AST抽象语法树和Babel插件
var a = 3;a + 5
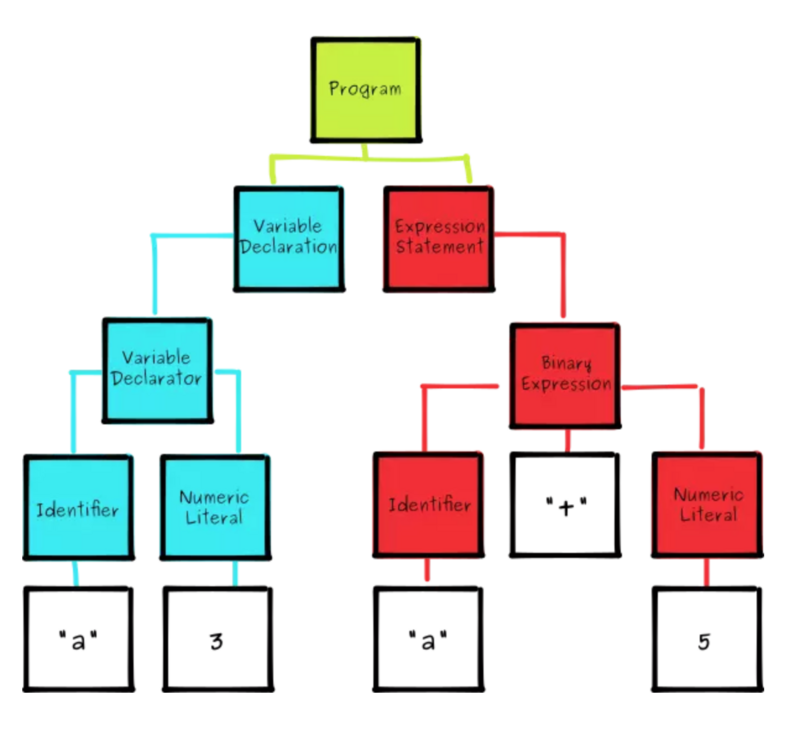
VariableDeclaration变量声明 Identifier标识符+Numeric Literal数字字面量 BinaryExpression(二项式) Identifier标识符,operator二项式运算符,Numeric Literal数字字面量
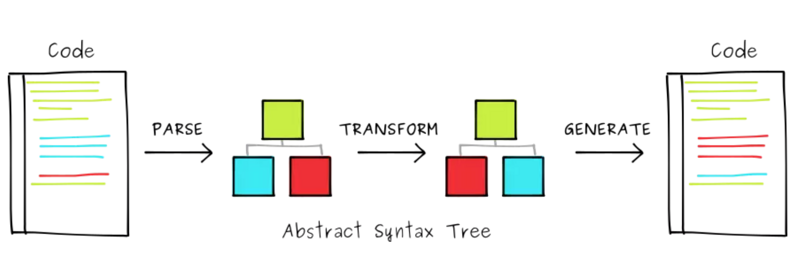
编译器过程
解析 转换 生成(代码生成)
npm install esprima estraverse escodegenconst esprima = require('esprima')const estraverse = require('estraverse')const escodegen = require('escodegen')let code = `var a = 3`// Parse(解析)let ast = esprima.parseScript(code);//Transform(转换)estraverse.traverse(ast, {enter(node) {console.log("enter",node.type);},leave(node) {console.log("leave",node.type);}});// Generate(代码生成)const result = escodegen.generate(ast);
Babel对于AST的遍历是深度优先遍历,对于AST上的每一个分支Babel都会先向下遍历走到尽头,然后再向上遍历退出刚遍历过的例程,然后寻找下一个分支。
enter Programenter VariableDeclarationenter VariableDeclaratorenter Identifierleave Identifierenter Literalleave Literalleave VariableDeclaratorleave VariableDeclarationleave Program
estraverse.traverse(ast, {enter(node) {if(node.type === "Literal"){node.value = "change";}}});// var a = "change";
babel插件
npm install @babel/core
// es2015 的 const 和 arrow functionconst add = (a, b) => a + b;// Babel 转译后var add = function add(a, b) {return a + b;};
{"type": "Program","body": [{"type": "VariableDeclaration", // 变量声明"declarations": [ // 具体声明{"type": "VariableDeclarator", // 变量声明"id": {"type": "Identifier", // 标识符(最基础的)"name": "add" // 函数名},"init": {"type": "ArrowFunctionExpression", // 箭头函数"id": null,"expression": true,"generator": false,"params": [ // 参数{"type": "Identifier","name": "a"},{"type": "Identifier","name": "b"}],"body": { // 函数体"type": "BinaryExpression", // 二项式"left": { // 二项式左边"type": "Identifier","name": "a"},"operator": "+", // 二项式运算符"right": { // 二项式右边"type": "Identifier","name": "b"}}}}],"kind": "const"}],"sourceType": "module"}
const babel = require('babel-core');const t = require('babel-types');let code = `let add = (a, b)=>{return a+b}`;let ArrowPlugins = {visitor: {ArrowFunctionExpression(path) {let { node } = path;let body = node.body;let params = node.params;let r = t.functionExpression(null, params, body, false, false);path.replaceWith(r);}}}let result = babel.transform(code, {plugins: [ArrowPlugins]})console.log(result.code);
类转换
const babel = require("@babel/core");const typs = require("@babel/types");const code = `class Animal {constructor(name){this.name = name}getName(){return this.name}}`const classPlugins = {visitor:{ClassDeclaration(path){let node = path.node;let body = node.body.body;let id = node.id;let params = node.params;let methods = body.map(method=>{if(method.kind === "constructor"){return typs.functionDeclaration(id, method.params, method.body)}else{// Animal.prototypelet left = typs.memberExpression(id,typs.identifier("prototype"));// Animal.prototype.getNameleft = typs.memberExpression(left,method.key);let right = typs.functionExpression(null,method.params,method.body);return typs.assignmentExpression("=",left,right);}})path.replaceWithMultiple(methods);}}}const result = babel.transform(code, {plugins: [classPlugins]})console.log(result.code)
导入转换
const babel = require('@babel/core');const types = require('@babel/types');const code = `import antd,{Button} from "antd"`;const importPlugin = {visitor: {ImportDeclaration(path) {let node = path.nodelet specifiers = node.specifiersif (!(specifiers.length == 1 &&types.isImportDefaultSpecifier(specifiers[0]))) {specifiers = specifiers.map((specifier) => {let local = types.importDefaultSpecifier(specifier.local);if (types.isImportDefaultSpecifier(specifier)) {return types.importDeclaration([local],types.stringLiteral(node.source.value))} else {return types.importDeclaration([local],types.stringLiteral(node.source.value+"/lib/"+specifier.local.name))}});path.replaceWithMultiple(specifiers)}},},}const result = babel.transform(code, {plugins: [importPlugin],});console.log(result.code)
参考链接
看了就懂的AST和Babel工作流程:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/m-EJljsARM5dUlu-IXJnKQ 编写自定义babel转换的分步指南:https://lihautan.com/step-by-step-guide-for-writing-a-babel-transformation/ 通过构建自己的Babel插件了解AST:https://www.sitepoint.com/understanding-asts-building-babel-plugin/
评论
