手把手教你用Scrapy爬取知乎大V粉丝列表
导读:通过获取知乎某个大V的关注列表和被关注列表,查看该大V以及其关注用户和被关注用户的详细信息,然后通过层层递归调用,实现获取关注用户和被关注用户的关注列表和被关注列表,最终实现获取大量用户信息。

新建一个Scrapy项目scrapy startproject zhihuuser,移动到新建目录cdzhihuuser下。新建Spider项目:scrapy genspider zhihu zhihu.com。
01 定义spider.py文件
定义爬取网址、爬取规则等。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import json
from scrapy import Spider, Request
from zhihuuser.items import UserItem
class ZhihuSpider(Spider):
name = 'zhihu'
allowed_domains = ['zhihu.com']
start_urls = ['http://zhihu.com/']
# 自定义爬取网址
start_user = 'excited-vczh'
user_url = 'https://www.zhihu.com/api/v4/members/{user}?include={include}'
user_query = 'allow_message,is_followed,is_following,is_org,is_blocking,employments,answer_count,follower_count,articles_count,gender,badge[?(type=best_answerer)].topics'
follows_url = 'https://www.zhihu.com/api/v4/members/{user}/followees?include= {include}&offset={offset}&limit={limit}'
follows_query = 'data[*].answer_count,articles_count,gender,follower_count,is_followed,is_following,badge[?(type=best_answerer)].topics'
followers_url = 'https://www.zhihu.com/api/v4/members/{user}/followees?include= {include}&offset={offset}&limit={limit}'
followers_query = 'data[*].answer_count,articles_count,gender,follower_count,is_followed,is_following,badge[?(type=best_answerer)].topics'
# 定义请求爬取用户信息、关注用户和被关注用户的函数
def start_requests(self):
yield Request(self.user_url.format(user=self.start_user, include=self.user_query), callback=self.parseUser)
yield Request(self.follows_url.format(user=self.start_user, include=self.follows_query, offset=0, limit=20), callback=self.parseFollows)
yield Request(self.followers_url.format(user=self.start_user, include=self.followers_query, offset=0, limit=20), callback=self.parseFollowers)
# 请求爬取用户详细信息
def parseUser(self, response):
result = json.loads(response.text)
item = UserItem()
for field in item.fields:
if field in result.keys():
item[field] = result.get(field)
yield item
# 定义回调函数,爬取关注用户与被关注用户的详细信息,实现层层迭代
yield Request(self.follows_url.format(user=result.get('url_token'), include=self.follows_query, offset=0, limit=20), callback=self.parseFollows)
yield Request(self.followers_url.format(user=result.get('url_token'), include=self.followers_query, offset=0, limit=20), callback=self.parseFollowers)
# 爬取关注者列表
def parseFollows(self, response):
results = json.loads(response.text)
if 'data' in results.keys():
for result in results.get('data'):
yield Request(self.user_url.format(user=result.get('url_token'), include=self.user_query), callback=self.parseUser)
if 'paging' in results.keys() and results.get('paging').get('is_end') == False:
next_page = results.get('paging').get('next')
yield Request(next_page, callback=self.parseFollows)
# 爬取被关注者列表
def parseFollowers(self, response):
results = json.loads(response.text)
if 'data' in results.keys():
for result in results.get('data'):
yield Request(self.user_url.format(user=result.get('url_token'), include=self.user_query), callback=self.parseUser)
if 'paging' in results.keys() and results.get('paging').get('is_end') == False:
next_page = results.get('paging').get('next')
yield Request(next_page, callback=self.parseFollowers)02 定义items.py文件
定义爬取数据的信息、使其规整等。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Define here the models for your scraped items
# See documentation in:
# https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/items.html
from scrapy import Field, Item
class UserItem(Item):
# define the fields for your item here like:
# name = scrapy.Field()
allow_message = Field()
answer_count = Field()
articles_count = Field()
avatar_url = Field()
avatar_url_template = Field()
badge = Field()
employments = Field()
follower_count = Field()
gender = Field()
headline = Field()
id = Field()
name = Field()
type = Field()
url = Field()
url_token = Field()
user_type = Field()
03 定义pipelines.py文件
存储数据到MongoDB。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Define your item pipelines here
# Don't forget to add your pipeline to the ITEM_PIPELINES setting
# See: https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html
import pymongo
# 存储到MongoDB
class MongoPipeline(object):
collection_name = 'users'
def __init__(self, mongo_uri, mongo_db):
self.mongo_uri = mongo_uri
self.mongo_db = mongo_db
@classmethod
def from_crawler(cls, crawler):
return cls(
mongo_uri=crawler.settings.get('MONGO_URI'),
mongo_db=crawler.settings.get('MONGO_DATABASE')
)
def open_spider(self, spider):
self.client = pymongo.MongoClient(self.mongo_uri)
self.db = self.client[self.mongo_db]
def close_spider(self, spider):
self.client.close()
def process_item(self, item, spider):
self.db[self.collection_name].update({'url_token':item['url_token']}, dict(item), True)
# 执行去重操作
return item
04 定义settings.py文件
开启MongoDB、定义请求头、不遵循robotstxt规则。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
BOT_NAME = 'zhihuuser'
SPIDER_MODULES = ['zhihuuser.spiders']
# Obey robots.txt rules
ROBOTSTXT_OBEY = False # 是否遵守robotstxt规则,限制爬取内容
# Override the default request headers(加载请求头):
DEFAULT_REQUEST_HEADERS = {
'Accept': 'text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8',
'Accept-Language': 'en',
'User-agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_11_6) AppleWebKit/ 537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/64.0.3282.140 Safari/537.36',
'authorization': 'oauth c3cef7c66a1843f8b3a9e6a1e3160e20'
}
# Configure item pipelines
# See https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html
ITEM_PIPELINES = {
'zhihuuser.pipelines.MongoPipeline': 300,
}
MONGO_URI = 'localhost'
MONGO_DATABASE = 'zhihu'
开启爬取:scrapycrawlzhihu。部分爬取过程中的信息如图8-4所示。

▲图8-4 部分爬取过程中的信息
存储到MongoDB的部分信息如图8-5所示。
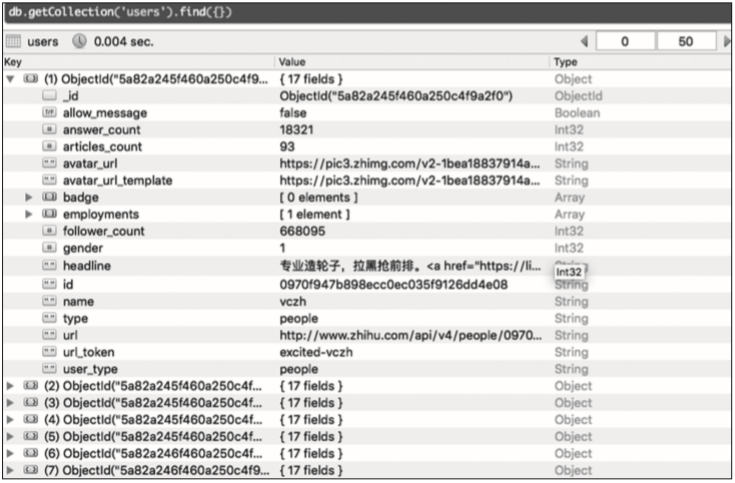
▲图8-5 MongoDB的部分信息


评论
