综述:目标检测中的多尺度检测方法
导读
本文从降低下采样率与空洞卷积、多尺度训练、优化Anchor尺寸设计、深层和浅层特征融合等多个方面入手,对目标检测中的多尺度检测方法进行了全面概述,并介绍了多尺度检测相关方法。
前面的话
小物体由于其尺寸较小,可利用的特征有限,这使得其检测较为困难。当前的检测算法对于小物体并不友好,体现在以下4个方面:
1 降低下采样率与空洞卷积
2 多尺度训练
3 优化Anchor尺寸设计
4 深层和浅层特征融合
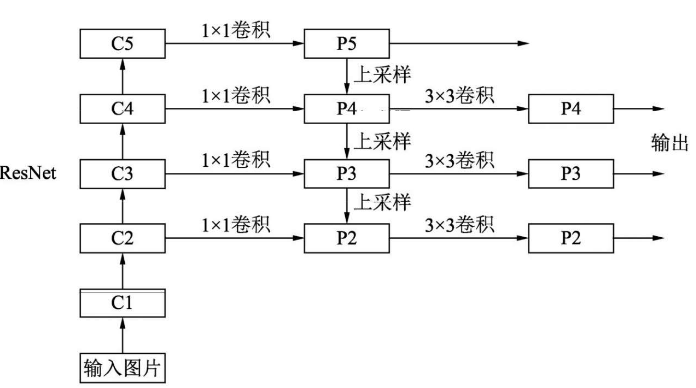
import torch.nn as nnimport torch.nn.functional as Fimport mathclass Bottleneck(nn.Module):expansion = 4def __init__(self, in_planes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None):super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()self.bottleneck = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(in_planes, planes, 1, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(planes),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),nn.Conv2d(planes, planes, 3, stride, 1, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(planes),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),nn.Conv2d(planes, self.expansion * planes, 1, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(self.expansion * planes),)self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)self.downsample = downsampledef forward(self, x):identity = xout = self.bottleneck(x)if self.downsample is not None:identity = self.downsample(x)out += identityout = self.relu(out)return outclass FPN(nn.Module):def __init__(self, layers):super(FPN, self).__init__()self.inplanes = 64self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 64, 7, 2, 3, bias=False)self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(3, 2, 1)self.layer1 = self._make_layer(64, layers[0])self.layer2 = self._make_layer(128, layers[1], 2)self.layer3 = self._make_layer(256, layers[2], 2)self.layer4 = self._make_layer(512, layers[3], 2)self.toplayer = nn.Conv2d(2048, 256, 1, 1, 0)self.smooth1 = nn.Conv2d(256, 256, 3, 1, 1)self.smooth2 = nn.Conv2d(256, 256, 3, 1, 1)self.smooth3 = nn.Conv2d(256, 256, 3, 1, 1)self.latlayer1 = nn.Conv2d(1024, 256, 1, 1, 0)self.latlayer2 = nn.Conv2d( 512, 256, 1, 1, 0)self.latlayer3 = nn.Conv2d( 256, 256, 1, 1, 0)def _make_layer(self, planes, blocks, stride=1):downsample = Noneif stride != 1 or self.inplanes != Bottleneck.expansion * planes:downsample = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(self.inplanes, Bottleneck.expansion * planes, 1, stride, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(Bottleneck.expansion * planes))layers = []layers.append(Bottleneck(self.inplanes, planes, stride, downsample))self.inplanes = planes * Bottleneck.expansionfor i in range(1, blocks):layers.append(Bottleneck(self.inplanes, planes))return nn.Sequential(*layers)def _upsample_add(self, x, y):_,_,H,W = y.shapereturn F.upsample(x, size=(H,W), mode='bilinear') + ydef forward(self, x):c1 = self.maxpool(self.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x))))c2 = self.layer1(c1)c3 = self.layer2(c2)c4 = self.layer3(c3)c5 = self.layer4(c4)p5 = self.toplayer(c5)p4 = self._upsample_add(p5, self.latlayer1(c4))p3 = self._upsample_add(p4, self.latlayer2(c3))p2 = self._upsample_add(p3, self.latlayer3(c2))p4 = self.smooth1(p4)p3 = self.smooth2(p3)p2 = self.smooth3(p2)return p2, p3, p4, p5
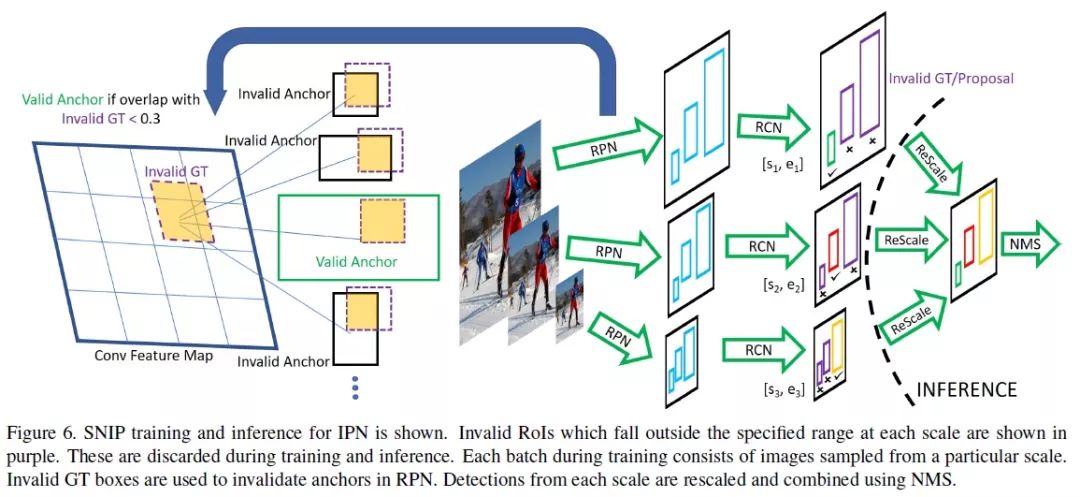
5 SNIP:尺度归一化
论文地址:
https://arxiv.org/abs/1711.08189
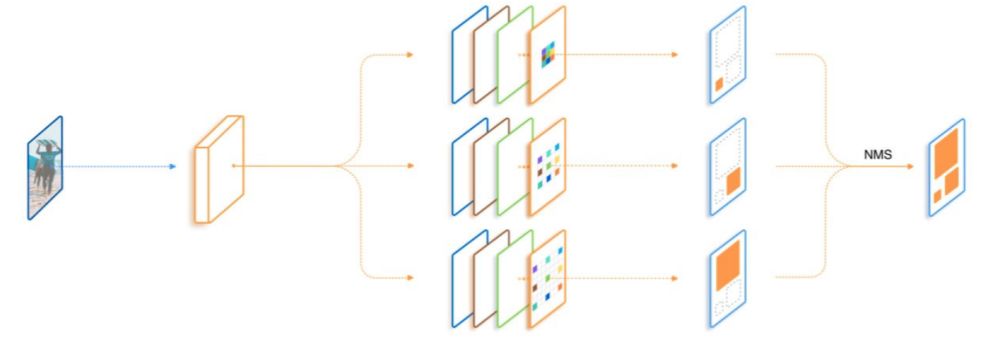
6 TridentNet:三叉戟网络
评论
