Mybatis-Plus,BaseMapper源码分析
抛出疑问
Mybatis-plus的确能让我们写少很多重复代码,非常好用。那么其中最方便的就是Mapper接口继承BaseMapper就能获得增删改查的这个功能。那么这个功能的底层代码,究竟是怎么实现的呢?
毕竟Mybatis-plus是Mybatis的加强,所以Mybatis-plus肯定是基于Mybatis原来的机制来扩展的,沿着这个思路,我们先搞清楚一个问题,就是原生的mapper.xml文件最后是怎么跟对应的Mapper接口产生联系的。
既然是配置,那么在Mybatis里肯定有对应的配置类,这个类就是MappedStatement。最终在Configuration类中把MappedStatement对象添加进mappedStatements集合中进行管理。源码如下:
public class Configuration {
protected final Map<String, MappedStatement> mappedStatements = new StrictMap<MappedStatement>("Mapped Statements collection");
public void addMappedStatement(MappedStatement ms) {
mappedStatements.put(ms.getId(), ms);
}
}
假如有个mapper.xml文件定义如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.yehongzhi.mydemo.mapper.UserMapper">
<select id="getUserList" resultType="com.yehongzhi.mydemo.model.User">
select * from user
</select>
</mapper>
我们用debug模式来验证一下:
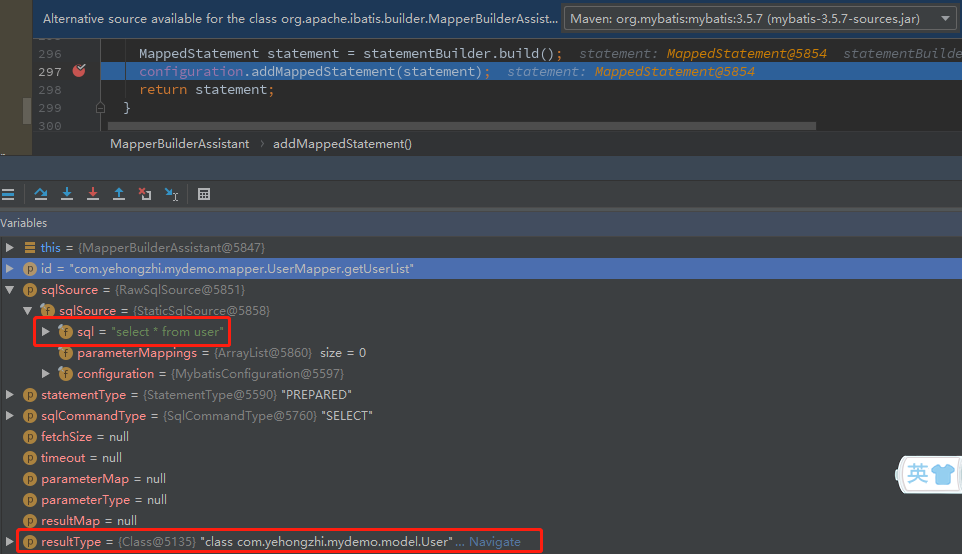
由此可以看出,Mybatis底层在解析Mapper.xml文件最后是转成一个MappedStatement对象进行管理。跟着这个思路,我们能不能根据特定的规律创建MappedStatement对象放进mappedStatements集合中,那不就能实现Mybatis-plus的BaseMapper的功能了吗!
首先找到MybatisPlusAutoConfiguration配置类,会创建MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean。
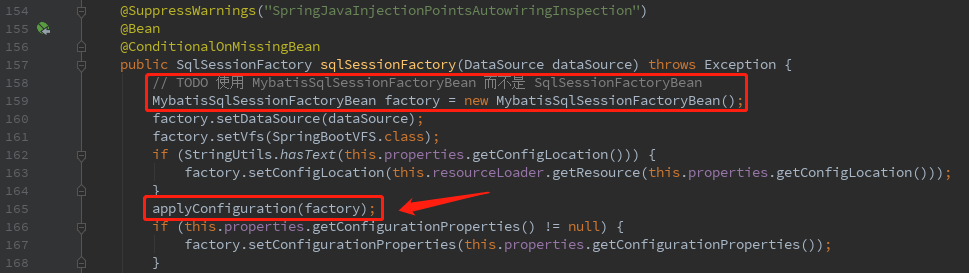
并设置MybatisConfiguration作为配置类。
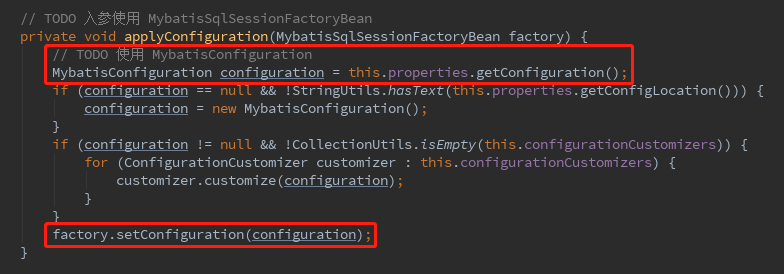
这个MybatisConfiguration是很重要的类,里面会初始化一个mybatisMapperRegistry,后面有用。
public class MybatisConfiguration extends Configuration {
/**
* Mapper 注册
*/
protected final MybatisMapperRegistry mybatisMapperRegistry = new MybatisMapperRegistry(this);
}
当创建MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean时,会调用afterPropertiesSet()方法创建sqlSessionFactory。
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
notNull(dataSource, "Property 'dataSource' is required");
state((configuration == null && configLocation == null) || !(configuration != null && configLocation != null),
"Property 'configuration' and 'configLocation' can not specified with together");
this.sqlSessionFactory = buildSqlSessionFactory();
}
然后buildSqlSessionFactory()方法的主要内容是解析mapper的xml文件。
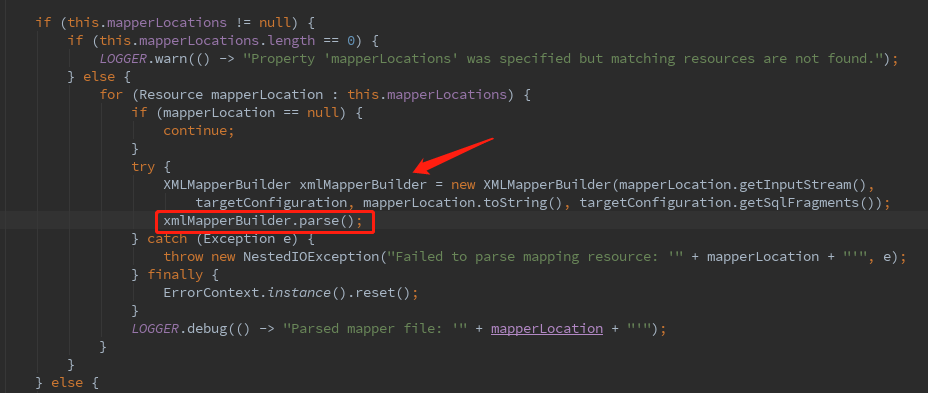

然后继续深入,看bindMapperForNamespace()方法。
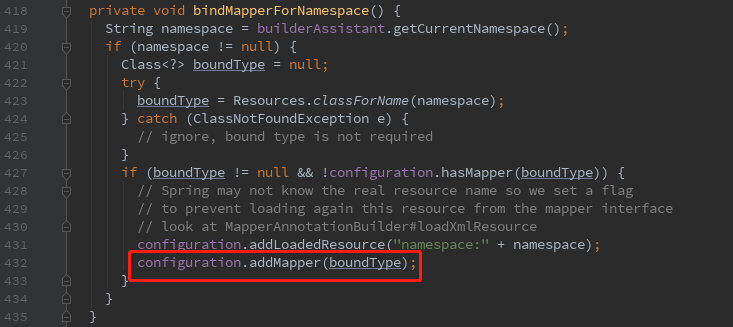
接着用MapperAnnotationBuilder类进行解析。
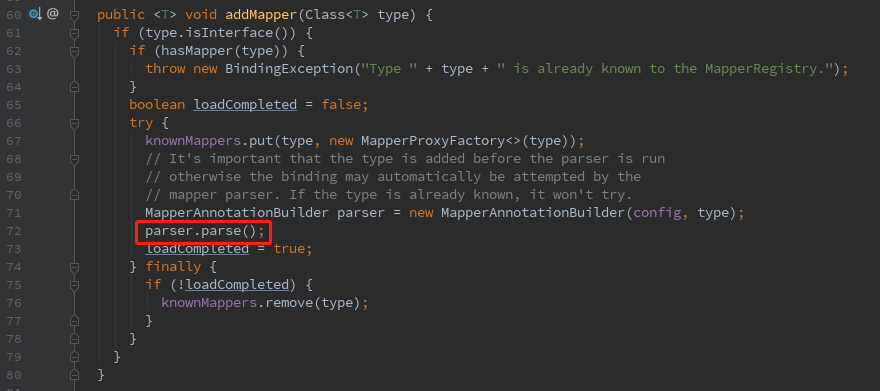
接着在parse()方法里进行基本的SQL注入:
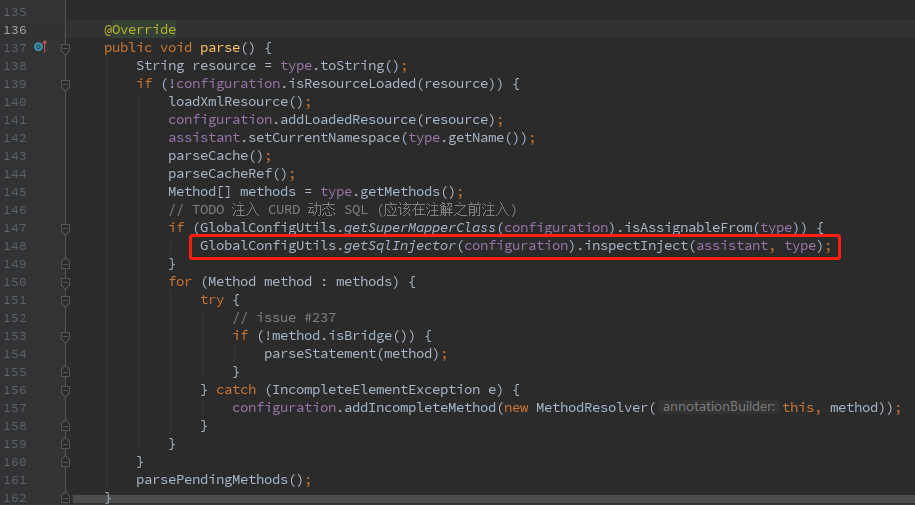
关键就在这个SQL注入器里。
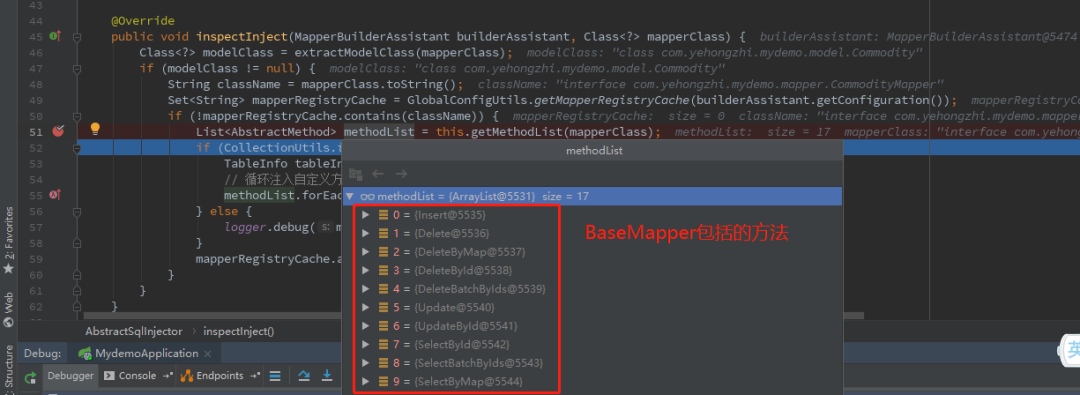
所以关键在于AbstractMethod,这里用了模板模式。
public abstract class AbstractMethod implements Constants {
protected Configuration configuration;
protected LanguageDriver languageDriver;
protected MapperBuilderAssistant builderAssistant;
/**
* 注入自定义方法
*/
public void inject(MapperBuilderAssistant builderAssistant, Class<?> mapperClass, Class<?> modelClass, TableInfo tableInfo) {
this.configuration = builderAssistant.getConfiguration();
this.builderAssistant = builderAssistant;
this.languageDriver = configuration.getDefaultScriptingLanguageInstance();
/* 注入自定义方法 */
injectMappedStatement(mapperClass, modelClass, tableInfo);
}
/**
* 注入自定义 MappedStatement
*
* @param mapperClass mapper 接口
* @param modelClass mapper 泛型
* @param tableInfo 数据库表反射信息
* @return MappedStatement
*/
public abstract MappedStatement injectMappedStatement(Class<?> mapperClass, Class<?> modelClass, TableInfo tableInfo);
}
利用模板模式,子类只需要重写injectMappedStatement()方法,上面初始化的部分都可以共用。AbstractMethod的子类有很多,我们选个有代表性的看一下,就可以推断其他的用途,比如Insert类。
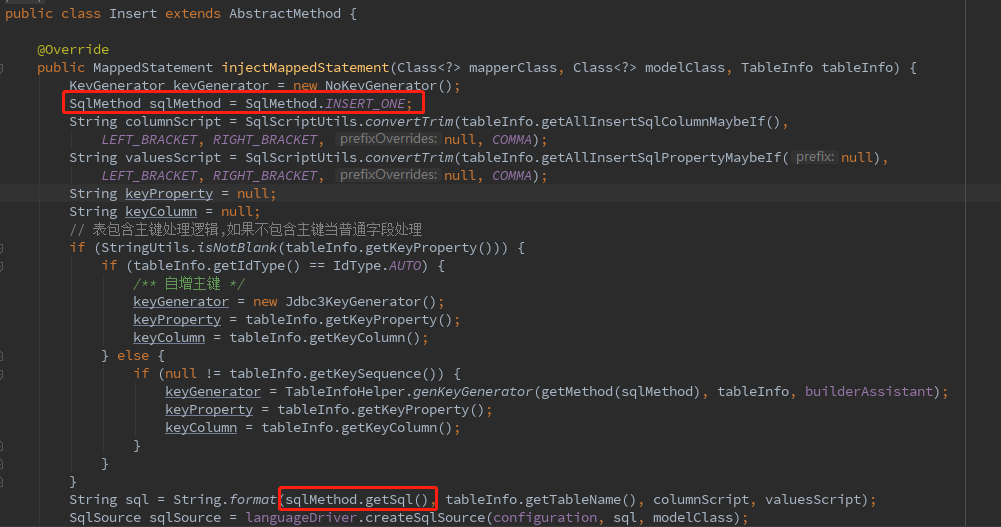
由此可看出,BaseMapper里的语句信息模板,来自于枚举SqlMethod。

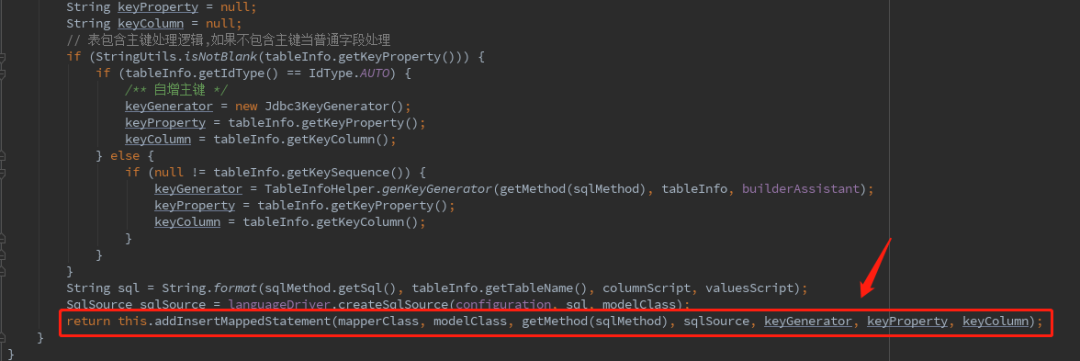
最终就是转成MappedStatement对象,然后添加注册,于是乎就有了这些CRUD操作的方法。
 总结
总结总结一下加载BaseMapper的过程:
- 初始化
MybatisConfiguration和mybatisMapperRegistry。 - 解析Mapper类,获取AbstractMethod集合。
- 遍历AbstractMethod集合,然后调用各自实现的
injectMappedStatement()方法,注入SQL。 - 添加注册
MappedStatement对象。
非常感谢你的阅读,希望这篇文章能给到你帮助和启发。
觉得有用就点个赞吧,你的点赞是我创作的最大动力~
我是一个努力让大家记住的程序员。我们下期再见!!!
能力有限,如果有什么错误或者不当之处,请大家批评指正,一起学习交流!
