由于篇幅限制,论文总结(一)主要讲解基于激光雷达点云的3D检测方法(LiDAR only)。LiDAR only 指的是此类方法仅仅采用点云数据作为输入,方法的主要区分性在于对点云数据不同的特征提取方式。
1. Part-A^2 (TPAMI 2020)
链接:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/436797682
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1907.03670.pdf
作者单位:The Chinese University of Hong Kong
代码地址:GitHub - open-mmlab/OpenPCDet: OpenPCDet Toolbox for LiDAR-based 3D Object Detection.
一句话读论文:The ground-truth boxes of 3D object detection not only automatically provide accurate segmentation mask because of the fact that 3D objects are naturally separated in 3D scenes, but also imply the relative locations for each foreground 3D point within the ground truth boxes.
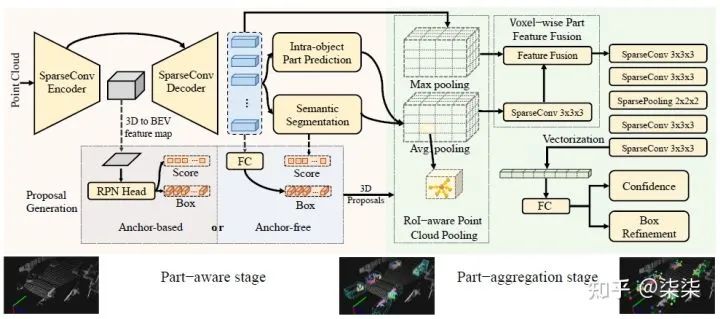
网络框架图
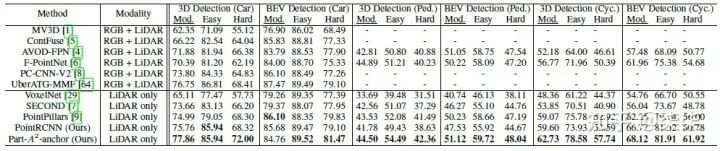
KITTI testset 实验结果
整体网络框架分为两个部分:Part-aware stage和Part-aggregation stage。
Part-aware stage:作者认为前景点的相对位置(intra-object part location)可以表征物体的形状信息。因此,通过估计前景点的相对位置,作者认为可以得到更具有辨别性的特征。
The part-aware network aims to extract discriminative features from the point cloud by learning to estimate the intra-object part locations of foreground points, since these part locations implicitly encode the 3D object’s shapes by indicating the relative locations of surface points of 3D objects.
Part-aggregation stage:既然是一个aggregation mechanism,作者具体聚合了哪些特征呢?文中作者主要融合了两部分特征,point-wise part location 以及 point-wise sementic features。利用融合后的特征,进一步预测每一个候选框的置信度和位置。
By considering the spatial distribution of the predicted intraobject part locations and the learned point-wise part features in a 3D box propsoal from stage-I, it is reasonable to aggregate all the information within a proposal for box proposal scoring and refinement.
2. Point RCNN (CVPR 2019)
链接:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/390767889
链接:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/436419513
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1812.04244.pdf
作者单位:The Chinese University of Hong Kong
代码地址:https://github.com/sshaoshuai/PointRCN
N一句话读论文:The learned point representation from segmentation is not only good at proposal generation but is also helpful for the later box refinement.
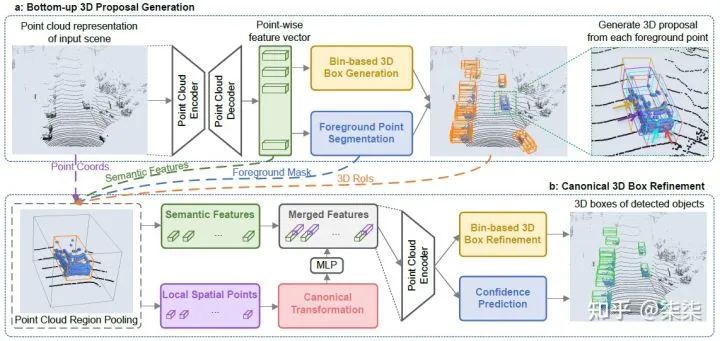
网络框架
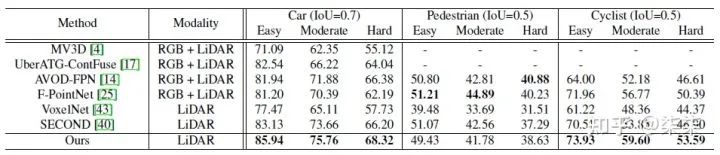
KITTI testset 实验结果
PointRCNN 整体为two-stage的框架,第一级生成proposal (Bottom-up 3D Proposal Generation),第二级对proposal进行微调并得到最终的检测结果 (Canonical 3D Box Refinement)。
Bottom-up 3D Proposal Generation:主要目的是做proposal的生成。对每一个point,提取point-wise feature,预测其属于前景点的概率和相应的proposal大小。对于生成的大量的proposal,利用NMS进行过滤,只保留其中的300个送入第二级进行微调。
We propose a novel bottom-up point cloud-based 3D bounding box proposal generation algorithm, which generates a small number of high-quality 3D proposals via segmenting the point cloud into foreground objects and background. The learned point representation from segmentation is not only good at proposal generation but is also helpful for the later box refinement.
Canonical 3D Box Refinement:提取第一级proposal更精细的特征用于分类回归。更精细的特征包括:点特征+空间位置特征+RoI特征。
The proposed canonical 3D bounding box refinement takes advantages of our highrecall box proposals generated from stage-1 and learns to predict box coordinates refinements in the canonical coordinates with robust bin-based losses.
3. STD (ICCV 2019)
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1907.10471v1.pdf
作者单位:Youtu Lab, Tencent 等
一句话读论文:They propose a point-based proposal generation paradigm on point cloud with spherical anchors.
网络框架
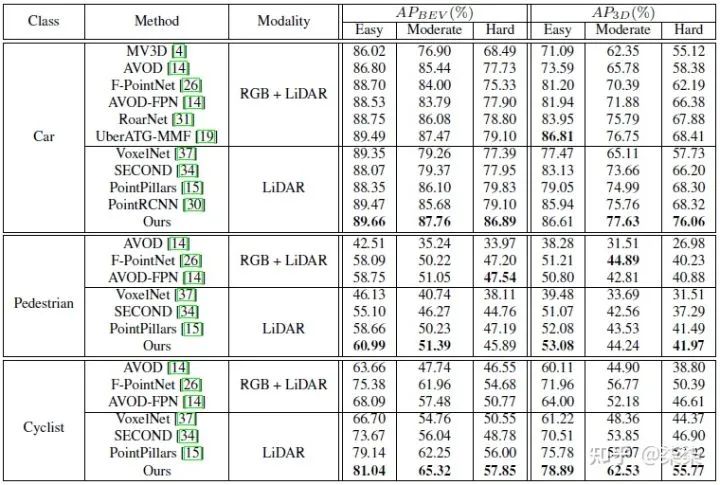
KITTI testset 实验结果
整体框架依然属于two-stage的网络,第一级生成proposal,第二级提取更精细的proposal (point+voxel)特征用于微调。与其他工作相比,STD 网络最大的不同之处在于proposal generation的过程种使用了球形anchor (spherical anchors)。那么如何从球形anchor得到proposal呢?其具体步骤是:
为所有点设定球形anchor → 判断其为前景点的概率 → NMS 过滤冗余anchor → 预测余下的anchor对应的proposal。
作者认为这种球形anchor的优点在于:
球形anchor可以不必考虑物体朝向问题,极大减小了计算量;
Considering that a 3D object could be with any orientations, we design spherical anchors rather than traditional cuboid anchors. As a result, the number of spherical anchors is not proportional to the number of pre-defined reference box orientation, leading to about 50% less anchors. With computation much reduced, we surprisingly achieve a much higher recall with spherical anchors than with traditional ones.
4. PV-RCNN/PV-RCNN++(CVPR 2020)
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2102.00463.pdf
作者单位:The Chinese University of Hong Kong
代码地址:https://github.com/open-mmlab/OpenPCDet
一句话读论文:They propose a novel two-stage detection network for accurate 3D object detection through a two-step strategy of point-voxel feature aggregation.
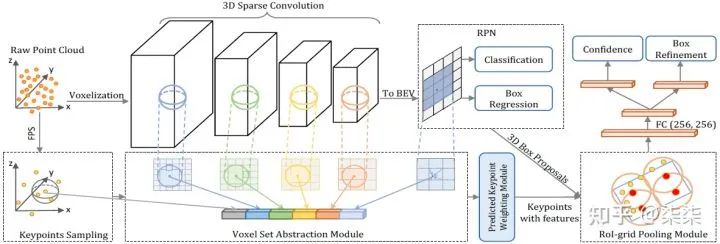
网络框架
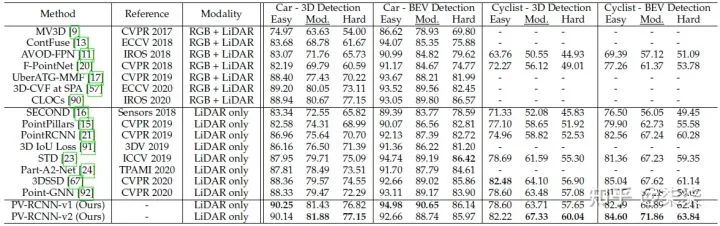
KITTI testset 实验结果
整体框架属于two-stage,有两个核心内容,第一个voxel feature → keypoints feature,第二个keypoints feature → proposal/grid feature。
voxel feature → keypoints feature。将大量的voxel feature 整合在少量的keypoints上,整合的过程包括了:原始raw points feature + multi-scale voxel feature + bev feature;
Our proposed PV-RCNN-v1 first aggregates the voxel-wise scene features at multiple neural layers of 3D voxel CNN into a small number of keypoints, which bridge the 3D voxel CNN feature encoder and the proposal refinement network.
keypoints feature → proposal/grid feature。这一步其实就是利用之前整合的keypoints feature对每一个proposal做RoI Grid Pooling。只是需要额外注意的是,这个的grid 半径是多尺度的,作者认为这种方式可以提取更丰富的proposal feature。
In this step, we propose keypoint-to-grid RoI feature abstraction to generate accurate proposal-aligned features from the keypoint features for fine-grained proposal refinement.
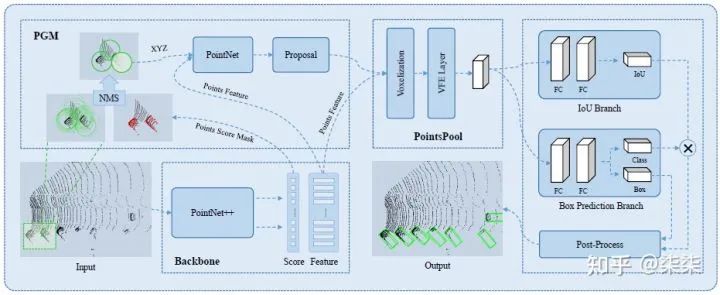
6. PointPillar(CVPR 2019)
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1812.05784.pdf
作者单位:Oscar Beijbom and nuTonomy: an APTIV company
一句话读论文:A novel encoder which utilizes PointNets to learn a representation of point clouds organized in vertical columns (pillars).
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/389034609
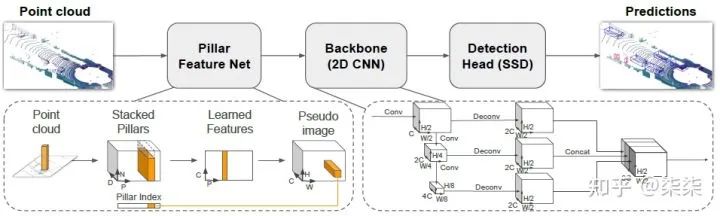
网络框架
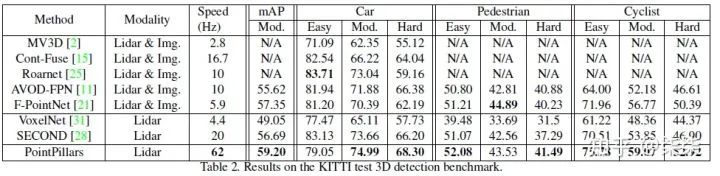
KITTI testset 实验结果
这篇文章的核心内容是Pillar Feature Network (Pillar点云提取)。主要作用是将点云数据处理为常见的三维数据,也就是point clouds → C×H×W。具体流程为:point clouds → D×P×N → C×P×N → C×P → C×H×W,其中:
D=9,包括每个点坐标(x, y, z),对应的pillar中心点坐标(x_c, y_c, z_c),该点到中心点的偏移(x_p, y_p),以及反射值r。P=12000,表示单场景中的pillar数目。N=100,表示每个pillar中采样的point数目。
The points in each pillar are then augmented with xc, yc, zc, xp and yp where the c subscript denotes distance to the arithmetic mean of all points in the pillar and the p subscript denotes the offset from the pillar x; y center.
2. D×P×N → C×P×N 通过卷积运算实现。
Next, we use a simplified version of PointNet where, for each point, a linear layer is applied followed by Batch- Norm and ReLU to generate a C×P×N sized tensor.
3. C×P×N → C×P是对N维度做max运算,类似max pooling。
This is followed by a max operation over the channels to create an output tensor of size C×P.
4. C×P → C×H×W是对P维度的展开,因为P=12000,表示该场景中的pillar数目,因此作者认为可以一定程度上描述完整场景,所以将P维度直接展开,可以得到我们熟悉的C×H×W三维数据。
Once encoded, the features are scattered back to the original pillar locations to create a pseudo-image of size C×H×W where H and W indicate the height and width of the canvas.
至此,其实核心部分已经处理完毕,接下来可以用我们熟知的检测方法处理此点云数据。
7. MVP(NIPS 2021)
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2111.06881.pdf
作者单位:https://www.utexas.edu/
代码地址:https://tianweiy.github.io/mvp/
一句话读论文:The approach takes a set of 2D detections to generate dense 3D virtual points to augment an otherwise sparse 3D point cloud.
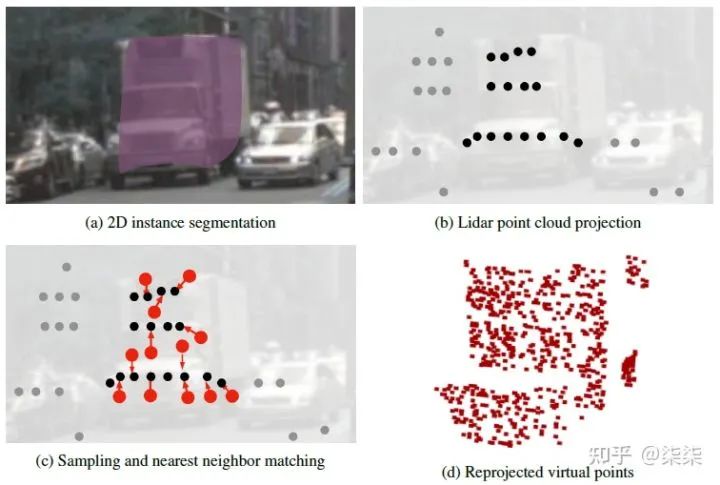
网络框架
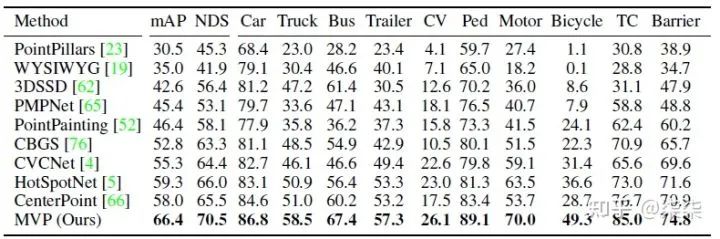
NuScenes testset 实验结果
这篇文章的核心内容是如何利用2D信息对3D点云进行补全,也就是2D instance segmentation → virtual 3D points。作者的具体做法是:3D raw points → 2D points → 3D virtual points。
3D raw points → 2D points。这一步是将3D物体上的所有点映射到2D图像上,但是映射之后的点仅考虑落在对应物体segmentation区域内的。
We start by projecting the 3D Lidar point cloud onto our detection. Specifically, we transform each Lidar point into the reference frame of the RGB camera, then project it into image coordinates with associated depth using a perspective projection. The frustum only considers projected 3D points that fall within a detection mask. Any Lidar measurement outside detection masks is discarded.
2. 2D points → 3D virtual points。我们知道,3D到2D的映射属于降维,而2D到3D的映射属于升维。因此,如果没有增加额外的depth信息,从2D映射到3D有无穷多解,这显然是不合适的。作者尝试通过补全每一个2D point的depth信息,将原本“一到无穷”的映射变换为“一到一”的映射。更具体的,对于一个random 2D point,作者将其depth估计为其最邻近的映射3D raw point的depth。
We start by randomly sampling 2D points from each instance mask. We sample points uniformly at random without repetition. For each sampled point, we retrieve a depth estimate from its nearest neighbor in the frustum.
8. SE-SSD(CVPR 2021)
论文地址:arxiv.org/pdf/2104.0980
作者单位:The Chinese University of Hong Kong
代码地址:GitHub - Vegeta2020/SE-SSD: SE-SSD: Self-Ensembling Single-Stage Object Detector From Point Cloud, CVPR 2021.
一句话读论文:The key focus is on exploiting both soft and hard targets with formulated constraints to jointly optimize the model, without introducing extra computation in the inference.
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/371520457
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/390167950

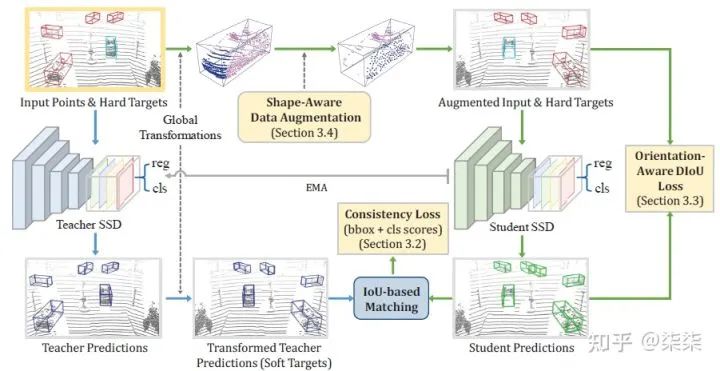
网络框架
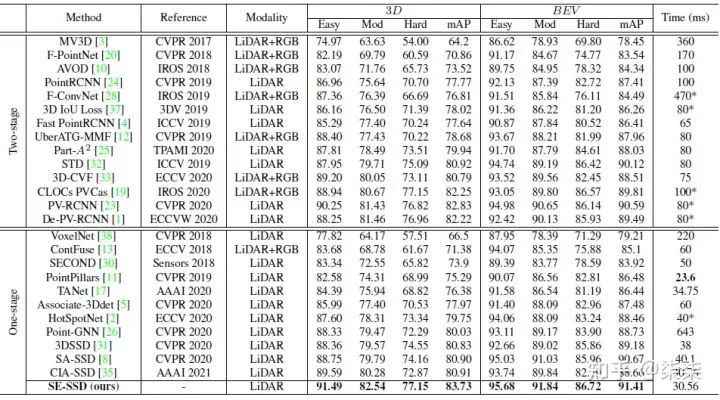
KITTI testset 实验结果
这篇文章的核心其实更偏向于augmentation,从本质上讲,本文中包含的两个核心模块soft targets生成训练(label space augmentation)和Shape-aware data augmentation (target space augmentation)均属于augmentation范畴。通过ensemble的形式,可以同时利用soft targets和hard targets的信息。
a)Hence, we exploit both soft and hard targets with our formulated constraints to jointly optimize the model, while incurring no extra inference time.
b)On the other hand, to enable the student SSD to effectively explore a larger data space, we design a new augmentation scheme on top of conventional augmentation strategies to produce augmented object samples in a shape-aware manner.
更具体地,有两个注意点:
第一,Shape-aware Data Augmentation是怎么做的?首先,shape-aware尝试解决的问题是:same samples but with different point representation,用作者文中的话说就是由于遮挡距离等问题的存在,相同物体具有不同的点云表达。
Our insight comes from the observation that the point cloud patterns of ground-truth objects could vary significantly due to occlusions, changes in distance, and diversity of object shapes in practice.
2. 第二,需要注意的是,作者这里是使用了不同loss监督student SSD的学习过程。其中,consistency loss用于监督predicitons和soft targets,orientation-aware DIoU loss用于监督predictions和hard targets。
Our consistency loss is to align the student predictions with the soft targets and when we augment the input, we bring along its hard targets to supervise the student with our orientationaware distance-IoU loss.
9. SA-SSD(CVPR 2020)
论文地址:https://www4.comp.polyu.edu.hk/~cslzhang/paper/SA-SSD.pdf
作者单位:The Hong Kong Polytechnic University 等
代码地址:https://github.com/skyhehe123/SA-SSD
一句话读论文:The auxiliary network is introduced, which is jointly optimized by two point-level supervisions, to guide the convolutional features in the backbone network to be aware of the object structure.
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/378017015
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/390452834
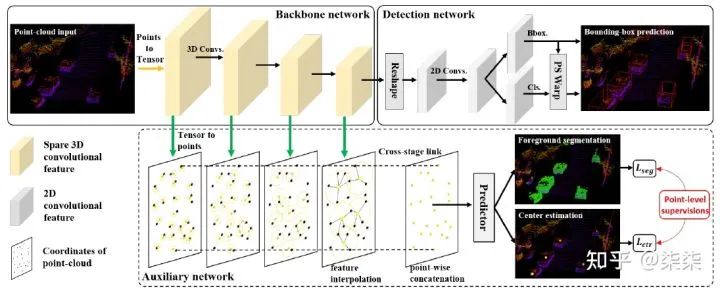
网络框架
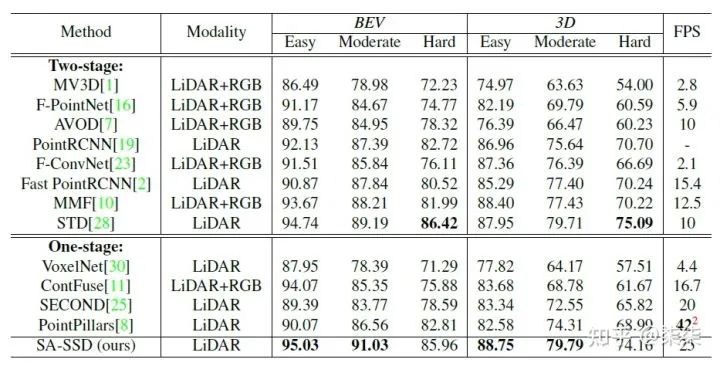
KITTI testset 实验结果
这篇文章的核心是利用辅助任务(auxiliary network)引导backbone学习到更丰富的结构信息。更具体地,这个辅助任务包含两个部分:前背景点分类(foreground/background classification)和中心点估计(center estimation)。
We propose a structure-aware single-stage 3D object detector, which employs a detachable auxiliary network to learn structure information and exhibits better localization performance without extra cost.
更具体地,
1.前背景点分类(foreground/background classification),这一步为每一个point输出其前/背景分类得分。这样做的好处是,可以促使backbone学习到更清晰的边界特征。
Specifically, we employ a sigmoid function to the segmentation branch to predict the foreground/background probability of each point. The segmentation task enables the backbone network to more precisely detect the object boundary.
2.中心点估计(center estimation),这一步通过整合intra-object points预测每一个object的中心点。这样做的好处是,可以促使backbone学习到更精准的shape和scale信息。
To further improve the localization accuracy, we employ another auxiliary task to learn the relative position of each object point to the object center. This intra-object relationship can help determine the scale and shape of the object, resulting in more precise localization.
10. HVPR(CVPR 2021)
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2104.00902.pdf
作者单位:School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Yonsei University
代码地址:https://cvlab.yonsei.ac.kr/projects/HVPR/
一句话读论文:It proposes a novel single-stage 3D detection method having the merit of both voxel-based and point-based features.
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/373069090
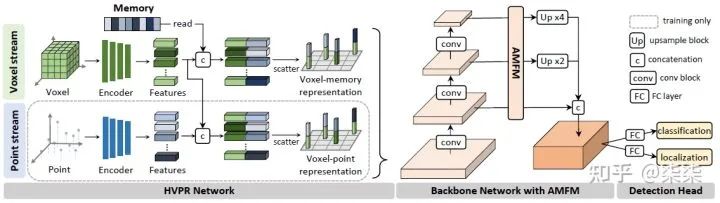
网络框架
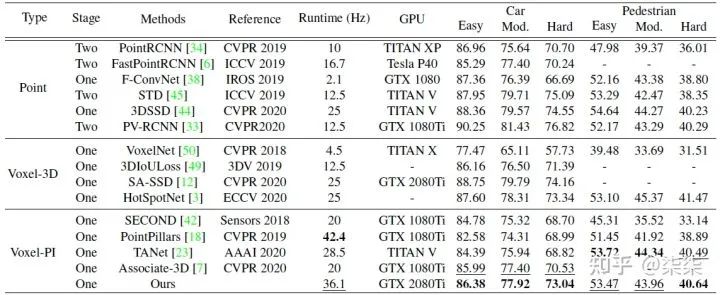
KITTI testset 实验结果
11. LiDAR RCNN(CVPR 2021)
论文地址:arxiv.org/pdf/2103.1529
作者单位:TuSimple
代码地址:GitHub - TuSimple/LiDAR_RCNN: LiDAR R-CNN: An Efficient and Universal 3D Object Detector
一句话读论文:The authors analyze the size ambiguity problem in detail and propose several methods to remedy it.
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2103.15297.pdf
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/372199358
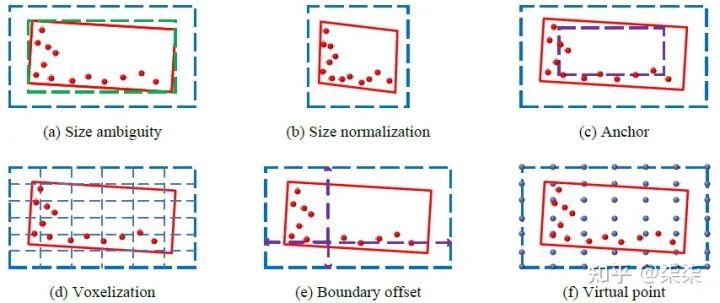
网络框架
KITTI testset 实验结果
12. SECOND(Sensors 2018)
论文地址:https://www.mdpi.com/1424-8220/18/10/3337
作者单位:Chongqing University 等
代码地址:https://github.com/traveller59/second.pytorch
一句话读论文:It investigates an improved sparse convolution method, which significantly increases the speed of both training and inference.
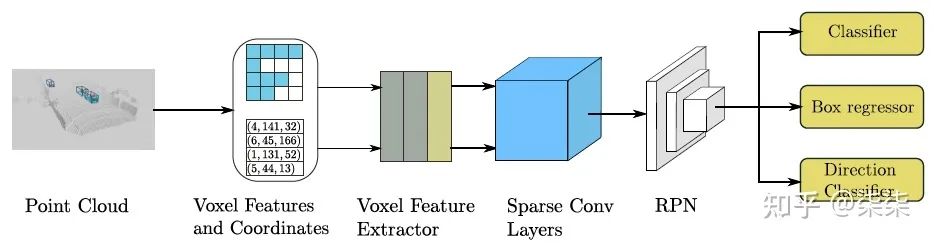
网络框架
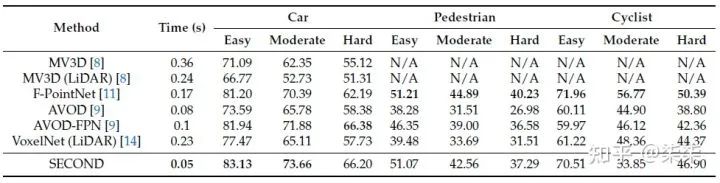
KITTI testset 实验结果
13. 3DIoUMatch(CVPR 2021)
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2012.04355.pdf
作者单位:Stanford University 等
代码地址:https://thu17cyz.github.io/3DIoUMatch/
一句话读论文:It proposes to use the estimated 3D IoU as a localization metric and set category-aware selfadjusted thresholds to filter poorly localized proposals.
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/390114438
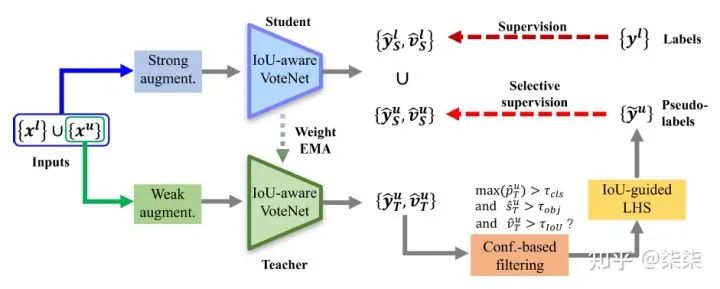
网络框架
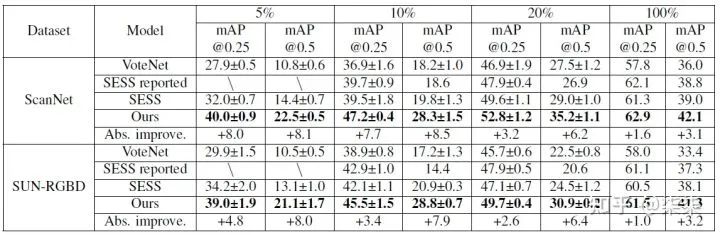
ScanNet & SUN-RGBD 实验结果
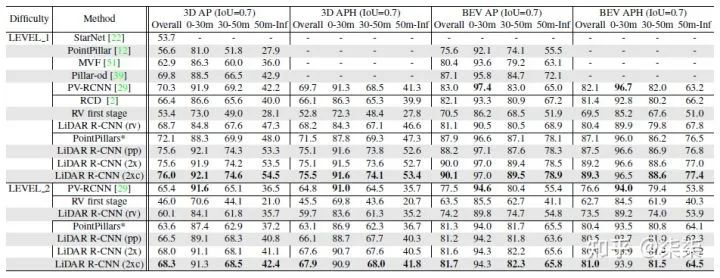
14. CenterPoint(CVPR 2021)
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2006.11275.pdf
作者单位:https://www.utexas.edu/
代码地址:https://github.com/tianweiy/CenterPoint
一句话读论文:It first detects centers of objects using a keypoint detector and regresses to other attributes, including 3D size, 3D orientation, and velocity.
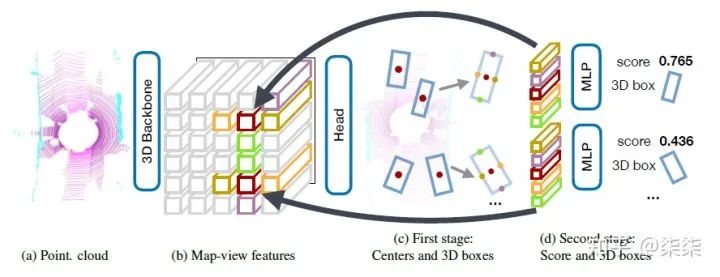
网络框架

nuScenes testset 实验结果
15. 3DSSD(CVPR 2021)
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2002.10187.pdf
作者单位:The Chinese University of Hong Kong 等
代码地址:https://github.com/dvlab-research/3DSSD
一句话读论文:It proposes a fusion sampling strategy in downsampling process to make detection on less representative points feasible.
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/380595350
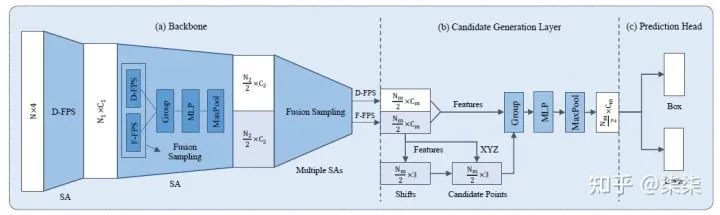
网络框架
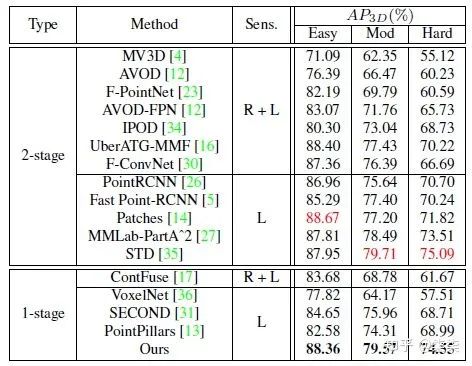
KITTI testset 实验结果
本文仅做学术分享,如有侵权,请联系删文。
