一个小改动,CNN输入固定尺寸图像改为任意尺寸图像
点击上方“小白学视觉”,选择加"星标"或“置顶”
重磅干货,第一时间送达
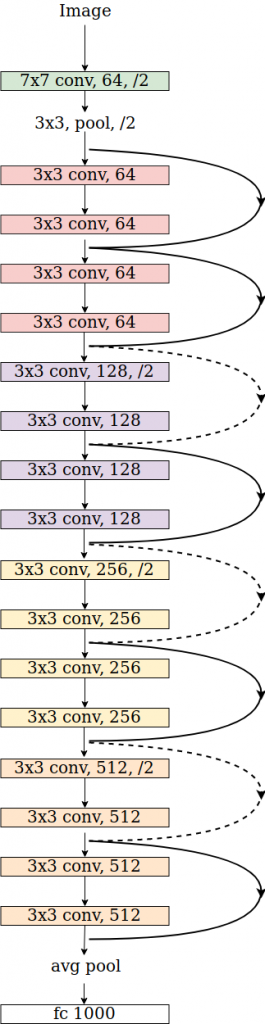
# from the torchvision's implementation of ResNetclass ResNet:# ...self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, self.inplanes, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3,bias=False)self.bn1 = norm_layer(self.inplanes)self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, layers[0])self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, layers[1], stride=2, dilate = replace_stride_with_dilation[0])self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, layers[2], stride=2, dilate = replace_stride_with_dilation[1])self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 512, layers[3], stride=2, dilate = replace_stride_with_dilation[2])self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))self.fc = nn.Linear(512 * block.expansion, num_classes)# ...def _forward_impl(self, x):# See note [TorchScript super()]x = self.conv1(x)x = self.bn1(x)x = self.relu(x)x = self.maxpool(x)x = self.layer1(x)x = self.layer2(x)x = self.layer3(x)x = self.layer4(x)x = self.avgpool(x)x = torch.flatten(x, 1)x = self.fc(x)return x
class FullyConvolutionalResnet18(models.ResNet):def __init__(self, num_classes=1000, pretrained=False, **kwargs):# Start with standard resnet18 defined heresuper().__init__(block = models.resnet.BasicBlock, layers = [2, 2, 2, 2], num_classes = num_classes, **kwargs)if pretrained:state_dict = load_state_dict_from_url( models.resnet.model_urls["resnet18"], progress=True)self.load_state_dict(state_dict)# Replace AdaptiveAvgPool2d with standard AvgPool2dself.avgpool = nn.AvgPool2d((7, 7))# Convert the original fc layer to a convolutional layer.self.last_conv = torch.nn.Conv2d( in_channels = self.fc.in_features, out_channels = num_classes, kernel_size = 1)self.last_conv.weight.data.copy_( self.fc.weight.data.view ( *self.fc.weight.data.shape, 1, 1))self.last_conv.bias.data.copy_ (self.fc.bias.data)# Reimplementing forward pass.def _forward_impl(self, x):# Standard forward for resnet18x = self.conv1(x)x = self.bn1(x)x = self.relu(x)x = self.maxpool(x)x = self.layer1(x)x = self.layer2(x)x = self.layer3(x)x = self.layer4(x)x = self.avgpool(x)# Notice, there is no forward pass# through the original fully connected layer.# Instead, we forward pass through the last conv layerx = self.last_conv(x)return x
#1. 导入标准库import torchimport torch.nn as nnfrom torchvision import modelsfrom torch.hub import load_state_dict_from_urlfrom PIL import Imageimport cv2import numpy as npfrom matplotlib import pyplot as plt#2. 读取ImageNet类ID到名称的映射if __name__ == "__main__":# Read ImageNet class id to name mappingwith open('imagenet_classes.txt') as f:labels = [line.strip() for line in f.readlines()]

# Read imageoriginal_image = cv2.imread('camel.jpg')# Convert original image to RGB formatimage = cv2.cvtColor(original_image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)# Transform input image# 1. Convert to Tensor# 2. Subtract mean# 3. Divide by standard deviationtransform = transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor(), #Convert image to tensor.transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], # Subtract meanstd=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225] # Divide by standard deviation)])image = transform(image)image = image.unsqueeze(0)
# Load modified resnet18 model with pretrained ImageNet weightsmodel = FullyConvolutionalResnet18(pretrained=True).eval()
with torch.no_grad():# Perform inference.# Instead of a 1x1000 vector, we will get a# 1x1000xnxm output ( i.e. a probabibility map# of size n x m for each 1000 class,# where n and m depend on the size of the image.)preds = model(image)preds = torch.softmax(preds, dim=1)print('Response map shape : ', preds.shape)# Find the class with the maximum score in the n x m output mappred, class_idx = torch.max(preds, dim=1)print(class_idx)row_max, row_idx = torch.max(pred, dim=1)col_max, col_idx = torch.max(row_max, dim=1)predicted_class = class_idx[0, row_idx[0, col_idx], col_idx]# Print top predicted classprint('Predicted Class : ', labels[predicted_class], predicted_class)
Response map shape : torch.Size([1, 1000, 3, 8])tensor([[[977, 977, 977, 977, 977, 978, 354, 437],[978, 977, 980, 977, 858, 970, 354, 461],[977, 978, 977, 977, 977, 977, 354, 354]]])Predicted Class : Arabian camel, dromedary, Camelus dromedarius tensor([354])
# Find the n x m score map for the predicted classscore_map = preds[0, predicted_class, :, :].cpu().numpy()score_map = score_map[0]# Resize score map to the original image sizescore_map = cv2.resize(score_map, (original_image.shape[1], original_image.shape[0]))# Binarize score map_, score_map_for_contours = cv2.threshold(score_map, 0.25, 1, type=cv2.THRESH_BINARY)score_map_for_contours = score_map_for_contours.astype(np.uint8).copy()# Find the countour of the binary blobcontours, _ = cv2.findContours(score_map_for_contours, mode=cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, method=cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)# Find bounding box around the object.rect = cv2.boundingRect(contours[0])
# Apply score map as a mask to original imagescore_map = score_map - np.min(score_map[:])score_map = score_map / np.max(score_map[:])接下来,我们将响应图与原始图像相乘并显示边界框。score_map = cv2.cvtColor(score_map, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)masked_image = (original_image * score_map).astype(np.uint8)# Display bounding boxcv2.rectangle(masked_image, rect[:2], (rect[0] + rect[2], rect[1] + rect[3]), (0, 0, 255), 2)# Display imagescv2.imshow("Original Image", original_image)cv2.imshow("scaled_score_map", score_map)cv2.imshow("activations_and_bbox", masked_image)cv2.waitKey(0)

交流群
欢迎加入公众号读者群一起和同行交流,目前有SLAM、三维视觉、传感器、自动驾驶、计算摄影、检测、分割、识别、医学影像、GAN、算法竞赛等微信群(以后会逐渐细分),请扫描下面微信号加群,备注:”昵称+学校/公司+研究方向“,例如:”张三 + 上海交大 + 视觉SLAM“。请按照格式备注,否则不予通过。添加成功后会根据研究方向邀请进入相关微信群。请勿在群内发送广告,否则会请出群,谢谢理解~
评论
