【41期】盘点那些必问的数据结构算法题之链表
阅读本文大概需要 11 分钟。
来自:juejin.im/post/5b8a0e99f265da43320730ba
0 概述
1 定义
// aslist.h
// 链表结点定义
typedef struct ListNode {
struct ListNode *next;
int value;
} listNode;
2 基本操作
/**
* 创建链表结点
*/
ListNode *listNewNode(int value)
{
ListNode *node;
if (!(node = malloc(sizeof(ListNode))))
return NULL;
node->value = value;
node->next = NULL;
return node;
}
/**
* 头插法插入结点。
*/
ListNode *listAddNodeHead(ListNode *head, int value)
{
ListNode *node;
if (!(node = listNewNode(value)))
return NULL;
if (head)
node->next = head;
head = node;
return head;
}
/**
* 尾插法插入值为value的结点。
*/
ListNode *listAddNodeTail(ListNode *head, int value)
{
ListNode *node;
if (!(node = listNewNode(value)))
return NULL;
return listAddNodeTailWithNode(head, node);
}
/**
* 尾插法插入结点。
*/
ListNode *listAddNodeTailWithNode(ListNode *head, ListNode *node)
{
if (!head) {
head = node;
} else {
ListNode *current = head;
while (current->next) {
current = current->next;
}
current->next = node;
}
return head;
}
/**
* 从链表删除值为value的结点。
*/
ListNode *listDelNode(ListNode *head, int value)
{
ListNode *current=head, *prev=NULL;
while (current) {
if (current->value == value) {
if (current == head)
head = head->next;
if (prev)
prev->next = current->next;
free(current);
break;
}
prev = current;
current = current->next;
}
return head;
}
/**
* 链表遍历。
*/
void listTraverse(ListNode *head)
{
ListNode *current = head;
while (current) {
printf("%d", current->value);
printf("->");
current = current->next;
if (current == head) // 处理首尾循环链表情况
break;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
/**
* 使用数组初始化一个链表,共len个元素。
*/
ListNode *listCreate(int a[], int len)
{
ListNode *head = NULL;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (!(head = listAddNodeTail(head, a[i])))
return NULL;
}
return head;
}
/**
* 链表长度函数
*/
int listLength(ListNode *head)
{
int len = 0;
while (head) {
len++;
head = head->next;
}
return len;
}
3 链表相关面试题
3.1 链表逆序
/**
* 链表逆序,非递归实现。
*/
ListNode *listReverse(ListNode *head)
{
ListNode *newHead = NULL, *current = head;
while (current) {
ListNode *next = current->next;
current->next = newHead;
newHead = current;
current = next;
}
return newHead;
}
/**
* 链表逆序,递归实现。
*/
ListNode *listReverseRecursive(ListNode *head)
{
if (!head || !head->next) {
return head;
}
ListNode *reversedHead = listReverseRecursive(head->next);
head->next->next = head;
head->next = NULL;
return reversedHead;
}
3.2 链表复制
/**
* 链表复制-非递归
*/
ListNode *listCopy(ListNode *head)
{
ListNode *current = head, *newHead = NULL, *newTail = NULL;
while (current) {
ListNode *node = listNewNode(current->value);
if (!newHead) { // 第一个结点
newHead = newTail = node;
} else {
newTail->next = node;
newTail = node;
}
current = current->next;
}
return newHead;
}
/**
* 链表复制-递归
*/
ListNode *listCopyRecursive(ListNode *head)
{
if (!head)
return NULL;
ListNode *newHead = listNewNode(head->value);
newHead->next = listCopyRecursive(head->next);
return newHead;
}
3.3 链表合并
/**
* 链表合并-非递归
*/
ListNode *listMerge(ListNode *list1, ListNode *list2)
{
ListNode dummy; // 使用空结点保存合并链表
ListNode *tail = &dummy;
if (!list1)
return list2;
if (!list2)
return list1;
while (list1 && list2) {
if (list1->value <= list2->value) {
tail->next = list1;
tail = list1;
list1 = list1->next;
} else {
tail->next = list2;
tail = list2;
list2 = list2->next;
}
}
if (list1) {
tail->next = list1;
} else if (list2) {
tail->next = list2;
}
return dummy.next;
}
ListNode *listMergeRecursive(ListNode *list1, ListNode *list2)
{
ListNode *result = NULL;
if (!list1)
return list2;
if (!list2)
return list1;
if (list1->value <= list2->value) {
result = list1;
result->next = listMergeRecursive(list1->next, list2);
} else {
result = list2;
result->next = listMergeRecursive(list1, list2->next);
}
return result;
}
3.4 链表相交判断
/**
* 链表相交判断,如果相交返回相交的结点,否则返回NULL。
*/
ListNode *listIntersect(ListNode *list1, ListNode *list2)
{
int len1 = listLength(list1);
int len2 = listLength(list2);
int delta = abs(len1 - len2);
ListNode *longList = list1, *shortList = list2;
if (len1 < len2) {
longList = list2;
shortList = list1;
}
int i;
for (i = 0; i < delta; i++) {
longList = longList->next;
}
while (longList && shortList) {
if (longList == shortList)
return longList;
longList = longList->next;
shortList = shortList->next;
}
return NULL;
}
3.5 判断链表是否存在环
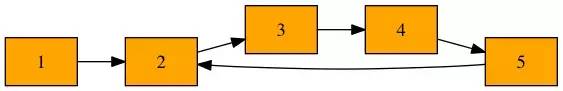
/**
* 检测链表是否有环-Flod判圈算法
* 若存在环,返回相遇结点,否则返回NULL
*/
ListNode *listDetectLoop(ListNode *head)
{
ListNode *slow, *fast;
slow = fast = head;
while (slow && fast && fast->next) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if (slow == fast) {
printf("Found Loop\n");
return slow;
}
}
printf("No Loop\n");
return NULL;
}
void testListDetectLoop()
{
printf("\nTestListDetectLoop\n");
int a[] = {1, 2, 3, 4};
ListNode *head = listCreate(a, ALEN(a));
listDetectLoop(head);
// 构造一个环
head->next->next->next = head;
listDetectLoop(head);
}
2s - s = nr => s = nr
s = r = a + x => a + x = (L-a) => a = L-x-a
/**
* 查找链表中环入口
*/
ListNode *findLoopNode(ListNode *head)
{
ListNode *meetNode = listDetectLoop(head);
if (!meetNode)
return NULL;
ListNode *headNode = head;
while (meetNode != headNode) {
meetNode = meetNode->next;
headNode = headNode->next;
}
return meetNode;
}
3.6 链表模拟加法
list1: (3 -> 1 -> 5 -> NULL)
list2: (5 -> 9 -> 2 -> NULL)
result: (8 -> 0 -> 8 -> NULL)
current->data = list1->data + list2->data + carry
(其中carry为低位的进位,如果有进位为1,否则为0)
/**
* 链表模拟加法-非递归解法
*/
ListNode *listEnumarateAdd(ListNode *list1, ListNode *list2)
{
int carry = 0;
ListNode *result = NULL;
while (list1 || list2 || carry) {
int value = carry;
if (list1) {
value += list1->value;
list1 = list1->next;
}
if (list2) {
value += list2->value;
list2 = list2->next;
}
result = listAddNodeTail(result, value % 10);
carry = ( value >= 10 ? 1: 0);
}
return result;
}
/**
* 链表模拟加法-递归解法
*/
ListNode *listEnumarateAddRecursive(ListNode *list1, ListNode *list2, int carry)
{
if (!list1 && !list2 && carry==0)
return NULL;
int value = carry;
if (list1)
value += list1->value;
if (list2)
value += list2->value;
ListNode *next1 = list1 ? list1->next : NULL;
ListNode *next2 = list2 ? list2->next : NULL;
ListNode *more = listEnumarateAddRecursive(next1, next2, (value >= 10 ? 1 : 0));
ListNode *result = listNewNode(carry);
result->value = value % 10;
result->next = more;
return result;
}
3.7 有序单向循环链表插入结点
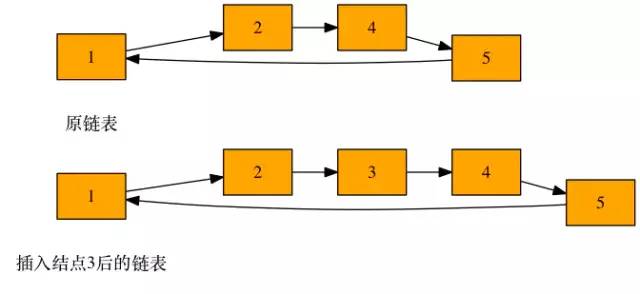
如果原来链表为空或者插入的结点值最小,则直接插入该结点并设置为头结点。
如果原来链表非空,则找到第一个大于该结点值的结点,并插入到该结点的前面。如果插入的结点值最大,则插入在尾部。
/**
* 简化版-有序无循环链表插入结点
*/
ListNode *sortedListAddNode(ListNode *head, int value)
{
ListNode *node = listNewNode(value);
if (!head || head->value >= value) { //情况1
node->next = head;
head = node;
} else { //情况2
ListNode *current = head;
while (current->next != NULL && current->next->value < value)
current = current->next;
node->next = current->next;
current->next = node;
}
return head;
}
/**
* 简化版-有序无循环链表插入结点(两种情况一起处理)
*/
void sortedListAddNodeUnify(ListNode **head, int value)
{
ListNode *node = listNewNode(value);
ListNode **current = head;
while ((*current) && (*current)->value < value) {
current = &((*current)->next);
}
node->next = *current;
*current = node;
}
插入到prev和current之间。
插入到首尾交接处,如果是最小值重新设置head值。
/**
* 有序循环链表插入结点
*/
ListNode *sortedLoopListAddNode(ListNode *head, int value)
{
ListNode *node = listNewNode(value);
ListNode *current = head, *prev = NULL;
do {
prev = current;
current = current->next;
if (value >= prev->value && value <= current->value)
break;
} while (current != head);
prev->next = node;
node->next = current;
if (current == head && value < current->value) // 判断是否要设置链表头
head = node;
return head;
}
3.8 输出链表倒数第K个结点
/**
* 链表倒数第K个结点-遍历两次算法
*/
ListNode *getLastKthNodeTwice(ListNode *head, int k)
{
int len = listLength(head);
if (k > len)
return NULL;
ListNode *current = head;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < len-k; i++) //遍历链表,找出第N-K+1个结点
current = current->next;
return current;
}
/**
* 链表倒数第K个结点-遍历一次算法
*/
ListNode *getLastKthNodeOnce(ListNode *head, int k)
{
ListNode *p1, *p2;
p1 = p2 = head;
for(; k > 0; k--) {
if (!p2) // 链表长度不够K
return NULL;
p2 = p2->next;
}
while (p2) {
p1 = p1->next;
p2 = p2->next;
}
return p1;
}
推荐阅读:
长按二维码,添加我微信
朕已阅 
评论


