从 Babel 到 AST 进阶,学起来!
大厂技术 高级前端 Node进阶
点击上方 程序员成长指北,关注公众号
回复1,加入高级Node交流群
Babel
在我很小的时候,有人告诉我代码要写的有艺术感。我当时内心:......真高级啊,装起来了。但是伴随着时代的变迁,各种提案的通过,js的写法也逐渐升级,语法糖也多了起来,原来的三四行代码,啪叽,一个不留神,一行就能搞定,整篇代码一眼望去,会让人觉得,嗯,有点东西。如下是一个小小的demo:
const demo = () => [1,2,3].map(e => e + 1)
Babel转换后,这行代码其实是这样子的:
var demo = function demo() {
return [1, 2, 3].map(function (e) {
return e + 1;
});
};
如此,才能做到向下兼容,以便可以运行在各种有可能存在的环境中,所以Babel的主要作用如下:
-
代码转换 -
通过Polyfill方式在目标环境中添加缺失的特性(@babel/polyfill)
@babel/polyfill 模块包括 core-js 和一个自定义的 regenerator runtime 模块,可以模拟完整的 ES2015+ 环境,这意味着可以使用诸如 Promise 和 WeakMap 之类的新的内置组件、 Array.from 或 Object.assign 之类的静态方法、Array.prototype.includes 之类的实例方法以及生成器函数(前提是使用了 @babel/plugin-transform-regenerator 插件)。为了添加这些功能,polyfill 将添加到全局范围和类似 String 这样的内置原型中(会对全局环境造成污染)。其实在Babel7.4.0以后,@babel/polyfill就已经被弃用,在源码中直接引入了corejs 和 regenerator,而在实际运用中可用@babel/preset-env进行替代。
在实际项目中,Babel可通过多种方式进行配置(详情可以在下文源码分析中有所了解),在这里,我们以babel.config.js为实例:
module.exports = {
presets: [...],
plugins: [...],
}
plugins插件是Babel得以进行转换的基础和规则,而presets预设则是一组插件的集合,具体可以在源码分析中进行了解。 当两个转换插件都将处理“程序(Program)”的某个代码片段,则将根据转换plugins或 presets的排列顺序依次执行:
-
插件在 Presets 前运行。 -
插件顺序从前往后排列。 -
Preset 顺序是颠倒的(从后往前(具体原因源码分析也会有所解释))。
而Babel的编译过程可以分为三个阶段:
-
解析(Parsing):将代码字符串解析成抽象语法树。 -
转换(Transformation):对抽象语法树进行转换操作。 -
生成(Code Generation): 根据变换后的抽象语法树再生成代码字符串。
而在这个过程中,最重要的便是AST,如下。
AST
What is AST
经典面试问题:Babel的原理是什么? 答:解析-转换-生成。其实说白了就是把代码通过某种规则变成一种特定的数据结构,然后在这种数据结构上做一些增删改查,然后再把这个数据结构变回代码,然后因为是《前端》,各种层级分明的树,所以AST就是这么一棵树。往深了走就是那门绝学--《编译原理》。
作为一名前端,很难不和AST有接触,Webpack、Eslint...又或者是底层、优化...都和AST有着密不可分的关系。
AST (abstract syntax tree (抽象语法树))作为源代码语法结构的一种抽象表示。它以树状的形式表现编程语言的语法结构,树上的每个节点都表示源代码中的一种结构。
生成AST主要分为两个步骤:
词法分析(lexical analyzer)
对代码进行拆分,通过预先设定好的规则遍历代码将每个字符转换为词法单元(token),从而生成token列表。 将demo代码转换为token如下:
[
{
"type": "Keyword",
"value": "const"
},
{
"type": "Identifier",
"value": "demo"
},
{
"type": "Punctuator",
"value": "="
},
{
"type": "Punctuator",
"value": "("
},
{
"type": "Punctuator",
"value": ")"
},
{
"type": "Punctuator",
"value": "=>"
},
{
"type": "Punctuator",
"value": "["
},
{
"type": "Numeric",
"value": "1"
},
{
"type": "Punctuator",
"value": ","
},
{
"type": "Numeric",
"value": "2"
},
{
"type": "Punctuator",
"value": ","
},
{
"type": "Numeric",
"value": "3"
},
{
"type": "Punctuator",
"value": "]"
},
{
"type": "Punctuator",
"value": "."
},
{
"type": "Identifier",
"value": "map"
},
{
"type": "Punctuator",
"value": "("
},
{
"type": "Identifier",
"value": "e"
},
{
"type": "Punctuator",
"value": "=>"
},
{
"type": "Identifier",
"value": "e"
},
{
"type": "Punctuator",
"value": "+"
},
{
"type": "Numeric",
"value": "1"
},
{
"type": "Punctuator",
"value": ")"
}
]
语法分析(Syntax analyzer)
在得到token列表之后,通过语法规则可以将其关联起来,形成AST,demo代码所生成的AST树如下所示(实在太长了,不全放出了):
在线AST转换网站:https://astexplorer.net/[1]
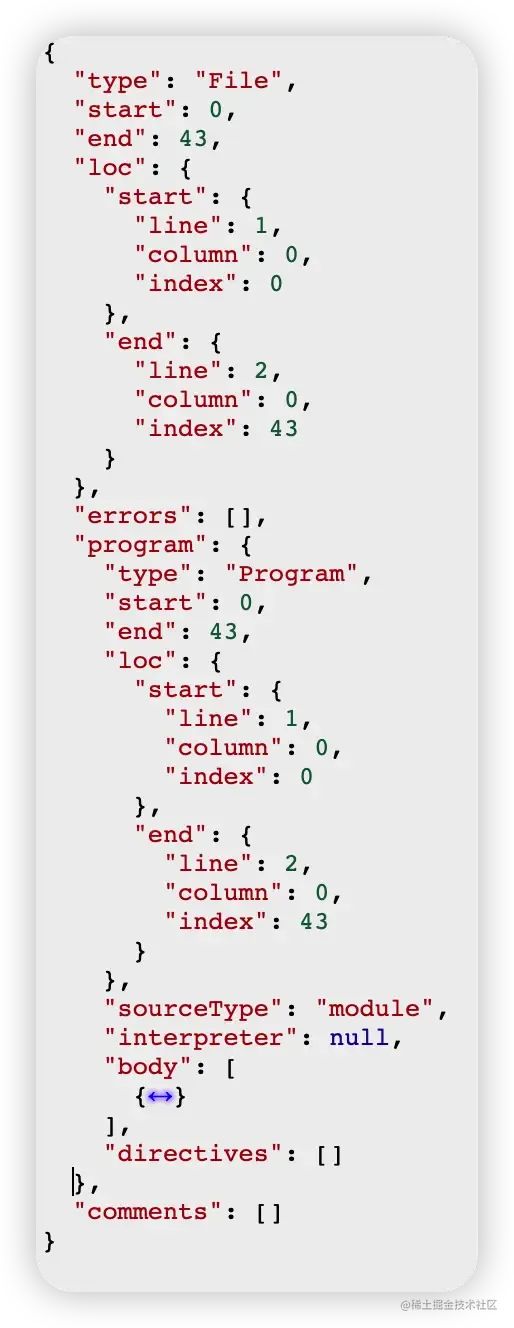

AST with Babel
ok, 我们想通过Babel做如此一系列操作,去生成AST,去转换AST,然后再变回js,我们以demo为例,通过调用Babel所提供的API实现这一操作:
const transformLetToVar = babel.transformSync(`${beforeFile}`, {
plugins: [
{
visitor: {
// [const, let] 转化为 var
VariableDeclaration(path) {
if (path.node.kind === 'let' || path.node.kind === 'const') {
path.node.kind = 'var';
}
},
// () => {} 转化为 function,注意没有{}的情况
ArrowFunctionExpression(path) {
let body = path.node.body;
if (!t.isBlockStatement(body)) {
body = t.blockStatement([t.returnStatement(body)]);
}
path.replaceWith(t.functionExpression(null, path.node.params, body, false, false));
},
// 处理数组
CallExpression(path) {
if (path.get('callee.property').node.name === 'map') {
const callback = path.node.arguments[0];
if (t.isArrowFunctionExpression(callback)) {
let body = callback.body;
if (!t.isBlockStatement(body)) {
body = t.blockStatement([t.returnStatement(body)]);
}
path.node.arguments[0] = t.functionExpression(
null,
callback.params,
body,
false,
false,
);
}
}
},
},
},
],
});
代码中采用了@Babel/core中的transformSync方法,它是@Babel/parser / @babel/traverse / @babel/generator的集合,如采用这三种方法,代码如下:
// Step 1: Parse the code to AST
const ast = parser.parse(code);
// Step 2: Traverse and modify the AST
traverse(ast, {
VariableDeclaration(path) {
if (path.node.kind === 'let' || path.node.kind === 'const') {
path.node.kind = 'var';
}
},
ArrowFunctionExpression(path) {
let body = path.node.body;
if (!t.isBlockStatement(body)) {
body = t.blockStatement([t.returnStatement(body)]);
}
path.replaceWith(t.functionExpression(null, path.node.params, body, false, false));
},
CallExpression(path) {
if (path.get('callee.property').node.name === 'map') {
const callback = path.node.arguments[0];
if (t.isArrowFunctionExpression(callback)) {
let body = callback.body;
if (!t.isBlockStatement(body)) {
body = t.blockStatement([t.returnStatement(body)]);
}
path.node.arguments[0] = t.functionExpression(null, callback.params, body, false, false);
}
}
},
});
// Step 3: Generate new code from the modified AST
const output = generator(ast, {}, code);
@Babel/core 源码解析
在上文通过Babel转换时,用到了babel.transformSync,其便是来自@Babel/core,我们以它为开始,进行一波较为简易的源码分析。 首先来到Babel/core/index.js,主要包含一些基本的导入导出,其中有关babel.transformSync的如下:
export {
transform,
transformSync,
transformAsync,
type FileResult,
} from "./transform";
直接来到Babel/core/transform:
type Transform = {
(code: string, callback: FileResultCallback): void,
(code: string, opts: InputOptions | undefined | null, callback: FileResultCallback): void,
(code: string, opts?: InputOptions | null): FileResult | null,
};
const transformRunner = gensync(function* transform(
code: string,
opts?: InputOptions,
): Handler<FileResult | null> {
const config: ResolvedConfig | null = yield* loadConfig(opts);
if (config === null) return null;
return yield* run(config, code);
});
export const transform: Transform = function transform(
code,
optsOrCallback?: InputOptions | null | undefined | FileResultCallback,
maybeCallback?: FileResultCallback,
) {
let opts: InputOptions | undefined | null;
let callback: FileResultCallback | undefined;
if (typeof optsOrCallback === 'function') {
callback = optsOrCallback;
opts = undefined;
} else {
opts = optsOrCallback;
callback = maybeCallback;
}
if (callback === undefined) {
if (process.env.BABEL_8_BREAKING) {
throw new Error(
"Starting from Babel 8.0.0, the 'transform' function expects a callback. If you need to call it synchronously, please use 'transformSync'.",
);
} else {
// console.warn(
// "Starting from Babel 8.0.0, the 'transform' function will expect a callback. If you need to call it synchronously, please use 'transformSync'.",
// );
return beginHiddenCallStack(transformRunner.sync)(code, opts);
}
}
beginHiddenCallStack(transformRunner.errback)(code, opts, callback);
};
export function transformSync(...args: Parameters<typeof transformRunner.sync>) {
return beginHiddenCallStack(transformRunner.sync)(...args);
}
export function transformAsync(...args: Parameters<typeof transformRunner.async>) {
return beginHiddenCallStack(transformRunner.async)(...args);
}
我们会发现其实他们都在调用transformRunner,该方法传入两个参数code和opts:
const transformRunner = gensync(function* transform(
code: string,
opts?: InputOptions,
): Handler<FileResult | null> {
const config: ResolvedConfig | null = yield* loadConfig(opts);
if (config === null) return null;
return yield* run(config, code);
});
其中InputOptions为:
export type InputOptions = ValidatedOptions;
export type ValidatedOptions = {
cwd?: string,
filename?: string,
filenameRelative?: string,
babelrc?: boolean,
babelrcRoots?: BabelrcSearch,
configFile?: ConfigFileSearch,
root?: string,
rootMode?: RootMode,
code?: boolean,
ast?: boolean,
cloneInputAst?: boolean,
inputSourceMap?: RootInputSourceMapOption,
envName?: string,
caller?: CallerMetadata,
extends?: string,
env?: EnvSet<ValidatedOptions>,
ignore?: IgnoreList,
only?: IgnoreList,
overrides?: OverridesList,
// Generally verify if a given config object should be applied to the given file.
test?: ConfigApplicableTest,
include?: ConfigApplicableTest,
exclude?: ConfigApplicableTest,
presets?: PluginList,
plugins?: PluginList,
passPerPreset?: boolean,
assumptions?: {
[name: string]: boolean,
},
// browserslists-related options
targets?: TargetsListOrObject,
browserslistConfigFile?: ConfigFileSearch,
browserslistEnv?: string,
// Options for @babel/generator
retainLines?: boolean,
comments?: boolean,
shouldPrintComment?: Function,
compact?: CompactOption,
minified?: boolean,
auxiliaryCommentBefore?: string,
auxiliaryCommentAfter?: string,
// Parser
sourceType?: SourceTypeOption,
wrapPluginVisitorMethod?: Function,
highlightCode?: boolean,
// Sourcemap generation options.
sourceMaps?: SourceMapsOption,
sourceMap?: SourceMapsOption,
sourceFileName?: string,
sourceRoot?: string,
// Deprecate top level parserOpts
parserOpts?: ParserOptions,
// Deprecate top level generatorOpts
generatorOpts?: GeneratorOptions,
};
这里面便包含例如plugins和presets这些属性,其中plugins便是上文我们调用babel.transformSync时的第二个参数,既插件,Babel的插件是实现代码转换的基础单位。每个插件都是一个小的 JavaScript 程序,它告诉 Babel 如何进行特定的代码转换。而presets则是一组预先定义好的插件的集合。因为 JavaScript 的新特性太多,如果每次都要手动指定所有需要的插件,那么配置起来会非常繁琐,因此Babel 提供了预设,让我们可以用一行代码引入一整组插件。
回到transformRunner,该方法主体分为两步,调用loadConfig方法和调用run方法。首先来看loadConfig,该方法实为babel-core/src/config/full.ts中的loadFullConfig方法,这个方法主体就干了三件事,分别是处理配置、处理presets以及处理plugins,源码如下逐步分解进行分析:
export default gensync(function* loadFullConfig(
inputOpts: unknown,
): Handler<ResolvedConfig | null> {
const result = yield* loadPrivatePartialConfig(inputOpts);
if (!result) {
return null;
}
const { options, context, fileHandling } = result;
if (fileHandling === 'ignored') {
return null;
}
const optionDefaults = {};
const { plugins, presets } = options;
if (!plugins || !presets) {
throw new Error('Assertion failure - plugins and presets exist');
}
// 创建presetContext对象,在原有context基础上增加options.targets
const presetContext: Context.FullPreset = {
...context,
targets: options.targets,
};
// ...
});
首先调用loadPrivatePartialConfig,构建配置链。该方法接收opts,通过各种验证和转换,最终返回一个处理后的配置对象。在这个过程中,它还将输入选项中的一些值转换成绝对路径,并创建了一些新的对象和属性:
export default function* loadPrivatePartialConfig(
inputOpts: unknown,
): Handler<PrivPartialConfig | null> {
if (inputOpts != null && (typeof inputOpts !== 'object' || Array.isArray(inputOpts))) {
throw new Error('Babel options must be an object, null, or undefined');
}
const args = inputOpts ? validate('arguments', inputOpts) : {};
const {
envName = getEnv(),
cwd = '.',
root: rootDir = '.',
rootMode = 'root',
caller,
cloneInputAst = true,
} = args;
// 将cwd和rootDir转化为绝对路径
const absoluteCwd = path.resolve(cwd);
const absoluteRootDir = resolveRootMode(path.resolve(absoluteCwd, rootDir), rootMode);
// 若filename为string,则转换为绝对路径
const filename = typeof args.filename === 'string' ? path.resolve(cwd, args.filename) : undefined;
// resolveShowConfigPath方法用于解析文件路径,若路径存在并指向一个文件,则返回该路径
const showConfigPath = yield* resolveShowConfigPath(absoluteCwd);
// 将转换好的数据重新组装成一个名为context的对象
const context: ConfigContext = {
filename,
cwd: absoluteCwd,
root: absoluteRootDir,
envName,
caller,
showConfig: showConfigPath === filename,
};
// 调用buildRootChain,buildRootChain源码分解在下方
const configChain = yield* buildRootChain(args, context);
if (!configChain) return null;
const merged: ValidatedOptions = {
assumptions: {},
};
// 遍历configChain.options,合并到merged
configChain.options.forEach(opts => {
mergeOptions(merged as any, opts);
});
// 定义一个新的options对象
const options: NormalizedOptions = {
...merged,
targets: resolveTargets(merged, absoluteRootDir),
// Tack the passes onto the object itself so that, if this object is
// passed back to Babel a second time, it will be in the right structure
// to not change behavior.
cloneInputAst,
babelrc: false,
configFile: false,
browserslistConfigFile: false,
passPerPreset: false,
envName: context.envName,
cwd: context.cwd,
root: context.root,
rootMode: 'root',
filename: typeof context.filename === 'string' ? context.filename : undefined,
plugins: configChain.plugins.map(descriptor => createItemFromDescriptor(descriptor)),
presets: configChain.presets.map(descriptor => createItemFromDescriptor(descriptor)),
};
return {
options,
context,
fileHandling: configChain.fileHandling,
ignore: configChain.ignore,
babelrc: configChain.babelrc,
config: configChain.config,
files: configChain.files,
};
}
buildRootChain方法源码分解如下,该方法加载了当前目录配置文件和相对配置文件,并合并成配置链:
export function* buildRootChain(
opts: ValidatedOptions,
context: ConfigContext,
): Handler<RootConfigChain | null> {
let configReport, babelRcReport;
const programmaticLogger = new ConfigPrinter();
// 生成programmatic options(编程选项),通过`@babel/cli`或者`babel.transfrom`的方式使用时会用到
const programmaticChain = yield* loadProgrammaticChain(
{
options: opts,
dirname: context.cwd,
},
context,
undefined,
programmaticLogger,
);
if (!programmaticChain) return null;
const programmaticReport = yield* programmaticLogger.output();
let configFile;
// 如果制定了配置文件,则调用loadConfig方法去加载,若没有,则调用findRootConfig加载根目录配置
if (typeof opts.configFile === 'string') {
configFile = yield* loadConfig(opts.configFile, context.cwd, context.envName, context.caller);
} else if (opts.configFile !== false) {
configFile = yield* findRootConfig(context.root, context.envName, context.caller);
}
// ...
}
loadConfig和findRootConfi方法如下,其中findRootConfig遍历ROOT_CONFIG_FILENAMES,逐个寻找根目录(当前执行目录)配置文件并加载,两种方法都是调用readConfig:
export const ROOT_CONFIG_FILENAMES = [
'babel.config.js',
'babel.config.cjs',
'babel.config.mjs',
'babel.config.json',
'babel.config.cts',
];
export function findRootConfig(
dirname: string,
envName: string,
caller: CallerMetadata | undefined,
): Handler<ConfigFile | null> {
// 调用loadOneConfig, 传入ROOT_CONFIG_FILENAMES
return loadOneConfig(ROOT_CONFIG_FILENAMES, dirname, envName, caller);
}
function* loadOneConfig(
names: string[],
dirname: string,
envName: string,
caller: CallerMetadata | undefined,
previousConfig: ConfigFile | null = null,
): Handler<ConfigFile | null> {
const configs = yield* gensync.all(
// 遍历调用readConfig,所以配置文件加载顺序为.js、.cjs、.mjs、.json以及.cts
names.map(filename => readConfig(path.join(dirname, filename), envName, caller)),
);
// 若存在重复配置文件则报错
const config = configs.reduce((previousConfig: ConfigFile | null, config) => {
if (config && previousConfig) {
throw new ConfigError(
`Multiple configuration files found. Please remove one:\n` +
` - ${path.basename(previousConfig.filepath)}\n` +
` - ${config.filepath}\n` +
`from ${dirname}`,
);
}
return config || previousConfig;
}, previousConfig);
if (config) {
debug('Found configuration %o from %o.', config.filepath, dirname);
}
return config;
}
export function* loadConfig(
name: string,
dirname: string,
envName: string,
caller: CallerMetadata | undefined,
): Handler<ConfigFile> {
const filepath = require.resolve(name, { paths: [dirname] });
const conf = yield* readConfig(filepath, envName, caller);
if (!conf) {
throw new ConfigError(`Config file contains no configuration data`, filepath);
}
debug('Loaded config %o from %o.', name, dirname);
return conf;
}
/**
* Read the given config file, returning the result. Returns null if no config was found, but will
* throw if there are parsing errors while loading a config.
*/
function readConfig(
filepath: string,
envName: string,
caller: CallerMetadata | undefined,
): Handler<ConfigFile | null> {
const ext = path.extname(filepath);
// 读取config内容
switch (ext) {
case '.js':
case '.cjs':
case '.mjs':
case '.cts':
return readConfigCode(filepath, { envName, caller });
default:
return readConfigJSON5(filepath);
}
}
然后继续分析buildRootChain:
{
// ...
let { babelrc, babelrcRoots } = opts;
let babelrcRootsDirectory = context.cwd;
// 生成一个空配置链,结构如下{options: [],presets: [],plugins: [],files: new Set(),}
const configFileChain = emptyChain();
const configFileLogger = new ConfigPrinter();
// 对加载的配置文件进行处理,并且与configFileChain合并
if (configFile) {
const validatedFile = validateConfigFile(configFile);
const result = yield * loadFileChain(validatedFile, context, undefined, configFileLogger);
if (!result) return null;
configReport = yield * configFileLogger.output();
// Allow config files to toggle `.babelrc` resolution on and off and
// specify where the roots are.
if (babelrc === undefined) {
babelrc = validatedFile.options.babelrc;
}
if (babelrcRoots === undefined) {
babelrcRootsDirectory = validatedFile.dirname;
babelrcRoots = validatedFile.options.babelrcRoots;
}
mergeChain(configFileChain, result);
}
let ignoreFile, babelrcFile;
let isIgnored = false;
const fileChain = emptyChain();
// resolve all .babelrc files
if ((babelrc === true || babelrc === undefined) && typeof context.filename === 'string') {
const pkgData = yield * findPackageData(context.filename);
if (pkgData && babelrcLoadEnabled(context, pkgData, babelrcRoots, babelrcRootsDirectory)) {
// 调用findRelativeConfig加载相对配置,相对位置为从当前目录向上寻找第一个包含package.json的目录
// findRelativeConfig源码分析在下方
({ ignore: ignoreFile, config: babelrcFile } =
yield * findRelativeConfig(pkgData, context.envName, context.caller));
if (ignoreFile) {
fileChain.files.add(ignoreFile.filepath);
}
if (ignoreFile && shouldIgnore(context, ignoreFile.ignore, null, ignoreFile.dirname)) {
isIgnored = true;
}
// 将读取的相对配置内容转换成配置链
if (babelrcFile && !isIgnored) {
const validatedFile = validateBabelrcFile(babelrcFile);
const babelrcLogger = new ConfigPrinter();
const result = yield * loadFileChain(validatedFile, context, undefined, babelrcLogger);
if (!result) {
isIgnored = true;
} else {
babelRcReport = yield * babelrcLogger.output();
mergeChain(fileChain, result);
}
}
if (babelrcFile && isIgnored) {
fileChain.files.add(babelrcFile.filepath);
}
}
}
if (context.showConfig) {
console.log(
`Babel configs on "${context.filename}" (ascending priority):\n` +
// print config by the order of ascending priority
[configReport, babelRcReport, programmaticReport].filter(x => !!x).join('\n\n') +
'\n-----End Babel configs-----',
);
}
// Insert file chain in front so programmatic options have priority
// over configuration file chain items.
// 将得到的配置链合并
const chain = mergeChain(
mergeChain(mergeChain(emptyChain(), configFileChain), fileChain),
programmaticChain,
);
return {
plugins: isIgnored ? [] : dedupDescriptors(chain.plugins),
presets: isIgnored ? [] : dedupDescriptors(chain.presets),
options: isIgnored ? [] : chain.options.map(o => normalizeOptions(o)),
fileHandling: isIgnored ? 'ignored' : 'transpile',
ignore: ignoreFile || undefined,
babelrc: babelrcFile || undefined,
config: configFile || undefined,
files: chain.files,
};
}
findRelativeConfig方法依次寻找.babelrc、.babelrc.js、.babelrc.cjs等等,找到一个加载并停止寻找
js
复制代码
const RELATIVE_CONFIG_FILENAMES = [
'.babelrc',
'.babelrc.js',
'.babelrc.cjs',
'.babelrc.mjs',
'.babelrc.json',
'.babelrc.cts',
];
export function* findRelativeConfig(
packageData: FilePackageData,
envName: string,
caller: CallerMetadata | undefined,
): Handler<RelativeConfig> {
let config = null;
let ignore = null;
const dirname = path.dirname(packageData.filepath);
// 调用loadOneConfig读取相对配置
// 第五个参数为packageData.pkg?.dirname === loc? packageToBabelConfig(packageData.pkg): null,
// 存在多个配置文件会覆盖,不会报错
for (const loc of packageData.directories) {
if (!config) {
config = yield* loadOneConfig(
RELATIVE_CONFIG_FILENAMES,
loc,
envName,
caller,
packageData.pkg?.dirname === loc ? packageToBabelConfig(packageData.pkg) : null,
);
}
// 读取忽略文件列表
if (!ignore) {
const ignoreLoc = path.join(loc, BABELIGNORE_FILENAME);
ignore = yield* readIgnoreConfig(ignoreLoc);
if (ignore) {
debug('Found ignore %o from %o.', ignore.filepath, dirname);
}
}
}
return { config, ignore };
}
ok,这一串子终于走完了,其实的配置文件读取的经验非常值得借鉴,回到loadFullConfig:
{
// ...
// 创建一个toDescriptor方法用于获取presets和plugin的描述符
const toDescriptor = (item: PluginItem) => {
const desc = getItemDescriptor(item);
if (!desc) {
throw new Error('Assertion failure - must be config item');
}
return desc;
};
// 映射所有presets和plugin以获取其描述符,并存储在presetsDescriptors和 initialPluginsDescriptors`中
const presetsDescriptors = presets.map(toDescriptor);
const initialPluginsDescriptors = plugins.map(toDescriptor);
// 初始化一个空数组用于存储描述符
const pluginDescriptorsByPass: Array<Array<UnloadedDescriptor>> = [[]];
// 初始化一个空数组用于存储pass
const passes: Array<Array<Plugin>> = [];
// 初始化一个空数组用于存储外部依赖
const externalDependencies: DeepArray<string> = [];
// 调用recursePresetDescriptors处理presets描述符,将presets描述符加载并处理,处理过程中如果遇到错误会抛出
const ignored =
yield *
enhanceError(
context,
function* recursePresetDescriptors(
rawPresets: Array<UnloadedDescriptor>,
pluginDescriptorsPass: Array<UnloadedDescriptor>,
): Handler<true | void> {
// 初始化一个presets
const presets: Array<{
preset: ConfigChain | null;
pass: Array<UnloadedDescriptor>;
}> = [];
// 遍历rawPresets
for (let i = 0; i < rawPresets.length; i++) {
const descriptor = rawPresets[i];
if (descriptor.options !== false) {
try {
// eslint-disable-next-line no-var
// 调用loadPrivatePartialConfig,构建preset配置链
var preset = yield* loadPresetDescriptor(descriptor, presetContext);
} catch (e) {
if (e.code === 'BABEL_UNKNOWN_OPTION') {
checkNoUnwrappedItemOptionPairs(rawPresets, i, 'preset', e);
}
throw e;
}
externalDependencies.push(preset.externalDependencies);
// Presets normally run in reverse order, but if they
// have their own pass they run after the presets
// in the previous pass.
// descriptor.ownPass为false时,则unshift处理过后的preset到presets,所以presets在执行时时倒序的
if (descriptor.ownPass) {
presets.push({ preset: preset.chain, pass: [] });
} else {
presets.unshift({
preset: preset.chain,
pass: pluginDescriptorsPass,
});
}
}
}
// resolve presets
if (presets.length > 0) {
// The passes are created in the same order as the preset list, but are inserted before any
// existing additional passes.
pluginDescriptorsByPass.splice(
1,
0,
...presets.map(o => o.pass).filter(p => p !== pluginDescriptorsPass),
);
for (const { preset, pass } of presets) {
if (!preset) return true;
// 如果preset有自己的pass,则添加到新的pass中
pass.push(...preset.plugins);
// 如果preset有自己的presets,则递归调用
const ignored = yield* recursePresetDescriptors(preset.presets, pass);
if (ignored) return true;
// 将preset的options进行合并
preset.options.forEach(opts => {
mergeOptions(optionDefaults, opts);
});
}
}
},
)(presetsDescriptors, pluginDescriptorsByPass[0]);
if (ignored) return null;
const opts: any = optionDefaults;
mergeOptions(opts, options);
const pluginContext: Context.FullPlugin = {
...presetContext,
assumptions: opts.assumptions ?? {},
};
// 加载插件描述符,如果加载过程中遇到错误会抛出
yield *
enhanceError(context, function* loadPluginDescriptors() {
pluginDescriptorsByPass[0].unshift(...initialPluginsDescriptors);
for (const descs of pluginDescriptorsByPass) {
const pass: Plugin[] = [];
// 将处理过的plugin放入passes,并返回
passes.push(pass);
for (let i = 0; i < descs.length; i++) {
const descriptor: UnloadedDescriptor = descs[i];
if (descriptor.options !== false) {
try {
// eslint-disable-next-line no-var
// 加载插件
var plugin = yield* loadPluginDescriptor(descriptor, pluginContext);
} catch (e) {
if (e.code === 'BABEL_UNKNOWN_PLUGIN_PROPERTY') {
// print special message for `plugins: ["@babel/foo", { foo: "option" }]`
checkNoUnwrappedItemOptionPairs(descs, i, 'plugin', e);
}
throw e;
}
pass.push(plugin);
externalDependencies.push(plugin.externalDependencies);
}
}
}
})();
opts.plugins = passes[0];
opts.presets = passes
.slice(1)
.filter(plugins => plugins.length > 0)
.map(plugins => ({ plugins }));
opts.passPerPreset = opts.presets.length > 0;
return {
options: opts,
passes: passes,
externalDependencies: freezeDeepArray(externalDependencies),
};
}
终于讲完了transformRunner方法中的loadConfig调用,接下来来到了至关重要的run,位于babel-core/src/transformation/index.ts,该方法接收三个参数,config为上文源码所处理的配置返回值,code为代码字符串,ast是一颗可选的AST:
export function* run(
config: ResolvedConfig,
code: string,
ast?: t.File | t.Program | null,
): Handler<FileResult> {
// 调用normalizeFile函数标准化文件
const file = yield* normalizeFile(
config.passes,
normalizeOptions(config),
code,
ast,
);
// ...
}
normalizeFile代码如下,该函数使用 config.passes(一组插件数组)、标准化后的配置、源代码和可选的 ast 作为参数:
export default function* normalizeFile(
pluginPasses: PluginPasses,
options: { [key: string]: any },
code: string,
ast?: t.File | t.Program | null,
): Handler<File> {
code = `${code || ''}`;
// 如果存在ast
if (ast) {
// 对ast进行校验,root是否type为Program
if (ast.type === 'Program') {
// 进一步校验
ast = file(ast, [], []);
} else if (ast.type !== 'File') {
throw new Error('AST root must be a Program or File node');
}
if (options.cloneInputAst) {
ast = cloneDeep(ast);
}
} else {
// 如果不存在ast,则调用parser生成
// @ts-expect-error todo: use babel-types ast typings in Babel parser
ast = yield* parser(pluginPasses, options, code);
}
let inputMap = null;
// 判断如果需要`sourceMap`的话,会尝试调用`convertSourceMap.fromObject`、 `convertSourceMap.fromComment`等生成`inputMap`
if (options.inputSourceMap !== false) {
// If an explicit object is passed in, it overrides the processing of
// source maps that may be in the file itself.
if (typeof options.inputSourceMap === 'object') {
inputMap = convertSourceMap.fromObject(options.inputSourceMap);
}
if (!inputMap) {
const lastComment = extractComments(INLINE_SOURCEMAP_REGEX, ast);
if (lastComment) {
try {
inputMap = convertSourceMap.fromComment(lastComment);
} catch (err) {
debug('discarding unknown inline input sourcemap', err);
}
}
}
if (!inputMap) {
const lastComment = extractComments(EXTERNAL_SOURCEMAP_REGEX, ast);
if (typeof options.filename === 'string' && lastComment) {
try {
// when `lastComment` is non-null, EXTERNAL_SOURCEMAP_REGEX must have matches
const match: [string, string] = EXTERNAL_SOURCEMAP_REGEX.exec(lastComment) as any;
const inputMapContent = fs.readFileSync(
path.resolve(path.dirname(options.filename), match[1]),
'utf8',
);
inputMap = convertSourceMap.fromJSON(inputMapContent);
} catch (err) {
debug('discarding unknown file input sourcemap', err);
}
} else if (lastComment) {
debug('discarding un-loadable file input sourcemap');
}
}
}
// 返回一个新的File对象
return new File(options, {
code,
ast: ast as t.File,
inputMap,
});
}
其中parser源码最终指向babel-core/src/parser/index.ts,如下:
export default function* parser(
pluginPasses: PluginPasses,
{ parserOpts, highlightCode = true, filename = 'unknown' }: any,
code: string,
): Handler<ParseResult> {
try {
const results = [];
// 从pluginPasses双重遍历取出plugin,并解构出其中的parser转换方法,如果存在该方法,则调用,并且push到results中
for (const plugins of pluginPasses) {
for (const plugin of plugins) {
const { parserOverride } = plugin;
if (parserOverride) {
const ast = parserOverride(code, parserOpts, parse);
if (ast !== undefined) results.push(ast);
}
}
}
// 如果results为空,则调用@babel/parser中的parser方法
if (results.length === 0) {
return parse(code, parserOpts);
} else if (results.length === 1) {
// @ts-expect-error - If we want to allow async parsers
yield* [];
if (typeof results[0].then === 'function') {
throw new Error(
`You appear to be using an async parser plugin, ` +
`which your current version of Babel does not support. ` +
`If you're using a published plugin, you may need to upgrade ` +
`your @babel/core version.`,
);
}
return results[0];
}
// TODO: Add an error code
throw new Error('More than one plugin attempted to override parsing.');
} catch (err) {
if (err.code === 'BABEL_PARSER_SOURCETYPE_MODULE_REQUIRED') {
err.message +=
"\nConsider renaming the file to '.mjs', or setting sourceType:module " +
'or sourceType:unambiguous in your Babel config for this file.';
// err.code will be changed to BABEL_PARSE_ERROR later.
}
const { loc, missingPlugin } = err;
if (loc) {
const codeFrame = codeFrameColumns(
code,
{
start: {
line: loc.line,
column: loc.column + 1,
},
},
{
highlightCode,
},
);
if (missingPlugin) {
err.message =
`${filename}: ` + generateMissingPluginMessage(missingPlugin[0], loc, codeFrame);
} else {
err.message = `${filename}: ${err.message}\n\n` + codeFrame;
}
err.code = 'BABEL_PARSE_ERROR';
}
throw err;
}
}
回到run方法,得到AST后调用transformFile方法进行转化:
{
// ...
const opts = file.opts;
try {
yield* transformFile(file, config.passes);
} catch (e) {
e.message = `${opts.filename ?? "unknown file"}: ${e.message}`;
if (!e.code) {
e.code = "BABEL_TRANSFORM_ERROR";
}
throw e;
}
// ...
}
transformFile方法源码如下:
function* transformFile(file: File, pluginPasses: PluginPasses): Handler<void> {
for (const pluginPairs of pluginPasses) {
// 初始化
const passPairs: [Plugin, PluginPass][] = [];
const passes = [];
const visitors = [];
for (const plugin of pluginPairs.concat([loadBlockHoistPlugin()])) {
// 为每个plugin创建一个新的pass
const pass = new PluginPass(file, plugin.key, plugin.options);
passPairs.push([plugin, pass]);
passes.push(pass);
// 将visitor(转换方法)push到visitors
visitors.push(plugin.visitor);
}
for (const [plugin, pass] of passPairs) {
// 判断插件是否有pre方法,如果有,则在当前的插件通道和文件上下文中调用该方法
const fn = plugin.pre;
if (fn) {
// eslint-disable-next-line @typescript-eslint/no-confusing-void-expression
const result = fn.call(pass, file);
// @ts-expect-error - If we want to support async .pre
yield* [];
// 若返回的是一个 Promise,报错
if (isThenable(result)) {
throw new Error(
`You appear to be using an plugin with an async .pre, ` +
`which your current version of Babel does not support. ` +
`If you're using a published plugin, you may need to upgrade ` +
`your @babel/core version.`,
);
}
}
}
// 合并所有插件中的visitors
const visitor = traverse.visitors.merge(visitors, passes, file.opts.wrapPluginVisitorMethod);
// 调用@babel/traverse进行转换
traverse(file.ast, visitor, file.scope);
for (const [plugin, pass] of passPairs) {
// 判断插件是否有post方法,如果有,则在当前的插件通道和文件上下文中调用该方法
const fn = plugin.post;
if (fn) {
// eslint-disable-next-line @typescript-eslint/no-confusing-void-expression
const result = fn.call(pass, file);
// @ts-expect-error - If we want to support async .post
yield* [];
if (isThenable(result)) {
throw new Error(
`You appear to be using an plugin with an async .post, ` +
`which your current version of Babel does not support. ` +
`If you're using a published plugin, you may need to upgrade ` +
`your @babel/core version.`,
);
}
}
}
}
}
在transformFile方法中依照顺序,前中后分别为pre,visitor和post,它们分别为:
-
pre(state: PluginPass): 这个方法在遍历开始前被调用。通常用于在插件状态对象上设置需要在整个遍历过程中保持的一些初始状态信息。state参数是一个PluginPass实例,它包含了与插件执行上下文相关的信息。 -
visitor: 这个对象定义了在遍历过程中需要调用的方法。每个方法的键是要访问的节点类型,值是对应的访问者方法或者一个包含enter和exit方法的对象。 -
post(state: PluginPass): 这个方法在遍历完成后被调用,通常用于执行一些清理工作,或者收集和使用在遍历过程中计算出的结果。state参数同pre方法。
接下来继续回到run方法:
{
// ...
let outputCode, outputMap;
try {
if (opts.code !== false) {
({ outputCode, outputMap } = generateCode(config.passes, file));
}
} catch (e) {
e.message = `${opts.filename ?? 'unknown file'}: ${e.message}`;
if (!e.code) {
e.code = 'BABEL_GENERATE_ERROR';
}
throw e;
}
return {
metadata: file.metadata,
options: opts,
ast: opts.ast === true ? file.ast : null,
code: outputCode === undefined ? null : outputCode,
map: outputMap === undefined ? null : outputMap,
sourceType: file.ast.program.sourceType,
externalDependencies: flattenToSet(config.externalDependencies),
};
}
最后调用generateCode方法将AST转换回code,源码如下,其和parser有异曲同工之妙:
export default function generateCode(
pluginPasses: PluginPasses,
file: File,
): {
outputCode: string;
outputMap: SourceMap | null;
} {
const { opts, ast, code, inputMap } = file;
const { generatorOpts } = opts;
generatorOpts.inputSourceMap = inputMap?.toObject();
const results = [];
// 取出plugin
for (const plugins of pluginPasses) {
for (const plugin of plugins) {
// 如果plugin中有生成方法,则调用,并push到results
const { generatorOverride } = plugin;
if (generatorOverride) {
const result = generatorOverride(ast, generatorOpts, code, generate);
if (result !== undefined) results.push(result);
}
}
}
let result;
// 如结果为空,调用@babel/generator
if (results.length === 0) {
result = generate(ast, generatorOpts, code);
} else if (results.length === 1) {
result = results[0];
if (typeof result.then === 'function') {
throw new Error(
`You appear to be using an async codegen plugin, ` +
`which your current version of Babel does not support. ` +
`If you're using a published plugin, ` +
`you may need to upgrade your @babel/core version.`,
);
}
} else {
throw new Error('More than one plugin attempted to override codegen.');
}
// Decoded maps are faster to merge, so we attempt to get use the decodedMap
// first. But to preserve backwards compat with older Generator, we'll fall
// back to the encoded map.
let { code: outputCode, decodedMap: outputMap = result.map } = result;
// For backwards compat.
if (result.__mergedMap) {
/**
* @see mergeSourceMap
*/
outputMap = { ...result.map };
} else {
if (outputMap) {
if (inputMap) {
// mergeSourceMap returns an encoded map
outputMap = mergeSourceMap(inputMap.toObject(), outputMap, generatorOpts.sourceFileName);
} else {
// We cannot output a decoded map, so retrieve the encoded form. Because
// the decoded form is free, it's fine to prioritize decoded first.
outputMap = result.map;
}
}
}
if (opts.sourceMaps === 'inline' || opts.sourceMaps === 'both') {
outputCode += '\n' + convertSourceMap.fromObject(outputMap).toComment();
}
if (opts.sourceMaps === 'inline') {
outputMap = null;
}
return { outputCode, outputMap };
}
至此run方法源码解析完成,同时以babel.transformSync为开始的@babel/core源码解析也一并完成!
简易javascript编译器(类Babel)
接下来,我们将以手撕一个以编译demo为目的的简易编译器,遵循的也是解析-转换-生成这么一套流程,如下:
节点类型(constants.js)
const TokenTypes = {
Keyword: "Keyword",
Identifier: "Identifier",
Punctuator: "Punctuator",
String: "String",
Numeric: "Numeric",
Paren: 'Paren',
Arrow: 'Arrow'
}
const AST_Types = {
Literal: "Literal",
Identifier: "Identifier",
AssignmentExpression: "AssignmentExpression",
VariableDeclarator: "VariableDeclarator",
VariableDeclaration: "VariableDeclaration",
Program: "Program",
NumericLiteral: "NumericLiteral",
ArrowFunctionExpression: 'ArrowFunctionExpression',
FunctionExpression: 'FunctionExpression'
}
module.exports = {
TokenTypes,
AST_Types
}
词法分析(tokenizer.js)
const tokens = require('./constants');
// 匹配关键字
const KEYWORD = /let/;
// 匹配"="、";"
const PUNCTUATOR = /[\=;]/;
// 匹配空格
const WHITESPACE = /\s/;
// 匹配字符
const LETTERS = /[A-Za-z]/i;
// 匹配数字
const NUMERIC = /[0-9]/i;
const PAREN = /[()]/;
const { TokenTypes } = tokens;
function tokenizer(input) {
const tokens = [];
let current = 0;
// 遍历字符串
while (current < input.length) {
let char = input[current];
// 处理关键字和变量名
if (LETTERS.test(char)) {
let value = '';
// 用一个循环遍历所有的字母,把它们存入 value 中
while (LETTERS.test(char)) {
value += char;
char = input[++current];
}
// 判断当前字符串是否是关键字
KEYWORD.test(value)
? tokens.push({
type: TokenTypes.Keyword,
value: value,
})
: tokens.push({
type: TokenTypes.Identifier,
value: value,
});
continue;
}
// 检查是否是括号
if (PAREN.test(char)) {
tokens.push({
type: TokenTypes.Paren,
value: char,
});
current++;
continue;
}
// 检查是否是箭头符号
if (char === '=' && input[current + 1] === '>') {
tokens.push({
type: TokenTypes.Arrow,
value: '=>',
});
current += 2; // Skip the two characters
continue;
}
// 判断是否为数字
if (NUMERIC.test(char)) {
let value = '' + char;
char = input[++current];
while (NUMERIC.test(char) && current < input.length) {
value += char;
char = input[++current];
}
tokens.push({ type: TokenTypes.Numeric, value });
continue;
}
// 检查是否是符号,"="、";"
if (PUNCTUATOR.test(char)) {
const punctuators = char; // 创建变量用于保存匹配的符号
current++;
tokens.push({
type: TokenTypes.Punctuator,
value: punctuators,
});
continue;
}
// 处理空格,遇到空格直接跳过
if (WHITESPACE.test(char)) {
current++;
continue;
}
// 处理字符串
if (char === '"') {
let value = '';
// 忽略掉开头的引号
char = input[++current];
// 直到遇到下一个引号结束遍历
while (char !== '"') {
value += char;
char = input[++current];
}
// 忽略掉结尾的引号
char = input[++current];
tokens.push({ type: TokenTypes.String, value: '"' + value + '"' });
continue;
}
// 如果不满足当前的匹配规则抛出错误
throw new TypeError('Unknown' + char);
}
return tokens;
}
module.exports = tokenizer;
语法分析(parser.js)
const { TokenTypes, AST_Types } = require('./constants');
function parser(tokens) {
let current = 0;
function walk() {
let token = tokens[current];
if (token.type === TokenTypes.Numeric) {
current++;
return {
type: AST_Types.NumericLiteral,
value: token.value,
};
}
if (token.type === TokenTypes.String) {
current++;
return {
type: AST_Types.Literal,
value: token.value,
};
}
if (token.type === TokenTypes.Identifier) {
current++;
return {
type: AST_Types.Identifier,
name: token.value,
};
}
if (token.type === TokenTypes.Keyword && token.value === 'let') {
token = tokens[++current];
let node = {
type: AST_Types.VariableDeclaration,
kind: 'let',
declarations: [],
};
while (token.type === TokenTypes.Identifier) {
node.declarations.push({
type: AST_Types.VariableDeclarator,
id: {
type: AST_Types.Identifier,
name: token.value,
},
init: null,
});
token = tokens[++current];
if (token && token.type === TokenTypes.Punctuator && token.value === '=') {
token = tokens[++current];
if (token && token.type === TokenTypes.Paren) {
token = tokens[++current];
if (token && token.type === TokenTypes.Paren) {
token = tokens[++current];
if (token && token.type === TokenTypes.Arrow) {
token = tokens[++current];
let arrowFunction = {
type: AST_Types.ArrowFunctionExpression,
params: [],
body: walk(),
};
node.declarations[node.declarations.length - 1].init = arrowFunction;
}
}
} else {
node.declarations[node.declarations.length - 1].init = walk();
}
}
token = tokens[current];
if (token && token.type === TokenTypes.Punctuator && token.value === ';') {
current++;
break;
}
}
return node;
}
throw new TypeError(token.type);
}
let ast = {
type: AST_Types.Program,
body: [],
};
while (current < tokens.length) {
ast.body.push(walk());
}
return ast;
}
module.exports = parser;
遍历器(traverser.js)
const constants = require('./constants');
const { AST_Types } = constants;
function traverser(ast, visitor) {
// 遍历节点,调用 traverseNode
function traverseArray(array, parent) {
array.forEach(function (child) {
traverseNode(child, parent);
});
}
function traverseNode(node, parent) {
// visitor 中有没有对应 type 的处理函数。
const method = visitor[node.type];
if (method) {
method(node, parent);
}
// 下面对每一个不同类型的结点分开处理。
switch (node.type) {
case AST_Types.Program:
// 顶层的 Program 开始,body是数组所以调用traverseArray
traverseArray(node.body, node);
break;
case AST_Types.VariableDeclaration:
traverseArray(node.declarations, node);
break;
case AST_Types.VariableDeclarator:
traverseNode(node.id, node);
traverseNode(node.init, node);
break;
case AST_Types.ArrowFunctionExpression:
traverseArray(node.params, node);
traverseNode(node.body, node);
case AST_Types.AssignmentExpression:
case AST_Types.Identifier:
case AST_Types.Literal:
case AST_Types.NumericLiteral:
break;
default:
throw new TypeError(node.type);
}
}
// 触发遍历AST,根节点没有父节点所以这里传入null
traverseNode(ast, null);
}
module.exports = traverser;
转换器(transformer.js)
const traverser = require('./traverser');
const constants = require('./constants');
const { AST_Types } = constants;
function transformer(ast) {
const newAst = {
type: AST_Types.Program,
body: [],
sourceType: 'script',
};
ast._context = newAst.body;
// 将 AST 和 visitor 传入traverser中
traverser(ast, {
// 将let转换为var
VariableDeclaration: function (node, parent) {
const variableDeclaration = {
type: AST_Types.VariableDeclaration,
declarations: node.declarations,
kind: 'var',
};
parent._context.push(variableDeclaration);
},
ArrowFunctionExpression: function (node, parent) {
const functionExpression = {
type: AST_Types.FunctionExpression,
params: node.params, // 参数列表保持不变
body: node.body, // 函数体保持不变
};
if (parent.type === AST_Types.VariableDeclarator) {
parent.init = functionExpression;
}
},
});
return newAst;
}
module.exports = transformer;
代码生成(codeGenerator.js)
const constants = require('./constants');
const { AST_Types } = constants;
function codeGenerator(node) {
// 处理不同类型的结点
switch (node.type) {
// 如果是 Program 结点,遍历它的 body 属性中的每一个结点并加入换行符号
case AST_Types.Program:
return node.body.map(codeGenerator).join('\n');
case AST_Types.VariableDeclaration:
return node.kind + ' ' + node.declarations.map(codeGenerator);
case AST_Types.VariableDeclarator:
return codeGenerator(node.id) + ' = ' + codeGenerator(node.init);
case AST_Types.Identifier:
return node.name;
case AST_Types.Literal:
return '"' + node.value + '"' + '; }';
case AST_Types.NumericLiteral:
return node.value + '; }';
case AST_Types.FunctionExpression:
return 'function(' + node.params + ') { return ' + codeGenerator(node.body);
default:
throw new TypeError(node.type);
}
}
module.exports = codeGenerator;
index.js
const tokenizer = require('./tokenizer')
const parser = require('./parser')
const transformer = require("./transformer")
const codeGenerator = require("./codeGenerator")
const demo = 'let a = () => 1;'
const tokens = tokenizer(demo)
const AST = parser(tokens)
const newAST = transformer(AST)
const newCode = codeGenerator(newAST)
console.log(newCode)
console.dir(newAST, {depth: null})
最终转换结果如下:
var a = function() { return 1; }
生成的新的AST树如下:
{
type: 'Program',
body: [
{
type: 'VariableDeclaration',
declarations: [
{
type: 'VariableDeclarator',
id: { type: 'Identifier', name: 'a' },
init: {
type: 'FunctionExpression',
params: [],
body: { type: 'NumericLiteral', value: '1' }
}
}
],
kind: 'var'
}
],
sourceType: 'script'
}
结束语
本来这篇文章是想从Babel开始去分析Babel所有核心库源码以及相关知识体系,以AST为核心去开阔javascript编译这一话题,然后再去讲一讲SWC等等,但是由于最近工作有点忙碌,而且硕士毕业答辩在即,所以内容咩有写完,剩下的@Babel/parser / @babel/traverse / @babel/generator / @Babel/types / @Babel/cli源码解析以及swc等等会在下一篇文章去展现!这篇文章断断续续写了大半个月,内容可能有点断断续续,还请见谅,有时间可能会做很多补全和修改。还是感谢我所参考的众多文章,都是很棒的前辈们。加油,希望自己也可以多写写,希望自己毕业顺利,快发双证,早点转正!
参考资料
https://astexplorer.net/: https://link.juejin.cn?target=https%3A%2F%2Fastexplorer.net%2F
最后
Node 社群
我组建了一个氛围特别好的 Node.js 社群,里面有很多 Node.js小伙伴,如果你对Node.js学习感兴趣的话(后续有计划也可以),我们可以一起进行Node.js相关的交流、学习、共建。下方加 考拉 好友回复「Node」即可。
“分享、点赞、在看” 支持一
