机器学习模型评估与超参数调优详解
↑↑↑关注后"星标"Datawhale
每日干货 & 每月组队学习,不错过
Datawhale干货作者:李祖贤 深圳大学,Datawhale高校群成员
机器学习分为两类基本问题----回归与分类。在之前的文章中,也介绍了很多基本的机器学习模型。可在Datawhale机器学习专辑中查看。但是,当我们建立好了相关模型以后我们怎么评价我们建立的模型的好坏以及优化我们建立的模型呢?那本次分享的内容就是关于机器学习模型评估与超参数调优的。本次分享的内容包括:用管道简化工作流
使用k折交叉验证评估模型性能
使用学习和验证曲线调试算法
通过网格搜索进行超参数调优
比较不同的性能评估指标
1. 加载基本工具库
import numpy as npimport pandas as pdimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt%matplotlib inlineplt.style.use("ggplot")import warningswarnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
2. 加载数据,并做基本预处理
# 加载数据df = pd.read_csv("http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/breast-cancer-wisconsin/wdbc.data",header=None)# 做基本的数据预处理from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoderX = df.iloc[:,2:].valuesy = df.iloc[:,1].valuesle = LabelEncoder() #将M-B等字符串编码成计算机能识别的0-1y = le.fit_transform(y)le.transform(['M','B'])# 数据切分8:2from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splitX_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(X,y,test_size=0.2,stratify=y,random_state=1)
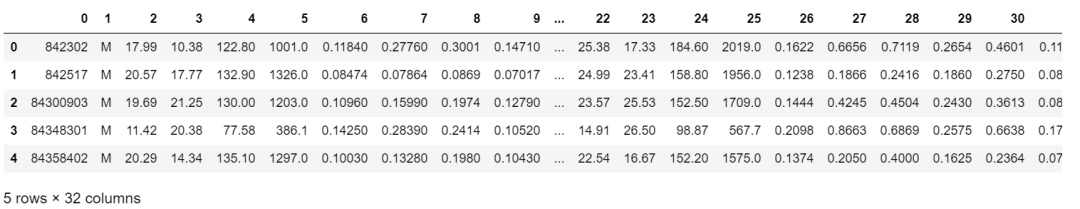
3. 把所有的操作全部封在一个管道pipeline内形成一个工作流:标准化+PCA+逻辑回归
完成以上操作,共有两种方式:
方式1:make_pipeline
# 把所有的操作全部封在一个管道pipeline内形成一个工作流:## 标准化+PCA+逻辑回归### 方式1:make_pipelinefrom sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScalerfrom sklearn.decomposition import PCAfrom sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegressionfrom sklearn.pipeline import make_pipelinepipe_lr1 = make_pipeline(StandardScaler(),PCA(n_components=2),LogisticRegression(random_state=1))pipe_lr1.fit(X_train,y_train)y_pred1 = pipe_lr.predict(X_test)print("Test Accuracy: %.3f"% pipe_lr1.score(X_test,y_test))
Test Accuracy: 0.956方式2:Pipeline
# 把所有的操作全部封在一个管道pipeline内形成一个工作流:## 标准化+PCA+逻辑回归### 方式2:Pipelinefrom sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScalerfrom sklearn.decomposition import PCAfrom sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegressionfrom sklearn.pipeline import Pipelinepipe_lr2 = Pipeline([['std',StandardScaler()],['pca',PCA(n_components=2)],['lr',LogisticRegression(random_state=1)]])pipe_lr2.fit(X_train,y_train)y_pred2 = pipe_lr2.predict(X_test)print("Test Accuracy: %.3f"% pipe_lr2.score(X_test,y_test))
Test Accuracy: 0.956
二、使用k折交叉验证评估模型性能

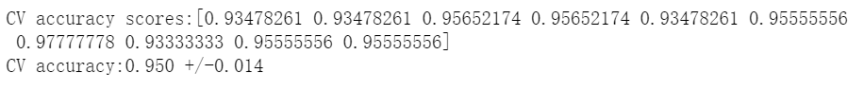
# 评估方式1:k折交叉验证from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_scorescores1 = cross_val_score(estimator=pipe_lr,X = X_train,y = y_train,cv=10,n_jobs=1)print("CV accuracy scores:%s" % scores1)print("CV accuracy:%.3f +/-%.3f"%(np.mean(scores1),np.std(scores1)))
# 评估方式2:分层k折交叉验证from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedKFoldkfold = StratifiedKFold(n_splits=10,random_state=1).split(X_train,y_train)scores2 = []for k,(train,test) in enumerate(kfold):pipe_lr.fit(X_train[train],y_train[train])score = pipe_lr.score(X_train[test],y_train[test])scores2.append(score)print('Fold:%2d,Class dist.:%s,Acc:%.3f'%(k+1,np.bincount(y_train[train]),score))print('\nCV accuracy :%.3f +/-%.3f'%(np.mean(scores2),np.std(scores2)))

三、 使用学习和验证曲线调试算法
如果模型过于复杂,即模型有太多的自由度或者参数,就会有过拟合的风险(高方差);而模型过于简单,则会有欠拟合的风险(高偏差)。
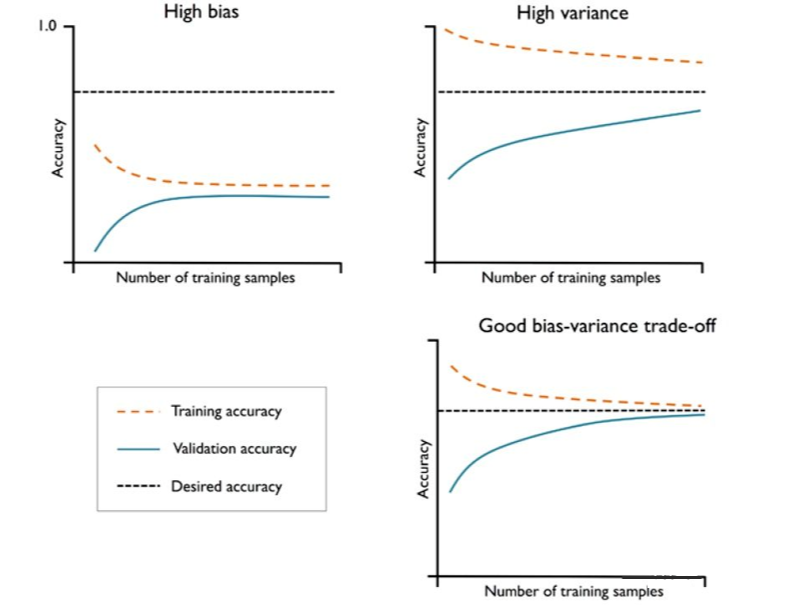
1. 用学习曲线诊断偏差与方差
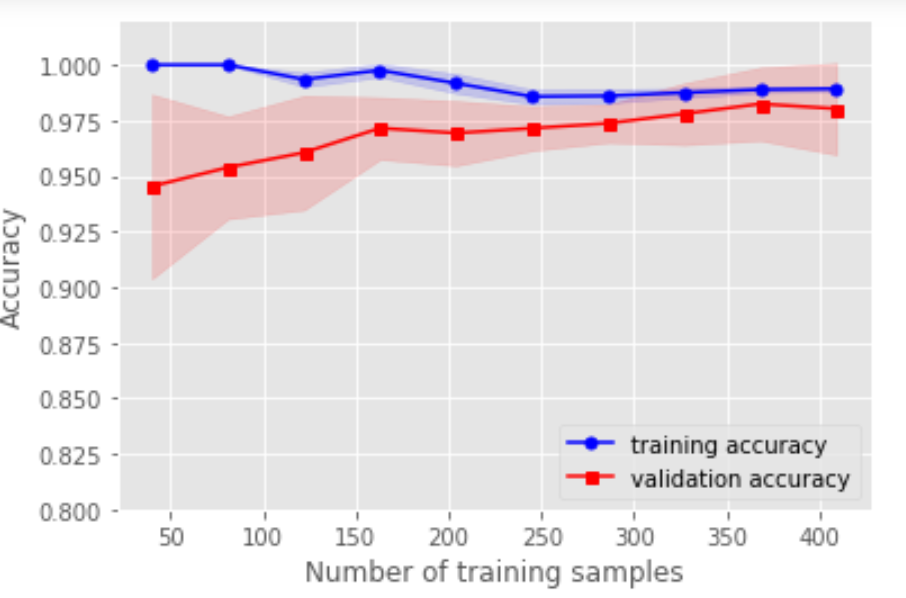
# 用学习曲线诊断偏差与方差from sklearn.model_selection import learning_curvepipe_lr3 = make_pipeline(StandardScaler(),LogisticRegression(random_state=1,penalty='l2'))train_sizes,train_scores,test_scores = learning_curve(estimator=pipe_lr3,X=X_train,y=y_train,train_sizes=np.linspace(0.1,1,10),cv=10,n_jobs=1)train_mean = np.mean(train_scores,axis=1)train_std = np.std(train_scores,axis=1)test_mean = np.mean(test_scores,axis=1)test_std = np.std(test_scores,axis=1)plt.plot(train_sizes,train_mean,color='blue',marker='o',markersize=5,label='training accuracy')plt.fill_between(train_sizes,train_mean+train_std,train_mean-train_std,alpha=0.15,color='blue')plt.plot(train_sizes,test_mean,color='red',marker='s',markersize=5,label='validation accuracy')plt.fill_between(train_sizes,test_mean+test_std,test_mean-test_std,alpha=0.15,color='red')plt.xlabel("Number of training samples")plt.ylabel("Accuracy")plt.legend(loc='lower right')plt.ylim([0.8,1.02])plt.show()
# 用验证曲线解决欠拟合和过拟合from sklearn.model_selection import validation_curvepipe_lr3 = make_pipeline(StandardScaler(),LogisticRegression(random_state=1,penalty='l2'))param_range = [0.001,0.01,0.1,1.0,10.0,100.0]train_scores,test_scores = validation_curve(estimator=pipe_lr3,X=X_train,y=y_train,param_name='logisticregression__C',param_range=param_range,cv=10,n_jobs=1)train_mean = np.mean(train_scores,axis=1)train_std = np.std(train_scores,axis=1)test_mean = np.mean(test_scores,axis=1)test_std = np.std(test_scores,axis=1)plt.plot(param_range,train_mean,color='blue',marker='o',markersize=5,label='training accuracy')plt.fill_between(param_range,train_mean+train_std,train_mean-train_std,alpha=0.15,color='blue')plt.plot(param_range,test_mean,color='red',marker='s',markersize=5,label='validation accuracy')plt.fill_between(param_range,test_mean+test_std,test_mean-test_std,alpha=0.15,color='red')plt.xscale('log')plt.xlabel("Parameter C")plt.ylabel("Accuracy")plt.legend(loc='lower right')plt.ylim([0.8,1.02])plt.show()
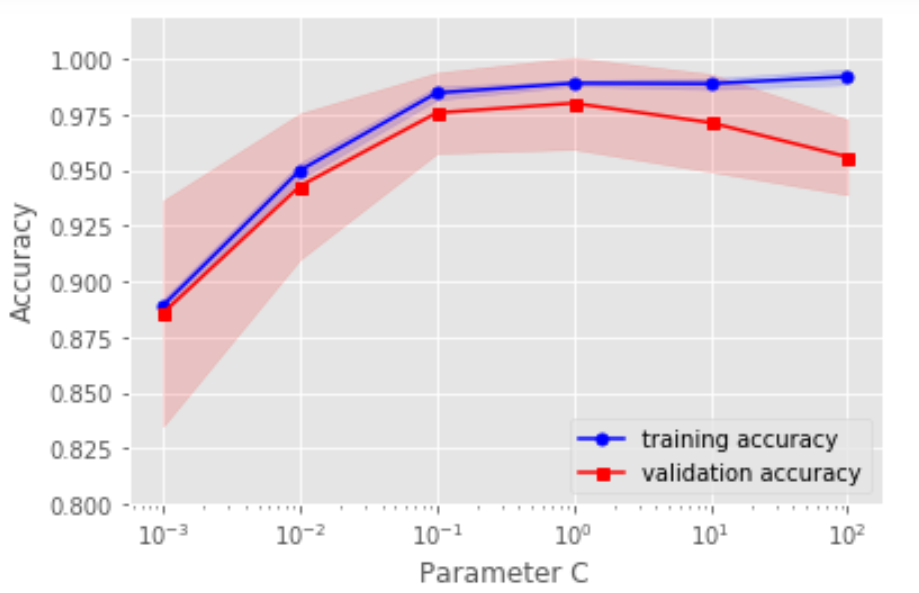
四、通过网格搜索进行超参数调优
如果只有一个参数需要调整,那么用验证曲线手动调整是一个好方法,但是随着需要调整的超参数越来越多的时候,我们能不能自动去调整呢?!!!注意对比各个算法的时间复杂度。(注意参数与超参数的区别:参数可以通过优化算法进行优化,如逻辑回归的系数;超参数是不能用优化模型进行优化的,如正则话的系数。)
方式1:网格搜索GridSearchCV()# 方式1:网格搜索GridSearchCV()from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCVfrom sklearn.svm import SVCimport timestart_time = time.time()pipe_svc = make_pipeline(StandardScaler(),SVC(random_state=1))param_range = [0.0001,0.001,0.01,0.1,1.0,10.0,100.0,1000.0]param_grid = [{'svc__C':param_range,'svc__kernel':['linear']},{'svc__C':param_range,'svc__gamma':param_range,'svc__kernel':['rbf']}]gs = GridSearchCV(estimator=pipe_svc,param_grid=param_grid,scoring='accuracy',cv=10,n_jobs=-1)gs = gs.fit(X_train,y_train)end_time = time.time()print("网格搜索经历时间:%.3f S" % float(end_time-start_time))print(gs.best_score_)print(gs.best_params_)

方式2:随机网格搜索RandomizedSearchCV()
# 方式2:随机网格搜索RandomizedSearchCV()from sklearn.model_selection import RandomizedSearchCVfrom sklearn.svm import SVCimport timestart_time = time.time()pipe_svc = make_pipeline(StandardScaler(),SVC(random_state=1))param_range = [0.0001,0.001,0.01,0.1,1.0,10.0,100.0,1000.0]param_grid = [{'svc__C':param_range,'svc__kernel':['linear']},{'svc__C':param_range,'svc__gamma':param_range,'svc__kernel':['rbf']}]# param_grid = [{'svc__C':param_range,'svc__kernel':['linear','rbf'],'svc__gamma':param_range}]gs = RandomizedSearchCV(estimator=pipe_svc, param_distributions=param_grid,scoring='accuracy',cv=10,n_jobs=-1)gs = gs.fit(X_train,y_train)end_time = time.time()print("随机网格搜索经历时间:%.3f S" % float(end_time-start_time))print(gs.best_score_)print(gs.best_params_)

# 方式3:嵌套交叉验证from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCVfrom sklearn.svm import SVCfrom sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_scoreimport timestart_time = time.time()pipe_svc = make_pipeline(StandardScaler(),SVC(random_state=1))param_range = [0.0001,0.001,0.01,0.1,1.0,10.0,100.0,1000.0]param_grid = [{'svc__C':param_range,'svc__kernel':['linear']},{'svc__C':param_range,'svc__gamma':param_range,'svc__kernel':['rbf']}]gs = GridSearchCV(estimator=pipe_svc, param_grid=param_grid,scoring='accuracy',cv=2,n_jobs=-1)scores = cross_val_score(gs,X_train,y_train,scoring='accuracy',cv=5)end_time = time.time()print("嵌套交叉验证:%.3f S" % float(end_time-start_time))print('CV accuracy :%.3f +/-%.3f'%(np.mean(scores),np.std(scores)))

有时候,准确率不是我们唯一需要考虑的评价指标,因为有时候会存在各类预测错误的代价不一样。例如:在预测一个人的肿瘤疾病的时候,如果病人A真实得肿瘤但是我们预测他是没有肿瘤,跟A真实是健康但是预测他是肿瘤,二者付出的代价很大区别(想想为什么)。所以我们需要其他更加广泛的指标:

# 绘制混淆矩阵from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrixpipe_svc.fit(X_train,y_train)y_pred = pipe_svc.predict(X_test)confmat = confusion_matrix(y_true=y_test,y_pred=y_pred)fig,ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(2.5,2.5))ax.matshow(confmat, cmap=plt.cm.Blues,alpha=0.3)for i in range(confmat.shape[0]):for j in range(confmat.shape[1]):ax.text(x=j,y=i,s=confmat[i,j],va='center',ha='center')plt.xlabel('predicted label')plt.ylabel('true label')plt.show()
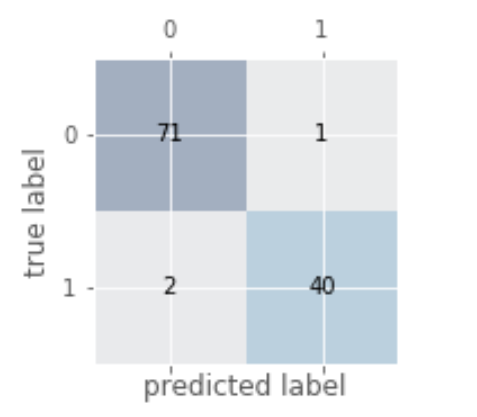
2. 各种指标的计算
# 各种指标的计算from sklearn.metrics import precision_score,recall_score,f1_scoreprint('Precision:%.3f'%precision_score(y_true=y_test,y_pred=y_pred))print('recall_score:%.3f'%recall_score(y_true=y_test,y_pred=y_pred))print('f1_score:%.3f'%f1_score(y_true=y_test,y_pred=y_pred))

3. 将不同的指标与GridSearch结合
# 将不同的指标与GridSearch结合from sklearn.metrics import make_scorer,f1_scorescorer = make_scorer(f1_score,pos_label=0)gs = GridSearchCV(estimator=pipe_svc,param_grid=param_grid,scoring=scorer,cv=10)gs = gs.fit(X_train,y_train)print(gs.best_score_)print(gs.best_params_)
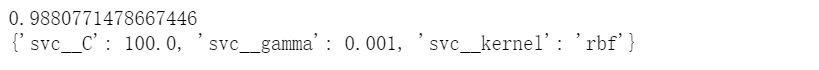
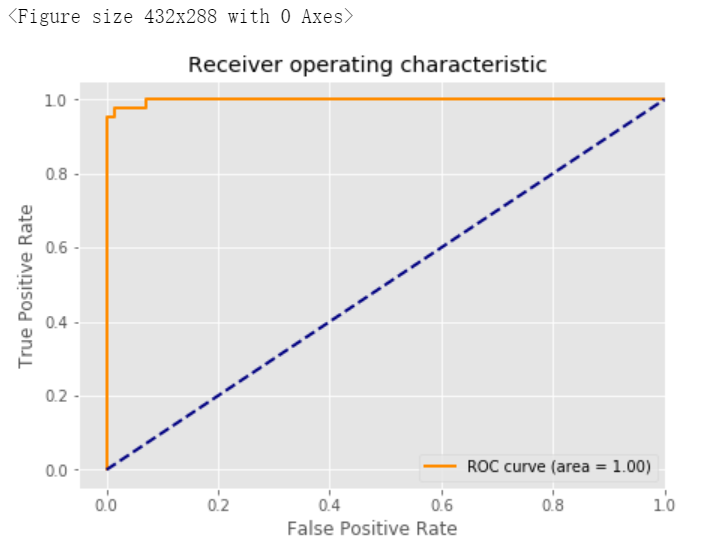
4. 绘制ROC曲线
# 绘制ROC曲线from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve,aucfrom sklearn.metrics import make_scorer,f1_scorescorer = make_scorer(f1_score,pos_label=0)gs = GridSearchCV(estimator=pipe_svc,param_grid=param_grid,scoring=scorer,cv=10)y_pred = gs.fit(X_train,y_train).decision_function(X_test)#y_pred = gs.predict(X_test)fpr,tpr,threshold = roc_curve(y_test, y_pred) ###计算真阳率和假阳率roc_auc = auc(fpr,tpr) ###计算auc的值plt.figure()lw = 2plt.figure(figsize=(7,5))plt.plot(fpr, tpr, color='darkorange',lw=lw, label='ROC curve (area = %0.2f)' % roc_auc) ###假阳率为横坐标,真阳率为纵坐标做曲线plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], color='navy', lw=lw, linestyle='--')plt.xlim([-0.05, 1.0])plt.ylim([-0.05, 1.05])plt.xlabel('False Positive Rate')plt.ylabel('True Positive Rate')plt.title('Receiver operating characteristic ')plt.legend(loc="lower right")plt.show()
本文电子版及代码源文件 后台回复 模型评估 获取
“感谢你的分享,点赞,在看三连↓
评论
