Python 机器学习:超参数调优

1.什么是超参数
RandomSearch GridSearch 贝叶斯优化(Bayesian optimization)
2. GridSearchCV
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import math
import warnings
import lightgbm as lgb
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
from sklearn.model_selection import RandomizedSearchCV
lg = lgb.LGBMClassifier(silent=False)
param_dist = {"max_depth": [2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 10],
"n_estimators": [50, 100, 150, 200],
"min_child_samples": [2,3,4,5,6]
}
grid_search = GridSearchCV(estimator=lg, n_jobs=10, param_grid=param_dist, cv = 5, scoring='f1', verbose=5)
grid_search.fit(X_train, y)
grid_search.best_estimator_, grid_search.best_score_
# Fitting 5 folds for each of 120 candidates, totalling 600 fits
# [Parallel(n_jobs=10)]: Using backend LokyBackend with 10 concurrent workers.
# [Parallel(n_jobs=10)]: Done 52 tasks | elapsed: 2.5s
# [Parallel(n_jobs=10)]: Done 142 tasks | elapsed: 6.6s
# [Parallel(n_jobs=10)]: Done 268 tasks | elapsed: 14.0s
# [Parallel(n_jobs=10)]: Done 430 tasks | elapsed: 25.5s
# [Parallel(n_jobs=10)]: Done 600 out of 600 | elapsed: 40.6s finished
# (LGBMClassifier(max_depth=10, min_child_samples=6, n_estimators=200,
# silent=False), 0.6359524127649383)
GridSearchCV搜索过程模型estimator:lgb.LGBMClassifier param_grid:模型的超参数,上面例子给出了3个参数,值得数量分别是6,4,5,组合起来的搜索空间是120个 cv:交叉验证的折数(上面例子5折交叉), 算法训练的次数总共为120*5=600 scoring:模型好坏的评价指标分数,如F1值 搜索返回: 最好的模型 best_estimator_和最好的分数
https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.model_selection.GridSearchCV.html#sklearn.model_selection.GridSearchCV
3. RandomSearchCV
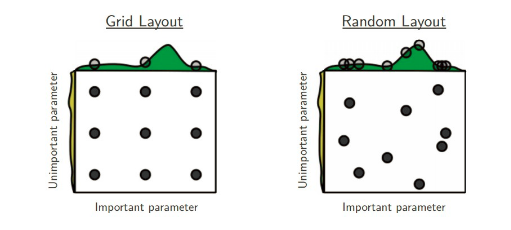
GridSearchCV一样,RandomSearchCV也是在有限的超参数空间(人为重要的超参数)中搜索最优超参数。不一样的地方在于搜索超参数的值不是固定,是在一定范围内随机的值。不同超参数值的组合也是随机的。值的随机性可能会弥补GridSearchCV超参数值固定的有限组合,但也可能更坏。Better than grid search in various senses but still expensive to guarantee good coverage
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import math
import warnings
import lightgbm as lgb
from scipy.stats import uniform
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
from sklearn.model_selection import RandomizedSearchCV
lg = lgb.LGBMClassifier(silent=False)
param_dist = {"max_depth": range(2,15,1),
"n_estimators": range(50,200,4),
"min_child_samples": [2,3,4,5,6],
}
random_search = RandomizedSearchCV(estimator=lg, n_jobs=10, param_distributions=param_dist, n_iter=100, cv = 5, scoring='f1', verbose=5)
random_search.fit(X_train, y)
random_search.best_estimator_, random_search.best_score_
# Fitting 5 folds for each of 100 candidates, totalling 500 fits
# [Parallel(n_jobs=10)]: Using backend LokyBackend with 10 concurrent workers.
# [Parallel(n_jobs=10)]: Done 52 tasks | elapsed: 6.6s
# [Parallel(n_jobs=10)]: Done 142 tasks | elapsed: 12.9s
# [Parallel(n_jobs=10)]: Done 268 tasks | elapsed: 22.9s
# [Parallel(n_jobs=10)]: Done 430 tasks | elapsed: 36.2s
# [Parallel(n_jobs=10)]: Done 500 out of 500 | elapsed: 42.0s finished
# (LGBMClassifier(max_depth=11, min_child_samples=3, n_estimators=198,
# silent=False), 0.628180299445963)
GridSearchCV类似,不同之处如下:n_iter:随机搜索值的数量 param_distributions:搜索值的范围,除了list之外,也可以是某种分布如uniform均匀分布等
https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.model_selection.RandomizedSearchCV.html#sklearn.model_selection.RandomizedSearchCV
4. 贝叶斯优化(Bayesian optimization)
GridSearchCV还是RandomSearchCV, 都是在调参者给定的有限范围内搜索全部或者部分参数的组合情况下模型的最佳表现;可想而知最优模型参数取决于先验的模型参数和有限范围,某些情况下并一定是最优的, 而且暴力搜索对于大的候选参数空间也是很耗时的。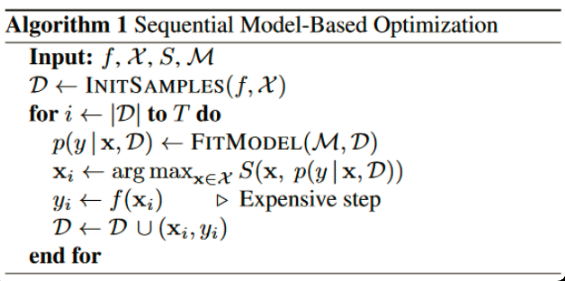
Input:f是模型, M是高斯拟合函数, X是参数, S是参数选择算法Acquisition Function 初始化高斯分布拟合的数据集D,为(x,y), x是超参数,y是超参数的x的执行结果(如精确率等) 迭代T次 每次迭代,用D数据集拟合高斯分布函数 根据拟合的函数,根据Acquisition Function(如Expected improvement算法),在参数空间选择一个比当前最优解更优的参数xi 将参数xi代入模型f(训练一个模型),得出相应的yi(新模型的精确率等) (xi,yi)重新加入拟合数据集D,再一次迭代
由此可知,贝叶斯优化每次都利用上一次参数选择。而GridSearchCV和RandomSearchCV每一次搜索都是独立的。
到此,简单介绍了贝叶斯优化的理论知识。有很多第三方库实现了贝叶斯优化的实现,如 advisor,bayesian-optimization,Scikit-Optimize和GPyOpt等。本文以GPyOpt和bayesian-optimization为例子。
pip install gpyopt
pip install bayesian-optimization
pip install scikit-optimize
gpyopt例子
import GPy
import GPyOpt
from GPyOpt.methods import BayesianOptimization
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from xgboost import XGBRegressor
import numpy as np
iris = load_iris()
X = iris.data
y = iris.target
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X,y,test_size = 0.3,random_state = 14)
# 超参数搜索空间
bds = [{'name': 'learning_rate', 'type': 'continuous', 'domain': (0, 1)},
{'name': 'gamma', 'type': 'continuous', 'domain': (0, 5)},
{'name': 'max_depth', 'type': 'continuous', 'domain': (1, 50)}]
# Optimization objective 模型F
def cv_score(parameters):
parameters = parameters[0]
score = cross_val_score(
XGBRegressor(learning_rate=parameters[0],
gamma=int(parameters[1]),
max_depth=int(parameters[2])),
X, y, scoring='neg_mean_squared_error').mean()
score = np.array(score)
return score
# acquisition就是选择不同的Acquisition Function
optimizer = GPyOpt.methods.BayesianOptimization(f = cv_score, # function to optimize
domain = bds, # box-constraints of the problem
acquisition_type ='LCB', # LCB acquisition
acquisition_weight = 0.1) # Exploration exploitation
x_best = optimizer.X[np.argmax(optimizer.Y)]
print("Best parameters: learning_rate="+str(x_best[0])+",gamma="+str(x_best[1])+",max_depth="+str(x_best[2]))
# Best parameters: learning_rate=0.4272184438229706,gamma=1.4805727469635759,max_depth=41.8460390442754
bayesian-optimization例子
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
from xgboost import XGBRegressor
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
from bayes_opt import BayesianOptimization
iris = load_iris()
X = iris.data
y = iris.target
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X,y,test_size = 0.3,random_state = 14)
bds ={'learning_rate': (0, 1),
'gamma': (0, 5),
'max_depth': (1, 50)}
# Optimization objective
def cv_score(learning_rate, gamma, max_depth):
score = cross_val_score(
XGBRegressor(learning_rate=learning_rate,
gamma=int(gamma),
max_depth=int(max_depth)),
X, y, scoring='neg_mean_squared_error').mean()
score = np.array(score)
return score
rf_bo = BayesianOptimization(
cv_score,
bds
)
rf_bo.maximize()
rf_bo.max
| iter | target | gamma | learni... | max_depth |
-------------------------------------------------------------
| 1 | -0.0907 | 0.7711 | 0.1819 | 20.33 |
| 2 | -0.1339 | 4.933 | 0.6599 | 8.972 |
| 3 | -0.07285 | 1.55 | 0.8247 | 33.94 |
| 4 | -0.1359 | 4.009 | 0.3994 | 25.55 |
| 5 | -0.08773 | 1.666 | 0.9551 | 48.67 |
| 6 | -0.05654 | 0.0398 | 0.3707 | 1.221 |
| 7 | -0.08425 | 0.6883 | 0.2564 | 33.25 |
| 8 | -0.1113 | 3.071 | 0.8913 | 1.051 |
| 9 | -0.9167 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.701 |
| 10 | -0.05267 | 0.0538 | 0.1293 | 1.32 |
| 11 | -0.08506 | 1.617 | 1.0 | 32.68 |
| 12 | -0.09036 | 2.483 | 0.2906 | 33.21 |
| 13 | -0.08969 | 0.4662 | 0.3612 | 34.74 |
| 14 | -0.0723 | 1.295 | 0.2061 | 1.043 |
| 15 | -0.07531 | 1.903 | 0.1182 | 35.11 |
| 16 | -0.08494 | 2.977 | 1.0 | 34.57 |
| 17 | -0.08506 | 1.231 | 1.0 | 36.05 |
| 18 | -0.07023 | 2.81 | 0.838 | 36.16 |
| 19 | -0.9167 | 1.94 | 0.0 | 36.99 |
| 20 | -0.09041 | 3.894 | 0.9442 | 35.52 |
| 21 | -0.1182 | 3.188 | 0.01882 | 35.14 |
| 22 | -0.08521 | 0.931 | 0.05693 | 31.66 |
| 23 | -0.1003 | 2.26 | 0.07555 | 31.78 |
| 24 | -0.1018 | 0.08563 | 0.9838 | 32.22 |
| 25 | -0.1017 | 0.8288 | 0.9947 | 30.57 |
| 26 | -0.9167 | 1.943 | 0.0 | 30.2 |
| 27 | -0.08506 | 1.518 | 1.0 | 35.04 |
| 28 | -0.08494 | 3.464 | 1.0 | 32.36 |
| 29 | -0.1224 | 4.296 | 0.4472 | 33.47 |
| 30 | -0.1017 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 35.86 |
=============================================================
{'target': -0.052665895082105285,
'params': {'gamma': 0.05379782654053811,
'learning_rate': 0.1292986176550608,
'max_depth': 1.3198257775801387}}
bayesian-optimization只支持最大化,如果score是越小越好,可以加一个负号转化为最大值优化。
5. 总结
GridSearchCV网格搜索,给定超参和取值范围,遍历所有组合得到最优参数。首先你要给定一个先验的取值,不能取得太多,否则组合太多,耗时太长。可以启发式的尝试。 RandomSearchCV随机搜索,搜索超参数的值不是固定,是在一定范围内随机的值 贝叶斯优化,采用高斯过程迭代式的寻找最优参数,每次迭代都是在上一次迭代基础上拟合高斯函数上,寻找比上一次迭代更优的参数,推荐gpyopt库
6. 参考资料
A Tutorial on Bayesian Optimization https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/93683454 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/29779000 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/53826787
作者简介:wedo实验君, 数据分析师;热爱生活,热爱写作
赞 赏 作 者

更多阅读
特别推荐

点击下方阅读原文加入社区会员
评论
