JS逆向之补浏览器环境的两种监控方式
1,首先要说的肯定是 Proxy 了,介绍就不说了,直接上代码:
window = new Proxy(global, {get: function (target, key, receiver) {console.log("window.get", key, target[key]);if (key=="location"){location = new Proxy(target[key], {get: function (_target, _key, _receiver) {console.log("window.get", key, _key, _target[_key]);if (_key=="port"){console.log("关注公众号【妄为写代码】")}return _target[_key];}})}return target[key];},set: function (target, key, value, receiver) {console.log("window.set", key, value);target[key] = value;}});window.a = {};window.a;window.location = {a: 2};window.location.a;window.b = {a: 2};window.b.a;location.port;console.log("--------------");window.location.port;
node 环境执行结果:
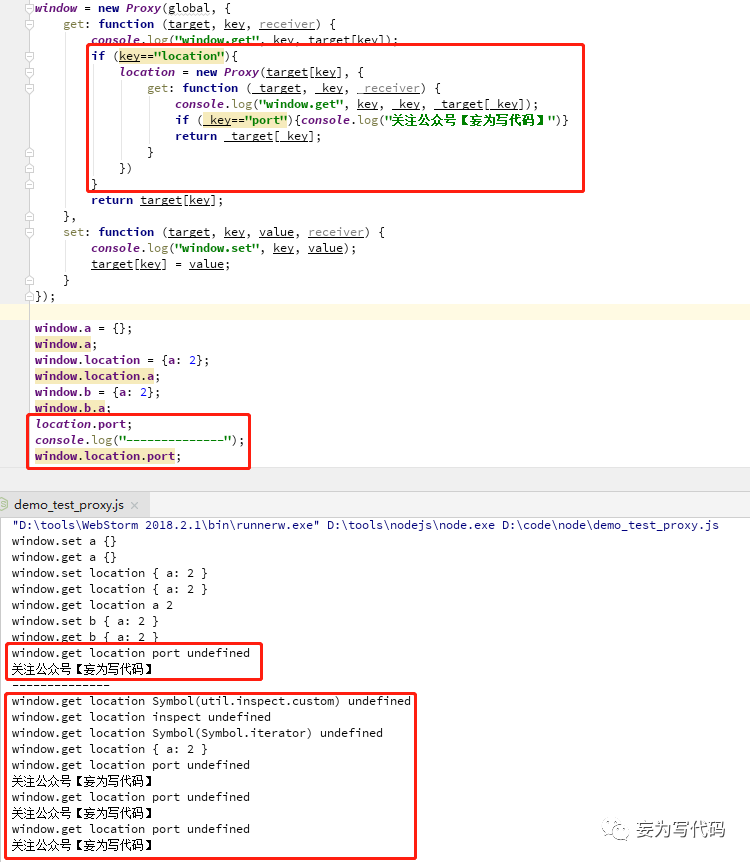
重点关注【嵌套Proxy】和【重复Proxy】
2,对象属性的 hook 方式
在浏览器中执行:

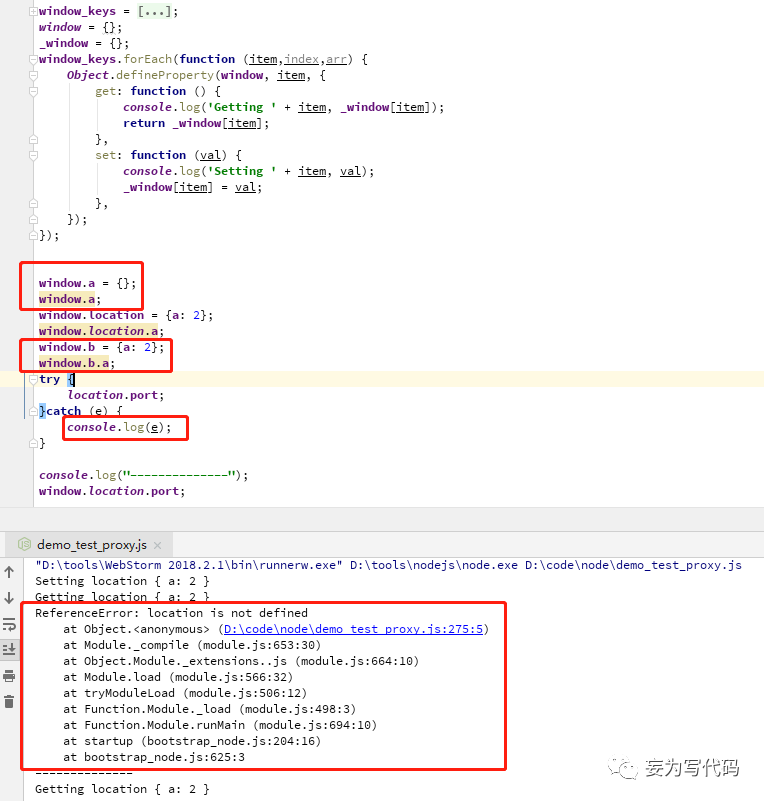
重点关注【未在固定范围的新增属性】和【对比两种方式的 location.port】和【多层属性的获取 window.location.port】
3,这个监控的作用就不用说了吧,就是大家常说的缺哪补哪需要用到的,现在补环境的场景越来越多了,一些知名 js 反爬产品,就可以用这个思路,环境补的好,可以到处用,还能省好多事,一举多得。
推荐阅读
THANKS
- End -
点个“在看”必升职加薪喔!
评论

