Spring Boot 四大核心组件,你知道几个?
来源:blog.csdn.net/u011909918/article/details/109647196
前言
先透露一下,四大组件分别是:starter, autoconfigure, CLI 以及actuator。
下面我们就来详细介绍一些他们有什么用。
一、Spring Boot Starter
1.1 Starter的应用示例
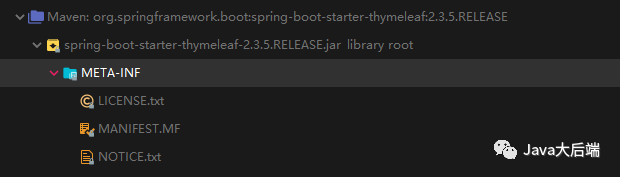
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf
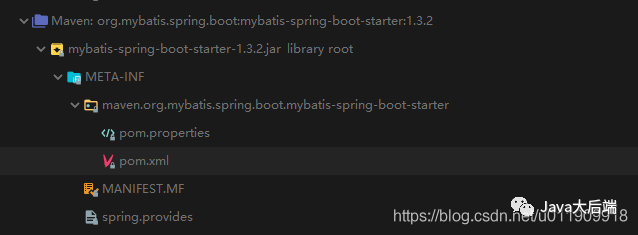
org.mybatis.spring.boot
mybatis-spring-boot-starter
1.3.2
Spring Boot 基础就不介绍了,推荐下这个实战教程:
https://github.com/javastacks/spring-boot-best-practice
在我们的Spring Boot项目种的POM文件中总会看到这两种依赖:
spring-boot-starter-xxx 和 xxx-spring-boot-starter。
这就是spring boot的四大组件之一的starter。
a、spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf
b、mybatis-spring-boot-starter
两种starter的区别就是 >>
其中xxx就是我们想要依赖的组件或者jar包。上例就是我们spring boot用来引入thymeleaf引擎和mybatis框架所配置的依赖。引入之后通过简单的约定配置就可以正常使用。
##前端引擎配置
spring:
thymeleaf:
enabled: true
servlet:
content-type: text/html
mode: HTML
## 页面前缀
prefix: classpath:/templates/
## 后缀
suffix: .html
mybatis:
mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*.xml #注意:一定要对应mapper映射xml文件的所在路径
type-aliases-package: com.hi.ld.vo.system # 注意:对应实体类的路径
configuration:
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
1.2 Spring Boot之前的Thymeleaf和Mybatis应用
废话不多说,直接上代码:
1.2.1 Thymeleaf配置
a. 添加对应依赖:
org.thymeleaf
thymeleaf-spring5
3.0.11.RELEASE
org.thymeleaf.extras
thymeleaf-extras-java8time
3.0.4.RELEASE
b. bean配置
"templateResolver"
class="org.thymeleaf.templateresolver.ServletContextTemplateResolver">
"prefix" value="/WEB-INF/templates/" />
"suffix" value=".html" />
"templateMode" value="HTML5" />
"templateEngine"
class="org.thymeleaf.spring4.SpringTemplateEngine">
"templateResolver" ref="templateResolver" />
"org.thymeleaf.spring4.view.ThymeleafViewResolver">
"templateEngine" ref="templateEngine" />
1.2.2 Mybatis配置
a. 添加对应依赖:
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-jdbc
org.mybatis
mybatis
org.mybatis
mybatis-spring
b. bean配置
下面的第3, 4步骤就是Mybatis相关配置。第一步是引入资源配置。第二步是配置数据源
"1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
"http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
"classpath:jdbc.properties" />
"dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
"driverClass" value="${jdbc.driver}" />
"jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}" />
"user" value="${jdbc.username}" />
"password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
"maxPoolSize" value="30" />
"minPoolSize" value="10" />
"autoCommitOnClose" value="false" />
"checkoutTimeout" value="10000" />
"acquireRetryAttempts" value="2" />
"sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
"dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
"configLocation" value="classpath:mybatis-config.xml" />
"typeAliasesPackage" value="com.soecode.lyf.entity" />
"mapperLocations" value="classpath:mapper/*.xml" />
"org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
"sqlSessionFactoryBeanName" value="sqlSessionFactory" />
"basePackage" value="com.soecode.lyf.dao" />
1.2.3 小结
a、Starter 帮我们封装好了所有需要的依赖,避免我们自己添加导致的一些Jar包冲突或者缺少包的情况;
b、Starter帮我们自动注入了需要的Bean实例到Spring 容器中,不需要我们手动配置(这个可以说是starter干的,实际上并不是,这里埋个坑,下面解答);
所以: starter包的内容就是pom文件,就是一个依赖传递包。
二、Spring Boot Autoconfigure
2.1 autoconfigure 简介
autoconfigure在我们的开发中并不会被感知,因为它是存在与我们的starter中的。所以我们的每个starter都是依赖autoconfigure的:
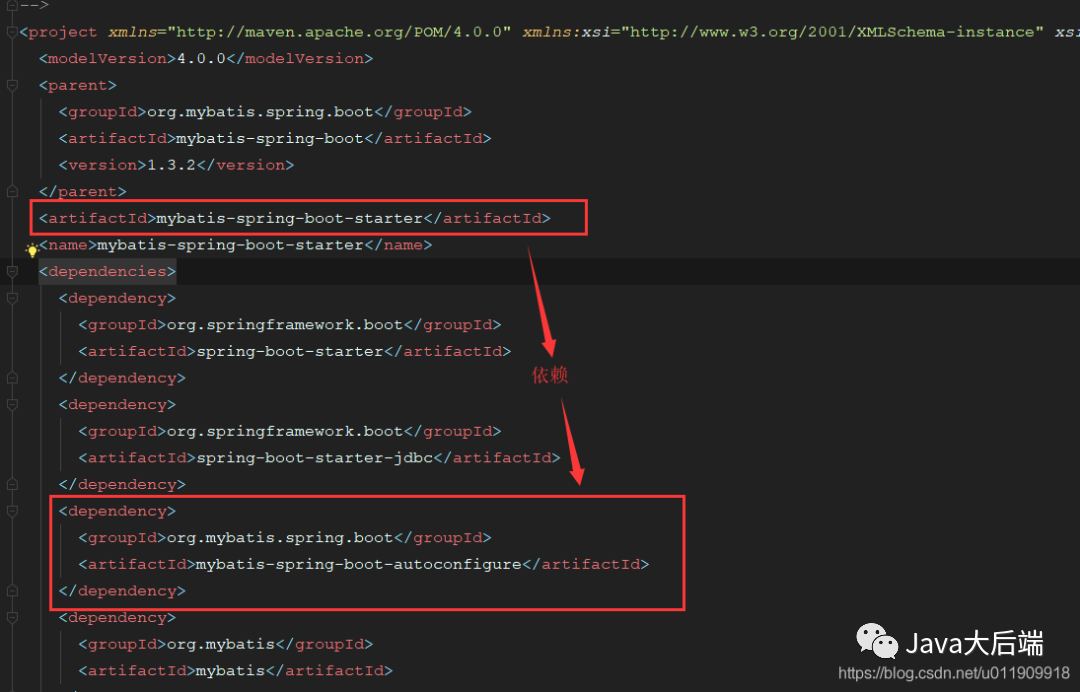
当然我们也可以把autoconfig的内容直接放在starter包里边。
a. spring-boot-autoconfigure:
注意:这里有个点,就是官网提供的configure大多数在spring-boot-autoconfigure包里边,并没有单独创建新包。
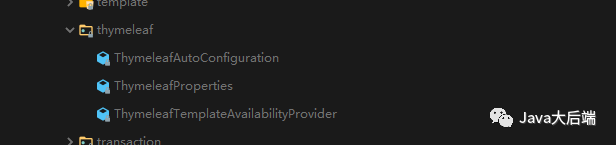
b、mybatis-spring-boot-autoconfigure
2.2 小结
autoconfigure内容是配置Bean实例到Spring容器的实际代码实现包,然后提供给starter依赖。所以说1.2.3中的b项所说的配置Bean实例到Spring容器中实际是autoconfigure做的,因为是starter依赖它,所以也可以说是starter干的。
所以:autocinfigure是starter体现出来的能力的代码实现
三、Spring Boot CLI
Spring Boot CLI是一个命令行使用Spring Boot的客户端工具;主要功能如下:
运行groovy脚本 => 官网2.1 打包groovy文件到jar => 官网2.3 初始化Spring Boot项目 => 官网2.4 其他
先上个官网文档:
https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/spring-boot-cli.html
因为这个我们用的比较少,所以就不多赘述了。个人感觉比较流脾的功能就是命令行直接执行groovy脚本了。
四、Spring Boot actuator
actuator是Spring Boot的监控插件,本身提供了很多接口可以获取当前项目的各项运行状态指标。Spring Boot 学习笔记,这个分享给你。
官网文档:
https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/2.4.0/reference/html/production-ready-features.html#production-ready
名词解释:
Endpoints: 需要监控的端点。参考官网第二节官网文档
可用的端点:
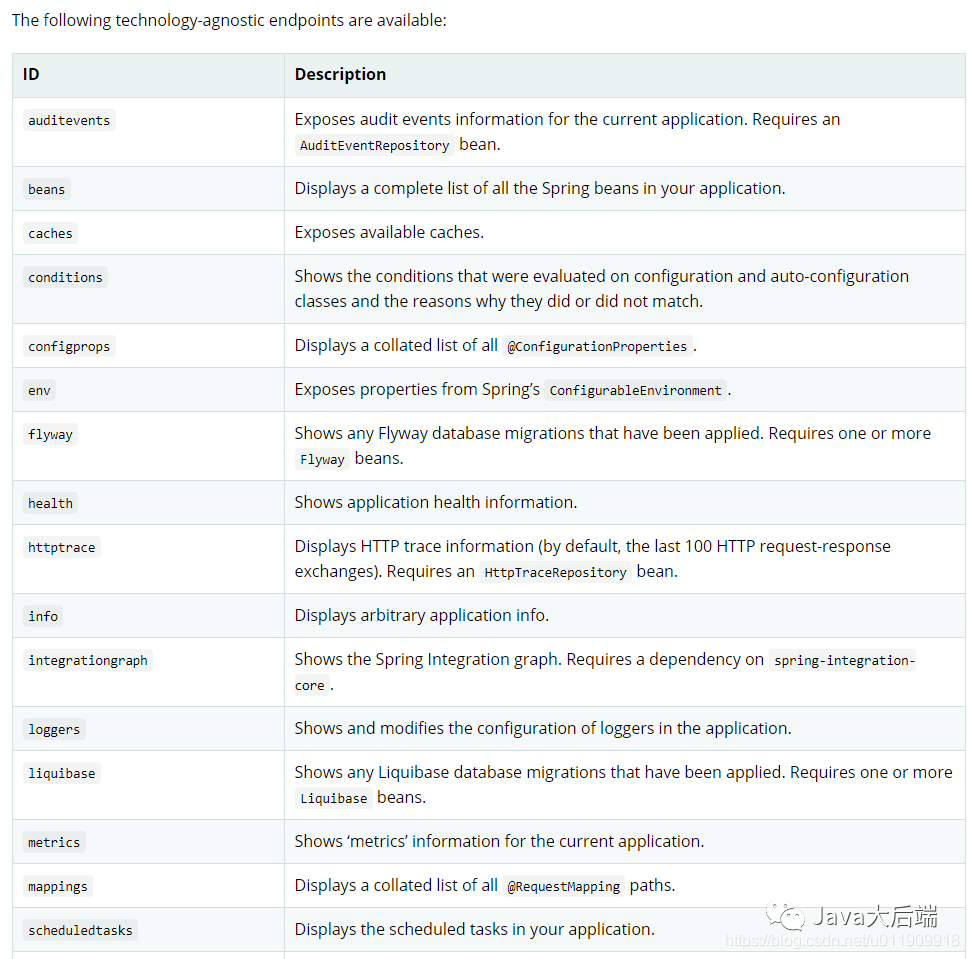
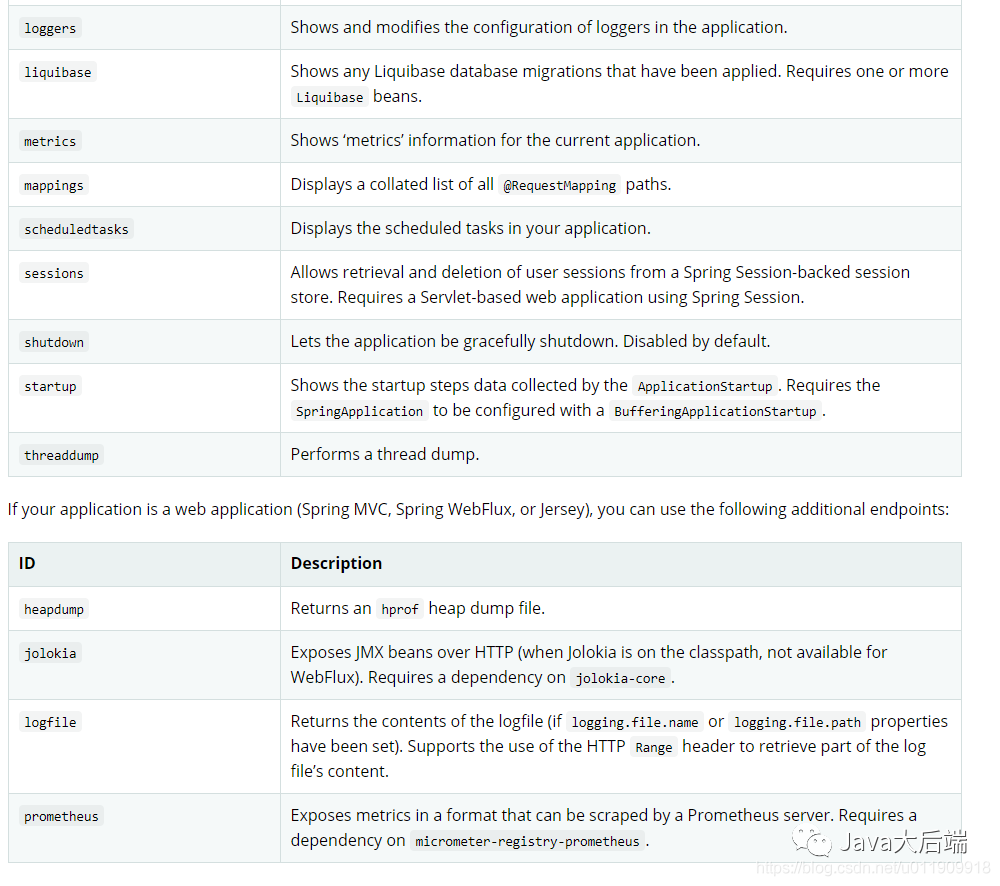
下方的是web工程的端点。
使用方法如下:
4.1 添加依赖
Spring Boot 基础就不介绍了,推荐下这个实战教程:
https://github.com/javastacks/spring-boot-best-practice
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-actuator
4.2 配置需要开启监控的端点
management:
endpoint:
health: ## 开启健康监控端点
enabled: true
beans: ## 开启Bean实例监控端点
enabled: true
4.3 启动服务并验证
4.3.1 启动结果
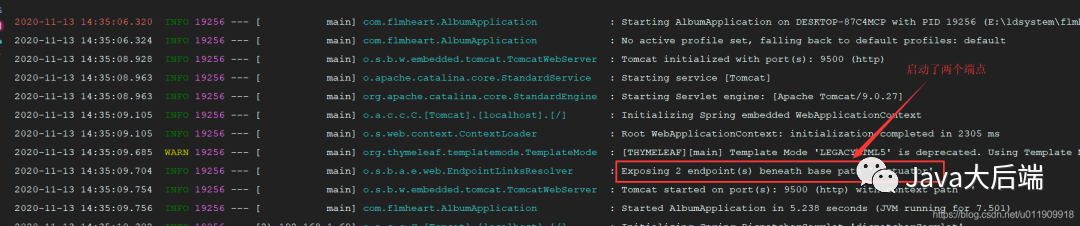
4.3.2 查看各个监控信息
浏览器访问(查看监控信息地址):http://localhost:9500/actuator
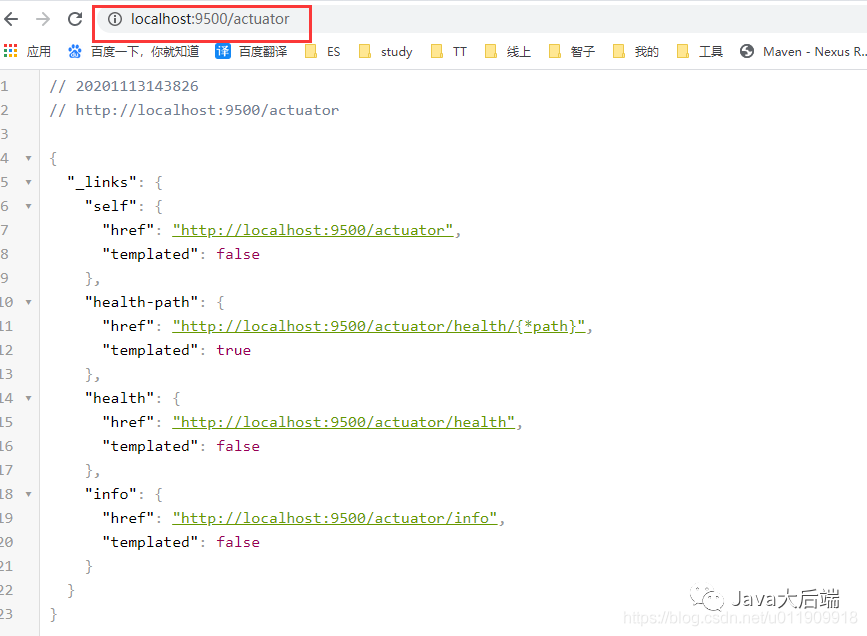
查看服务健康状态:
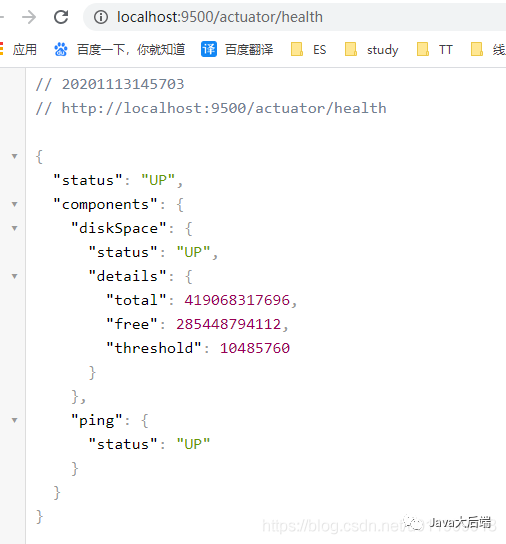
其他API查看官方文档了解或者留言一起研究一下,厚着脸皮我也没怎么用过这个。不过下一章介绍了starter和autoconfigure之后我们就可以去研究actuator的源码了。。。。
总结
本章主要介绍了Spring Boot的四大组件的作用,其中主要是starter和autoconfigure,另外的CLI和actuator用的并不多,所以没有仔细介绍。
-End-
最近有一些小伙伴,让我帮忙找一些 面试题 资料,于是我翻遍了收藏的 5T 资料后,汇总整理出来,可以说是程序员面试必备!所有资料都整理到网盘了,欢迎下载!
面试题】即可获取