【统计学习方法】 第3章 k近邻法(四)课后习题
点击上方“公众号”可订阅哦!
1
●
习题3.1
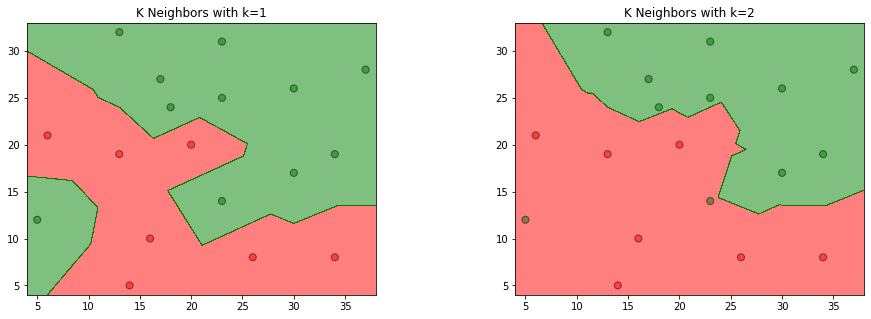
参照图3.1,在二维空间中给出实例点,画出为1和2时的近邻法构成的空间划分,并对其进行比较,体会值选择与模型复杂度及预测准确率的关系。
答:
导入包:
%matplotlib inlineimport numpy as npfrom sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifierimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
加载数据
前面两位是特征数据,第三维是标签
建立模型
data = np.array([[5, 12, 1], [6, 21, 0], [14, 5, 0], [16, 10, 0], [13, 19, 0],[13, 32, 1], [17, 27, 1], [18, 24, 1], [20, 20,0], [23, 14, 1],[23, 25, 1], [23, 31, 1], [26, 8, 0], [30, 17, 1],[30, 26, 1], [34, 8, 0], [34, 19, 1], [37, 28, 1]])X_train = data[:, 0:2]y_train = data[:, 2]models = (KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=1, n_jobs=-1),KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=2, n_jobs=-1))models = (clf.fit(X_train, y_train) for clf in models)
建立坐标矩阵:
titles = ('K Neighbors with k=1', 'K Neighbors with k=2')fig = plt.figure(figsize=(15, 5))plt.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.4, hspace=0.4)X0, X1 = X_train[:, 0], X_train[:, 1]x_min, x_max = X0.min() - 1, X0.max() + 1y_min, y_max = X1.min() - 1, X1.max() + 1xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, 0.02),np.arange(y_min, y_max, 0.02))
训练模型:
for clf, title, ax in zip(models, titles, fig.subplots(1, 2).flatten()):Z = clf.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)colors = ('red', 'green', 'lightgreen', 'gray', 'cyan')cmap = ListedColormap(colors[:len(np.unique(Z))])ax.contourf(xx, yy, Z, cmap=cmap, alpha=0.5)ax.scatter(X0, X1, c=y_train, s=50, edgecolors='k', cmap=cmap, alpha=0.5)ax.set_title(title)plt.show()
效果图:
2
●
习题3.2
利用例题3.2构造的
答:
import numpy as npfrom sklearn.neighbors import KDTreenp.random.seed(0)X = np.array([[2, 3], [5, 4], [9, 6], [4, 7], [8, 1], [7, 2]])tree = KDTree(X, leaf_size=2)dist, ind = tree.query([[3, 4.5]], k=3) #查询树中最近的3个邻居,并返回距离和索引print(dist) # 3个最近的距离print(ind) # 3个最近的索引print(X[ind]) # 3个最近的点
输出结果:
[[1.80277564 2.06155281 2.6925824 ]][[0 1 3]][[[2 3][5 4][4 7]]]
3
●
习题3.3
参照算法3.3.写出输出为x的k近邻算法。
答:
# 构建kd树,搜索待预测点所属区域from collections import namedtupleimport numpy as np# 建立节点类class Node(namedtuple("Node", "location left_child right_child")):def __repr__(self):return str(tuple(self))# kd tree类class KdTree():def __init__(self, k=1):self.k = kself.kdtree = None# 构建kd treedef _fit(self, X, depth=0):try:k = self.kexcept IndexError as e:return None# 这里可以展开,通过方差选择axisaxis = depth % kX = X[X[:, axis].argsort()]median = X.shape[0] // 2try:X[median]except IndexError:return Nonereturn Node(location=X[median],left_child=self._fit(X[:median], depth + 1),right_child=self._fit(X[median + 1:], depth + 1))def _search(self, point, tree=None, depth=0, best=None):if tree is None:return bestk = self.k# 更新 branchif point[0][depth % k] < tree.location[depth % k]:next_branch = tree.left_childelse:next_branch = tree.right_childif not next_branch is None:best = next_branch.locationreturn self._search(point,tree=next_branch,depth=depth + 1,best=best)def fit(self, X):self.kdtree = self._fit(X)return self.kdtreedef predict(self, X):res = self._search(X, self.kdtree)return res
KNN = KdTree()X_train = np.array([[2, 3], [5, 4], [9, 6], [4, 7], [8, 1], [7, 2]])KNN.fit(X_train)X_new = np.array([[3, 4.5]])res = KNN.predict(X_new)x1 = res[0]x2 = res[1]print("x点的最近邻点是({0}, {1})".format(x1, x2))
x点的最近邻点是(2, 3)END

深度学习入门笔记
微信号:sdxx_rmbj
日常更新学习笔记、论文简述
评论
