Flink SQL流式聚合Mini-Batch优化原理浅析

Hi,我是王知无,一个大数据领域的原创作者。 放心关注我,获取更多行业的一手消息。
前言
流式聚合(streaming aggregation)是我们编写实时业务逻辑时非常常见的场景,当然也比较容易出现各种各样的性能问题。Flink SQL使得用户可以通过简单的聚合函数和GROUP BY子句实现流式聚合,同时也内置了一些优化机制来解决部分case下可能遇到的瓶颈。本文对其中常用的Mini-Batch做个简要的介绍,顺便从源码看一看它的实现思路。
注意:截至当前版本,Flink SQL的流式聚合优化暂时对窗口聚合(即
GROUP BY TUMBLE/HOP/SESSION)无效,仅对纯无界流上的聚合有效。
Mini-Batch概述
Flink SQL中的Mini-Batch概念与Spark Streaming有些类似,即微批次处理。
在默认情况下,聚合算子对摄入的每一条数据,都会执行“读取累加器状态→修改状态→写回状态”的操作。如果数据流量很大,状态操作的overhead也会随之增加,影响效率(特别是RocksDB这种序列化成本高的Backend)。开启Mini-Batch之后,摄入的数据会攒在算子内部的buffer中,达到指定的容量或时间阈值后再做聚合逻辑。这样,一批数据内的每个key只需要执行一次状态读写。如果key的量相对比较稀疏,优化效果更加明显。
未开启和开启Mini-Batch聚合机制的对比示意图如下。
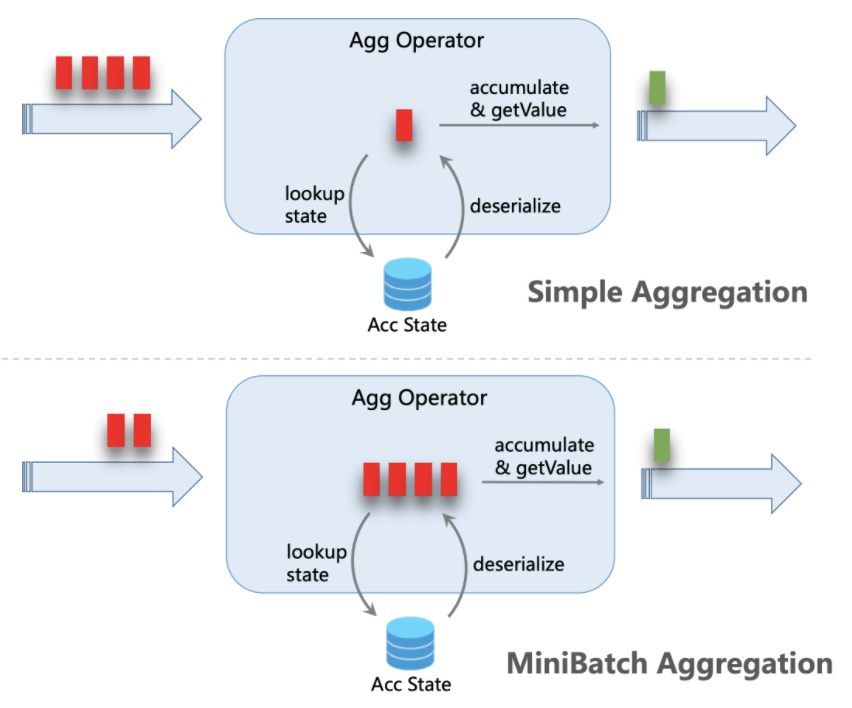
显然,Mini-Batch机制会导致数据处理出现一定的延迟,用户需要自己权衡时效性和吞吐量的重要程度再决定。
Mini-Batch聚合默认是关闭的。要开启它,可以设定如下3个参数。
val tEnv: TableEnvironment = ...
val configuration = tEnv.getConfig().getConfiguration()
configuration.setString("table.exec.mini-batch.enabled", "true") // 启用
configuration.setString("table.exec.mini-batch.allow-latency", "5 s") // 缓存超时时长
configuration.setString("table.exec.mini-batch.size", "5000") // 缓存大小
开启Mini-Batch并执行一个简单的无界流聚合查询,观察Web UI上展示的JobGraph如下。
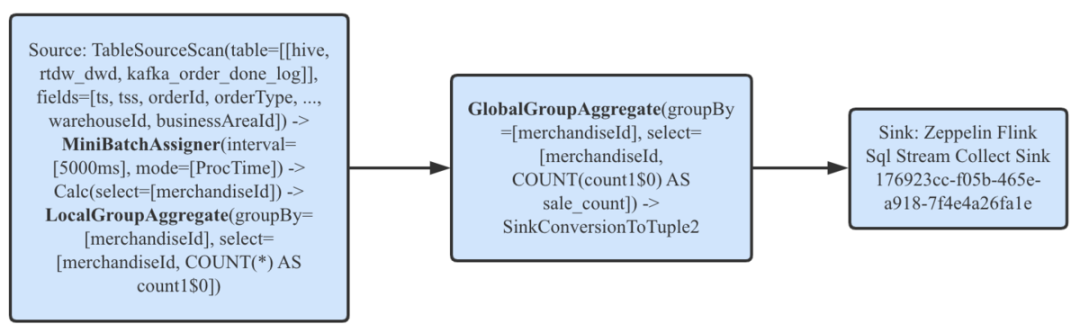
注意LocalGroupAggregate和GlobalGroupAggregate就是基于Mini-Batch的Local-Global机制优化的结果,在分析完原生Mini-Batch后会简单说明。
Mini-Batch原理解析
产生水印
Mini-Batch机制底层对应的优化器规则名为MiniBatchIntervalInferRule(代码略去),产生的物理节点为StreamExecMiniBatchAssigner,直接附加在Source节点的后面。其translateToPlanInternal()方法的源码如下。
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
protected Transformation translateToPlanInternal(PlannerBase planner) {
final Transformation inputTransform =
(Transformation) getInputEdges().get(0).translateToPlan(planner);
final OneInputStreamOperator operator;
if (miniBatchInterval.mode() == MiniBatchMode.ProcTime()) {
operator = new ProcTimeMiniBatchAssignerOperator(miniBatchInterval.interval());
} else if (miniBatchInterval.mode() == MiniBatchMode.RowTime()) {
operator = new RowTimeMiniBatchAssginerOperator(miniBatchInterval.interval());
} else {
throw new TableException(
String.format(
"MiniBatchAssigner shouldn't be in %s mode this is a bug, please file an issue.",
miniBatchInterval.mode()));
}
return new OneInputTransformation<>(
inputTransform,
getDescription(),
operator,
InternalTypeInfo.of(getOutputType()),
inputTransform.getParallelism());
}
可见,根据作业时间语义的不同,产生的算子也不同(本质上都是OneInputStreamOperator)。先看processing time时间语义下产生的算子ProcTimeMiniBatchAssignerOperator的相关方法。
@Override
public void processElement(StreamRecord element) throws Exception {
long now = getProcessingTimeService().getCurrentProcessingTime();
long currentBatch = now - now % intervalMs;
if (currentBatch > currentWatermark) {
currentWatermark = currentBatch;
// emit
output.emitWatermark(new Watermark(currentBatch));
}
output.collect(element);
}
@Override
public void onProcessingTime(long timestamp) throws Exception {
long now = getProcessingTimeService().getCurrentProcessingTime();
long currentBatch = now - now % intervalMs;
if (currentBatch > currentWatermark) {
currentWatermark = currentBatch;
// emit
output.emitWatermark(new Watermark(currentBatch));
}
getProcessingTimeService().registerTimer(currentBatch + intervalMs, this);
}
processing time语义下本不需要用到水印,但这里的处理非常巧妙,即借用水印作为分隔批次的标记。每处理一条数据,都检查其时间戳是否处于当前批次内,若新的批次已经开始,则发射一条新的水印,另外也注册了Timer用于发射水印,且保证发射周期是上述table.exec.mini-batch.allow-latency参数指定的间隔。
event time语义下的思路相同,只需要检查Source产生的水印的时间戳,并只发射符合周期的水印,不符合周期的水印不会流转到下游。RowTimeMiniBatchAssginerOperator类中对应的代码如下。
@Override
public void processWatermark(Watermark mark) throws Exception {
// if we receive a Long.MAX_VALUE watermark we forward it since it is used
// to signal the end of input and to not block watermark progress downstream
if (mark.getTimestamp() == Long.MAX_VALUE && currentWatermark != Long.MAX_VALUE) {
currentWatermark = Long.MAX_VALUE;
output.emitWatermark(mark);
return;
}
currentWatermark = Math.max(currentWatermark, mark.getTimestamp());
if (currentWatermark >= nextWatermark) {
advanceWatermark();
}
}
private void advanceWatermark() {
output.emitWatermark(new Watermark(currentWatermark));
long start = getMiniBatchStart(currentWatermark, minibatchInterval);
long end = start + minibatchInterval - 1;
nextWatermark = end > currentWatermark ? end : end + minibatchInterval;
}
攒批处理
在实现分组聚合的物理节点StreamExecGroupAggregate中,会对启用了Mini-Batch的情况做特殊处理。
final OneInputStreamOperator operator;
if (isMiniBatchEnabled) {
MiniBatchGroupAggFunction aggFunction =
new MiniBatchGroupAggFunction(
aggsHandler,
recordEqualiser,
accTypes,
inputRowType,
inputCountIndex,
generateUpdateBefore,
tableConfig.getIdleStateRetention().toMillis());
operator =
new KeyedMapBundleOperator<>(
aggFunction, AggregateUtil.createMiniBatchTrigger(tableConfig));
} else {
GroupAggFunction aggFunction = new GroupAggFunction(/*...*/);
operator = new KeyedProcessOperator<>(aggFunction);
}
可见,生成的负责攒批处理的算子为KeyedMapBundleOperator,对应的Function则是MiniBatchGroupAggFunction。先来看前者,在它的抽象基类中,有如下三个重要的属性。
/** The map in heap to store elements. */
private transient Map bundle;
/** The trigger that determines how many elements should be put into a bundle. */
private final BundleTrigger bundleTrigger;
/** The function used to process when receiving element. */
private final MapBundleFunction function;
bundle:即用于暂存数据的buffer。 bundleTrigger:与CountTrigger类似,负责在bundle内的数据量达到阈值(即上文所述table.exec.mini-batch.size)时触发计算。源码很简单,不再贴出。 function:即MiniBatchGroupAggFunction,承载具体的计算逻辑。
算子内对应的处理方法如下。
@Override
public void processElement(StreamRecord element) throws Exception {
// get the key and value for the map bundle
final IN input = element.getValue();
final K bundleKey = getKey(input);
final V bundleValue = bundle.get(bundleKey);
// get a new value after adding this element to bundle
final V newBundleValue = function.addInput(bundleValue, input);
// update to map bundle
bundle.put(bundleKey, newBundleValue);
numOfElements++;
bundleTrigger.onElement(input);
}
@Override
public void finishBundle() throws Exception {
if (!bundle.isEmpty()) {
numOfElements = 0;
function.finishBundle(bundle, collector);
bundle.clear();
}
bundleTrigger.reset();
}
@Override
public void processWatermark(Watermark mark) throws Exception {
finishBundle();
super.processWatermark(mark);
}
每来一条数据,就将其加入bundle中,增加计数,并调用BundleTrigger#onElement()方法检查是否达到了触发阈值,如是,则回调finishBundle()方法处理已经收齐的批次,并清空bundle。当水印到来时也同样处理,即可满足批次超时的设定。
finishBundle()方法实际上代理了MiniBatchGroupAggFunction#finishBundle()方法,代码比较冗长,看官可自行查阅,但是流程很简单:先创建累加器实例,再根据输入数据的RowKind执行累加或回撤操作(同时维护每个key对应的状态),最后输出批次聚合结果的changelog。值得注意的是,MiniBatchGroupAggFunction中利用了代码生成技术来自动生成聚合函数的底层handler(即AggsHandleFunction),在Flink Table模块中很常见。
Local-Global简述
Local-Global其实就是自动利用两阶段聚合思想解决数据倾斜的优化方案(是不是很方便),与MapReduce中引入Combiner类似。话休絮烦,直接上官网的图吧。
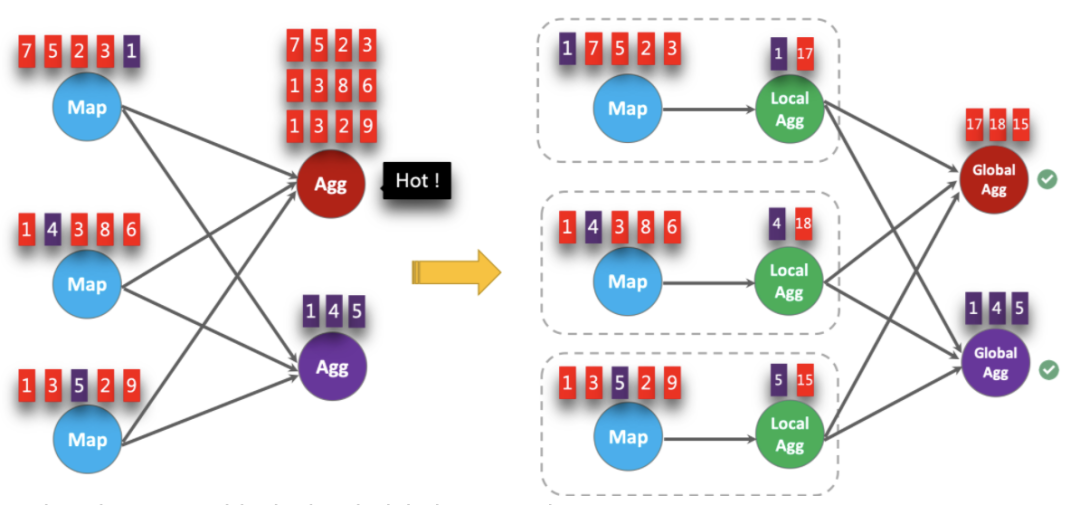
要启用Local-Global聚合,需要在启用Mini-Batch的基础上指定如下参数。
configuration.setString("table.optimizer.agg-phase-strategy", "TWO_PHASE")
Local-Global机制底层对应的优化器规则名为TwoStageOptimizedAggregateRule,产生的物理节点分别是StreamExecLocalGroupAggregate(本地聚合)和StreamExecGlobalGroupAggregate(全局聚合)。在它们各自的translateToPlanInternal()方法中也都运用了代码生成技术生成对应的聚合函数MiniBatchLocalGroupAggFunction和MiniBatchGlobalGroupAggFunction,代码比较多,但思路同样清晰,看官可自行找来看看。

