一种写法统一人脸Loss:Pytorch实现及Mnist可视化

极市导读
本文主要总结了softmax、Modified Softmax、NormFace、SphereFace、InsightFace、Center Loss六种loss的Pytorch实现以及Mnist的可视化实验,让大家能够借助代码更深刻的理解Loss的设计以及直观的比较各种Loss的有效性。 >>加入极市CV技术交流群,走在计算机视觉的最前沿
写在前面
Softmax
公式推导

Pytorch代码实现
class Linear(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Linear, self).__init__()
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(2, 10)) # (input,output)
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.weight)
def forward(self, x, label):
out = x.mm(self.weight)
loss = F.cross_entropy(out, label)
return out, loss
可视化
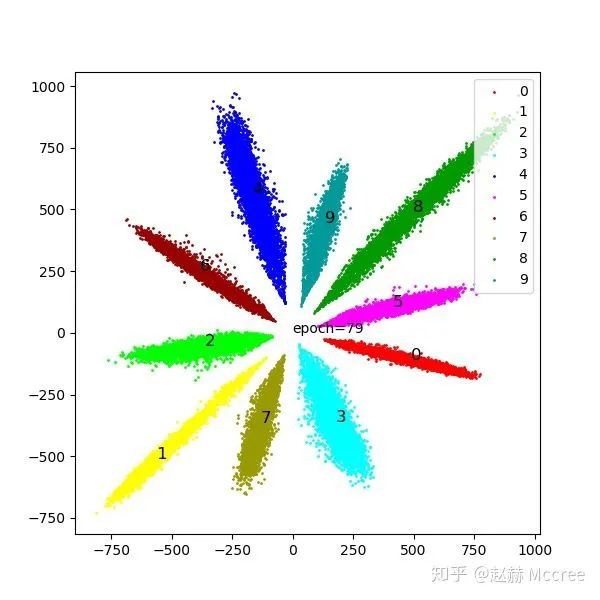
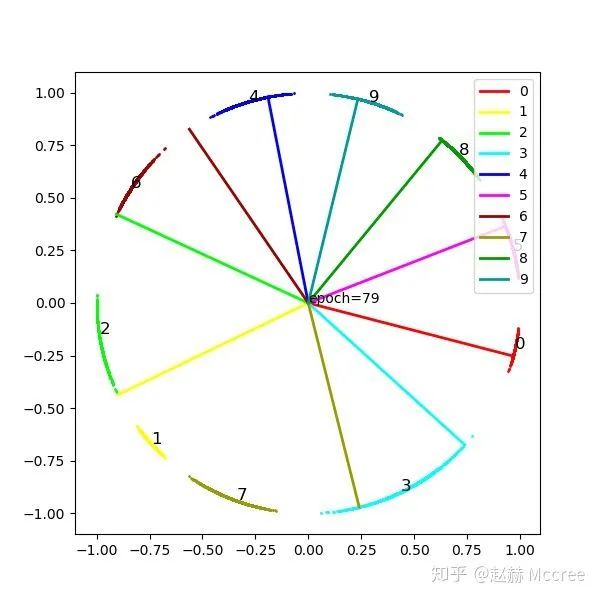
Modified Softmax
公式推导

Pytorch代码实现
class Modified(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Modified, self).__init__()
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(2,10))#(input,output)
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.weight)
self.weight.data.uniform_(-1,1).renorm_(2,1,1e-5).mul_(1e5)
#因为renorm采用的是maxnorm,所以先缩小再放大以防止norm结果小于1
def forward(self, x):
w=self.weight
ww=w.renorm(2,1,1e-5).mul(1e5)
out = x.mm(ww)
return out
可视化
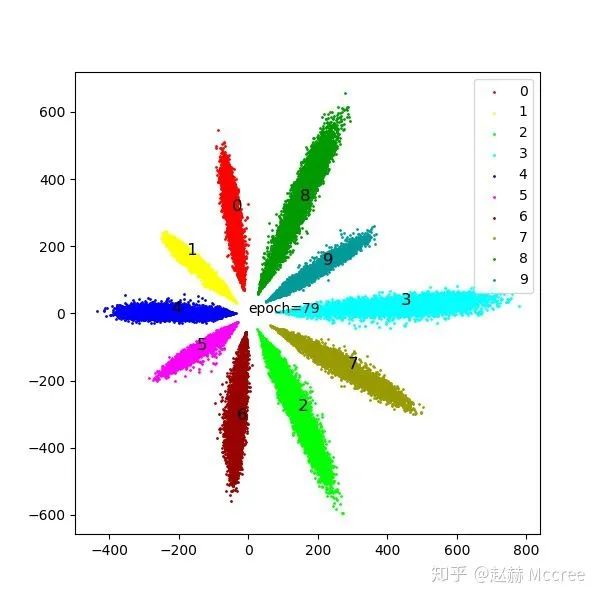
NormFace
公式推导

可视化
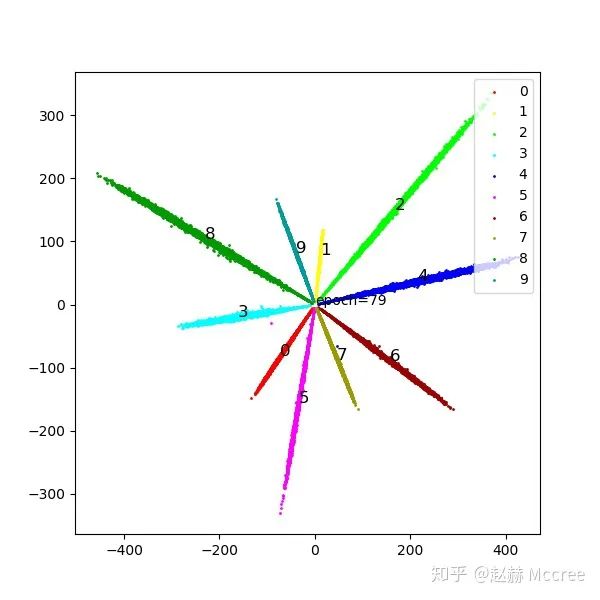
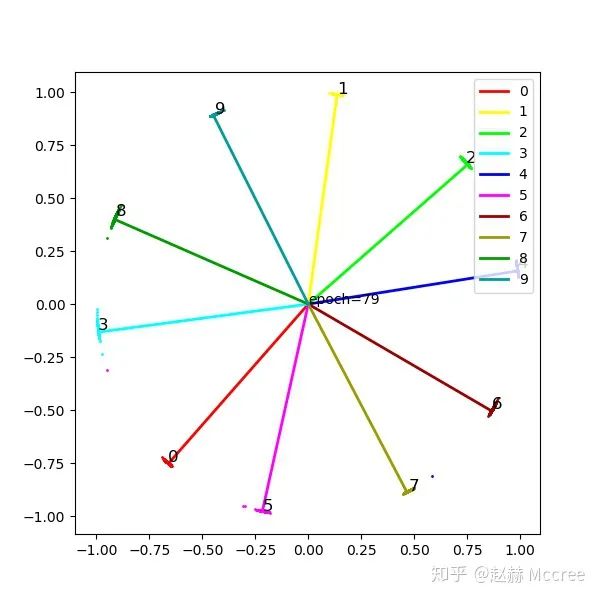
Pytorch代码实现
class NormFace(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(NormFace, self).__init__()
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(2, 10)) # (input,output)
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.weight)
self.weight.data.uniform_(-1, 1).renorm_(2, 1, 1e-5).mul_(1e5)
self.s = 16
# 因为renorm采用的是maxnorm,所以先缩小再放大以防止norm结果小于1
def forward(self, x, label):
cosine = F.normalize(x).mm(F.normalize(self.weight, dim=0))
loss = F.cross_entropy(self.s * cosine, label)
return cosine, loss
SphereFace:A-softmax
公式推导

Pytorch代码实现
class SphereFace(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, m=4):
super(SphereFace, self).__init__()
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(2, 10)) # (input,output)
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.weight)
self.weight.data.renorm_(2, 1, 1e-5).mul_(1e5)
self.m = m
self.mlambda = [ # calculate cos(mx)
lambda x: x ** 0,
lambda x: x ** 1,
lambda x: 2 * x ** 2 - 1,
lambda x: 4 * x ** 3 - 3 * x,
lambda x: 8 * x ** 4 - 8 * x ** 2 + 1,
lambda x: 16 * x ** 5 - 20 * x ** 3 + 5 * x
]
self.it = 0
self.LambdaMin = 3
self.LambdaMax = 30000.0
self.gamma = 0
def forward(self, input, label):
# 注意,在原始的A-softmax中是不对x进行标准化的,
# 标准化可以提升性能,也会增加收敛难度,A-softmax本来就很难收敛
cos_theta = F.normalize(input).mm(F.normalize(self.weight, dim=0))
cos_theta = cos_theta.clamp(-1, 1) # 防止出现异常
# 以上计算出了传统意义上的cos_theta,但为了cos(m*theta)的单调递减,需要使用phi_theta
cos_m_theta = self.mlambda[self.m](cos_theta)
# 计算theta,依据theta的区间把k的取值定下来
theta = cos_theta.data.acos()
k = (self.m * theta / 3.1415926).floor()
phi_theta = ((-1) ** k) * cos_m_theta - 2 * k
x_norm = input.pow(2).sum(1).pow(0.5) # 这个地方决定x带不带模长,不带就要乘s
x_cos_theta = cos_theta * x_norm.view(-1, 1)
x_phi_theta = phi_theta * x_norm.view(-1, 1)
############ 以上计算target logit,下面构造loss,退火训练#####
self.it += 1 # 用来调整lambda
target = label.view(-1, 1) # (B,1)
onehot = torch.zeros(target.shape[0], 10).cuda().scatter_(1, target, 1)
lamb = max(self.LambdaMin, self.LambdaMax / (1 + 0.2 * self.it))
output = x_cos_theta * 1.0 # 如果不乘可能会有数值错误?
output[onehot.byte()] -= x_cos_theta[onehot.byte()] * (1.0 + 0) / (1 + lamb)
output[onehot.byte()] += x_phi_theta[onehot.byte()] * (1.0 + 0) / (1 + lamb)
# 到这一步可以等同于原来的Wx+b=y的输出了,
# 到这里使用了Focal Loss,如果直接使用cross_Entropy的话似乎效果会减弱许多
log = F.log_softmax(output, 1)
log = log.gather(1, target)
log = log.view(-1)
pt = log.data.exp()
loss = -1 * (1 - pt) ** self.gamma * log
loss = loss.mean()
# loss = F.cross_entropy(x_cos_theta,target.view(-1))#换成crossEntropy效果会差
return output, loss
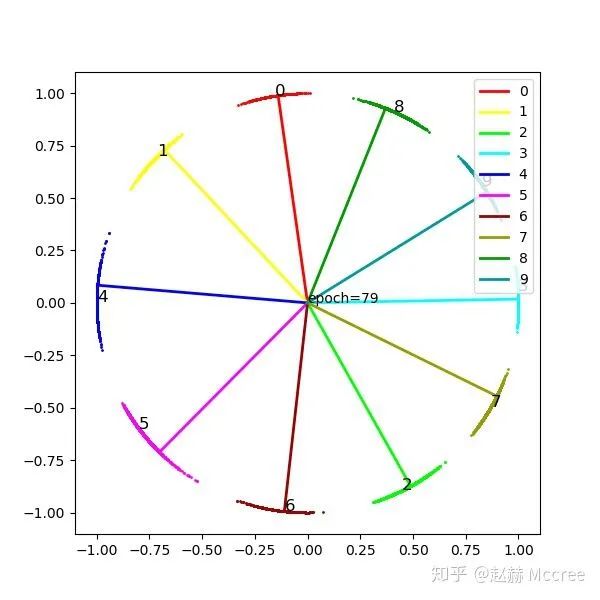
可视化
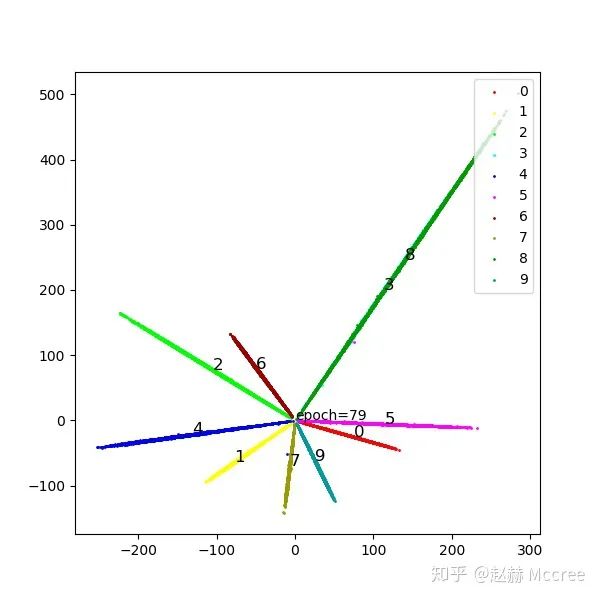
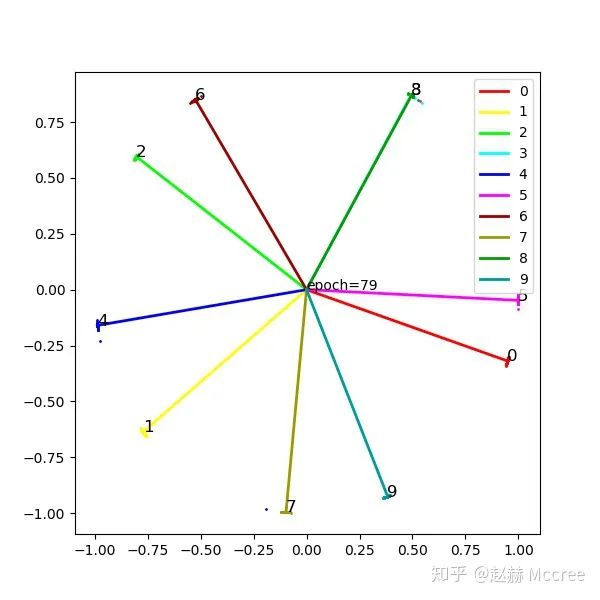
InsightFace(ArcSoftmax)
公式推导

Pytorch代码实现
class ArcMarginProduct(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, s=32, m=0.5):
super(ArcMarginProduct, self).__init__()
self.in_feature = 2
self.out_feature = 10
self.s = s
self.m = m
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(2, 10)) # (input,output)
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.weight)
self.weight.data.renorm_(2, 1, 1e-5).mul_(1e5)
self.cos_m = math.cos(m)
self.sin_m = math.sin(m)
# 为了保证cos(theta+m)在0-pi单调递减:
self.th = math.cos(3.1415926 - m)
self.mm = math.sin(3.1415926 - m) * m
def forward(self, x, label):
cosine = F.normalize(x).mm(F.normalize(self.weight, dim=0))
cosine = cosine.clamp(-1, 1) # 数值稳定
sine = torch.sqrt(torch.max(1.0 - torch.pow(cosine, 2), torch.ones(cosine.shape).cuda() * 1e-7)) # 数值稳定
##print(self.sin_m)
phi = cosine * self.cos_m - sine * self.sin_m # 两角和公式
# # 为了保证cos(theta+m)在0-pi单调递减:
# phi = torch.where((cosine - self.th) > 0, phi, cosine - self.mm)#必要性未知
#
one_hot = torch.zeros_like(cosine)
one_hot.scatter_(1, label.view(-1, 1), 1)
output = (one_hot * phi) + ((1.0 - one_hot) * cosine)
output = output * self.s
loss = F.cross_entropy(output, label)
return output, loss
可视化
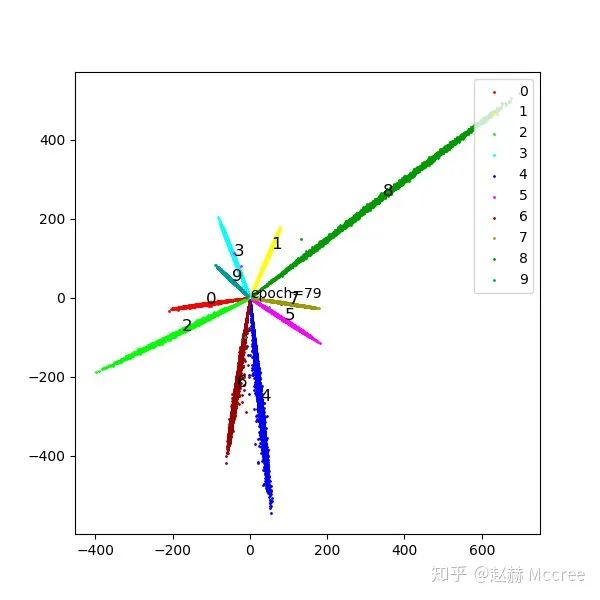
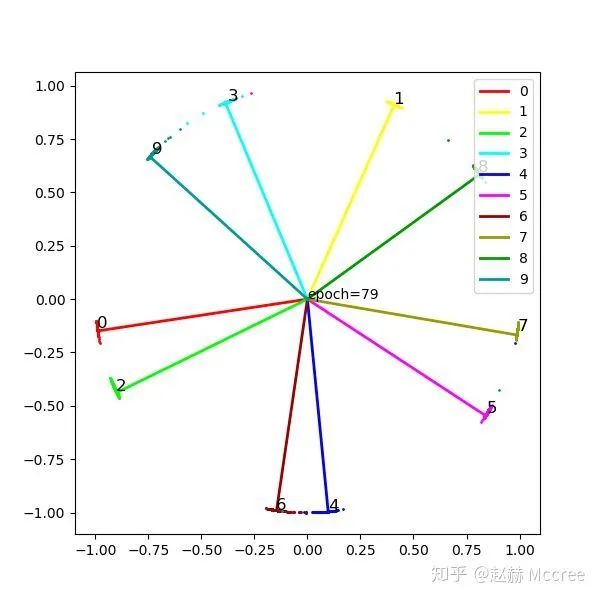
Center Loss
公式推导

 是每个类别对应的一个中心,在这里就是一个二维坐标啦。
是每个类别对应的一个中心,在这里就是一个二维坐标啦。Pytorch代码实现
class centerloss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(centerloss, self).__init__()
self.center = nn.Parameter(10 * torch.randn(10, 2))
self.lamda = 0.2
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(2, 10)) # (input,output)
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.weight)
def forward(self, feature, label):
batch_size = label.size()[0]
nCenter = self.center.index_select(dim=0, index=label)
distance = feature.dist(nCenter)
centerloss = (1 / 2.0 / batch_size) * distance
out = feature.mm(self.weight)
ceLoss = F.cross_entropy(out, label)
return out, ceLoss + self.lamda * centerloss
可视化
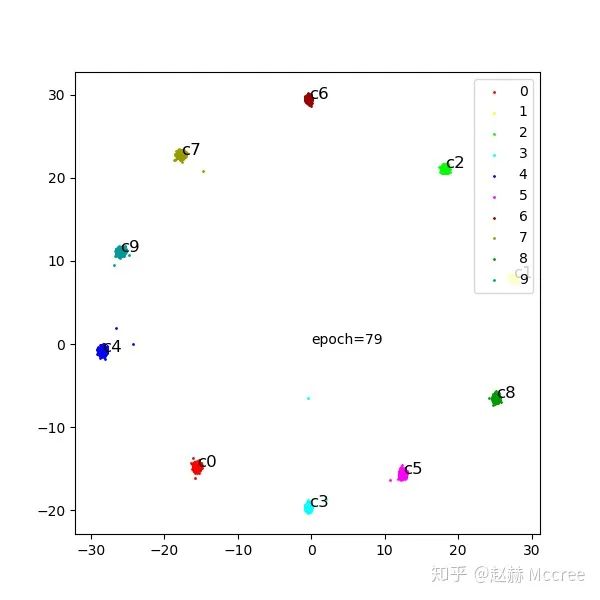
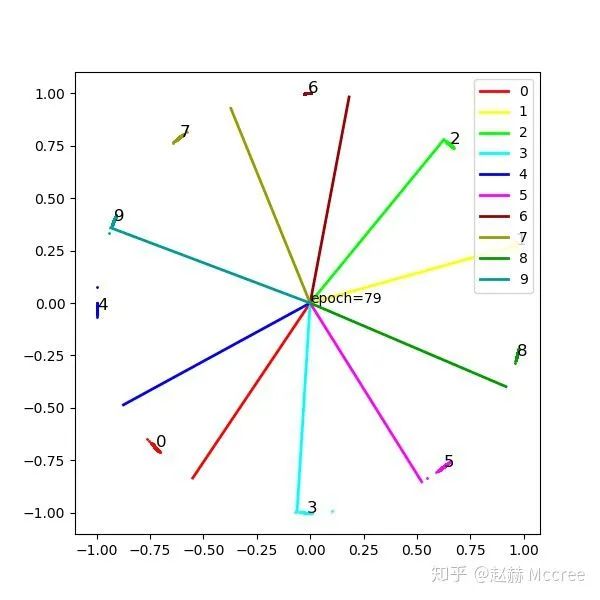
总结
推荐阅读
评论
