Matplotlib可视化三大步骤,教你轻松制图
来源:数据分析1480
确定问题,选择图形 转换数据,应用函数 参数设置,一目了然
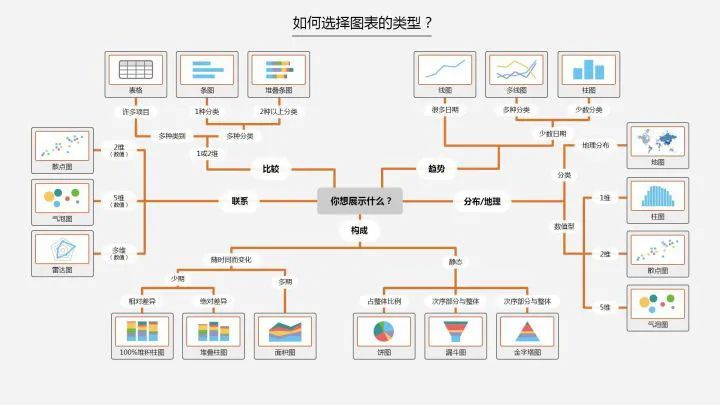
点:scatter plot 二维数据,适用于简单二维关系; 线:line plot 二维数据,适用于时间序列; 柱状:bar plot 二维数据,适用于类别统计; 颜色:heatmap 适用于展示第三维度;
合并:merge,concat,combine_frist(类似于数据库中的全外连接) 重塑:reshape;轴向旋转:pivot(类似excel数据透视表) 去重:drop_duplicates 映射:map 填充替换:fillna,replace 重命名轴索引:rename
#导入包import numpy as npimport pandas as pdimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#创建画布fig = plt.figure()#创建subplot,221表示这是2行2列表格中的第1个图像。ax1 = fig.add_subplot(221)#但现在更习惯使用以下方法创建画布和图像,2,2表示这是一个2*2的画布,可以放置4个图像fig , axes = plt.subplots(2,2,sharex=True,sharey=True)#plt.subplot的sharex和sharey参数可以指定所有的subplot使用相同的x,y轴刻度。
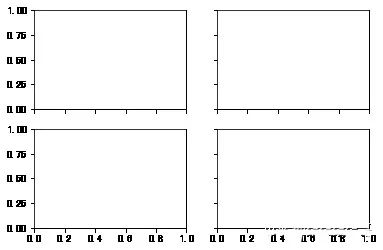
subplots_adjust(left=None,bottom=None,right=None,top=None,wspace=None,hspace=None)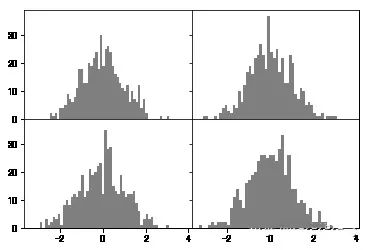
plt.plot(np.random.randn(30),color='g',linestyle='--',marker='o')[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x8c919b0>]
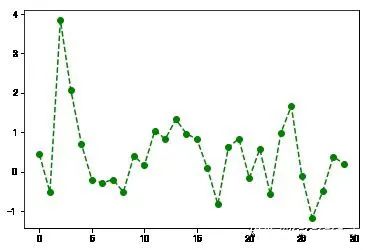
plt.plot(np.random.randn(30),color='g',linestyle='--',marker='o')plt.xlim() #不带参数调用,显示当前参数;#可将xlim替换为另外两个方法试试(-1.4500000000000002, 30.45)
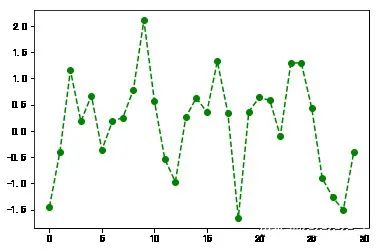
plt.plot(np.random.randn(30),color='g',linestyle='--',marker='o')plt.xlim([0,15]) #横轴刻度变成0-15(0, 15)
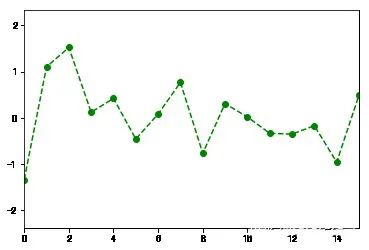
fig = plt.figure();ax = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)ax.plot(np.random.randn(1000).cumsum())ticks = ax.set_xticks([0,250,500,750,1000]) #设置刻度值labels = ax.set_xticklabels(['one','two','three','four','five']) #设置刻度标签ax.set_title('My first Plot') #设置标题ax.set_xlabel('Stage') #设置轴标签Text(0.5,0,'Stage')
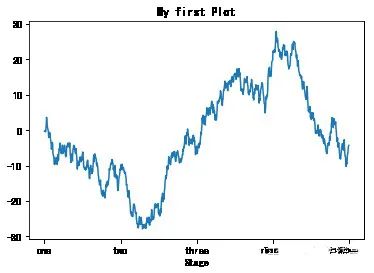
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12,5));ax = fig.add_subplot(111)ax.plot(np.random.randn(1000).cumsum(),'k',label='one') #传入label参数,定义label名称ax.plot(np.random.randn(1000).cumsum(),'k--',label='two')ax.plot(np.random.randn(1000).cumsum(),'k.',label='three')#图形创建完后,只需要调用legend参数将label调出来即可。ax.legend(loc='best') #要求不是很严格的话,建议使用loc=‘best’参数来让它自己选择最佳位置
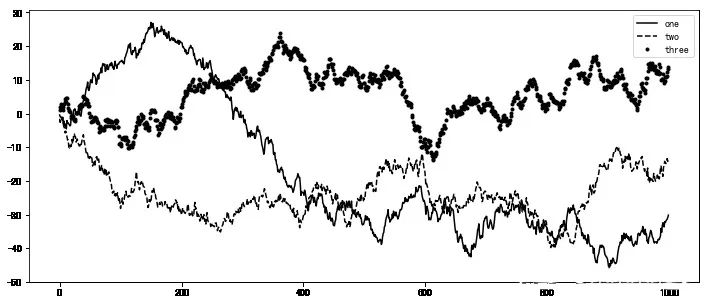
plt.plot(np.random.randn(1000).cumsum())plt.text(600,10,'test ',family='monospace',fontsize=10)#中文注释在默认环境下并不能正常显示,需要修改配置文件,使其支持中文字体。具体步骤请自行搜索。
fname:含有文件路径的字符串,拓展名指定文件类型 dpi:分辨率,默认100 facecolor,edgcolor 图像的背景色,默认‘w’白色 format:显示设置文件格式('png','pdf','svg','ps','jpg'等) bbox_inches:图表需要保留的部分。如果设置为“tight”,则将尝试剪除图像周围的空白部分
plt.savefig('./plot.jpg') #保存图像为plot名称的jpg格式图像432 x288 with 0 Axes>
import matplotlib.pyplot as plts = pd.Series(np.random.randn(10).cumsum(),index=np.arange(0,100,10))s.plot() #Series对象的索引index会传给matplotlib用作绘制x轴。
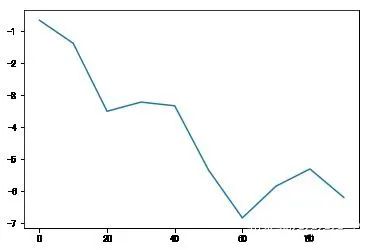
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(10,4).cumsum(0),columns=['A','B','C','D'])df.plot() #plot会自动为不同变量改变颜色,并添加图例
label:用于图表的标签 style:风格字符串,'g--' alpha:图像的填充不透明度(0-1) kind:图表类型(bar,line,hist,kde等) xticks:设定x轴刻度值 yticks:设定y轴刻度值 xlim,ylim:设定轴界限,[0,10] grid:显示轴网格线,默认关闭 rot:旋转刻度标签 use_index:将对象的索引用作刻度标签 logy:在Y轴上使用对数标尺
subplots:将各个DataFrame列绘制到单独的subplot中 sharex,sharey:共享x,y轴 figsize:控制图像大小 title:图像标题 legend:添加图例,默认显示 sort_columns:以字母顺序绘制各列,默认使用当前顺序
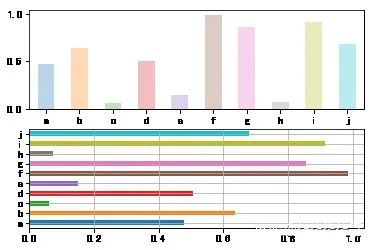
fig,axes = plt.subplots(2,1)data = pd.Series(np.random.rand(10),index=list('abcdefghij'))data.plot(kind='bar',ax=axes[0],rot=0,alpha=0.3)data.plot(kind='barh',ax=axes[1],grid=True)0xfe39898 >
Python大数据分析
data creates value
扫码关注我们
评论
