浅谈JsonPath
JsonPath,类似于XPath在XML中的作用。其提供了对Json格式数据的解析能力

操作符
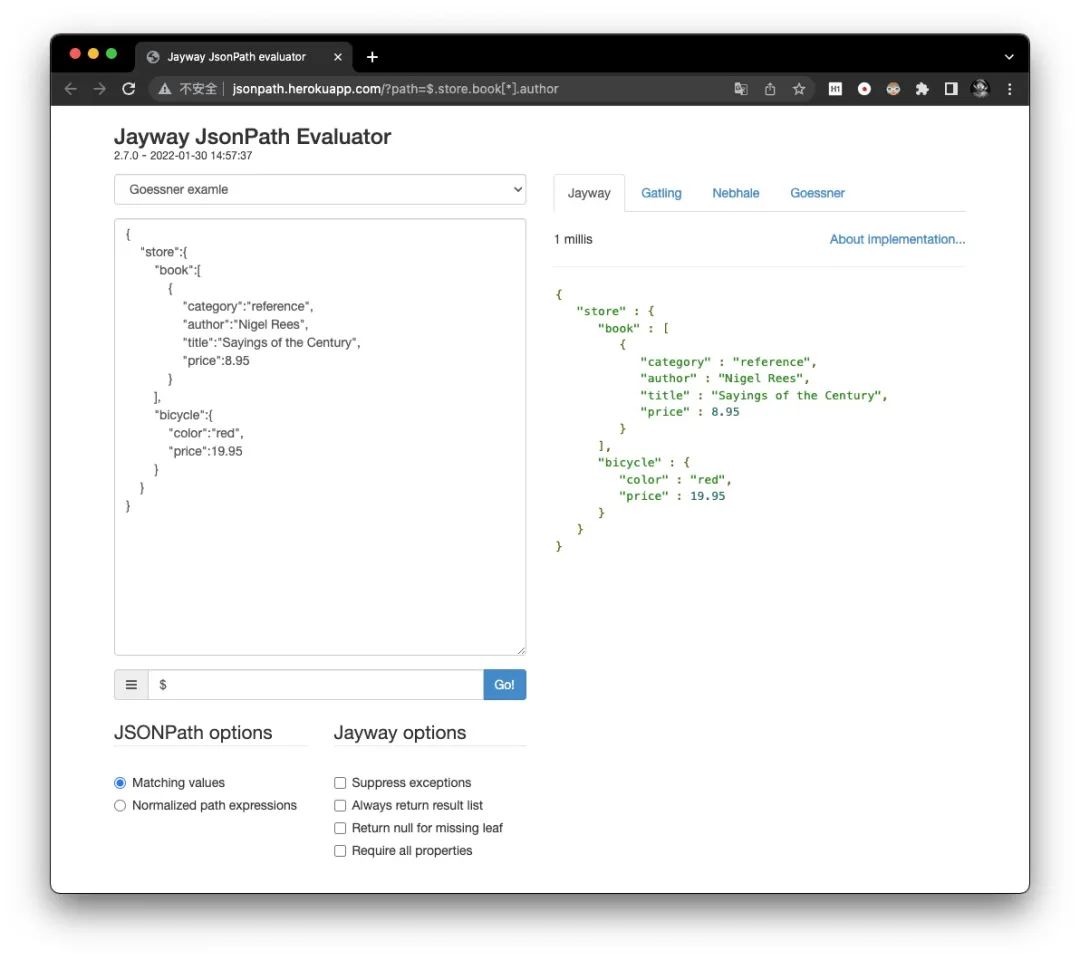
$
查询的根节点,其中根节点可以是数组或对象
.或 ['name']
在JsonPath表达式可以使用点语法、括号语法来访问子节点
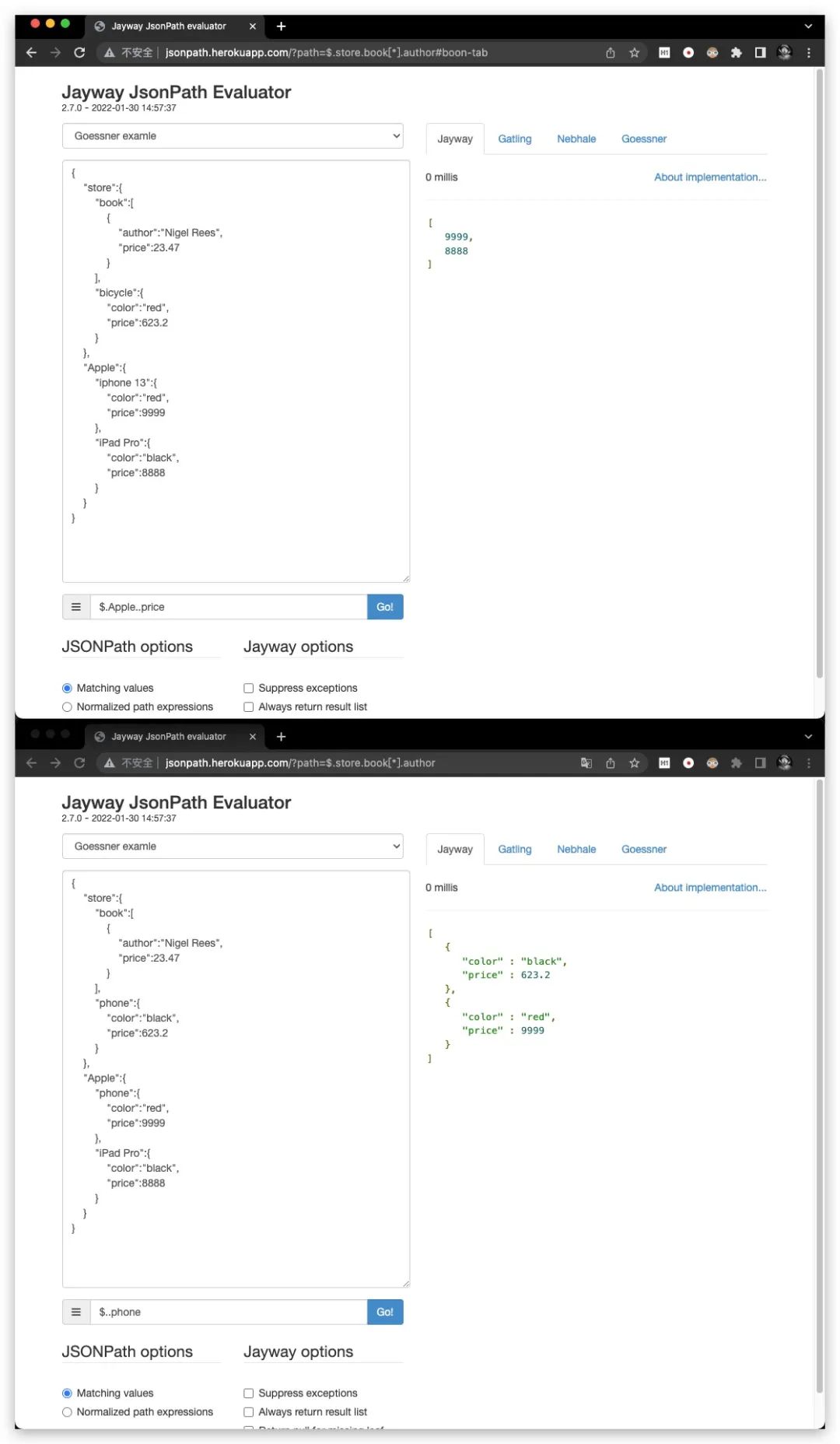
..
可进行递归搜索
['name'(, 'name')]
对于括号语法而言,其还支持访问多个子节点
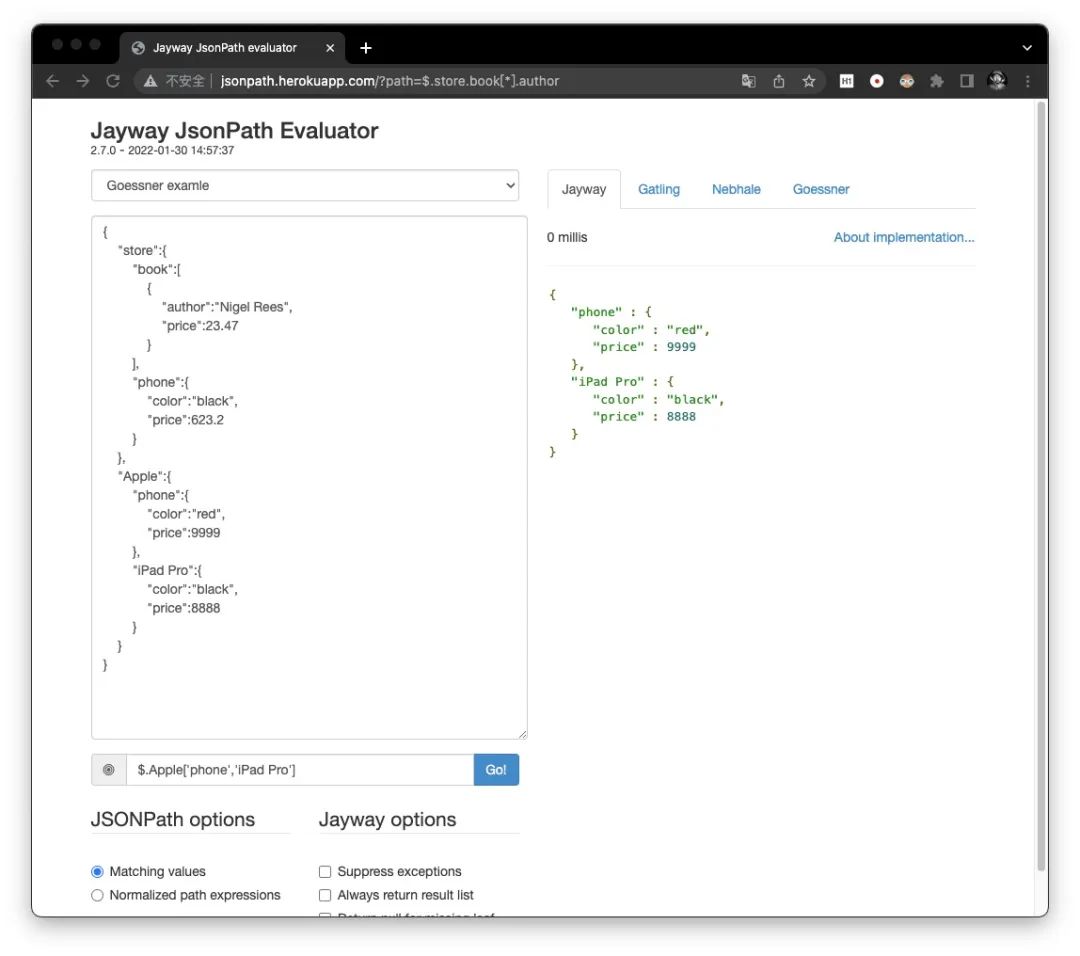
[(,)]
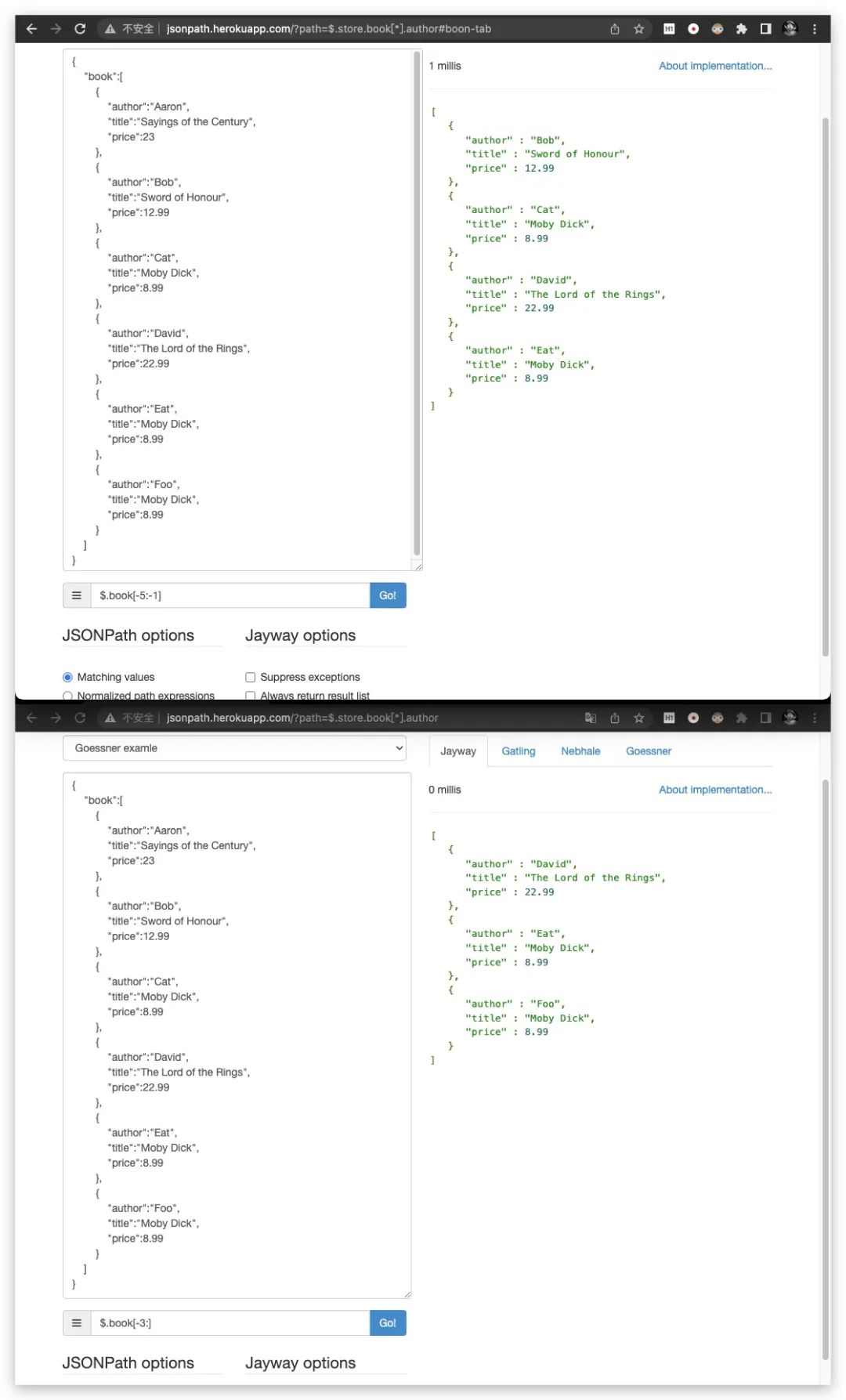
针对数组元素的索引操作符,其中0为起始索引。负数索引表示数组中倒数第几个元素,例如,-1表示倒数第一个元素,-2表示倒数第2个元素
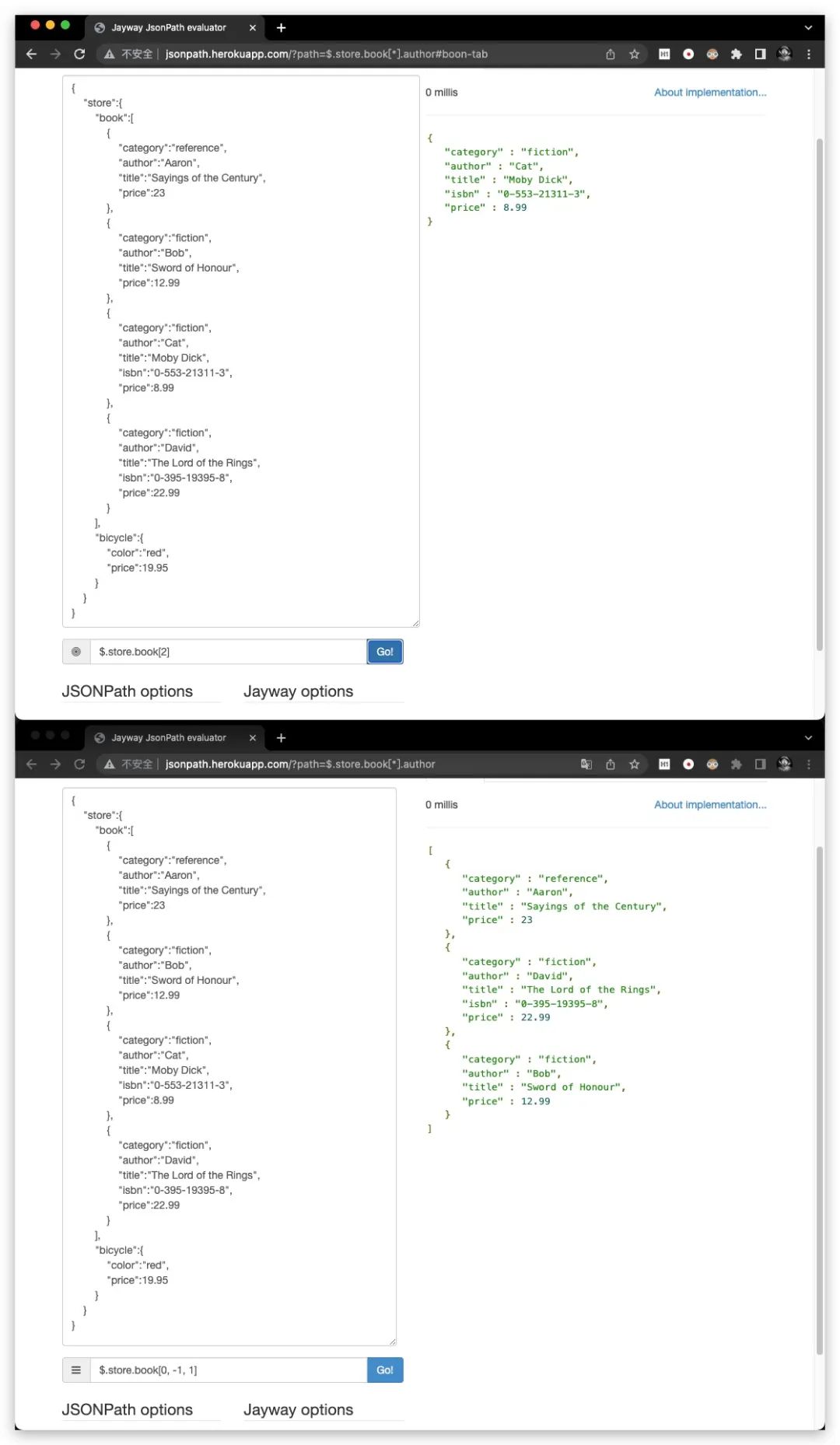
[start:end]
针对数组元素的切片操作符,其表示获取索引在[start,end)区间范围的元素。显然这里是左闭右开区间
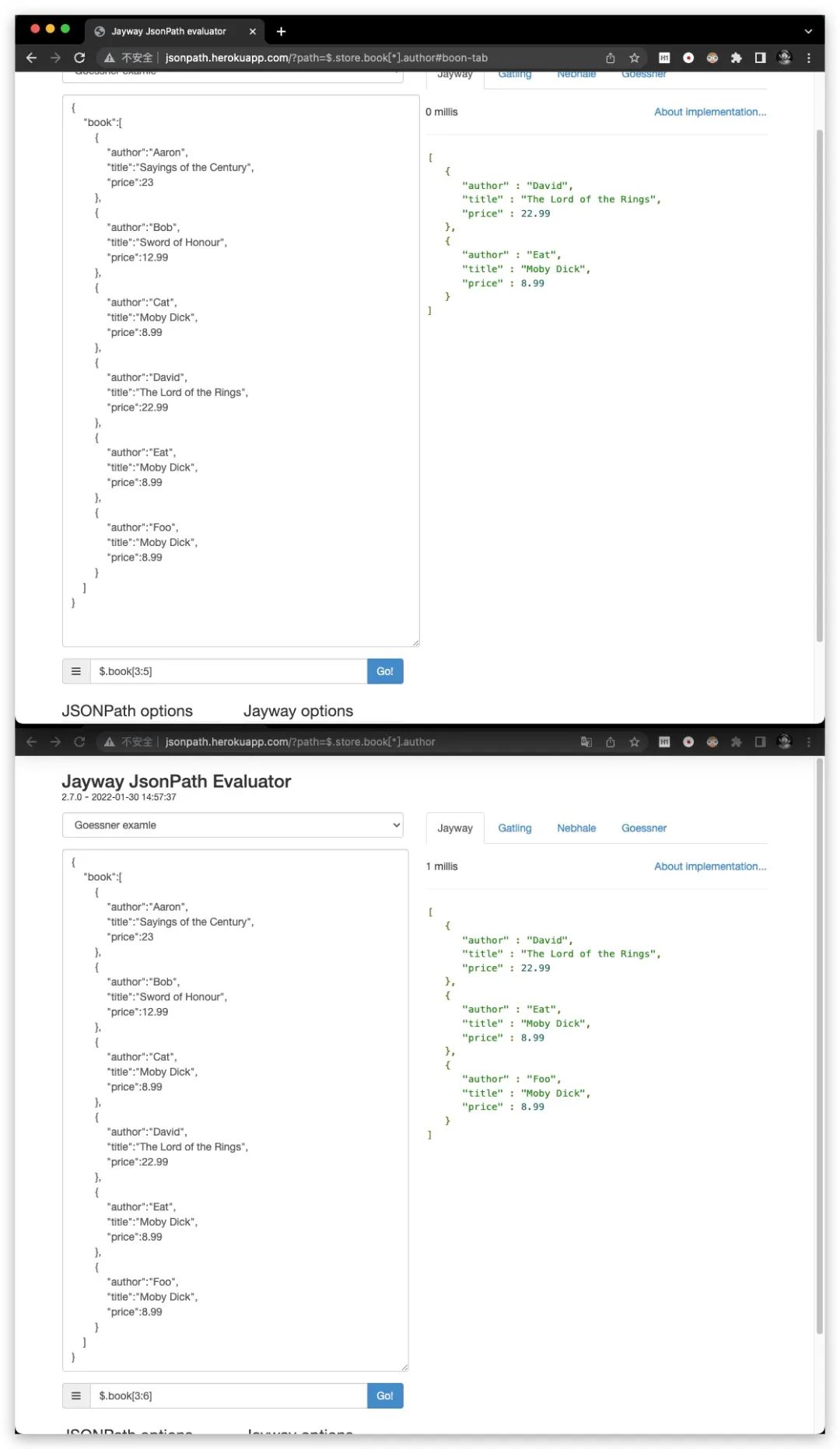
特别地,当start省略时,默认为0;当end省略时,则可以获取数组中剩余部分的全部元素。但二者不可同时省略
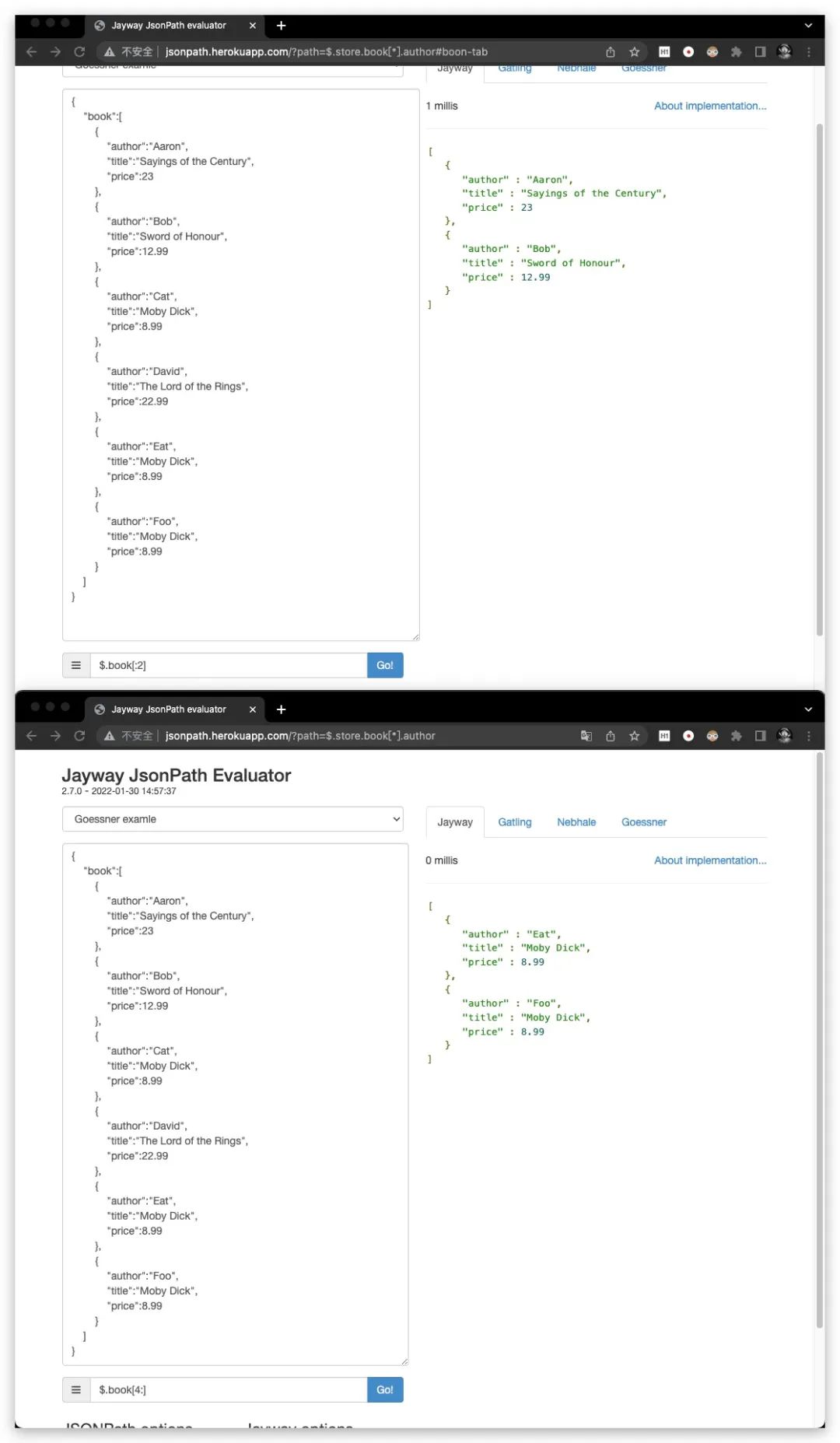
此外,在切片操作符中同样支持负数索引
*
通配符,在任何需要名称、数字的地方都可以使用
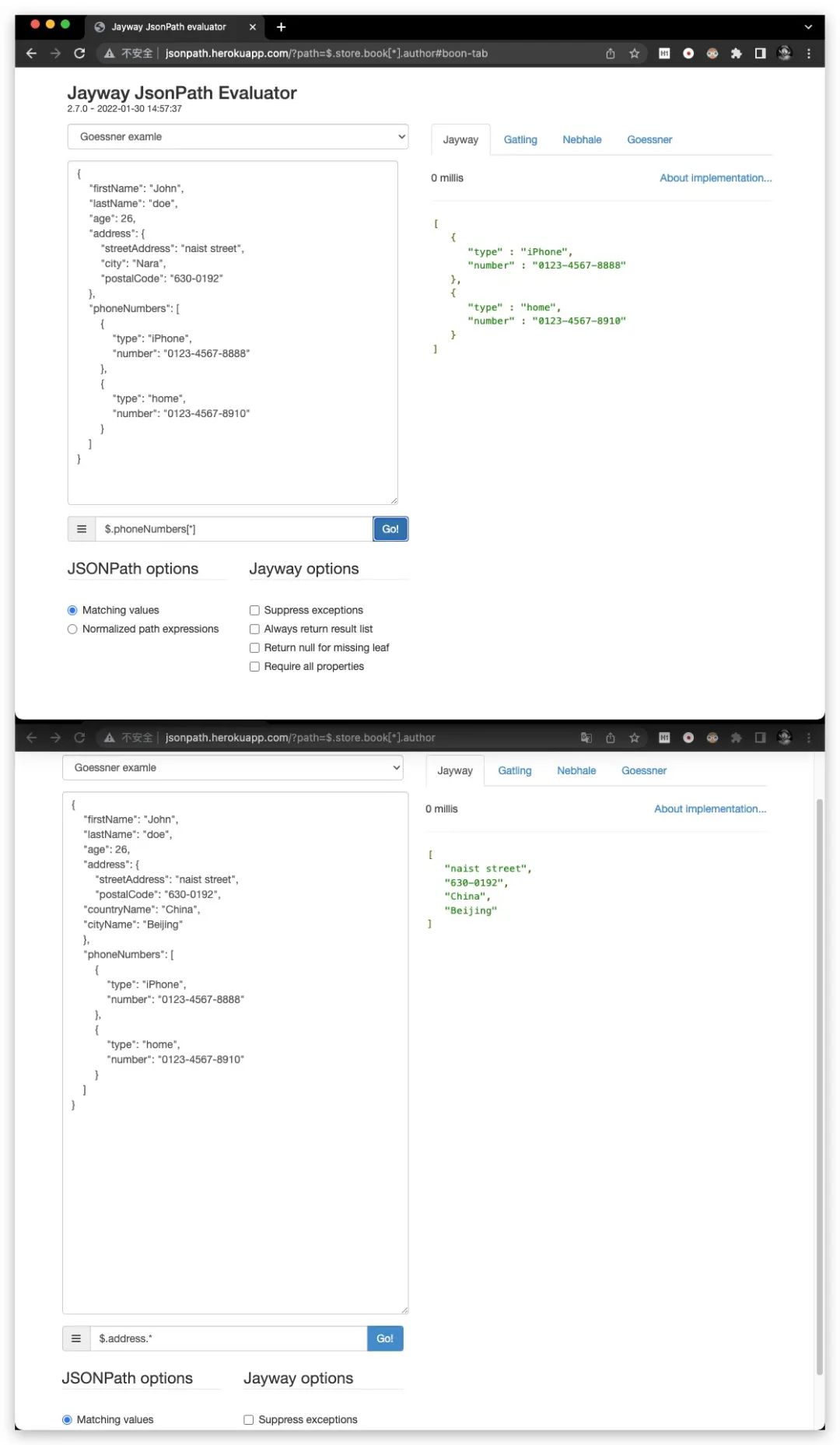
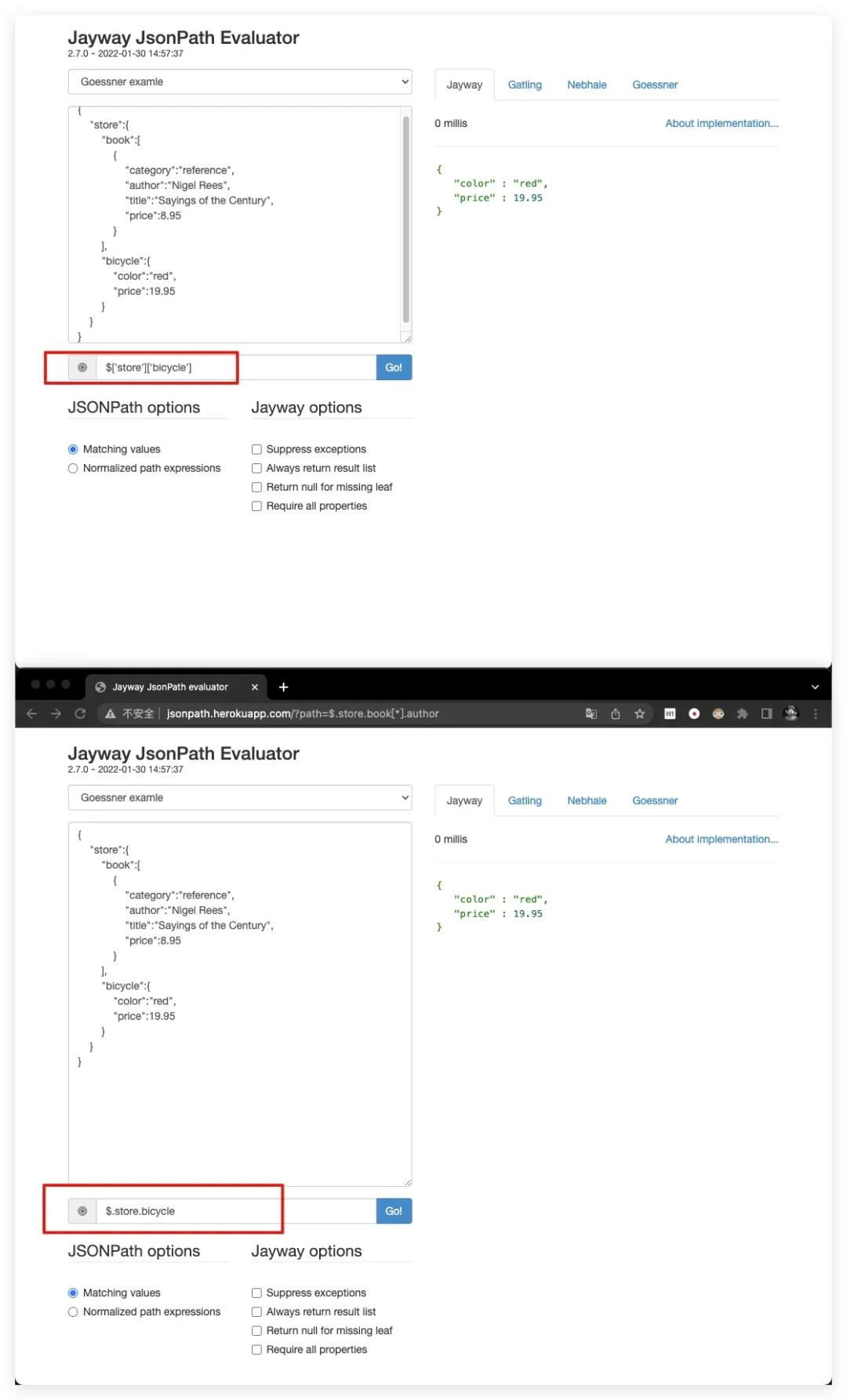
@
用于下文所述过滤器表达式当中,用于指代过滤器当前正在处理的节点对象。其效果类似于Java中的this关键字
[?()]
过滤器表达式,表达式结果必须是布尔值。下图即是一个典型的使用过滤器对数组元素进行过滤的示例
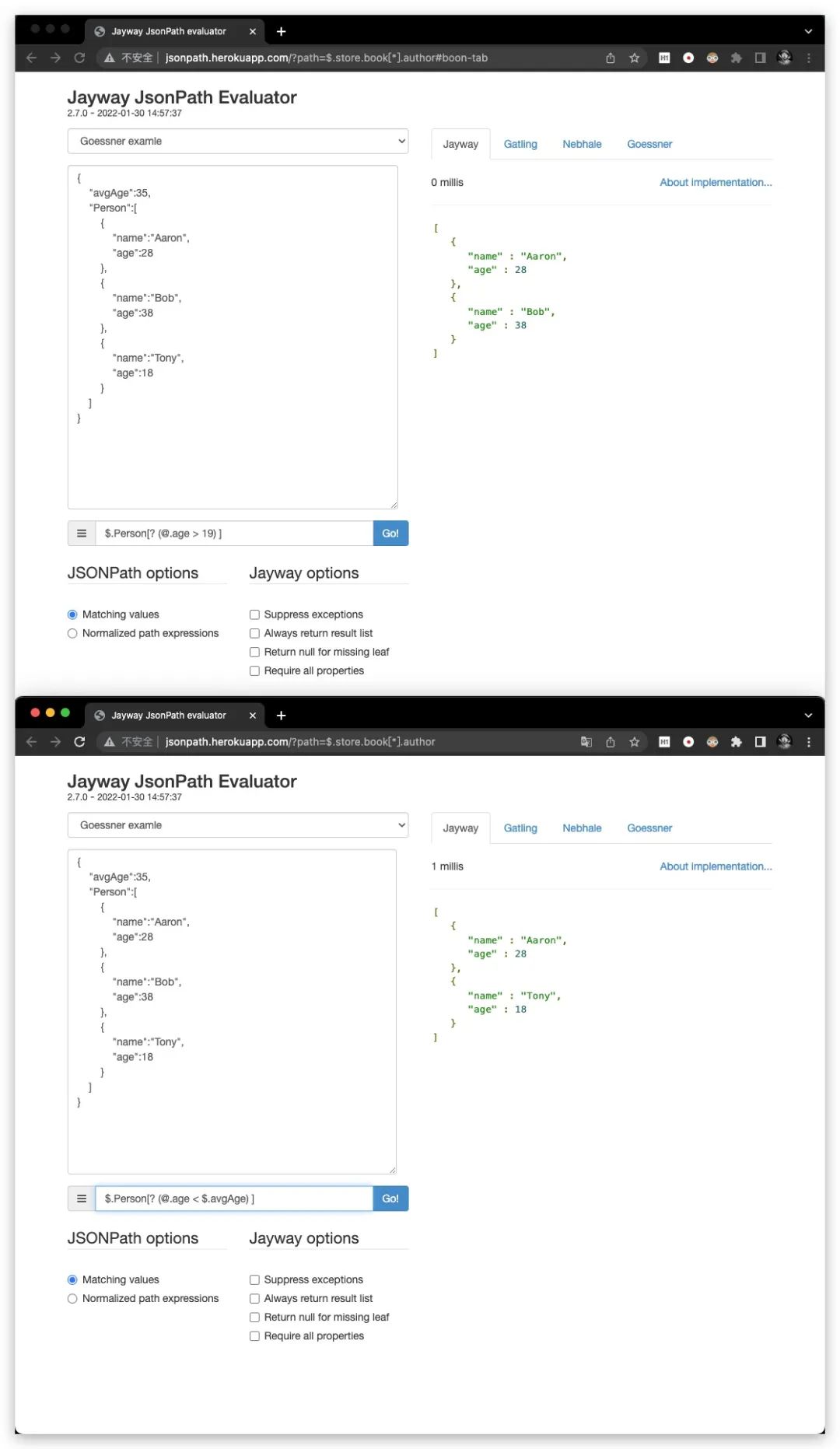
其中过滤器支持地操作符,常见地有:
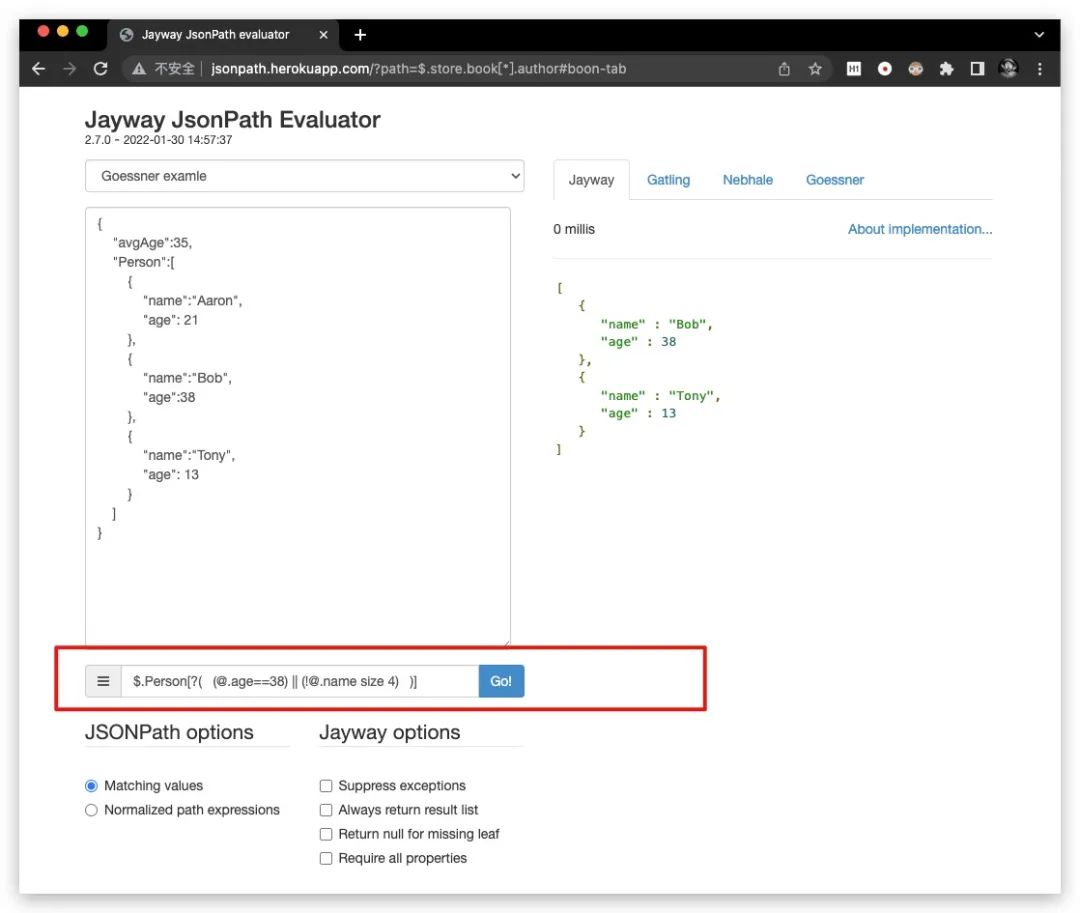
「==」 :判断是否相等 「!=」 :判断是否不相等 「<」 :判断是否小于 「<=」 :判断是否小于等于 「>」 :判断是否大于 「>=」 :判断是否大于等于 「=~」 :判断左侧 是否 匹配右侧的正则。例如:[? (@.age =~ /\d+/)] 「in」 :判断左侧 是否 存在于 右侧的集合中。例如:[? (@.size in ['S','M','L'])] 「nin」 :判断左侧 是否 不存在于 右侧的集合中。例如:[? (@.size nin ['S','M','L'])] 「subsetof」 :判断左侧 是否为 右侧集合的子集。例如:[? (@.sizes subsetof ['S','M','L'])] 「anyof」 :判断左侧 是否与 右侧集合 存在交集。例如:[? (@.sizes anyof ['S','M','L'])] 「noneof」 :判断左侧 是否与 右侧集合 无交集。例如:[? (@.sizes noneof ['S','M','L'])] 「size」 :判断左侧 数组长度 或 字符串长度 是否为 指定值。例如:[? (@.name size 3)]
此外对于
基于Java的实践——Jayway JsonPath
Jayway JsonPath则提供了Java版本的实现,方便开发者进行集成使用。只需引入下述依赖即可
<!--Json Path-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.jayway.jsonpath</groupId>
<artifactId>json-path</artifactId>
<version>2.7.0</version>
</dependency>
为了便于后续行文演示方便,这里准备了一个较为复杂的Json数据
{
"store":{
"book":[
{
"category":"reference",
"author":"Nigel Rees",
"title":"Sayings of the Century",
"price":8.95
},
{
"category":"fiction",
"author":"Evelyn Waugh",
"title":"Sword of Honour",
"price":12.99
},
{
"category":"fiction",
"author":"Herman Melville",
"title":"Moby Dick",
"isbn":"0-553-21311-3",
"price":8.99
},
{
"category":"fiction",
"author":"J. R. R. Tolkien",
"title":"The Lord of the Rings",
"isbn":"0-395-19395-8",
"price":22.99
}
],
"bicycle":{
"color":"red",
"price":19.95
},
"clothes":[
{
"name":"牛仔裤",
"sizes":"S",
"price":94
},
{
"name":"背心",
"sizes":"M",
"price":48
},
{
"name":"裙子",
"sizes":["S", "M"],
"price":1.24
},
{
"name":"羊毛衫",
"sizes":["XS", "XL"],
"price":78.99
},
{
"name":"Polo衫",
"sizes":["XS", "XL", "M"],
"price":18.99
}
]
},
"expensive":10
}
快速入门
Jayway JsonPath 非常方便,开箱即用
public class Demo1 {
private String json = "{\"store\":{\"book\":[{\"category\":\"reference\",\"author\":\"Nigel Rees\",\"title\":\"Sayings of the Century\",\"price\":8.95},{\"category\":\"fiction\",\"author\":\"Evelyn Waugh\",\"title\":\"Sword of Honour\",\"price\":12.99},{\"category\":\"fiction\",\"author\":\"Herman Melville\",\"title\":\"Moby Dick\",\"isbn\":\"0-553-21311-3\",\"price\":8.99},{\"category\":\"fiction\",\"author\":\"J. R. R. Tolkien\",\"title\":\"The Lord of the Rings\",\"isbn\":\"0-395-19395-8\",\"price\":22.99}],\"bicycle\":{\"color\":\"red\",\"price\":19.95},\"clothes\":[{\"name\":\"牛仔裤\",\"sizes\":\"S\",\"price\":94},{\"name\":\"背心\",\"sizes\":\"M\",\"price\":48},{\"name\":\"裙子\",\"sizes\":[\"S\",\"M\"],\"price\":1.24},{\"name\":\"羊毛衫\",\"sizes\":[\"XS\",\"XL\"],\"price\":78.99},{\"name\":\"Polo衫\",\"sizes\":[\"XS\",\"M\",\"XL\"],\"price\":18.99}]},\"expensive\":10}\n";
/**
* 每次读取时均会解析
*/
@Test
public void start1() {
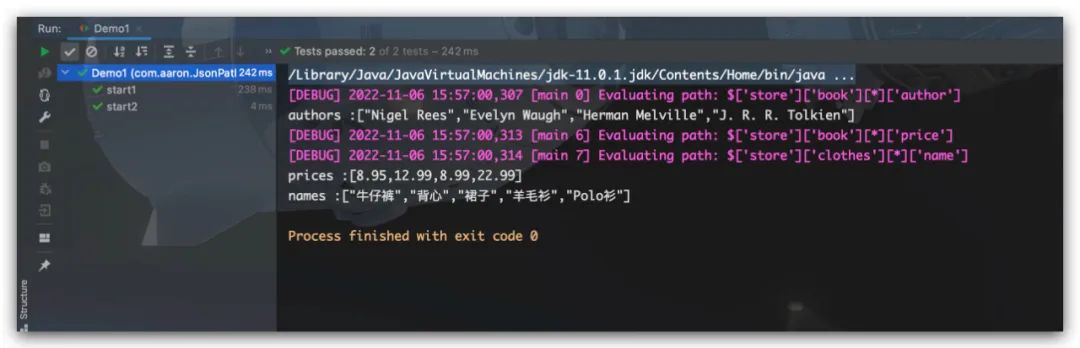
List<String> authors = JsonPath.read(json, "$.store.book[*].author");
System.out.println("authors :" + authors);
}
/**
* 多次读取路径时, 避免重复解析
*/
@Test
public void start2() {
Object document = Configuration.defaultConfiguration()
.jsonProvider()
.parse(json);
List<String> prices = JsonPath.read(document, "$.store.book[*].price");
List<String> names = JsonPath.read(document, "$.store.clothes[*].name");
System.out.println("prices :" + prices);
System.out.println("names :" + names);
}
}
其中,start1的方式适用于仅仅需要读取1次数据;而start2则通过先解析后读取的方式,适用于多次读取的场景。避免start1方式重复解析带来损耗
反序列化
在Jayway JsonPath中提供了多种JsonProvider,其中默认的为JsonSmartJsonProvider。这里我们期望能够直接对读取的数据进行反序列化,这里我们选用JacksonJsonProvider,此时要求jackson-databind依赖的版本至少为2.4.5。故这里我们先添加Jackson依赖
<!--Jackson-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.12.7</version>
</dependency>
Demo如下所示
import com.jayway.jsonpath.Configuration;
import com.jayway.jsonpath.JsonPath;
import com.jayway.jsonpath.ReadContext;
import com.jayway.jsonpath.TypeRef;
import com.jayway.jsonpath.spi.mapper.JacksonMappingProvider;
public class Demo1 {
private String json = "{\"store\":{\"book\":[{\"category\":\"reference\",\"author\":\"Nigel Rees\",\"title\":\"Sayings of the Century\",\"price\":8.95},{\"category\":\"fiction\",\"author\":\"Evelyn Waugh\",\"title\":\"Sword of Honour\",\"price\":12.99},{\"category\":\"fiction\",\"author\":\"Herman Melville\",\"title\":\"Moby Dick\",\"isbn\":\"0-553-21311-3\",\"price\":8.99},{\"category\":\"fiction\",\"author\":\"J. R. R. Tolkien\",\"title\":\"The Lord of the Rings\",\"isbn\":\"0-395-19395-8\",\"price\":22.99}],\"bicycle\":{\"color\":\"red\",\"price\":19.95},\"clothes\":[{\"name\":\"牛仔裤\",\"sizes\":\"S\",\"price\":94},{\"name\":\"背心\",\"sizes\":\"M\",\"price\":48},{\"name\":\"裙子\",\"sizes\":[\"S\",\"M\"],\"price\":1.24},{\"name\":\"羊毛衫\",\"sizes\":[\"XS\",\"XL\"],\"price\":78.99},{\"name\":\"Polo衫\",\"sizes\":[\"XS\",\"M\",\"XL\"],\"price\":18.99}]},\"expensive\":10}\n";
@Test
public void start3() {
// 使用 JacksonJsonProvider 实现反序列化
Configuration conf = Configuration
.builder()
.mappingProvider( new JacksonMappingProvider() )
.build();
ReadContext ctx = JsonPath.using( conf )
.parse(json);
TypeRef<List<Book>> typeRef = new TypeRef<List<Book>>() {};
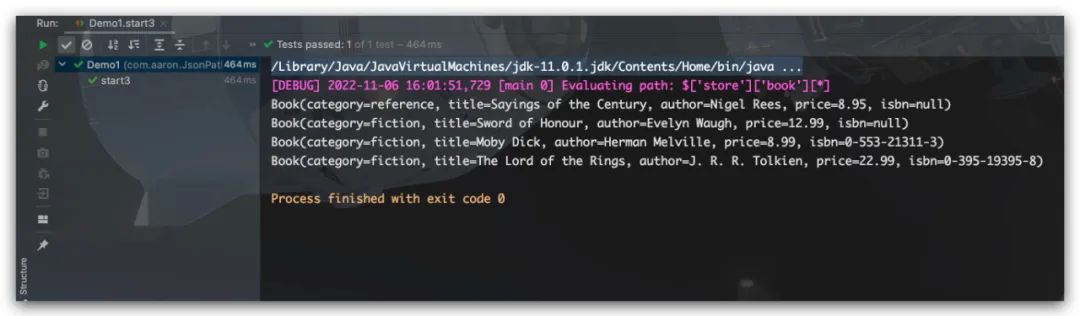
List<Book> books = ctx.read("$.store.book[*]", typeRef);
books.forEach( System.out::println );
}
}
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Builder
@Data
class Book {
private String category;
private String title;
private String author;
private Double price;
private String isbn;
}
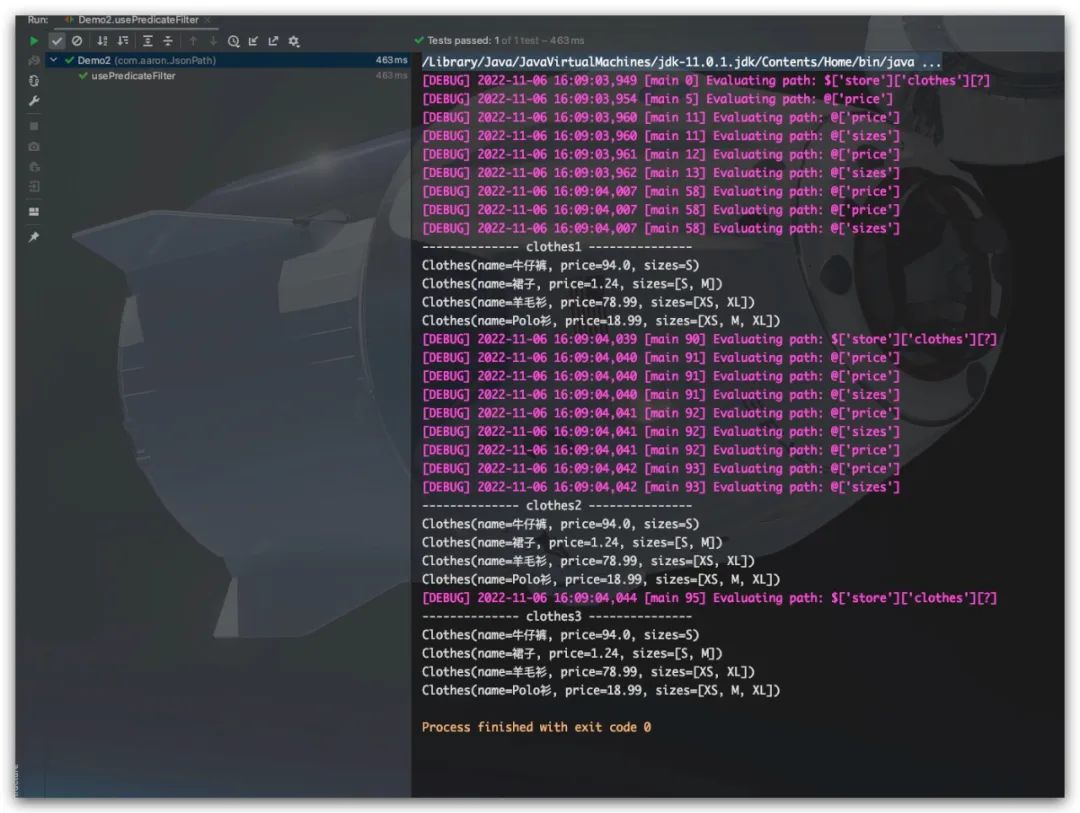
效果如下所示
过滤器谓词
前面提到JsonPath中支持过滤器表达式,为此在Jayway JsonPath中提供了相应的谓词过滤器。具体地,我们可以使用内联谓词、Filter谓词、自定义谓词3种方式进行实践。其中对于Filter谓词、自定义谓词而言,需要在jsonpath字符串中使用占位符?来代替所传递的过滤器谓词。如果jsonpath字符串中使用多个占位符?,则应按相应顺序传入过滤器谓词参数
import com.jayway.jsonpath.*;
import com.jayway.jsonpath.spi.mapper.JacksonMappingProvider;
import static com.jayway.jsonpath.Criteria.where;
import static com.jayway.jsonpath.Filter.filter;
public class Demo2 {
private String json = "{\"store\":{\"book\":[{\"category\":\"reference\",\"author\":\"Nigel Rees\",\"title\":\"Sayings of the Century\",\"price\":8.95},{\"category\":\"fiction\",\"author\":\"Evelyn Waugh\",\"title\":\"Sword of Honour\",\"price\":12.99},{\"category\":\"fiction\",\"author\":\"Herman Melville\",\"title\":\"Moby Dick\",\"isbn\":\"0-553-21311-3\",\"price\":8.99},{\"category\":\"fiction\",\"author\":\"J. R. R. Tolkien\",\"title\":\"The Lord of the Rings\",\"isbn\":\"0-395-19395-8\",\"price\":22.99}],\"bicycle\":{\"color\":\"red\",\"price\":19.95},\"clothes\":[{\"name\":\"牛仔裤\",\"sizes\":\"S\",\"price\":94},{\"name\":\"背心\",\"sizes\":\"M\",\"price\":48},{\"name\":\"裙子\",\"sizes\":[\"S\",\"M\"],\"price\":1.24},{\"name\":\"羊毛衫\",\"sizes\":[\"XS\",\"XL\"],\"price\":78.99},{\"name\":\"Polo衫\",\"sizes\":[\"XS\",\"M\",\"XL\"],\"price\":18.99}]},\"expensive\":10}\n";
/**
* Predicate Filter 谓词过滤器
*/
@Test
public void usePredicateFilter() {
// 使用 JacksonJsonProvider 实现反序列化
Configuration conf = Configuration
.builder()
.mappingProvider( new JacksonMappingProvider() )
.build();
ReadContext ctx = JsonPath.using( conf )
.parse(json);
// 方式1 : 内联谓词
TypeRef<List<Clothes>> typeRef = new TypeRef<List<Clothes>>() {};
List<Clothes> clothes1 = ctx.read("$.store.clothes[?( @.price>50 || @.sizes anyof ['M'] ) ]", typeRef);
System.out.println("-------------- clothes1 ---------------");
clothes1.forEach( System.out::println );
// 方式2 : Filter谓词
Filter filter = filter( where("price").gt(50) )
.or( where("sizes").anyof( Arrays.asList("M") ) );
// 使用谓词的占位符?
Clothes[] clothes2 = ctx.read("$.store.clothes[?]", Clothes[].class, filter);
System.out.println("-------------- clothes2 ---------------");
for (Clothes clothes : clothes2) {
System.out.println(clothes);
}
// 方式3 : 自定义谓词
Predicate rule = ctx1 -> {
Map map = ctx1.item( Map.class );
boolean b1 = false;
Object priceObj = map.getOrDefault("price",null);
if( priceObj!=null ) {
String priceStr = priceObj.toString();
Double price = 0d;
try {
price = Double.parseDouble( priceStr );
} catch (Exception e) {
}
b1 = price > 50d;
}
boolean b2 = false;
Object sizes = map.getOrDefault("sizes", null);
if( sizes!=null && sizes instanceof List ) {
List<String> sizeList = (List<String>) sizes;
List<String> targetList = Arrays.asList("M");
for (String size : sizeList) {
if( targetList.contains(size) ) {
b2 = true;
break;
}
}
}
return b1 || b2;
};
// 使用谓词的占位符?
Clothes[] clothes3 = ctx.read("$.store.clothes[?]", Clothes[].class, rule);
System.out.println("-------------- clothes3 ---------------");
for (Clothes clothes : clothes3) {
System.out.println(clothes);
}
}
}
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Builder
@Data
class Clothes {
private String name;
private Double price;
private Object sizes;
}
效果如下所示