目标检测新范式!港大同济伯克利提出Sparse R-CNN,代码已开源
新智元报道
新智元报道
来源:知乎
作者:孙培泽
【新智元导读】Sparse R-CNN建立了一种彻底的Sparse框架, 脱离anchor box,reference point,Region Proposal Network(RPN)等概念,无需Non-Maximum Suppression(NMS)后处理。
本文主要介绍一下我们最近的一篇工作:
Sparse R-CNN: End-to-End Object Detection with Learnable Proposals

沿着目标检测领域中Dense和Dense-to-Sparse的框架,Sparse R-CNN建立了一种彻底的Sparse框架, 脱离anchor box,reference point,Region Proposal Network(RPN)等概念,无需Non-Maximum Suppression(NMS)后处理, 在标准的COCO benchmark上使用ResNet-50 FPN单模型在标准3x training schedule达到了44.5 AP和 22 FPS。
Motivation
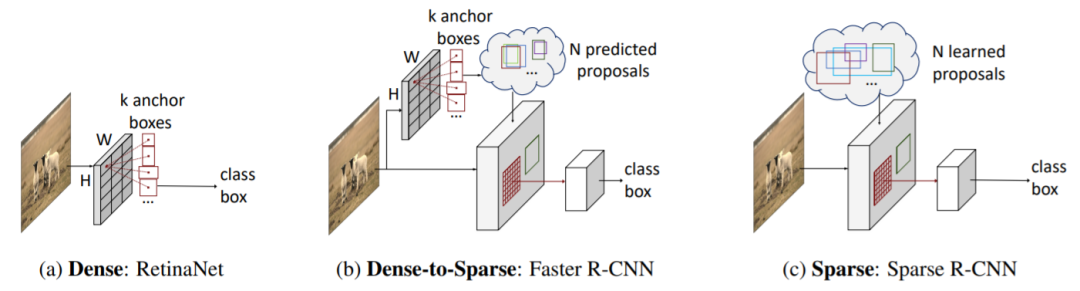
我们先简单回顾一下目标检测领域中主流的两大类方法。
第一大类是从非Deep时代就被广泛应用的dense detector,例如DPM,YOLO,RetinaNet,FCOS。在dense detector中,大量的object candidates例如sliding-windows,anchor-boxes, reference-points等被提前预设在图像网格或者特征图网格上,然后直接预测这些candidates到gt的scaling/offest和物体类别。
第二大类是dense-to-sparse detector,例如R-CNN家族。这类方法的特点是对一组sparse的candidates预测回归和分类,而这组sparse的candidates来自于dense detector。
这两类框架推动了整个领域的学术研究和工业应用。目标检测领域看似已经饱和,然而dense属性的一些固有局限总让人难以满意:
NMS 后处理
many-to-one 正负样本分配
prior candidates的设计
所以,一个很自然的思考方向就是:能不能设计一种彻底的sparse框架?最近,DETR给出了一种sparse的设计方案。
candidates是一组sparse的learnable object queries,正负样本分配是one-to-one的optimal bipartite matching,无需nms直接输出最终的检测结果。
然而,DETR中每个object query都和全局的特征图做attention交互,这本质上也是dense。
而我们认为,sparse的检测框架应该体现在两个方面:sparse candidates和sparse feature interaction。基于此,我们提出了Sparse R-CNN。
Sparse R-CNN抛弃了anchor boxes或者reference point等dense概念,直接从a sparse set of learnable proposals出发,没有NMS后处理,整个网络异常干净和简洁,可以看做是一个全新的检测范式。
Sparse R-CNN
Sparse R-CNN的object candidates是一组可学习的参数,N*4,N代表object candidates的个数,一般为100~300,4代表物体框的四个边界。
这组参数和整个网络中的其他参数一起被训练优化。That's it,完全没有dense detector中成千上万的枚举。
这组sparse的object candidates作为proposal boxes用以提取Region of Interest(RoI),预测回归和分类。
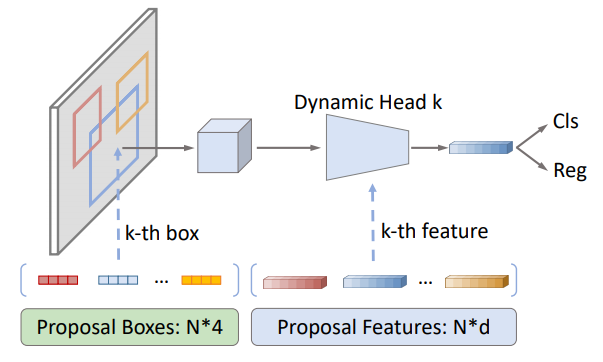
这组学习到的proposal boxes可以理解为图像中可能出现物体的位置的统计值,这样coarse的表征提取出来的RoI feature显然不足以精确定位和分类物体。
于是,我们引入一种特征层面的candidates,proposal features,这也是一组可学习的参数,N*d,N代表object candidates的个数,与proposal boxes一一对应,d代表feature的维度,一般为256。
这组proposal features与proposal boxes提取出来的RoI feature做一对一的交互,从而使得RoI feature的特征更有利于定位和分类物体。
相比于原始的2-fc Head,我们的设计称为Dynamic Instance Interactive Head.
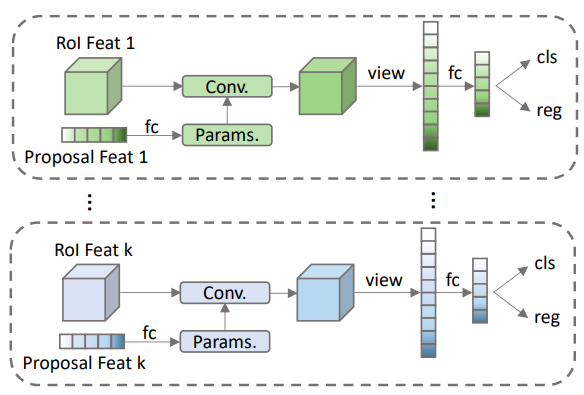
Sparse R-CNN的两个显著特点就是sparse object candidates和sparse feature interaction,既没有dense的成千上万的candidates,也没有dense的global feature interaction。
Sparse R-CNN可以看作是目标检测框架从dense到dense-to-sparse到sparse的一个方向拓展。
Architecture Design
Sparse R-CNN的网络设计原型是R-CNN家族。
Backbone是基于ResNet的FPN。
Head是一组iterative的Dynamic Instance Interactive Head,上一个head的output features和output boxes作为下一个head的proposal features和proposal boxes。Proposal features在与RoI features交互之前做self-attention。
训练的损失函数是基于optimal bipartite matching的set prediction loss。
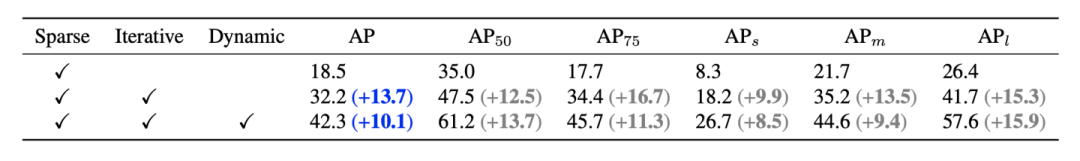
从Faster R-CNN(40.2 AP)出发,直接将RPN替换为a sparse set of learnable proposal boxes,AP降到18.5;引入iterative结构提升AP到32.2;引入dynamic instance interaction最终提升到42.3 AP。
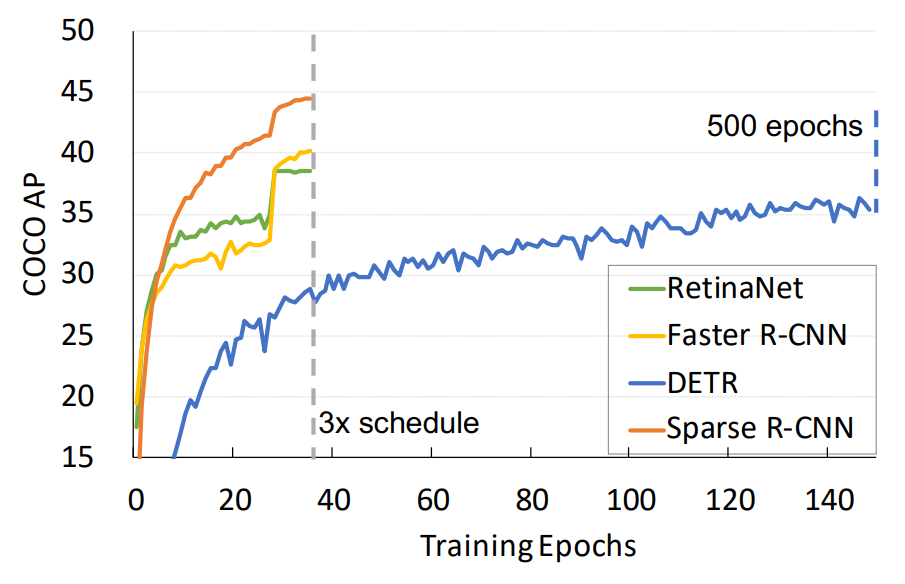
Performance
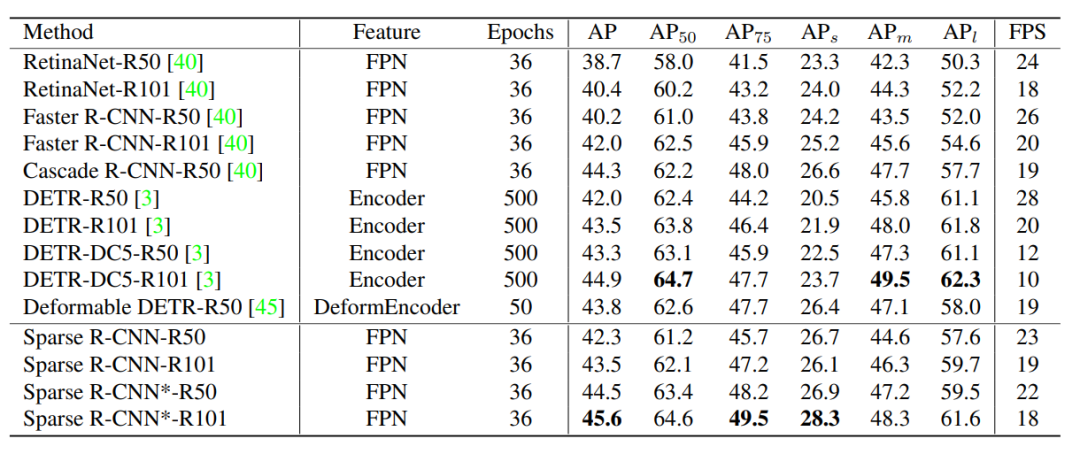
我们沿用了Detectron2的3x training schedule,因此将Sparse R-CNN和Detectorn2中的detectors做比较(很多方法没有报道3x的性能,所以没有列出)。
同时,我们也列出了同样不需要NMS后处理的DETR和Deformable DETR的性能。Sparse R-CNN在检测精度,推理时间和训练收敛速度都展现了相当有竞争力的性能。
Conclusion
R-CNN和Fast R-CNN出现后的一段时期内,目标检测领域的一个重要研究方向是提出更高效的region proposal generator。
Faster R-CNN和RPN作为其中的佼佼者展现出广泛而持续的影响力。
Sparse R-CNN首次展示了简单的一组可学习的参数作为proposal boxes即可达到comparable的性能。
我们希望我们的工作能够带给大家一些关于end-to-end object detection的启发。
代码: https://github.com/PeizeSun/SparseR-CNN
论文链接:
https://msc.berkeley.edu/research/autonomous-vehicle/sparse_rcnn.pdf


