【Python】简约而不简单|值得收藏的Numpy小抄表(含主要语法、代码)
Numpy是一个用python实现的科学计算的扩展程序库,包括:
1、一个强大的N维数组对象Array;
2、比较成熟的(广播)函数库;
3、用于整合C/C++和Fortran代码的工具包;
4、实用的线性代数、傅里叶变换和随机数生成函数。numpy和稀疏矩阵运算包scipy配合使用更加方便。
NumPy(Numeric Python)提供了许多高级的数值编程工具,如:矩阵数据类型、矢量处理,以及精密的运算库。专为进行严格的数字处理而产生。多为很多大型金融公司使用,以及核心的科学计算组织如:Lawrence Livermore,NASA用其处理一些本来使用C++,Fortran或Matlab等所做的任务。
本文整理了一个Numpy的小抄表,总结了Numpy的常用操作,可以收藏慢慢看。
安装Numpy
可以通过 Pip 或者 Anaconda安装Numpy:
$ pip install numpy或
$ conda install numpy本文目录
基础 占位符 数组 增加或减少元素 合并数组 分割数组 数组形状变化
拷贝 /排序
数组操作 其他 数学计算 数学计算 比较 基础统计 更多 切片和子集 小技巧
基础
NumPy最常用的功能之一就是NumPy数组:列表和NumPy数组的最主要区别在于功能性和速度。
列表提供基本操作,但NumPy添加了FTTs、卷积、快速搜索、基本统计、线性代数、直方图等。
两者数据科学最重要的区别是能够用NumPy数组进行元素级计算。
axis 0 通常指行
axis 1 通常指列
| 操作 | 描述 | 文档 |
|---|---|---|
np.array([1,2,3]) | 一维数组 | https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.array.html#numpy.array |
np.array([(1,2,3),(4,5,6)]) | 二维数组 | https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.array.html#numpy.array |
np.arange(start,stop,step) | 等差数组 | https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.arange.html |
占位符
| 操作 | 描述 | 文档 |
np.linspace(0,2,9) | 数组中添加等差的值 | https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.linspace.html |
np.zeros((1,2)) | 创建全0数组 | docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.zeros.html |
np.ones((1,2)) | 创建全1数组 | https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.ones.html#numpy.ones |
np.random.random((5,5)) | 创建随机数的数组 | https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.random.random.html |
np.empty((2,2)) | 创建空数组 | https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.empty.html |
举例:
import numpy as np# 1 dimensionalx = np.array([1,2,3])# 2 dimensionaly = np.array([(1,2,3),(4,5,6)])x = np.arange(3)>>> array([0, 1, 2])y = np.arange(3.0)>>> array([ 0., 1., 2.])x = np.arange(3,7)>>> array([3, 4, 5, 6])y = np.arange(3,7,2)>>> array([3, 5])
数组属性
数组属性
| 语法 | 描述 | 文档 |
|---|---|---|
array.shape | 维度(行,列) | https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.ndarray.shape.html |
len(array) | 数组长度 | https://docs.python.org/3.5/library/functions.html#len |
array.ndim | 数组的维度数 | https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.ndarray.ndim.html |
array.size | 数组的元素数 | https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.ndarray.size.html |
array.dtype | 数据类型 | https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/arrays.dtypes.html |
array.astype(type) | 转换数组类型 | https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.ndarray.astype.html |
type(array) | 显示数组类型 | https://numpy.org/doc/stable/user/basics.types.html |
拷贝 /排序
| 操作 | 描述 | 文档 |
|---|---|---|
np.copy(array) | 创建数组拷贝 | https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.copy.html |
other = array.copy() | 创建数组深拷贝 | https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.copy.html |
array.sort() | 排序一个数组 | https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.sort.html |
array.sort(axis=0) | 按照指定轴排序一个数组 | https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.sort.html |
举例
import numpy as np# Sort sorts in ascending ordery = np.array([10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1])y.sort()print(y)>>> [ 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10]
数组操作例程
增加或减少元素
| 操作 | 描述 | 文档 |
|---|---|---|
np.append(a,b) | 增加数据项到数组 | https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.append.html |
np.insert(array, 1, 2, axis) | 沿着数组0轴或者1轴插入数据项 | https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.insert.html |
np.resize((2,4)) | 将数组调整为形状(2,4) | https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.resize.html |
np.delete(array,1,axis) | 从数组里删除数据项 | https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.delete.html |
举例
import numpy as np# Append items to arraya = np.array([(1, 2, 3),(4, 5, 6)])b = np.append(a, [(7, 8, 9)])print(b)>>> [1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]# Remove index 2 from previous arrayprint(np.delete(b, 2))>>> [1 2 4 5 6 7 8 9]
组合数组
| 操作 | 描述 | 文档 |
|---|---|---|
np.concatenate((a,b),axis=0) | 连接2个数组,添加到末尾 | https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.concatenate.html |
np.vstack((a,b)) | 按照行堆叠数组 | https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.vstack.html |
np.hstack((a,b)) | 按照列堆叠数组 | docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.hstack.html#numpy.hstack |
举例
import numpy as npa = np.array([1, 3, 5])b = np.array([2, 4, 6])# Stack two arrays row-wiseprint(np.vstack((a,b)))>>> [[1 3 5][2 4 6]]# Stack two arrays column-wiseprint(np.hstack((a,b)))>>> [1 3 5 2 4 6]
分割数组
| 操作 | 描述 | 文档 |
numpy.split() | 分割数组 | https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.split.html |
np.array_split(array, 3) | 将数组拆分为大小(几乎)相同的子数组 | https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.array_split.html#numpy.array_split |
numpy.hsplit(array, 3) | 在第3个索引处水平拆分数组 | https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.hsplit.html#numpy.hsplit |
举例
# Split array into groups of ~3a = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8])print(np.array_split(a, 3))>>> [array([1, 2, 3]), array([4, 5, 6]), array([7, 8])]
数组形状变化
操作
| 操作 | 描述 | 文档 |
|---|---|---|
other = ndarray.flatten() | 平铺一个二维数组到一维数组 | https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.ndarray.flatten.html |
| numpy.flip() | 翻转一维数组中元素的顺序 | https://docs.scipy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.flip.html |
| np.ndarray[::-1] | 翻转一维数组中元素的顺序 | |
| reshape | 改变数组的维数 | https://docs.scipy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.reshape.html |
| squeeze | 从数组的形状中删除单维度条目 | https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.squeeze.html |
| expand_dims | 扩展数组维度 | https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy-1.13.0/reference/generated/numpy.expand_dims.html |
其他
| 操作 | 描述 | 文档 |
|---|---|---|
other = ndarray.flatten() | 平铺2维数组到1维数组 | https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.ndarray.flatten.html |
array = np.transpose(other)array.T | 数组转置 | https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.transpose.html |
inverse = np.linalg.inv(matrix) | 求矩阵的逆矩阵 | https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.linalg.inv.html |
举例
# Find inverse of a given matrixnp.linalg.inv([[3,1],[2,4]])array([[ 0.4, -0.1],[-0.2, 0.3]])
数学计算
操作
| 操作 | 描述 | 文档 |
|---|---|---|
np.add(x,y)x + y | 加 | https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.add.html |
np.substract(x,y)x - y | 减 | https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.subtract.html#numpy.subtract |
np.divide(x,y)x / y | 除 | https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.divide.html#numpy.divide |
np.multiply(x,y)x @ y | 乘 | https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.multiply.html#numpy.multiply |
np.sqrt(x) | 平方根 | https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.sqrt.html#numpy.sqrt |
np.sin(x) | 元素正弦 | https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.sin.html#numpy.sin |
np.cos(x) | 元素余弦 | https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.cos.html#numpy.cos |
np.log(x) | 元素自然对数 | https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.log.html#numpy.log |
np.dot(x,y) | 点积 | https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.dot.html |
np.roots([1,0,-4]) | 给定多项式系数的根 | https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.roots.html |
举例
# If a 1d array is added to a 2d array (or the other way), NumPy# chooses the array with smaller dimension and adds it to the one# with bigger dimensiona = np.array([1, 2, 3])b = np.array([(1, 2, 3), (4, 5, 6)])print(np.add(a, b))>>> [[2 4 6][5 7 9]]# Example of np.roots# Consider a polynomial function (x-1)^2 = x^2 - 2*x + 1# Whose roots are 1,1>>> np.roots([1,-2,1])array([1., 1.])# Similarly x^2 - 4 = 0 has roots as x=±2>>> np.roots([1,0,-4])array([-2., 2.])
比较
| 操作 | 描述 | 文档 |
|---|---|---|
== | 等于 | https://docs.python.org/2/library/stdtypes.html |
!= | 不等于 | https://docs.python.org/2/library/stdtypes.html |
< | 小于 | https://docs.python.org/2/library/stdtypes.html |
> | 大于 | https://docs.python.org/2/library/stdtypes.html |
<= | 小于等于 | https://docs.python.org/2/library/stdtypes.html |
>= | 大于等于 | https://docs.python.org/2/library/stdtypes.html |
np.array_equal(x,y) | 数组比较 | https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.array_equal.html |
举例:
# Using comparison operators will create boolean NumPy arraysz = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10])c = z < 6print(c)>>> [ True True True True True False False False False False]
基本的统计
| 操作 | 描述 | 文档 |
|---|---|---|
np.mean(array) | Mean | https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.mean.html#numpy.mean |
np.median(array) | Median | https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.median.html#numpy.median |
array.corrcoef() | Correlation Coefficient | https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.corrcoef.html#numpy.corrcoef |
np.std(array) | Standard Deviation | https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.std.html#numpy.std |
举例
# Statistics of an arraya = np.array([1, 1, 2, 5, 8, 10, 11, 12])# Standard deviationprint(np.std(a))>>> 4.2938910093294167# Medianprint(np.median(a))>>> 6.5
更多
| 操作 | 描述 | 文档 |
|---|---|---|
array.sum() | 数组求和 | https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.sum.html |
array.min() | 数组求最小值 | https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.ndarray.min.html |
array.max(axis=0) | 数组求最大值(沿着0轴) | |
array.cumsum(axis=0) | 指定轴求累计和 | https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.cumsum.html |
切片和子集
| 操作 | 描述 | 文档 |
|---|---|---|
array[i] | 索引i处的一维数组 | https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/arrays.indexing.html |
array[i,j] | 索引在[i][j]处的二维数组 | https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/arrays.indexing.html |
array[i<4] | 布尔索引 | https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/arrays.indexing.html |
array[0:3] | 选择索引为 0, 1和 2 | https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/arrays.indexing.html |
array[0:2,1] | 选择第0,1行,第1列 | https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/arrays.indexing.html |
array[:1] | 选择第0行数据项 (与[0:1, :]相同) | https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/arrays.indexing.html |
array[1:2, :] | 选择第1行 | https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/arrays.indexing.html |
| [comment]: <> " | array[1,...] | 等同于 array[1,:,:] |
array[ : :-1] | 反转数组 | 同上 |
举例
b = np.array([(1, 2, 3), (4, 5, 6)])# The index *before* the comma refers to *rows*,# the index *after* the comma refers to *columns*print(b[0:1, 2])>>> [3]print(b[:len(b), 2])>>> [3 6]print(b[0, :])>>> [1 2 3]print(b[0, 2:])>>> [3]print(b[:, 0])>>> [1 4]c = np.array([(1, 2, 3), (4, 5, 6)])d = c[1:2, 0:2]print(d)>>> [[4 5]]
切片举例
import numpy as npa1 = np.arange(0, 6)a2 = np.arange(10, 16)a3 = np.arange(20, 26)a4 = np.arange(30, 36)a5 = np.arange(40, 46)a6 = np.arange(50, 56)a = np.vstack((a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, a6))

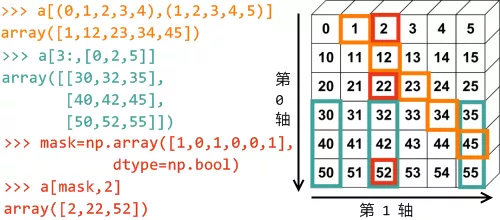
例子将会越来越多的,欢迎大家提交。
布尔索引
# Index trick when working with two np-arraysa = np.array([1,2,3,6,1,4,1])b = np.array([5,6,7,8,3,1,2])# Only saves a at index where b == 1other_a = a[b == 1]#Saves every spot in a except at index where b != 1other_other_a = a[b != 1]
import numpy as npx = np.array([4,6,8,1,2,6,9])y = x > 5print(x[y])>>> [6 8 6 9]# Even shorterx = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 35, 212, 5, 5, 6])print(x[x < 5])>>> [1 2 3 4 4]
https://github.com/juliangaal/python-cheat-sheet
往期精彩回顾 本站qq群851320808,加入微信群请扫码:
评论
