【Plotly快速入门】用Plotly绘制了几张精湛的图表,美翻了!!
说到
Python当中的可视化模块,相信大家用的比较多的还是matplotlib、seaborn等模块,今天小编来尝试用Plotly模块为大家绘制可视化图表,和前两者相比,用Plotly模块会指出来的可视化图表有着很强的交互性。
柱状图
我们先导入后面需要用到的模块并且生成一批假数据,
import numpy as np
import plotly.graph_objects as go
# create dummy data
vals = np.ceil(100 * np.random.rand(5)).astype(int)
keys = ["A", "B", "C", "D", "E"]
我们基于所生成的假数据来绘制柱状图,代码如下
fig = go.Figure()
fig.add_trace(
go.Bar(x=keys, y=vals)
)
fig.update_layout(height=600, width=600)
fig.show()
output
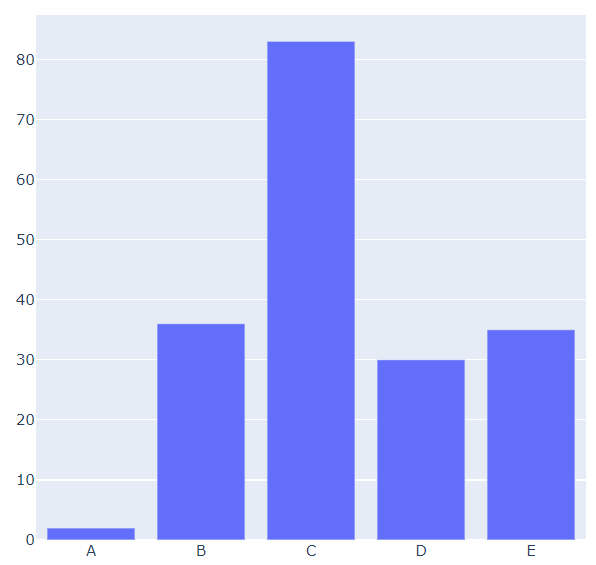
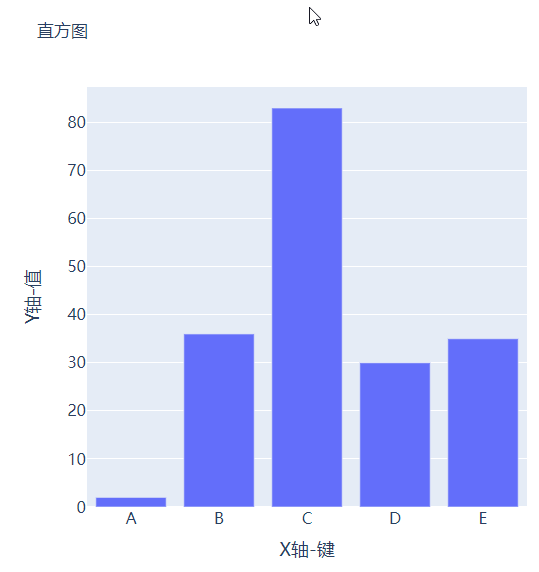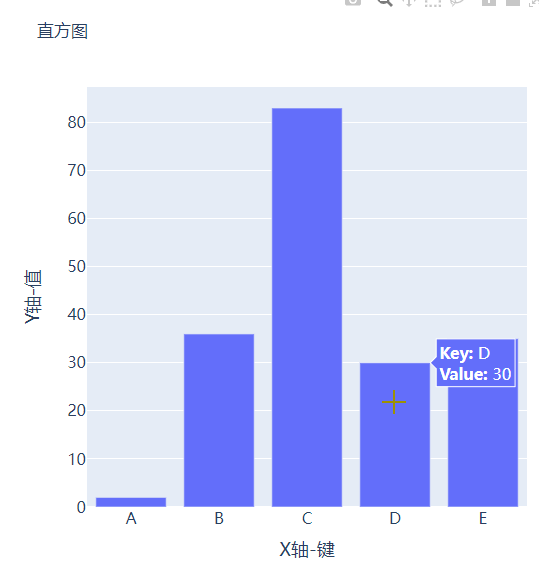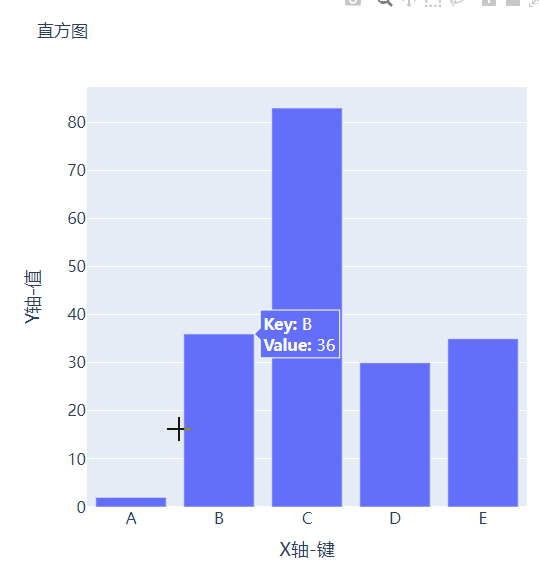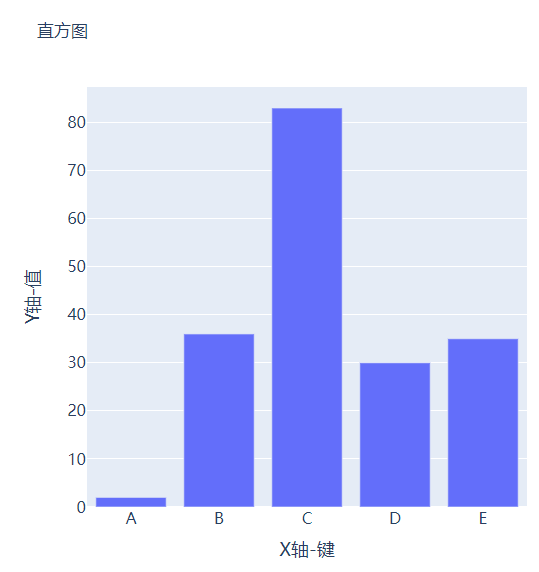
可能读者会感觉到绘制出来的图表略显简单,我们再来完善一下,添加上标题和注解,代码如下
# create figure
fig = go.Figure()
# 绘制图表
fig.add_trace(
go.Bar(x=keys, y=vals, hovertemplate="<b>Key:</b> %{x}<br><b>Value:</b> %{y}<extra></extra>")
)
# 更新完善图表
fig.update_layout(
font_family="Averta",
hoverlabel_font_family="Averta",
title_text="直方图",
xaxis_title_text="X轴-键",
xaxis_title_font_size=18,
xaxis_tickfont_size=16,
yaxis_title_text="Y轴-值",
yaxis_title_font_size=18,
yaxis_tickfont_size=16,
hoverlabel_font_size=16,
height=600,
width=600
)
fig.show()
output
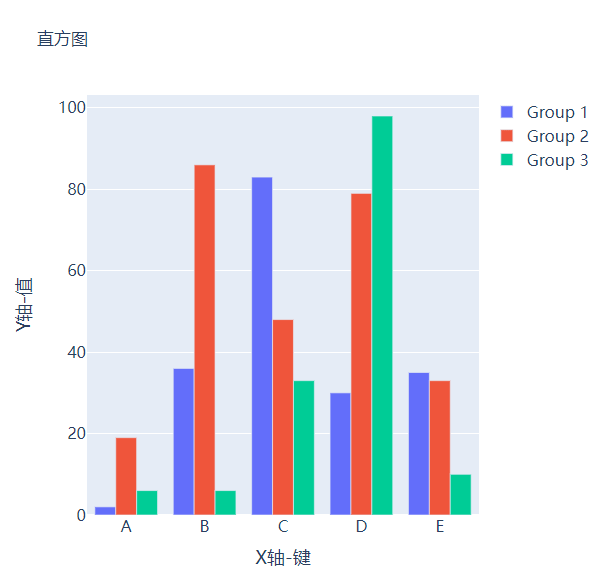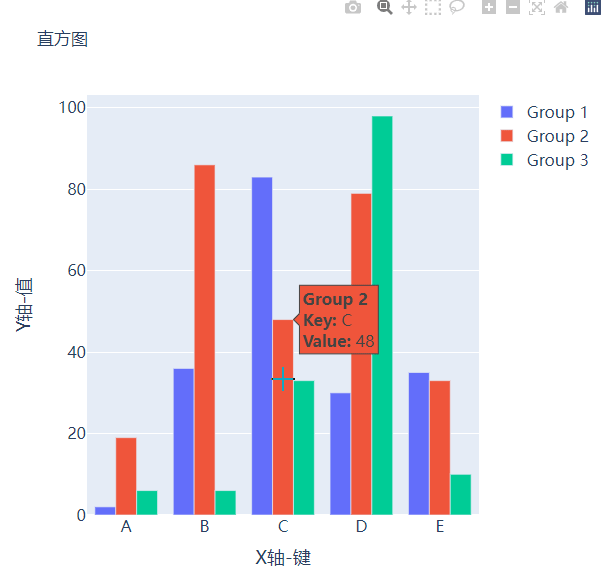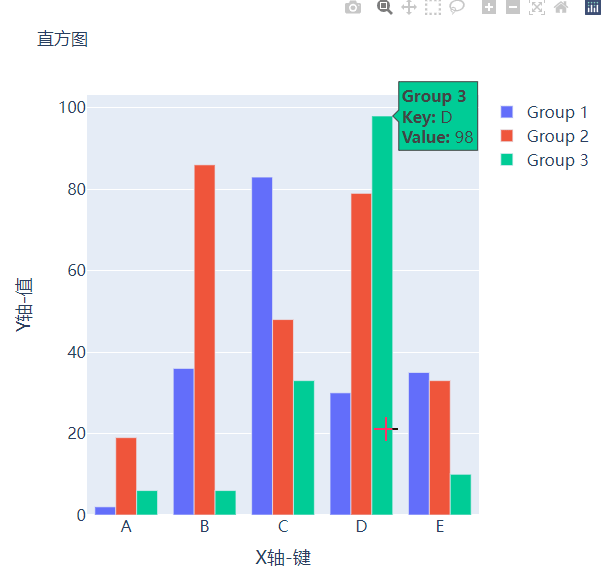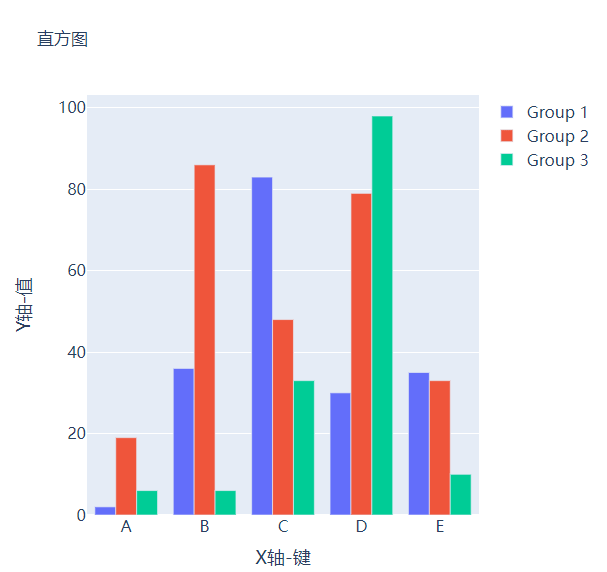
分组条形图和堆积条形图
例如我们有多组数据想要绘制成柱状图的话,我们先来创建好数据集
vals_2 = np.ceil(100 * np.random.rand(5)).astype(int)
vals_3 = np.ceil(100 * np.random.rand(5)).astype(int)
vals_array = [vals, vals_2, vals_3]
然后我们遍历获取列表中的数值并且绘制成条形图,代码如下
# 生成画布
fig = go.Figure()
# 绘制图表
for i, vals in enumerate(vals_array):
fig.add_trace(
go.Bar(x=keys, y=vals, name=f"Group {i+1}", hovertemplate=f"<b>Group {i+1}</b><br><b>Key:</b> %{{x}}<br><b>Value:</b> %{{y}}<extra></extra>")
)
# 完善图表
fig.update_layout(
barmode="group",
......
)
fig.show()
output
而我们想要变成堆积状的条形图,只需要修改代码中的一处即可,将
fig.update_layout(barmode="group")修改成fig.update_layout(barmode="group")即可,我们来看一下出来的样子
箱型图
箱型图在数据统计分析当中也是应用相当广泛的,我们先来创建两个假数据
# create dummy data for boxplots
y1 = np.random.normal(size=1000)
y2 = np.random.normal(size=1000)
我们将上面生成的数据绘制成箱型图,代码如下
# 生成画布
fig = go.Figure()
# 绘制图表
fig.add_trace(
go.Box(y=y1, name="Dataset 1"),
)
fig.add_trace(
go.Box(y=y2, name="Dataset 2"),
)
fig.update_layout(
......
)
fig.show()
output
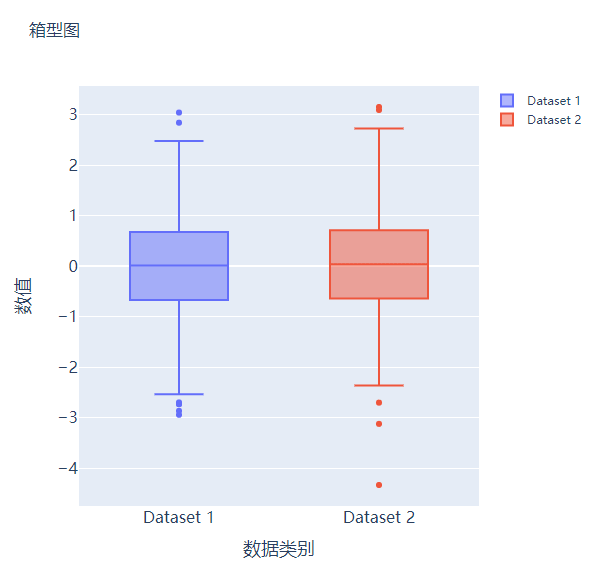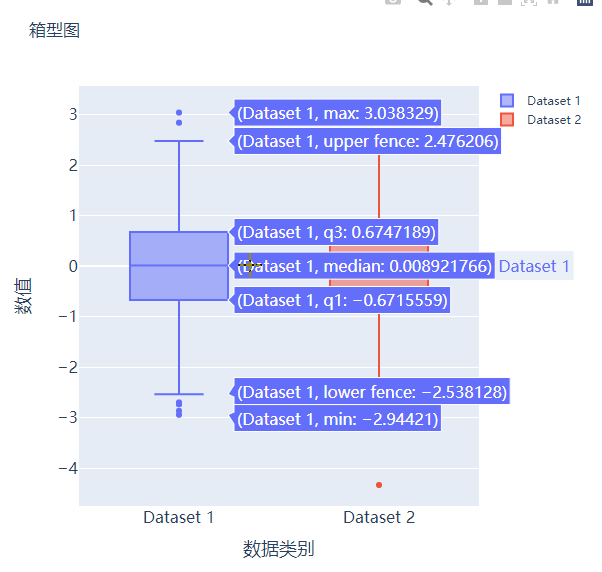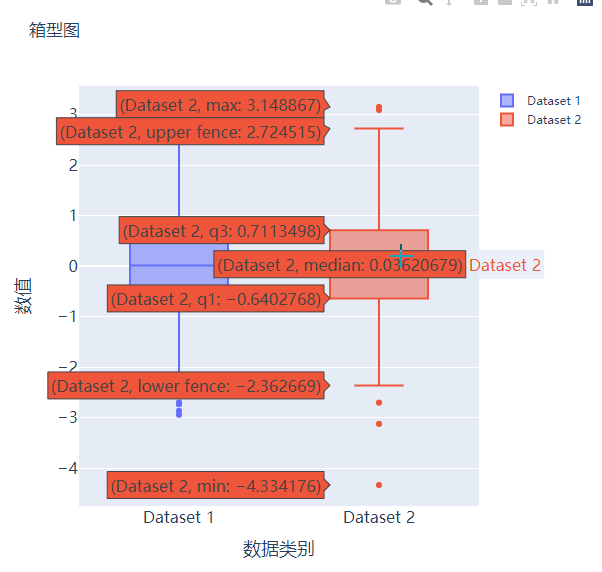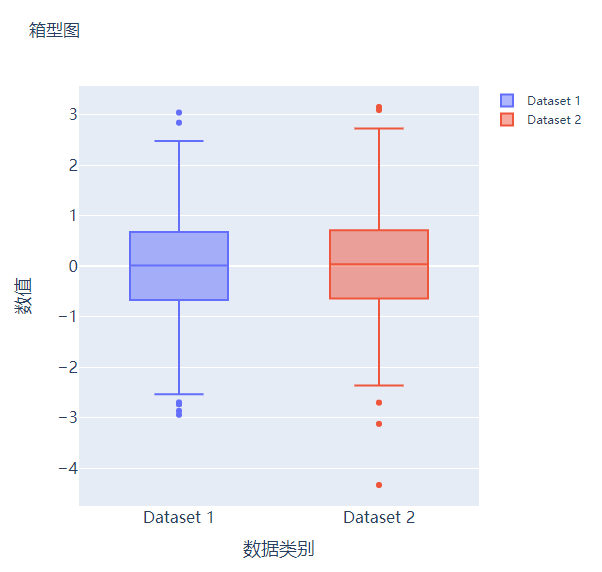
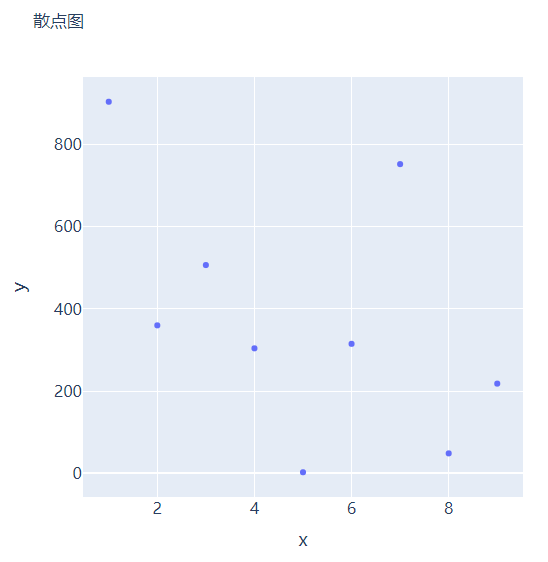
散点图和气泡图
接下来我们尝试来绘制一张散点图,也是一样的步骤,我们想尝试生成一些假数据,代码如下
x = [i for i in range(1, 10)]
y = np.ceil(1000 * np.random.rand(10)).astype(int)
然后我们来绘制散点图,调用的是Scatter()方法,代码如下
# create figure
fig = go.Figure()
fig.add_trace(
go.Scatter(x=x, y=y, mode="markers", hovertemplate="<b>x:</b> %{x}<br><b>y:</b> %{y}<extra></extra>")
)
fig.update_layout(
.......
)
fig.show()
output
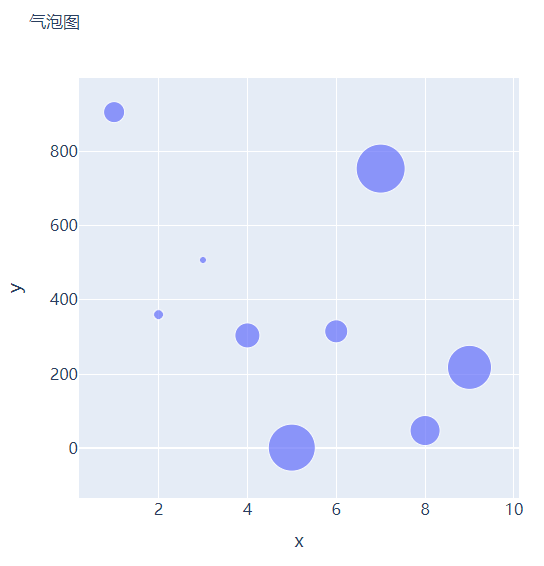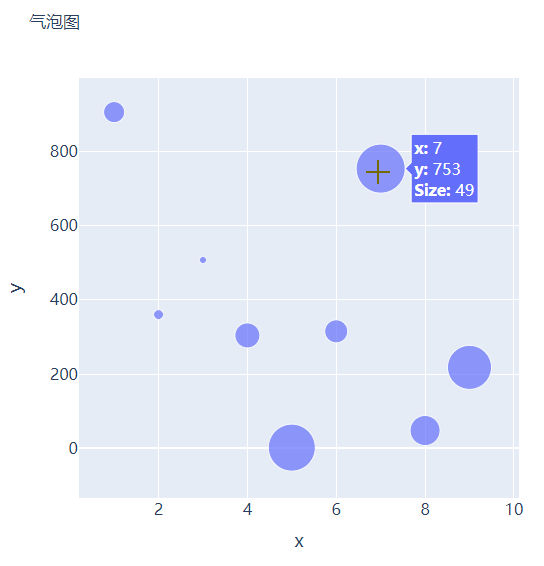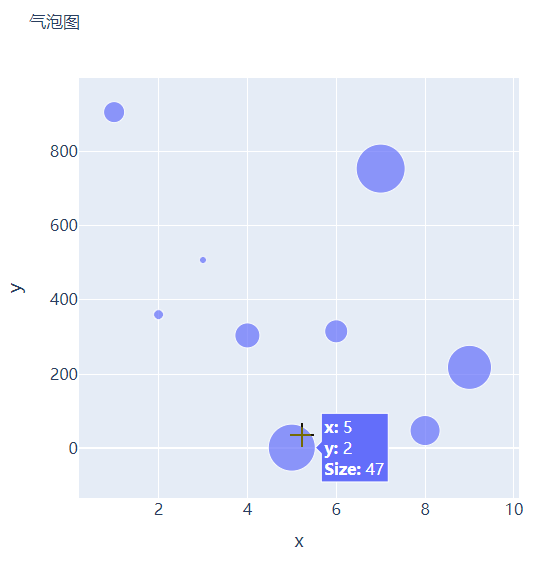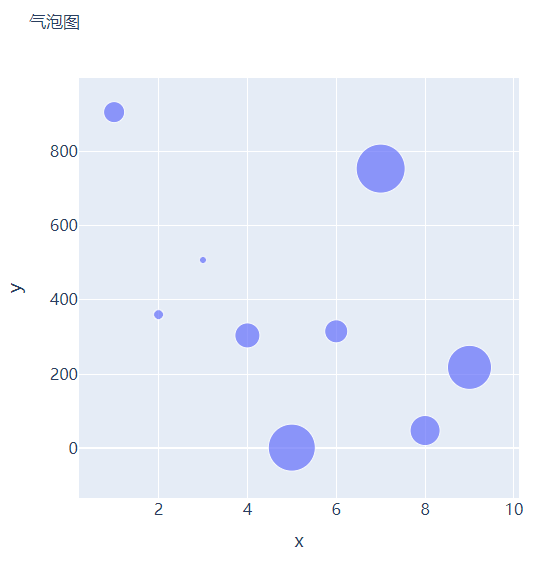
那么气泡图的话就是在散点图的基础上,根据数值的大小来设定散点的大小,我们再来创建一些假数据用来设定散点的大小,代码如下
s = np.ceil(30 * np.random.rand(5)).astype(int)
我们将上面用作绘制散点图的代码稍作修改,通过marker_size参数来设定散点的大小,如下所示
fig = go.Figure()
fig.add_trace(
go.Scatter(x=x, y=y, mode="markers", marker_size=s, text=s, hovertemplate="<b>x:</b> %{x}<br><b>y:</b> %{y}<br><b>Size:</b> %{text}<extra></extra>")
)
fig.update_layout(
......
)
fig.show()
output
直方图
直方图相比较于上面提到的几种图表,总体上来说会稍微有点丑,但是通过直方图,读者可以更加直观地感受到数据的分布,我们先来创建一组假数据,代码如下
## 创建假数据
data = np.random.normal(size=1000)
然后我们来绘制直方图,调用的是Histogram()方法,代码如下
# 创建画布
fig = go.Figure()
# 绘制图表
fig.add_trace(
go.Histogram(x=data, hovertemplate="<b>Bin Edges:</b> %{x}<br><b>Count:</b> %{y}<extra></extra>")
)
fig.update_layout(
height=600,
width=600
)
fig.show()
output
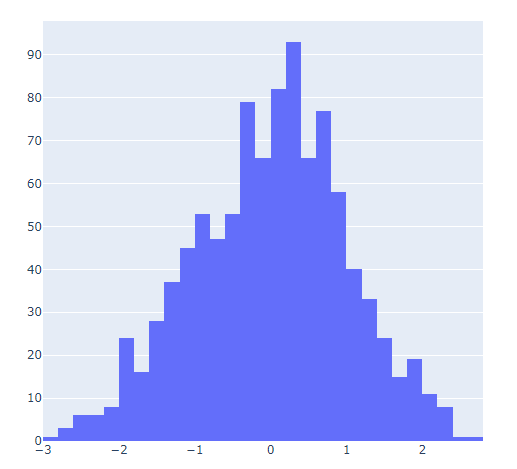
我们再在上述图表的基础之上再进行进一步的格式优化,代码如下
# 生成画布
fig = go.Figure()
# 绘制图表
fig.add_trace(
go.Histogram(x=data, histnorm="probability", hovertemplate="<b>Bin Edges:</b> %{x}<br><b>Count:</b> %{y}<extra></extra>")
)
fig.update_layout(
......
)
fig.show()
output
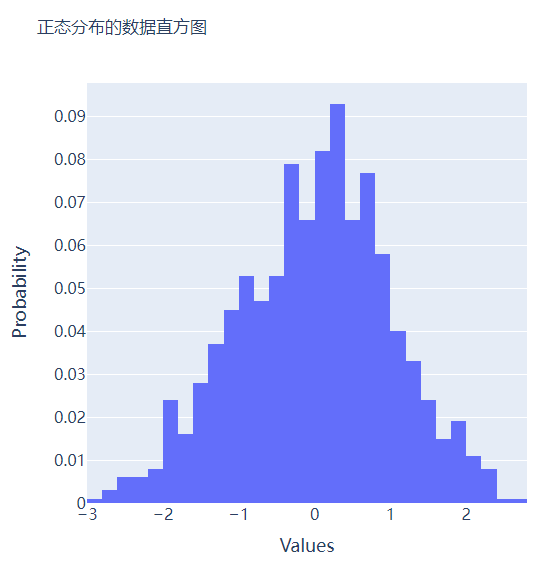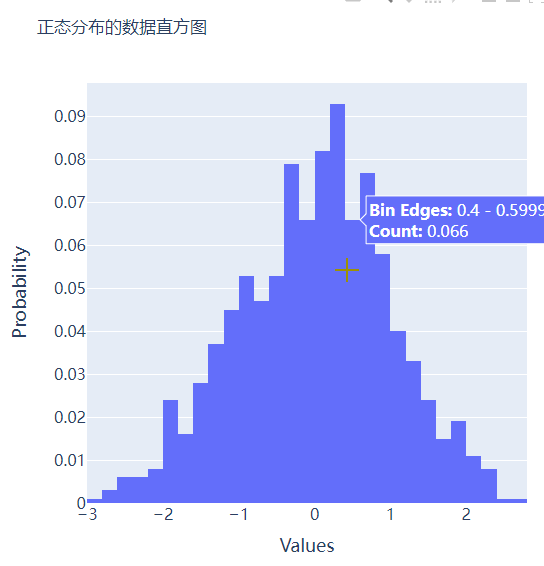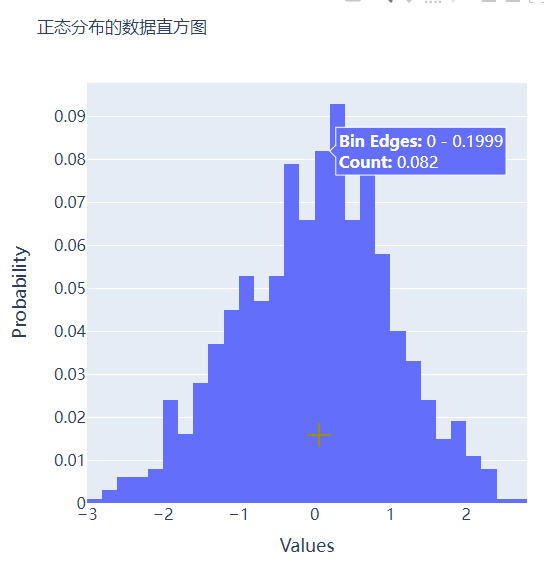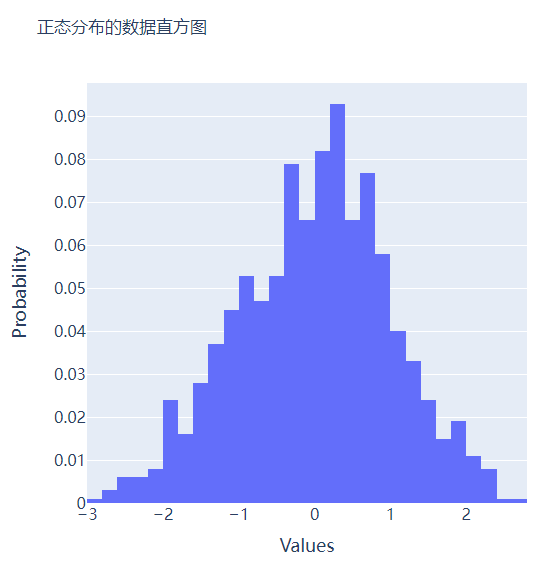
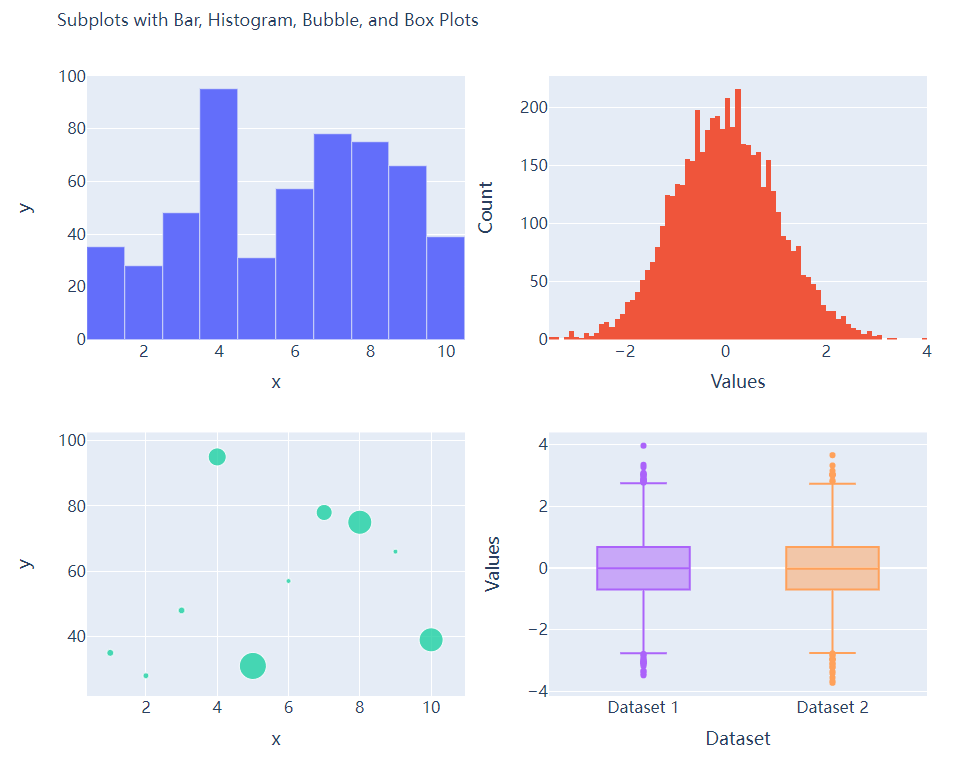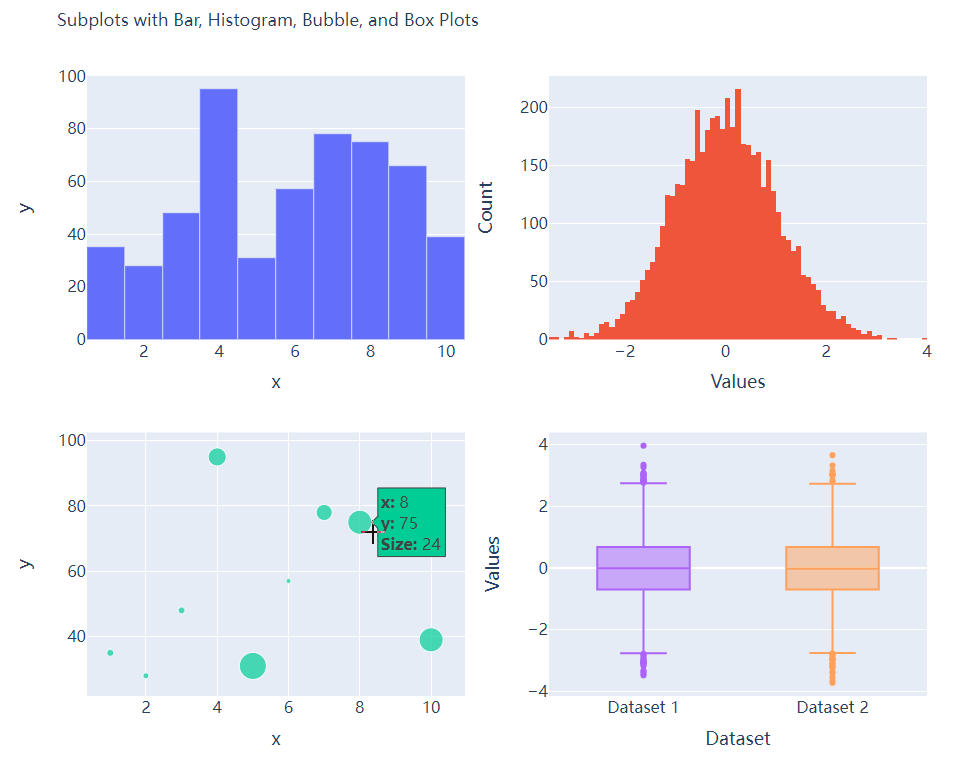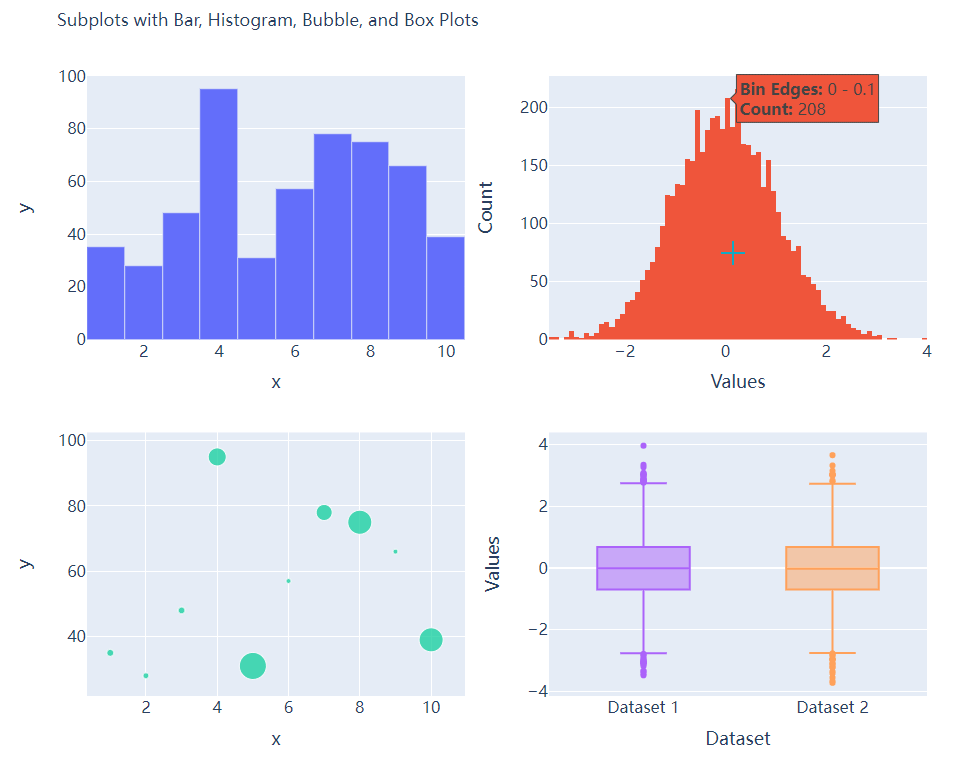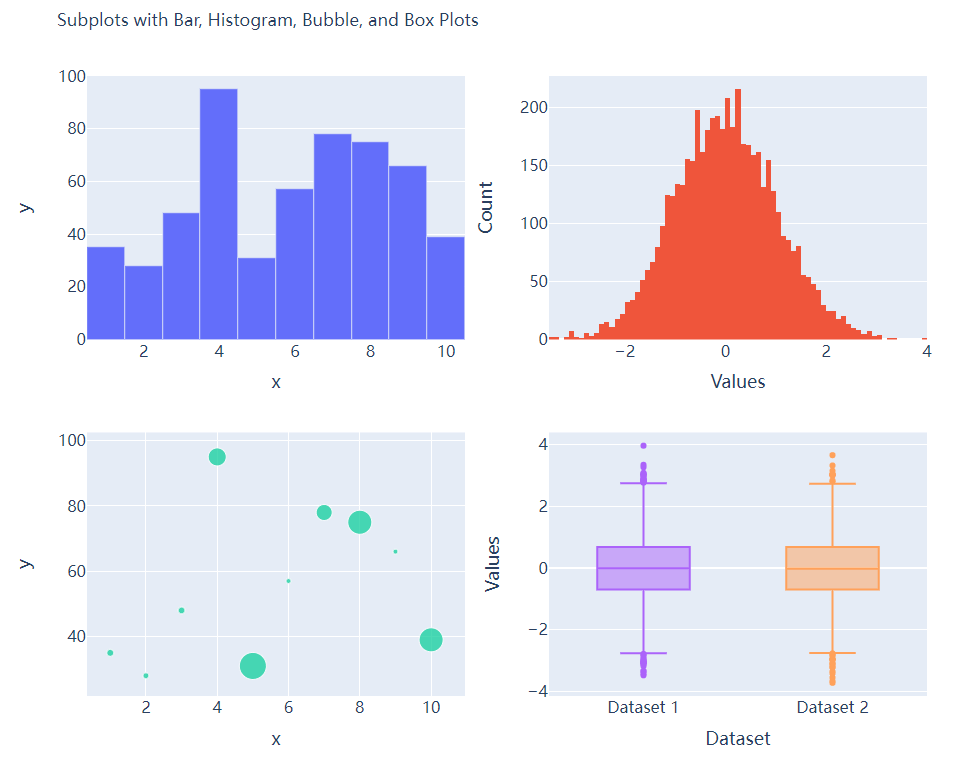
多个子图拼凑到一块儿
相信大家都知道在
matplotlib模块当中的subplots()方法可以将多个子图拼凑到一块儿,那么同样地在plotly当中也可以同样地将多个子图拼凑到一块儿,调用的是plotly模块当中make_subplots函数from plotly.subplots import make_subplots
## 2行2列的图表
fig = make_subplots(rows=2, cols=2)
## 生成一批假数据用于图表的绘制
x = [i for i in range(1, 11)]
y = np.ceil(100 * np.random.rand(10)).astype(int)
s = np.ceil(30 * np.random.rand(10)).astype(int)
y1 = np.random.normal(size=5000)
y2 = np.random.normal(size=5000)
接下来我们将所要绘制的图表添加到add_trace()方法当中,代码如下
# 绘制图表
fig.add_trace(
go.Bar(x=x, y=y, hovertemplate="<b>x:</b> %{x}<br><b>y:</b> %{y}<extra></extra>"),
row=1, col=1
)
fig.add_trace(
go.Histogram(x=y1, hovertemplate="<b>Bin Edges:</b> %{x}<br><b>Count:</b> %{y}<extra></extra>"),
row=1, col=2
)
fig.add_trace(
go.Scatter(x=x, y=y, mode="markers", marker_size=s, text=s, hovertemplate="<b>x:</b> %{x}<br><b>y:</b> %{y}<br><b>Size:</b> %{text}<extra></extra>"),
row=2, col=1
)
fig.add_trace(
go.Box(y=y1, name="Dataset 1"),
row=2, col=2
)
fig.add_trace(
go.Box(y=y2, name="Dataset 2"),
row=2, col=2
)
fig.update_xaxes(title_font_size=18, tickfont_size=16)
fig.update_yaxes(title_font_size=18, tickfont_size=16)
fig.update_layout(
......
)
fig.show()
output
END
推荐阅读
牛逼!Python的判断、循环和各种表达式(长文系列第②篇)
吴恩达deeplearining.ai的经典总结资料
Ps:从小程序直接获取下载
