Flink1.12集成Hive打造自己的批流一体数仓
 简介
简介小编在去年之前分享过参与的实时数据平台的建设,关于实时数仓也进行过分享。客观的说,我们当时做不到批流一体,小编当时的方案是将实时消息数据每隔15分钟文件同步到离线数据平台,然后用同一套SQL代码进行离线入库操作。
但是随着 Flink1.12版本的发布,Flink使用HiveCatalog可以通过批或者流的方式来处理Hive中的表。这就意味着Flink既可以作为Hive的一个批处理引擎,也可以通过流处理的方式来读写Hive中的表,从而为实时数仓的应用和流批一体的落地实践奠定了坚实的基础。
Flink 与 Hive 的集成包含两个层面。
一是利用了 Hive 的 MetaStore 作为持久化的 Catalog,用户可通过HiveCatalog将不同会话中的 Flink 元数据存储到 Hive Metastore 中。例如,用户可以使用HiveCatalog将其 Kafka 表或 Elasticsearch 表存储在 Hive Metastore 中,并后续在 SQL 查询中重新使用它们。
二是利用 Flink 来读写 Hive 的表。
HiveCatalog的设计提供了与 Hive 良好的兼容性,用户可以”开箱即用”的访问其已有的 Hive 数仓。您不需要修改现有的 Hive Metastore,也不需要更改表的数据位置或分区。
Flink1.12 对Hive的支持
从 1.11.0 开始,在使用 Hive 方言时,Flink 允许用户用 Hive 语法来编写 SQL 语句。通过提供与 Hive 语法的兼容性,我们旨在改善与 Hive 的互操作性,并减少用户需要在 Flink 和 Hive 之间切换来执行不同语句的情况。
Flink 支持的 Hive 版本如下图所示:

某些功能是否可用取决于您使用的 Hive 版本,这些限制不是由 Flink 所引起的:
Hive 内置函数在使用 Hive-1.2.0 及更高版本时支持。
列约束,也就是 PRIMARY KEY 和 NOT NULL,在使用 Hive-3.1.0 及更高版本时支持。
更改表的统计信息,在使用 Hive-1.2.0 及更高版本时支持。
DATE列统计信息,在使用 Hive-1.2.0 及更高版时支持。
使用 Hive-2.0.x 版本时不支持写入 ORC 表。
要与 Hive 集成,我们需要在 Flink 下的/lib/目录中添加一些额外的依赖包, 以便通过 Table API 或 SQL Client 与 Hive 进行交互。
Apache Hive 是基于 Hadoop 之上构建的, 首先您需要 Hadoop 的依赖:
export HADOOP_CLASSPATH=`hadoop classpath`有两种添加 Hive 依赖项的方法。第一种是使用 Flink 提供的 Hive Jar包。我们根据使用的 Metastore 的版本来选择对应的 Hive jar。第二个方式是分别添加每个所需的 jar 包。如果您使用的 Hive 版本尚未在此处列出,则第二种方法会更适合。
注意:建议优先使用 Flink 提供的 Hive jar 包。仅在 Flink 提供的 Hive jar 不满足您的需求时,再考虑使用分开添加 jar 包的方式。
本文我们使用的Flink和Hive版本是1.12+2.3.6,集成Hive时还需要一些额外的Jar包依赖,将其放置在Flink安装目录下的lib文件夹下,这样我们才能通过 Table API 或 SQL Client 与 Hive 进行交互。
下图列举了Hive版本相对应的Jar包:

此外,我们还需要添加下面两个jar包:
flink-connector-hive_2.11-1.12.0.jar和hive-exec-2.3.6.jar。其中hive-exec-2.3.6.jar包我们可以在Hive安装路径下的lib文件夹中找到。官网给出了下载地址,大家可以参考:https://ci.apache.org/projects/flink/flink-docs-release-1.12/zh/dev/table/connectors/hive/#%E4%BE%9D%E8%B5%96%E9%A1%B9
如果你需要构建工程,那么只需要在pom.xml中新增以下依赖即可:
org.apache.flink
flink-connector-hive_2.11
1.12.0
provided
org.apache.flink
flink-table-api-java-bridge_2.11
1.12.0
provided
org.apache.hive
hive-exec
${hive.version}
provided
使用Blink Planner连接Hive
请大家注意,Flink 1.12版本中虽然 HiveCatalog 不需要特定的 planner,但读写Hive表仅适用于 Blink planner。因此,强烈建议您在连接到Hive仓库时使用 Blink planner。
EnvironmentSettings settings = EnvironmentSettings.newInstance().useBlinkPlanner().build();
TableEnvironment tableEnv = TableEnvironment.create(settings);
String name = "myhive";
String defaultDatabase = "mydatabase";
String hiveConfDir = "/opt/hive-conf";
HiveCatalog hive = new HiveCatalog(name, defaultDatabase, hiveConfDir);
tableEnv.registerCatalog("myhive", hive);
#### 然后我们就可以愉快的对Hive表进行操作了,例如:
// 随便读取一些数据
String mySql = "select * from my_table limit 10'";
TableResult result = tableEnv.executeSql(mySql);
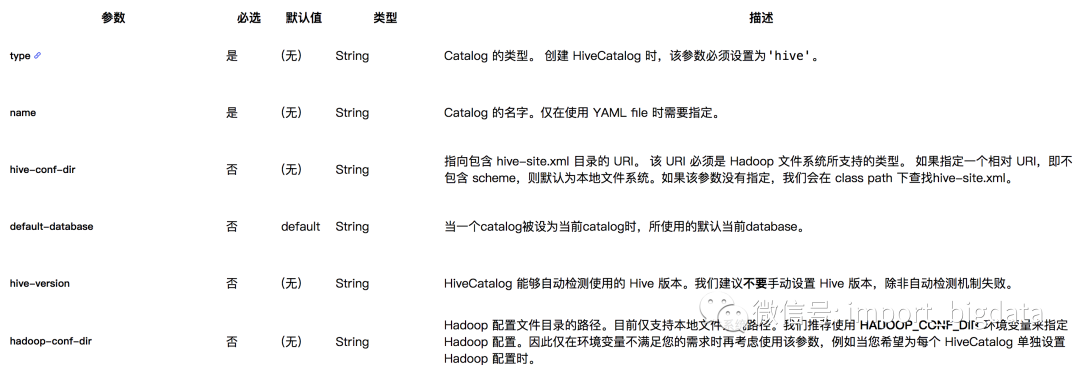
System.out.println(result.getJobClient().get().getJobStatus());下表列出了通过 YAML 文件或 DDL 定义 HiveCatalog 时所支持的参数。后续的版本规划中将会支持在 Flink 中创建 Hive 表,视图,分区和函数的DDL。
使用 FlinkCli 连接Hive
我们把三个必须依赖的包放到 Flink 的lib目录下:
flink-sql-connector-hive-2.3.6
flink-connector-hive_2.11-1.12.0.jar
hive-exec-2.3.4.jar然后,最重要的一步来了我们需要修改 conf/sql-cli-defaults.yaml配置文件:
execution:
planner: blink
type: streaming
...
current-catalog: myhive # set the HiveCatalog as the current catalog of the session
current-database: mydatabase
catalogs:
- name: myhive
type: hive
hive-conf-dir: /opt/hive-conf # contains hive-site.xml然后就可以愉快的玩耍了:
##命令行启动
bin/sql-client.sh embedded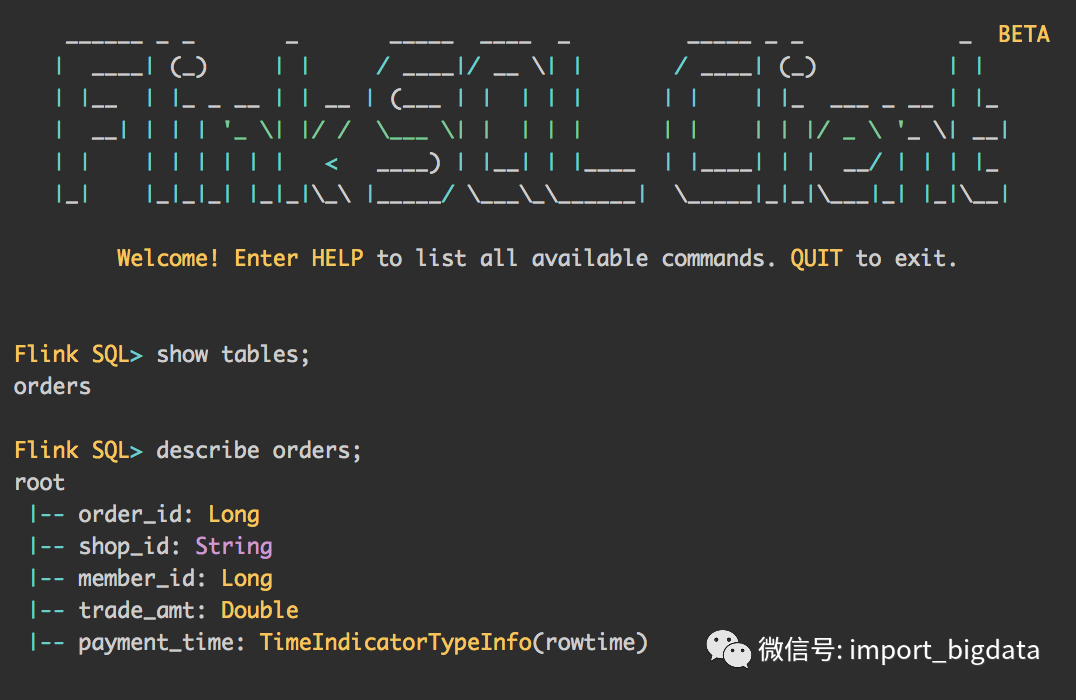
使用Hive Dialect
Flink 目前支持两种 SQL 方言: default 和 hive。你需要先切换到 Hive 方言,然后才能使用 Hive 语法编写。下面介绍如何使用 SQL 客户端和 Table API 设置方言。还要注意,你可以为执行的每个语句动态切换方言。无需重新启动会话即可使用其他方言。
方言切换
SQL 方言可以通过 table.sql-dialect 属性指定。我们需要在sql-client-defaults.yaml配置文件中进行配置:
execution:
planner: blink
type: batch
result-mode: table
configuration:
table.sql-dialect: hive同样我们也可以在 SQL 客户端启动后设置方言:
Flink SQL> set table.sql-dialect=hive; -- to use hive dialect
[INFO] Session property has been set.
Flink SQL> set table.sql-dialect=default; -- to use default dialect
[INFO] Session property has been set.Table API中使用Dialect
EnvironmentSettings settings = EnvironmentSettings.newInstance().useBlinkPlanner()...build();
TableEnvironment tableEnv = TableEnvironment.create(settings);
// to use hive dialect
tableEnv.getConfig().setSqlDialect(SqlDialect.HIVE);
// to use default dialect
tableEnv.getConfig().setSqlDialect(SqlDialect.DEFAULT);以下是使用 Hive 方言的一些注意事项。
Hive 方言只能用于操作 Hive 表,不能用于一般表。Hive 方言应与HiveCatalog一起使用。
虽然所有 Hive 版本支持相同的语法,但是一些特定的功能是否可用仍取决于你使用的Hive 版本。例如,更新数据库位置 只在 Hive-2.4.0 或更高版本支持。
Hive 和 Calcite 有不同的保留关键字集合。例如,default 是 Calcite 的保留关键字,却不是 Hive 的保留关键字。即使使用 Hive 方言, 也必须使用反引号引用此类关键字才能将其用作标识符。
由于扩展的查询语句的不兼容性,在 Flink 中创建的视图是不能在 Hive 中查询的。
使用Hive UDF
在 Flink SQL 和 Table API 中,可以通过系统内置的 HiveModule 来使用 Hive 内置函数,
String name = "myhive";
String version = "2.3.4";
tableEnv.loadModue(name, new HiveModule(version));在 Flink 中用户可以使用 Hive 里已经存在的 UDF 函数。
支持的 UDF 类型包括:
UDF
GenericUDF
GenericUDTF
UDAF
GenericUDAFResolver2
在进行查询规划和执行时,Hive UDF 和 GenericUDF 函数会自动转换成 Flink 中的 ScalarFunction,GenericUDTF 会被自动转换成 Flink 中的 TableFunction,UDAF 和 GenericUDAFResolver2 则转换成 Flink 聚合函数(AggregateFunction)。
想要使用 Hive UDF 函数,需要如下几步:
通过 Hive Metastore 将带有 UDF 的 HiveCatalog 设置为当前会话的 catalog 后端。
将带有 UDF 的 jar 包放入 Flink classpath 中,并在代码中引入。
使用 Blink planner。
假设我们在 Hive Metastore 中已经注册了下面的 UDF 函数:
/**
* 注册为 'myudf' 的简单 UDF 测试类.
*/
public class TestHiveSimpleUDF extends UDF {
public IntWritable evaluate(IntWritable i) {
return new IntWritable(i.get());
}
public Text evaluate(Text text) {
return new Text(text.toString());
}
}
/**
* 注册为 'mygenericudf' 的普通 UDF 测试类
*/
public class TestHiveGenericUDF extends GenericUDF {
@Override
public ObjectInspector initialize(ObjectInspector[] arguments) throws UDFArgumentException {
checkArgument(arguments.length == 2);
checkArgument(arguments[1] instanceof ConstantObjectInspector);
Object constant = ((ConstantObjectInspector) arguments[1]).getWritableConstantValue();
checkArgument(constant instanceof IntWritable);
checkArgument(((IntWritable) constant).get() == 1);
if (arguments[0] instanceof IntObjectInspector ||
arguments[0] instanceof StringObjectInspector) {
return arguments[0];
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Not support argument: " + arguments[0]);
}
}
@Override
public Object evaluate(DeferredObject[] arguments) throws HiveException {
return arguments[0].get();
}
@Override
public String getDisplayString(String[] children) {
return "TestHiveGenericUDF";
}
}
/**
* 注册为 'mygenericudtf' 的字符串分割 UDF 测试类
*/
public class TestHiveUDTF extends GenericUDTF {
@Override
public StructObjectInspector initialize(ObjectInspector[] argOIs) throws UDFArgumentException {
checkArgument(argOIs.length == 2);
// TEST for constant arguments
checkArgument(argOIs[1] instanceof ConstantObjectInspector);
Object constant = ((ConstantObjectInspector) argOIs[1]).getWritableConstantValue();
checkArgument(constant instanceof IntWritable);
checkArgument(((IntWritable) constant).get() == 1);
return ObjectInspectorFactory.getStandardStructObjectInspector(
Collections.singletonList("col1"),
Collections.singletonList(PrimitiveObjectInspectorFactory.javaStringObjectInspector));
}
@Override
public void process(Object[] args) throws HiveException {
String str = (String) args[0];
for (String s : str.split(",")) {
forward(s);
forward(s);
}
}
@Override
public void close() {
}
}在 Hive CLI 中,可以查询到已经注册的 UDF 函数:
hive> show functions;
OK
......
mygenericudf
myudf
myudtf此时,用户如果想使用这些 UDF,在 SQL 中就可以这样写:
Flink SQL> select mygenericudf(myudf(name), 1) as a, mygenericudf(myudf(age), 1) as b, s from mysourcetable, lateral table(myudtf(name, 1)) as T(s);此外,Flink1.12有了一个巨大的突破就是和Hive进行维表Join。我们在官网上可以看到如下信息:
Flink support tracking the latest partition(version) of temporal table automatically in processing time temporal join, the latest partition(version) is defined by ‘streaming-source.partition-order’ option, This is the most common user cases that use Hive table as dimension table in a Flink stream application job.
NOTE: This feature is only support in Flink STREAMING Mode.
Flink 1.12 支持了 Hive 最新的分区作为时态表的功能,可以通过 SQL 的方式直接关联 Hive 分区表的最新分区,并且会自动监听最新的 Hive 分区,当监控到新的分区后,会自动地做维表数据的全量替换。
Flink支持的是processing-time的temporal join,也就是说总是与最新版本的时态表进行JOIN。另外,Flink既支持非分区表的temporal join,又支持分区表的temporal join。对于分区表而言,Flink会监听Hive表的最新分区数据。值得注意的是,Flink尚不支持 event-time temporal join。同时给出了一个案例:
-- Assume the data in hive table is updated per day, every day contains the latest and complete dimension data
SET table.sql-dialect=hive;
CREATE TABLE dimension_table (
product_id STRING,
product_name STRING,
unit_price DECIMAL(10, 4),
pv_count BIGINT,
like_count BIGINT,
comment_count BIGINT,
update_time TIMESTAMP(3),
update_user STRING,
...
) PARTITIONED BY (pt_year STRING, pt_month STRING, pt_day STRING) TBLPROPERTIES (
-- using default partition-name order to load the latest partition every 12h (the most recommended and convenient way)
'streaming-source.enable' = 'true',
'streaming-source.partition.include' = 'latest',
'streaming-source.monitor-interval' = '12 h',
'streaming-source.partition-order' = 'partition-name', -- option with default value, can be ignored.
-- using partition file create-time order to load the latest partition every 12h
'streaming-source.enable' = 'true',
'streaming-source.partition.include' = 'latest',
'streaming-source.partition-order' = 'create-time',
'streaming-source.monitor-interval' = '12 h'
-- using partition-time order to load the latest partition every 12h
'streaming-source.enable' = 'true',
'streaming-source.partition.include' = 'latest',
'streaming-source.monitor-interval' = '12 h',
'streaming-source.partition-order' = 'partition-time',
'partition.time-extractor.kind' = 'default',
'partition.time-extractor.timestamp-pattern' = '$pt_year-$pt_month-$pt_day 00:00:00'
);
SET table.sql-dialect=default;
CREATE TABLE orders_table (
order_id STRING,
order_amount DOUBLE,
product_id STRING,
log_ts TIMESTAMP(3),
proctime as PROCTIME()
) WITH (...);
-- streaming sql, kafka temporal join a hive dimension table. Flink will automatically reload data from the
-- configured latest partition in the interval of 'streaming-source.monitor-interval'.
SELECT * FROM orders_table AS order
JOIN dimension_table FOR SYSTEM_TIME AS OF o.proctime AS dim
ON order.product_id = dim.product_id;万事俱备只欠东风
在 Flink 1.11 之前,Flink 对接 Hive 会做些批处理的计算,并且只支持离线的场景。离线的场景一个问题是延迟比较大,批作业的调度一般都会通过一些调度的框架去调度。这样其实延迟会有累加的作用。例如第一个 job 跑完,才能去跑第二个 job...这样依次执行。所以端对端的延迟就是所有 job 的叠加。
然而随着Flink在1.12中对Hive的友好支持情况变得不一样了。在 Flink中文网上,社区分享了阿里巴巴之信和天离两位同学关于建设 Flink 批流一体的实时数仓应用:
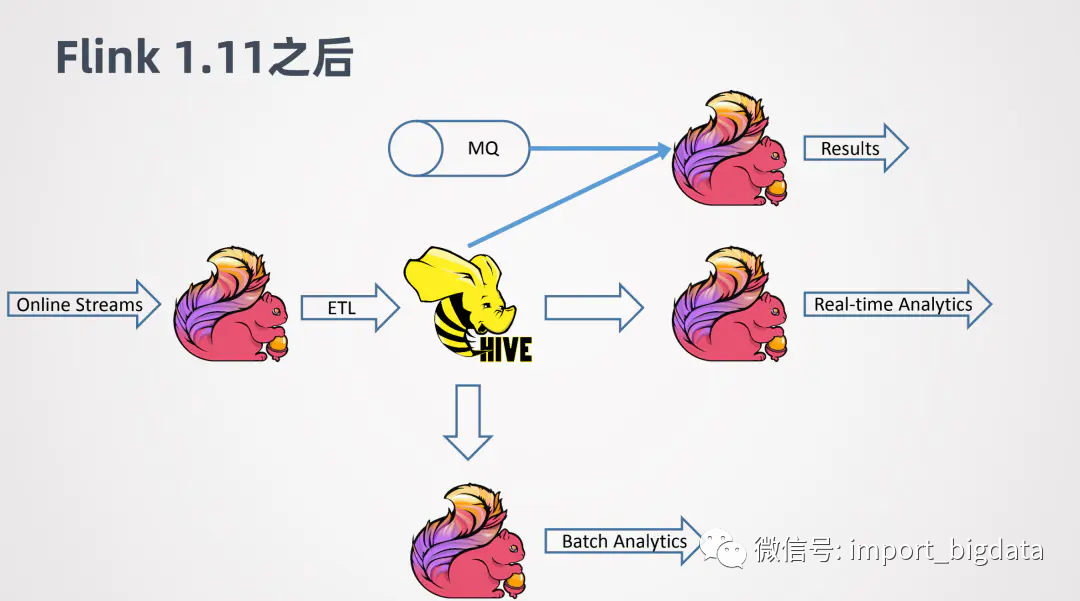
例如 Online 的一些数据,可以用 Flink 做 ETL,去实时的写入 Hive。当数据写入 Hive之后,可以进一步接一个新的 Flink job,来做实时的查询或者近似实时的查询,可以很快的返回结果。同时,其他的 Flink job 还可以利用写入 Hive 数仓的数据作为维表,来跟其它线上的数据进行关联整合,来得到分析的结果。
此时我们的典型的架构就变成了:
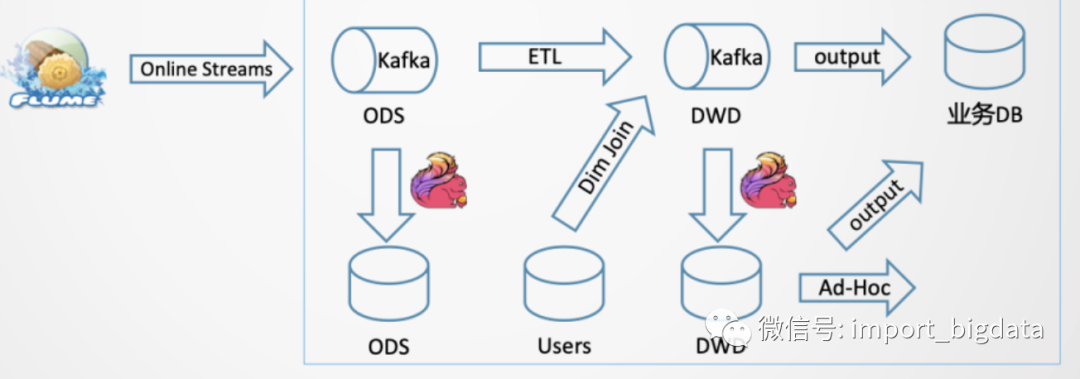
一个典型的Demo实现如下:
#### 初始化环境
val streamEnv = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
streamEnv.setStreamTimeCharacteristic(TimeCharacteristic.EventTime)
streamEnv.setParallelism(3)
val tableEnvSettings = EnvironmentSettings.newInstance()
.useBlinkPlanner()
.inStreamingMode()
.build()
val tableEnv = StreamTableEnvironment.create(streamEnv, tableEnvSettings)
tableEnv.getConfig.getConfiguration.set(ExecutionCheckpointingOptions.CHECKPOINTING_MODE, CheckpointingMode.EXACTLY_ONCE)
tableEnv.getConfig.getConfiguration.set(ExecutionCheckpointingOptions.CHECKPOINTING_INTERVAL, Duration.ofSeconds(20))
#### 连接Hive
val name = "myhive";
val defaultDatabase = "mydatabase";
val hiveConfDir = "/opt/hive-conf";
val catalog = new HiveCatalog(name, defaultDatabase, hiveConfDir);
tableEnv.registerCatalog("myhive", hive);
tableEnv.useCatalog(catalogName);
#### 读写hive
tableEnv.executeSql("CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS kafka_stream")
tableEnv.executeSql("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS kafka_stream.kafka_source_topic")
tableEnv.executeSql(
"""
|CREATE TABLE kafka_stream.kafka_source_topic (
| ts BIGINT,
| userId BIGINT,
| username STRING,
| gender STRING,
| procTime AS PROCTIME(),
| eventTime AS TO_TIMESTAMP(FROM_UNIXTIME(ts / 1000,'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss')),
| WATERMARK FOR eventTime AS eventTime - INTERVAL '15' SECOND
|) WITH (
| 'connector' = 'kafka',
| 'topic' = 'kafka_source_topic',
| 'properties.bootstrap.servers' = 'localhost:9092'
| 'properties.group.id' = 'flink_hive',
| 'scan.startup.mode' = 'latest-offset',
| 'format' = 'json',
| 'json.fail-on-missing-field' = 'false',
| 'json.ignore-parse-errors' = 'true'
|)
""".stripMargin
)
####其他操作如Hive建表、消费源数据写入Kafka分区等关于Flink读写Hive的详细实现,小编会单独开文章进行详细介绍。

