Apache thrift 之请求处理流程
本文我们以 HelloService 为例,来分析thrfit的请求处理流程。
服务端启动
HelloService 的服务端启动在 HelloServer,这是我们自定义的类,其中就只有一个main方法:
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 创建处理器,这个就是最终处理请求的类
HelloService.Processor processor = new HelloService.Processor<>(new HelloServiceImpl());
// 配置传输类型
TServerTransport transport = new TServerSocket(SERVER_PORT);
// 配置服务器
TServer server = new TSimpleServer(new TServer.Args(transport).processor(processor));
System.out.println("Starting the simple server...");
// 对外提供服务
server.serve();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
该方法的关键部分在注释中已经详细说明了,接下来我们来一步步分析这些步骤。
创建处理器
创建处理器的代码为
HelloService.Processor processor = new HelloService.Processor<>(new HelloServiceImpl())
我们进入HelloService.Processor#Processor(I)方法:
public Processor(I iface) {
super(iface, getProcessMap(new java.util.HashMap<java.lang.String,
org.apache.thrift.ProcessFunction<I, ? extends org.apache.thrift.TBase>>()));
}
Processor(I)方法的参数是iface,即HelloServiceImpl的对象,也是我们自己实现的内容:
public class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService.Iface {
@Override
public String hello(String text) throws TException {
return "hello, " + text + " !";
}
}
getProcessMap(...)方法
在Processor(I)方法中,会调用super(...)方法,注意到super(...)方法的参数中调用了getProcessMap(...)方法,我们进入其中,来到HelloService.Processor#getProcessMap方法:
private static <I extends Iface> java.util.Map<...>
getProcessMap(java.util.Map<...> processMap) {
processMap.put("hello", new hello());
return processMap;
}
processMap.put("hello", new hello());中的"hello",是HelloService中的方法名,如果有HelloService中有多个方法,processMap就会put多个对象。
需要注意的是,这里的key是方法名,如果多个方法同名,那么先放入的对象会被后放入的对象覆盖,也就是说,「thrift不支持方法重载」!
那么new hello()是啥呢?我们进入其中:
public static class hello<I extends Iface>
extends org.apache.thrift.ProcessFunction<I, hello_args> {
public hello() {
super("hello");
}
...
}
hello继承了ProcessFunction,继续到父类ProcessFunction#ProcessFunction:
public abstract class ProcessFunction<I, T extends TBase> {
private final String methodName;
public ProcessFunction(String methodName) {
this.methodName = methodName;
}
...
}
这里我们大概就知道它是把hello的方法名包装成了ProcessFunction对象。
TBaseProcessor#TBaseProcessor
我们再回到HelloService.Processor#Processor(I)方法:
public Processor(I iface) {
super(iface, getProcessMap(new java.util.HashMap<java.lang.String,
org.apache.thrift.ProcessFunction<I, ? extends org.apache.thrift.TBase>>()));
}
进入super(...),也就是TBaseProcessor#TBaseProcessor:
protected TBaseProcessor(I iface, Map<String,
ProcessFunction<I, ? extends TBase>> processFunctionMap) {
this.iface = iface;
this.processMap = processFunctionMap;
}
TBaseProcessor 中保存了两个内容:
服务的实现类(由开发者提供),这里就是 HelloServiceImpl服务的方法及方法对象(由 thrift生成)
从代码来看,这一步就是把自主实现的HelloServiceImpl包装成thrift的Processor。
new TServerSocket(SERVER_PORT)
我们继续,接下来分析配置传输类型,进入 TServerSocket#TServerSocket(int):
public TServerSocket(ServerSocketTransportArgs args) throws TTransportException {
clientTimeout_ = args.clientTimeout;
if (args.serverSocket != null) {
this.serverSocket_ = args.serverSocket;
return;
}
try {
// 创建 ServerSocket
serverSocket_ = new ServerSocket();
// 地址重用,也就是ip与端口重用
serverSocket_.setReuseAddress(true);
// 绑定ip与端口
serverSocket_.bind(args.bindAddr, args.backlog);
} catch (IOException ioe) {
close();
throw new TTransportException("Could not create ServerSocket on address "
+ args.bindAddr.toString() + ".", ioe);
}
}
这个方法主要是用来开启socket服务的,使用的是ServerSocket,也就是阻塞IO。
new TServer.Args(transport)
接下我们来看看配置服务器的操作,进入new TServer.Args(transport):
public abstract class TServer {
public static class Args extends AbstractServerArgs<Args> {
public Args(TServerTransport transport) {
// 调用的是 AbstractServerArgs 的构造方法
super(transport);
}
}
/**
* 存放参数的类
*/
public static abstract class AbstractServerArgs<T extends AbstractServerArgs<T>> {
final TServerTransport serverTransport;
TProcessorFactory processorFactory;
TTransportFactory inputTransportFactory = new TTransportFactory();
TTransportFactory outputTransportFactory = new TTransportFactory();
TProtocolFactory inputProtocolFactory = new TBinaryProtocol.Factory();
TProtocolFactory outputProtocolFactory = new TBinaryProtocol.Factory();
// 最终调用的方法
public AbstractServerArgs(TServerTransport transport) {
serverTransport = transport;
}
...
}
}
这一块主要是做一些配置,也就是把前面创建的ServerSocket对象保存到AbstractServerArgs对象中。
new TServer.Args(transport).processor(processor)
TServer.AbstractServerArgs#processor方法内容如下:
public T processor(TProcessor processor) {
this.processorFactory = new TProcessorFactory(processor);
return (T) this;
}
返回的对象类型还是TServer.Args。
这一步仅仅是把processor放入到TProcessorFactory中,TProcessorFactory内容如下:
public class TProcessorFactory {
private final TProcessor processor_;
public TProcessorFactory(TProcessor processor) {
processor_ = processor;
}
public TProcessor getProcessor(TTransport trans) {
return processor_;
}
public boolean isAsyncProcessor() {
return processor_ instanceof TAsyncProcessor;
}
}
其中仅有一个processor_,并且会在getProcessor()方法中原样返回。
new TSimpleServer()
继续,进入TSimpleServer的构造方法:
public TSimpleServer(AbstractServerArgs args) {
super(args);
}
TSimpleServer实现了TServer,TServer的构造方法如下:
protected TServer(AbstractServerArgs args) {
processorFactory_ = args.processorFactory;
serverTransport_ = args.serverTransport;
inputTransportFactory_ = args.inputTransportFactory;
outputTransportFactory_ = args.outputTransportFactory;
inputProtocolFactory_ = args.inputProtocolFactory;
outputProtocolFactory_ = args.outputProtocolFactory;
}
这一步是为TSimpleServer设置各种属性,即将AbstractServerArgs中的属性赋值到TServer的属性中 。args中的属性值,就是TServer.Args(transport)中设置的以及thrift提供的默认内容。
server.serve()
接下来就是服务端的重头戏了:提供对外服务,方法为TSimpleServer#serve:
public void serve() {
try {
// 启动监听,表示可以监听端口的连接了
serverTransport_.listen();
} catch (TTransportException ttx) {
LOGGER.error("Error occurred during listening.", ttx);
return;
}
if (eventHandler_ != null) {
// 运行 eventHandler_.preServe() 方法
eventHandler_.preServe();
}
setServing(true);
// 死循环不断获取连接
while (!stopped_) {
TTransport client = null;
TProcessor processor = null;
TTransport inputTransport = null;
TTransport outputTransport = null;
TProtocol inputProtocol = null;
TProtocol outputProtocol = null;
ServerContext connectionContext = null;
try {
// 获取连接,这里会阻塞
client = serverTransport_.accept();
if (client != null) {
processor = processorFactory_.getProcessor(client);
inputTransport = inputTransportFactory_.getTransport(client);
outputTransport = outputTransportFactory_.getTransport(client);
inputProtocol = inputProtocolFactory_.getProtocol(inputTransport);
outputProtocol = outputProtocolFactory_.getProtocol(outputTransport);
if (eventHandler_ != null) {
// 运行 eventHandler_.createContext(...) 方法
connectionContext = eventHandler_.createContext(inputProtocol, outputProtocol);
}
while (true) {
if (eventHandler_ != null) {
// 运行 eventHandler_.processContext(...) 方法
eventHandler_.processContext(connectionContext, inputTransport, outputTransport);
}
// 处理方法操作,这里会执行 HelloServiceImpl 的方法
processor.process(inputProtocol, outputProtocol);
}
}
} catch (...) {
...
}
if (eventHandler_ != null) {
// 运行 eventHandler_.deleteContext(...) 方法
eventHandler_.deleteContext(connectionContext, inputProtocol, outputProtocol);
}
if (inputTransport != null) {
inputTransport.close();
}
if (outputTransport != null) {
outputTransport.close();
}
}
setServing(false);
}
这个就是服务端处理请求的整个流程了,下面我们一步步来分析。
启动服务监听:serverTransport_.listen()
TServerSocket#listen方法内容如下:
public void listen() throws TTransportException {
// Make sure to block on accept
if (serverSocket_ != null) {
try {
serverSocket_.setSoTimeout(0);
} catch (SocketException sx) {
LOGGER.error("Could not set socket timeout.", sx);
}
}
}
可以看到,仅是配置了一个属性:soTimeout,这个soTimeout是啥意思呢?我们直接看它的注释:
以指定的超时时间启用/禁用SO_TIMEOUT ,以毫秒为单位。
通过将此选项设置为非零超时,对此ServerSocket的accept()调用将仅在此时间量内阻塞。
如果超时到期,则将抛出java.net.SocketTimeoutException ,尽管ServerSocket仍然有效。
必须先启用该选项,然后才能执行阻止操作。
超时时间必须> 0 。 零超时被解释为无限超时。Enable/disable {@link SocketOptions#SO_TIMEOUT SO_TIMEOUT} with the
specified timeout, in milliseconds. With this option set to a non-zero
timeout, a call to accept() for this ServerSocket
will block for only this amount of time. If the timeout expires,
a java.net.SocketTimeoutException is raised, though the
ServerSocket is still valid. The option must be enabled
prior to entering the blocking operation to have effect. The
timeout must be {@code > 0}.
A timeout of zero is interpreted as an infinite timeout.
也不是说,这个参数是用来设置超时时间的,这里设置成了0,表示不限超时时间。
运行 eventHandler_.xxx(...) 方法
eventHandler_类型为TServerEventHandler,它的定义如下:
public interface TServerEventHandler {
/**
* Called before the server begins.
* 服务开启前调用
*/
void preServe();
/**
* Called when a new client has connected and is about to being processing.
* 服务创建 context 时调用
*/
ServerContext createContext(TProtocol input,
TProtocol output);
/**
* Called when a client has finished request-handling to delete server
* context.
* 服务关闭时调用
*/
void deleteContext(ServerContext serverContext, TProtocol input, TProtocol output);
/**
* Called when a client is about to call the processor.
* 处理连接请求
*/
void processContext(ServerContext serverContext,
TTransport inputTransport, TTransport outputTransport);
可以看到这是个接口,里面定义了几个方法,会在服务处理的过程中调用,当我们要监听连接的某些操作时,就可以实现这个接口,然后将其添加到TServerSocket,像这样:
TServerTransport transport = new TServerSocket(port);
TServer server = new TSimpleServer(new TServer.Args(transport).processor(processor));
// 设置 ServerEventHandler
server.setServerEventHandler(new MyTServerEventHandler());
server.serve();
获取连接与处理
server.serve()的核心功能如下:
while (!stopped_) {
...
try {
// 获取连接,这里会阻塞
client = serverTransport_.accept();
if (client != null) {
processor = processorFactory_.getProcessor(client);
...
while (true) {
...
// 处理方法操作,这里会执行 HelloServiceImpl 的方法
processor.process(inputProtocol, outputProtocol);
}
}
} catch (...) {
...
}
使用 TServerSocket#accept获取连接请求,这是jdk提供的方法使用 processorFactory_.getProcessor(client);方法获取processor使用 processor.process(...)执行具体的方法
这块先有个印象吧,后面分析执行时,再使用调试的方式来具体分析。
客户端启动
客户端启动类为HelloClient,这个类是我们自主实现的,代码如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
TTransport transport = null;
try {
// 打开连接
transport = new TSocket("localhost", SERVER_PORT);
transport.open();
// 指定传输协议
TProtocol protocol = new TBinaryProtocol(transport);
// 创建客户端
HelloService.Client client = new HelloService.Client(protocol);
// 调用 HelloService#hello 方法
String result = client.hello("thrift world");
System.out.println("result=" + result);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(null != transport) {
transport.close();
}
}
}
打开一个连接
打开连接的操作如下:
transport = new TSocket("localhost", SERVER_PORT);
transport.open();
进入TSocket的构造方法:
public TSocket(TConfiguration config, String host, int port, int socketTimeout,
int connectTimeout) throws TTransportException {
// 参数赋值
super(config);
host_ = host;
port_ = port;
socketTimeout_ = socketTimeout;
connectTimeout_ = connectTimeout;
initSocket();
}
/**
* 初始化 socket 对象
*/
private void initSocket() {
socket_ = new Socket();
try {
socket_.setSoLinger(false, 0);
socket_.setTcpNoDelay(true);
socket_.setKeepAlive(true);
socket_.setSoTimeout(socketTimeout_);
} catch (SocketException sx) {
LOGGER.error("Could not configure socket.", sx);
}
}
这一步只是创建了TSocket对象,TSocket的构造方法里只是做了一些赋值操作。
再来看看TSocket#open方法:
public void open() throws TTransportException {
// 省略判断操作
...
try {
// 连接
socket_.connect(new InetSocketAddress(host_, port_), connectTimeout_);
inputStream_ = new BufferedInputStream(socket_.getInputStream());
outputStream_ = new BufferedOutputStream(socket_.getOutputStream());
} catch (IOException iox) {
close();
throw new TTransportException(TTransportException.NOT_OPEN, iox);
}
}
打开连接的方法为java.net.Socket#connect(java.net.SocketAddress, int),使用的是BIO.
获取一个客户端
TProtocol protocol = new TBinaryProtocol(transport);
HelloService.Client client = new HelloService.Client(protocol);
这段代码先使用new TBinaryProtocol(transport)创建了一个二进制协议对象,进入TBinaryProtocol#TBinaryProtocol(...) 方法:
public TBinaryProtocol(TTransport trans, long stringLengthLimit,
long containerLengthLimit, boolean strictRead, boolean strictWrite) {
super(trans);
stringLengthLimit_ = stringLengthLimit;
containerLengthLimit_ = containerLengthLimit;
strictRead_ = strictRead;
strictWrite_ = strictWrite;
}
这个方法先是调用了父类的构造方法,然后是一堆的赋值操作,我们进入父类的构造方法TProtocol#TProtocol(...)中:
protected TProtocol(TTransport trans) {
trans_ = trans;
}
可以看到,整个创建过程就只是一些赋值操作。
我们来看看看客户端的获取,进入HelloService.Client#Client(...)方法:
public Client(org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocol prot)
{
super(prot, prot);
}
继续,进入TServiceClient:
public abstract class TServiceClient {
public TServiceClient(TProtocol prot) {
this(prot, prot);
}
public TServiceClient(TProtocol iprot, TProtocol oprot) {
iprot_ = iprot;
oprot_ = oprot;
}
...
}
可以看到,客户端的创建依然是一些赋值操作。
执行操作
准备就绪后,接下来就可以执行方法了,即:
String result = client.hello("thrift world");
这一行代码最终调用的是服务端的HelloService#hello方法,也就是HelloServiceHandler#hello:
public class HelloServiceHandler implements HelloService.Iface {
@Override
public String hello(String text) throws TException {
return "hello " + text;
}
}
在客户端调用本地方法,如何能调用到远程服务的方法呢?接下来我们就来分析这其中的操作。
执行流程
客户端调用服务端由HelloService.Client#hello发起,我们进入该方法:
public java.lang.String hello(java.lang.String text) throws org.apache.thrift.TException
{
send_hello(text);
return recv_hello();
}
这个方法就两行代码,从代码的命名来看,大致能猜出这两行代码的含义:
send_hello(...):发送hello()方法的调用请求recv_hello(...):接收hello()方法的调用结果
客户端发送请求:send_hello(text)
进入 send_hello(text) 方法:
public void send_hello(java.lang.String text) throws org.apache.thrift.TException
{
hello_args args = new hello_args();
args.setText(text);
sendBase("hello", args);
}
hello_args 封装就是方法的参数,设置完参数后,最终调用sendBase(...)方法:
TServiceClient#sendBase(String, TBase<?,?>, byte)
private void sendBase(String methodName, TBase<?,?> args, byte type) throws TException {
oprot_.writeMessageBegin(new TMessage(methodName, type, ++seqid_));
args.write(oprot_);
oprot_.writeMessageEnd();
oprot_.getTransport().flush();
}
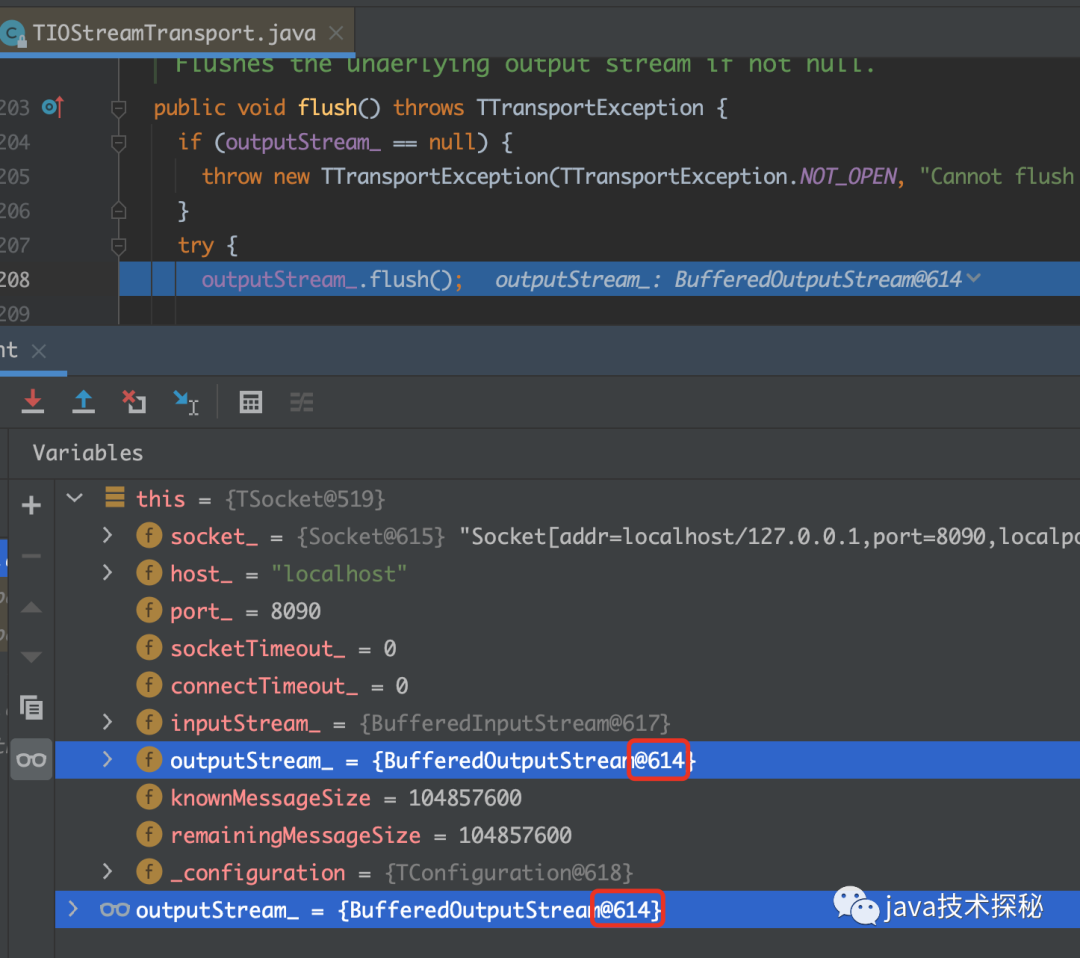
当前对象是TSocket的实例,outputStream_.flush()中的outputStream_就是TSocket持有的outputStream_。执行完成flush操作后,数据就发送到服务端了,发送的数据主要为方法名与参数值。
客户端接收响应:recv_hello()
接下来我们来看看数据的接收流程,也就是recv_hello()方法:
HelloService.Client#recv_hello
public java.lang.String recv_hello() throws org.apache.thrift.TException
{
hello_result result = new hello_result();
// 继续处理
receiveBase(result, "hello");
if (result.isSetSuccess()) {
return result.success;
}
throw new org.apache.thrift.TApplicationException(
org.apache.thrift.TApplicationException.MISSING_RESULT,
"hello failed: unknown result");
}
在以上方法中,先是创建了一个hello_result对象,该对象用来保存方法的执行结果,然后调用receiveBase(...)方法:TServiceClient#receiveBase
protected void receiveBase(TBase<?,?> result, String methodName) throws TException {
TMessage msg = iprot_.readMessageBegin();
...
// read 操作
result.read(iprot_);
iprot_.readMessageEnd();
}
这个方法主要调用了result.read(iprot_)方法,继续:
HelloService.hello_result.hello_resultStandardScheme#read
public void read(org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocol iprot, hello_result struct)
throws org.apache.thrift.TException {
org.apache.thrift.protocol.TField schemeField;
iprot.readStructBegin();
while (true)
{
schemeField = iprot.readFieldBegin();
// 阅读完成的标识
if (schemeField.type == org.apache.thrift.protocol.TType.STOP) {
break;
}
switch (schemeField.id) {
case 0: // SUCCESS
if (schemeField.type == org.apache.thrift.protocol.TType.STRING) {
// 在这里读取结果,返回结果是String类型,直接读取
struct.success = iprot.readString();
struct.setSuccessIsSet(true);
} else {
org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocolUtil.skip(iprot, schemeField.type);
}
break;
default:
org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocolUtil.skip(iprot, schemeField.type);
}
iprot.readFieldEnd();
}
iprot.readStructEnd();
struct.validate();
}
这一步就是读取返回结果的内容了。
到了这里,客户端的读写操作也就完成了。
服务端处理:TSimpleServer#serve
接下来我们来看看服务端是如何处理请求的,进入TSimpleServer#serve方法:
public void serve() {
...
while (!stopped_) {
...
try {
client = serverTransport_.accept();
if (client != null) {
...
while (true) {
if (eventHandler_ != null) {
eventHandler_.processContext(connectionContext,
inputTransport, outputTransport);
}
// 这里处理请求
processor.process(inputProtocol, outputProtocol);
}
}
} catch (...) {
...
}
...
}
setServing(false);
}
继续进入 org.apache.thrift.TBaseProcessor#process:
@Override
public void process(TProtocol in, TProtocol out) throws TException {
TMessage msg = in.readMessageBegin();
// 获取 ProcessFunction
ProcessFunction fn = processMap.get(msg.name);
if (fn == null) {
...
} else {
// 继续处理
fn.process(msg.seqid, in, out, iface);
}
}
通过调试的方式,可以看到得到的fn如下:
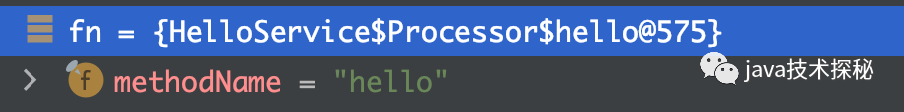
继续进入 org.apache.thrift.ProcessFunction#process 方法:
public final void process(int seqid, TProtocol iprot, TProtocol oprot, I iface) throws TException {
T args = getEmptyArgsInstance();
try {
// 读取参数
args.read(iprot);
} catch (TProtocolException e) {
...
return;
}
iprot.readMessageEnd();
TSerializable result = null;
byte msgType = TMessageType.REPLY;
try {
// 处理结果
result = getResult(iface, args);
} catch (...) {
...
}
if(!isOneway()) {
...
}
}
这个方法中主要是读取方法的执行参数,读取到的内容如下:

到这里,服务端的类、方法以及方法的参数都已经获取了,接下来就是方法的执行了,继续进入HelloService.Processor.hello#getResult:
public hello_result getResult(I iface, hello_args args) throws org.apache.thrift.TException {
hello_result result = new hello_result();
result.success = iface.hello(args.text);
return result;
}
这个iface就是HelloServiceImpl,最终执行的就是HelloServiceImpl#hello方法了。
总结
本文主要分析了thrift请求处理流程,过程如下:
客户端调用本地方法时,本地方法会把调用的类名、方法名以及方法参数通过 socket连接发往服务端;服务端收到客户端的数据后,根据类名与方法名找到对应的处理方法,调用方法时使用的参数值就是客户端传递的参数值; 服务端调用完具体的方法后,再将方法的执行结果通过 socket返回给客户端;客户端通过 socket接收到结果后,再把结果返回给本地方法。
限于作者个人水平,文中难免有错误之处,欢迎指正!原创不易,商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
本文首发于微信公众号 「Java技术探秘」,如果您喜欢本文,欢迎关注该公众号,让我们一起在技术的世界里探秘吧!
