大梳理!深度学习优化算法:从 SGD 到 AdamW 原理和代码解读
统一框架:
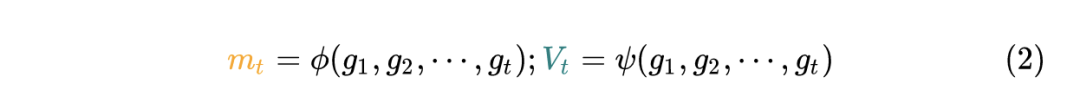
共性的方法有:
add_param_group(param_group):把参数放进优化器中,这在 Fine-tune 预训练网络时很有用,因为可以使冻结层可训练并随着训练的进行添加到优化器中。load_state_dict(state_dict):把优化器的状态加载进去。state_dict():返回优化器的状态,以dict的形式返回。step(closure=None):优化一步参数。zero_grad(set_to_none=False):把所有的梯度值设为0。
使用方法:
for input, target in dataset:
def closure():
optimizer.zero_grad()
output = model(input)
loss = loss_fn(output, target)
loss.backward()
return loss
optimizer.step(closure)
SGD
SGD with Momentum
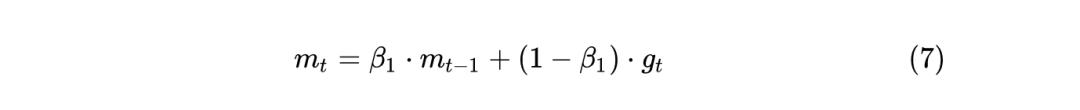
SGD with Nesterov Acceleration
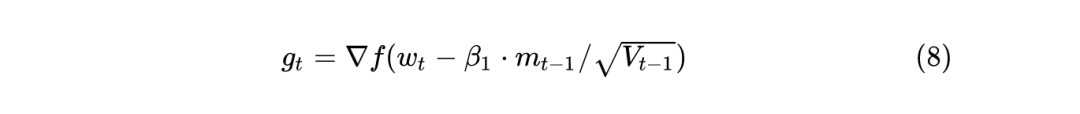
定义优化器:
CLASS torch.optim.SGD(params, lr=<required parameter>, momentum=0, dampening=0, weight_decay=0, nesterov=False)
参数:
params (iterable) – 优化器作用的模型参数。 lr (float) – learning rate,相当于是统一框架中的 。 momentum (float, optional) – 动量参数。(默认值:0) weight_decay (float, optional) – 权重衰减系数 weight decay (L2 penalty) (默认值:0) dampening (float, optional) – dampening for momentum (默认值:0) nesterov (bool, optional) – 允许 Nesterov momentum (默认值:False)
源码解读:
import torch
from .optimizer import Optimizer, required
[docs]class SGD(Optimizer):
r"""Implements stochastic gradient descent (optionally with momentum).
Nesterov momentum is based on the formula from
`On the importance of initialization and momentum in deep learning`__.
Args:
params (iterable): iterable of parameters to optimize or dicts defining
parameter groups
lr (float): learning rate
momentum (float, optional): momentum factor (default: 0)
weight_decay (float, optional): weight decay (L2 penalty) (default: 0)
dampening (float, optional): dampening for momentum (default: 0)
nesterov (bool, optional): enables Nesterov momentum (default: False)
Example:
>>> optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.1, momentum=0.9)
>>> optimizer.zero_grad()
>>> loss_fn(model(input), target).backward()
>>> optimizer.step()
__ http://www.cs.toronto.edu/%7Ehinton/absps/momentum.pdf
.. note::
The implementation of SGD with Momentum/Nesterov subtly differs from
Sutskever et. al. and implementations in some other frameworks.
Considering the specific case of Momentum, the update can be written as
.. math::
\begin{aligned}
v_{t+1} & = \mu * v_{t} + g_{t+1}, \\
p_{t+1} & = p_{t} - \text{lr} * v_{t+1},
\end{aligned}
where :math:`p`, :math:`g`, :math:`v` and :math:`\mu` denote the
parameters, gradient, velocity, and momentum respectively.
This is in contrast to Sutskever et. al. and
other frameworks which employ an update of the form
.. math::
\begin{aligned}
v_{t+1} & = \mu * v_{t} + \text{lr} * g_{t+1}, \\
p_{t+1} & = p_{t} - v_{t+1}.
\end{aligned}
The Nesterov version is analogously modified.
"""
def __init__(self, params, lr=required, momentum=0, dampening=0,
weight_decay=0, nesterov=False):
if lr is not required and lr < 0.0:
raise ValueError("Invalid learning rate: {}".format(lr))
if momentum < 0.0:
raise ValueError("Invalid momentum value: {}".format(momentum))
if weight_decay < 0.0:
raise ValueError("Invalid weight_decay value: {}".format(weight_decay))
defaults = dict(lr=lr, momentum=momentum, dampening=dampening,
weight_decay=weight_decay, nesterov=nesterov)
if nesterov and (momentum <= 0 or dampening != 0):
raise ValueError("Nesterov momentum requires a momentum and zero dampening")
super(SGD, self).__init__(params, defaults)
def __setstate__(self, state):
super(SGD, self).__setstate__(state)
for group in self.param_groups:
group.setdefault('nesterov', False)
[docs] @torch.no_grad()
def step(self, closure=None):
"""Performs a single optimization step.
Arguments:
closure (callable, optional): A closure that reevaluates the model
and returns the loss.
"""
loss = None
if closure is not None:
with torch.enable_grad():
loss = closure()
for group in self.param_groups:
weight_decay = group['weight_decay']
momentum = group['momentum']
dampening = group['dampening']
nesterov = group['nesterov']
for p in group['params']:
if p.grad is None:
continue
d_p = p.grad
if weight_decay != 0:
d_p = d_p.add(p, alpha=weight_decay)
if momentum != 0:
param_state = self.state[p]
if 'momentum_buffer' not in param_state:
buf = param_state['momentum_buffer'] = torch.clone(d_p).detach()
else:
buf = param_state['momentum_buffer']
buf.mul_(momentum).add_(d_p, alpha=1 - dampening)
if nesterov:
d_p = d_p.add(buf, alpha=momentum)
else:
d_p = buf
p.add_(d_p, alpha=-group['lr'])
return loss
这里通过 d_p=p.grad 得到每个参数的梯度,也就是1式的 。 如果使用 weight_decay 的话,那么相当于目标函数加上 ,所以相当于是梯度相当于要再加上 ,所以使用了 d_p = d_p.add(p, alpha=weight_decay)。 通过 buf.mul_(momentum).add_(d_p, alpha=1 - dampening) 来计算动量,momentum参数 一般取0.9,就相当于是之前的动量buf乘以 ,再加上此次的梯度d_p乘以 。 如果不通过nesterov方式更新参数,那么3式中的 就相当于是上一步计算出的动量 了。如果通过nesterov方式更新参数,那么3式中的 就相当于 ,和不用nesterov方式相比,相差了 。 最后通过 p.add_(d_p, alpha=-group['lr']) 更新梯度,相当于是上面的 3 式。
AdaGrad
定义优化器:
CLASS torch.optim.Adagrad(params,lr=0.01,lr_decay=0,weight_decay=0,initial_accumulator_value=0,eps=1e-10)
参数:
params (iterable) – 优化器作用的模型参数。 lr (float) – learning rate – 相当于是统一框架中的 。 lr_decay(float,optional) – 学习率衰减 (默认值:0) weight_decay (float, optional) – 权重衰减系数 weight decay (L2 penalty) (默认值:0) eps(float,optional):防止分母为0的一个小数 (默认值:1e-10)
源码解读:
[docs]class Adagrad(Optimizer):
"""Implements Adagrad algorithm.
It has been proposed in `Adaptive Subgradient Methods for Online Learning
and Stochastic Optimization`_.
Arguments:
params (iterable): iterable of parameters to optimize or dicts defining
parameter groups
lr (float, optional): learning rate (default: 1e-2)
lr_decay (float, optional): learning rate decay (default: 0)
weight_decay (float, optional): weight decay (L2 penalty) (default: 0)
eps (float, optional): term added to the denominator to improve
numerical stability (default: 1e-10)
.. _Adaptive Subgradient Methods for Online Learning and Stochastic
Optimization: http://jmlr.org/papers/v12/duchi11a.html
"""
def __init__(self, params, lr=1e-2, lr_decay=0, weight_decay=0, initial_accumulator_value=0, eps=1e-10):
if not 0.0 <= lr:
raise ValueError("Invalid learning rate: {}".format(lr))
if not 0.0 <= lr_decay:
raise ValueError("Invalid lr_decay value: {}".format(lr_decay))
if not 0.0 <= weight_decay:
raise ValueError("Invalid weight_decay value: {}".format(weight_decay))
if not 0.0 <= initial_accumulator_value:
raise ValueError("Invalid initial_accumulator_value value: {}".format(initial_accumulator_value))
if not 0.0 <= eps:
raise ValueError("Invalid epsilon value: {}".format(eps))
defaults = dict(lr=lr, lr_decay=lr_decay, eps=eps, weight_decay=weight_decay,
initial_accumulator_value=initial_accumulator_value)
super(Adagrad, self).__init__(params, defaults)
for group in self.param_groups:
for p in group['params']:
state = self.state[p]
state['step'] = 0
state['sum'] = torch.full_like(p, initial_accumulator_value, memory_format=torch.preserve_format)
def share_memory(self):
for group in self.param_groups:
for p in group['params']:
state = self.state[p]
state['sum'].share_memory_()
[docs] @torch.no_grad()
def step(self, closure=None):
"""Performs a single optimization step.
Arguments:
closure (callable, optional): A closure that reevaluates the model
and returns the loss.
"""
loss = None
if closure is not None:
with torch.enable_grad():
loss = closure()
for group in self.param_groups:
params_with_grad = []
grads = []
state_sums = []
state_steps = []
for p in group['params']:
if p.grad is not None:
params_with_grad.append(p)
grads.append(p.grad)
state = self.state[p]
state_sums.append(state['sum'])
# update the steps for each param group update
state['step'] += 1
# record the step after step update
state_steps.append(state['step'])
F.adagrad(params_with_grad,
grads,
state_sums,
state_steps,
group['lr'],
group['weight_decay'],
group['lr_decay'],
group['eps'])
return loss
AdaDelta / RMSProp
RMSProp
定义优化器:
CLASS torch.optim.RMSprop(params, lr=0.01, alpha=0.99, eps=1e-08, weight_decay=0, momentum=0, centered=False)
参数:
params (iterable) – 优化器作用的模型参数。 lr (float) – learning rate – 相当于是统一框架中的 。 momentum (float, optional) – 动量参数。(默认值:0)。 alpha(float,optional) – 平滑常数 (默认值:0.99)。 centered(bool,optional) – if True, compute the centered RMSProp, the gradient is normalized by an estimation of its variance,就是这一项是 True 的话就把方差使用梯度作归一化。weight_decay (float, optional) – 权重衰减系数 weight decay (L2 penalty) (默认值:0) eps(float,optional):防止分母为0的一个小数 (默认值:1e-10)
源码解读:
import torch
from .optimizer import Optimizer
[docs]class RMSprop(Optimizer):
r"""Implements RMSprop algorithm.
Proposed by G. Hinton in his
`course <https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~tijmen/csc321/slides/lecture_slides_lec6.pdf>`_.
The centered version first appears in `Generating Sequences
With Recurrent Neural Networks <https://arxiv.org/pdf/1308.0850v5.pdf>`_.
The implementation here takes the square root of the gradient average before
adding epsilon (note that TensorFlow interchanges these two operations). The effective
learning rate is thus :math:`\alpha/(\sqrt{v} + \epsilon)` where :math:`\alpha`
is the scheduled learning rate and :math:`v` is the weighted moving average
of the squared gradient.
Arguments:
params (iterable): iterable of parameters to optimize or dicts defining
parameter groups
lr (float, optional): learning rate (default: 1e-2)
momentum (float, optional): momentum factor (default: 0)
alpha (float, optional): smoothing constant (default: 0.99)
eps (float, optional): term added to the denominator to improve
numerical stability (default: 1e-8)
centered (bool, optional) : if ``True``, compute the centered RMSProp,
the gradient is normalized by an estimation of its variance
weight_decay (float, optional): weight decay (L2 penalty) (default: 0)
"""
def __init__(self, params, lr=1e-2, alpha=0.99, eps=1e-8, weight_decay=0, momentum=0, centered=False):
if not 0.0 <= lr:
raise ValueError("Invalid learning rate: {}".format(lr))
if not 0.0 <= eps:
raise ValueError("Invalid epsilon value: {}".format(eps))
if not 0.0 <= momentum:
raise ValueError("Invalid momentum value: {}".format(momentum))
if not 0.0 <= weight_decay:
raise ValueError("Invalid weight_decay value: {}".format(weight_decay))
if not 0.0 <= alpha:
raise ValueError("Invalid alpha value: {}".format(alpha))
defaults = dict(lr=lr, momentum=momentum, alpha=alpha, eps=eps, centered=centered, weight_decay=weight_decay)
super(RMSprop, self).__init__(params, defaults)
def __setstate__(self, state):
super(RMSprop, self).__setstate__(state)
for group in self.param_groups:
group.setdefault('momentum', 0)
group.setdefault('centered', False)
[docs] @torch.no_grad()
def step(self, closure=None):
"""Performs a single optimization step.
Arguments:
closure (callable, optional): A closure that reevaluates the model
and returns the loss.
"""
loss = None
if closure is not None:
with torch.enable_grad():
loss = closure()
for group in self.param_groups:
for p in group['params']:
if p.grad is None:
continue
grad = p.grad
if grad.is_sparse:
raise RuntimeError('RMSprop does not support sparse gradients')
state = self.state[p]
# State initialization
if len(state) == 0:
state['step'] = 0
state['square_avg'] = torch.zeros_like(p, memory_format=torch.preserve_format)
if group['momentum'] > 0:
state['momentum_buffer'] = torch.zeros_like(p, memory_format=torch.preserve_format)
if group['centered']:
state['grad_avg'] = torch.zeros_like(p, memory_format=torch.preserve_format)
square_avg = state['square_avg']
alpha = group['alpha']
state['step'] += 1
if group['weight_decay'] != 0:
grad = grad.add(p, alpha=group['weight_decay'])
square_avg.mul_(alpha).addcmul_(grad, grad, value=1 - alpha)
if group['centered']:
grad_avg = state['grad_avg']
grad_avg.mul_(alpha).add_(grad, alpha=1 - alpha)
avg = square_avg.addcmul(grad_avg, grad_avg, value=-1).sqrt_().add_(group['eps'])
else:
avg = square_avg.sqrt().add_(group['eps'])
if group['momentum'] > 0:
buf = state['momentum_buffer']
buf.mul_(group['momentum']).addcdiv_(grad, avg)
p.add_(buf, alpha=-group['lr'])
else:
p.addcdiv_(grad, avg, value=-group['lr'])
return loss
这里通过 grad = p.grad 得到每个参数的梯度,也就是1式的 。 如果使用 weight_decay 的话,那么相当于目标函数加上 ,所以相当于是梯度相当于要再加上 ,故使用了 grad = grad.add(p, alpha=group['weight_decay'])。 square_avg.mul_(alpha).addcmul_(grad, grad, value=1 - alpha) 对应10式,计算当前步的 。 centered 这一项是 False 的话直接 square_avg.sqrt().add_(group['eps']) 对 开根号。
centered 这一项是 True 的话就把方差使用梯度作归一化。最后通过 p.addcdiv_(grad, avg, value=-group['lr']) 更新梯度,相当于是上面的 3 式。
RMSprop算是Adagrad的一种发展,和Adadelta的变体,效果趋于二者之间
AdaDelta
定义优化器:
CLASS torch.optim.Adadelta(params, lr=1.0, rho=0.9, eps=1e-06, weight_decay=0)
参数:
params (iterable) – 优化器作用的模型参数。 lr (float) – learning rate – 相当于是统一框架中的 。 rho(float,optional) – 计算梯度平方的滑动平均超参数 (默认值:0.9) weight_decay (float, optional) – 权重衰减系数 weight decay (L2 penalty) (默认值:0) eps(float,optional):防止分母为0的一个小数 (默认值:1e-10)
源码解读:
import torch
from .optimizer import Optimizer
[docs]class Adadelta(Optimizer):
"""Implements Adadelta algorithm.
It has been proposed in `ADADELTA: An Adaptive Learning Rate Method`__.
Arguments:
params (iterable): iterable of parameters to optimize or dicts defining
parameter groups
rho (float, optional): coefficient used for computing a running average
of squared gradients (default: 0.9)
eps (float, optional): term added to the denominator to improve
numerical stability (default: 1e-6)
lr (float, optional): coefficient that scale delta before it is applied
to the parameters (default: 1.0)
weight_decay (float, optional): weight decay (L2 penalty) (default: 0)
__ https://arxiv.org/abs/1212.5701
"""
def __init__(self, params, lr=1.0, rho=0.9, eps=1e-6, weight_decay=0):
if not 0.0 <= lr:
raise ValueError("Invalid learning rate: {}".format(lr))
if not 0.0 <= rho <= 1.0:
raise ValueError("Invalid rho value: {}".format(rho))
if not 0.0 <= eps:
raise ValueError("Invalid epsilon value: {}".format(eps))
if not 0.0 <= weight_decay:
raise ValueError("Invalid weight_decay value: {}".format(weight_decay))
defaults = dict(lr=lr, rho=rho, eps=eps, weight_decay=weight_decay)
super(Adadelta, self).__init__(params, defaults)
[docs] @torch.no_grad()
def step(self, closure=None):
"""Performs a single optimization step.
Arguments:
closure (callable, optional): A closure that reevaluates the model
and returns the loss.
"""
loss = None
if closure is not None:
with torch.enable_grad():
loss = closure()
for group in self.param_groups:
for p in group['params']:
if p.grad is None:
continue
grad = p.grad
if grad.is_sparse:
raise RuntimeError('Adadelta does not support sparse gradients')
state = self.state[p]
# State initialization
if len(state) == 0:
state['step'] = 0
state['square_avg'] = torch.zeros_like(p, memory_format=torch.preserve_format)
state['acc_delta'] = torch.zeros_like(p, memory_format=torch.preserve_format)
square_avg, acc_delta = state['square_avg'], state['acc_delta']
rho, eps = group['rho'], group['eps']
state['step'] += 1
if group['weight_decay'] != 0:
grad = grad.add(p, alpha=group['weight_decay'])
square_avg.mul_(rho).addcmul_(grad, grad, value=1 - rho)
std = square_avg.add(eps).sqrt_()
delta = acc_delta.add(eps).sqrt_().div_(std).mul_(grad)
p.add_(delta, alpha=-group['lr'])
acc_delta.mul_(rho).addcmul_(delta, delta, value=1 - rho)
return loss
这里通过 grad = p.grad 得到每个参数的梯度,也就是1式的 。 如果使用 weight_decay 的话,那么相当于目标函数加上 ,所以相当于是梯度相当于要再加上 ,故使用了 grad = grad.add(p, alpha=group['weight_decay'])。 square_avg.mul_(rho).addcmul_(grad, grad, value=1 - rho) 对应10式,计算当前步的 。std = square_avg.add(eps).sqrt_() 对 开根号。 最后通过 p.add_(delta, alpha=-group['lr']) 更新梯度,相当于是上面的 3 式。
delta 的分子项是 ,分母项是 开根号。acc_delta 是对 delta 的滑动平均。
Adam
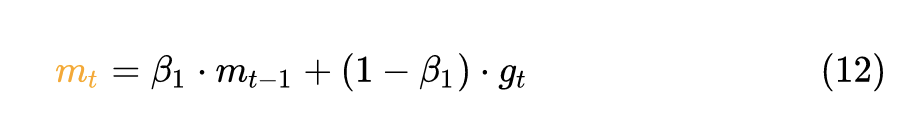
Nadam

定义优化器:
CLASS torch.optim.Adam(params, lr=0.001, betas=(0.9, 0.999), eps=1e-08, weight_decay=0, amsgrad=False)
参数:
params (iterable) – 优化器作用的模型参数。 lr (float) – learning rate – 相当于是统一框架中的 。 betas(Tuple[float,float],optional) – coefficients used for computing running averages of gradient and its square ((默认值:(0.9, 0.999)) weight_decay (float, optional) – 权重衰减系数 weight decay (L2 penalty) (默认值:0) eps(float,optional):防止分母为0的一个小数 (默认值:1e-10)
源码解读:
import math
import torch
from .optimizer import Optimizer
[docs]class Adam(Optimizer):
r"""Implements Adam algorithm.
It has been proposed in `Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization`_.
Arguments:
params (iterable): iterable of parameters to optimize or dicts defining
parameter groups
lr (float, optional): learning rate (default: 1e-3)
betas (Tuple[float, float], optional): coefficients used for computing
running averages of gradient and its square (default: (0.9, 0.999))
eps (float, optional): term added to the denominator to improve
numerical stability (default: 1e-8)
weight_decay (float, optional): weight decay (L2 penalty) (default: 0)
amsgrad (boolean, optional): whether to use the AMSGrad variant of this
algorithm from the paper `On the Convergence of Adam and Beyond`_
(default: False)
.. _Adam\: A Method for Stochastic Optimization:
https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6980
.. _On the Convergence of Adam and Beyond:
https://openreview.net/forum?id=ryQu7f-RZ
"""
def __init__(self, params, lr=1e-3, betas=(0.9, 0.999), eps=1e-8,
weight_decay=0, amsgrad=False):
if not 0.0 <= lr:
raise ValueError("Invalid learning rate: {}".format(lr))
if not 0.0 <= eps:
raise ValueError("Invalid epsilon value: {}".format(eps))
if not 0.0 <= betas[0] < 1.0:
raise ValueError("Invalid beta parameter at index 0: {}".format(betas[0]))
if not 0.0 <= betas[1] < 1.0:
raise ValueError("Invalid beta parameter at index 1: {}".format(betas[1]))
if not 0.0 <= weight_decay:
raise ValueError("Invalid weight_decay value: {}".format(weight_decay))
defaults = dict(lr=lr, betas=betas, eps=eps,
weight_decay=weight_decay, amsgrad=amsgrad)
super(Adam, self).__init__(params, defaults)
def __setstate__(self, state):
super(Adam, self).__setstate__(state)
for group in self.param_groups:
group.setdefault('amsgrad', False)
[docs] @torch.no_grad()
def step(self, closure=None):
"""Performs a single optimization step.
Arguments:
closure (callable, optional): A closure that reevaluates the model
and returns the loss.
"""
loss = None
if closure is not None:
with torch.enable_grad():
loss = closure()
for group in self.param_groups:
for p in group['params']:
if p.grad is None:
continue
grad = p.grad
if grad.is_sparse:
raise RuntimeError('Adam does not support sparse gradients, please consider SparseAdam instead')
amsgrad = group['amsgrad']
state = self.state[p]
# State initialization
if len(state) == 0:
state['step'] = 0
# Exponential moving average of gradient values
state['exp_avg'] = torch.zeros_like(p, memory_format=torch.preserve_format)
# Exponential moving average of squared gradient values
state['exp_avg_sq'] = torch.zeros_like(p, memory_format=torch.preserve_format)
if amsgrad:
# Maintains max of all exp. moving avg. of sq. grad. values
state['max_exp_avg_sq'] = torch.zeros_like(p, memory_format=torch.preserve_format)
exp_avg, exp_avg_sq = state['exp_avg'], state['exp_avg_sq']
if amsgrad:
max_exp_avg_sq = state['max_exp_avg_sq']
beta1, beta2 = group['betas']
state['step'] += 1
bias_correction1 = 1 - beta1 ** state['step']
bias_correction2 = 1 - beta2 ** state['step']
if group['weight_decay'] != 0:
grad = grad.add(p, alpha=group['weight_decay'])
# Decay the first and second moment running average coefficient
exp_avg.mul_(beta1).add_(grad, alpha=1 - beta1)
exp_avg_sq.mul_(beta2).addcmul_(grad, grad, value=1 - beta2)
if amsgrad:
# Maintains the maximum of all 2nd moment running avg. till now
torch.max(max_exp_avg_sq, exp_avg_sq, out=max_exp_avg_sq)
# Use the max. for normalizing running avg. of gradient
denom = (max_exp_avg_sq.sqrt() / math.sqrt(bias_correction2)).add_(group['eps'])
else:
denom = (exp_avg_sq.sqrt() / math.sqrt(bias_correction2)).add_(group['eps'])
step_size = group['lr'] / bias_correction1
p.addcdiv_(exp_avg, denom, value=-step_size)
return loss
这里通过 grad = p.grad 得到每个参数的梯度,也就是1式的 。 如果使用 weight_decay 的话,那么相当于目标函数加上 ,所以相当于是梯度相当于要再加上 ,故使用了 grad = grad.add(p, alpha=group['weight_decay'])。 exp_avg.mul_(beta1).add_(grad, alpha=1 - beta1) 计算12式。
exp_avg_sq.mul_(beta2).addcmul_(grad, grad, value=1 - beta2) 计算13式。
因为15式的缘故,要给分母除以 math**.**sqrt(bias_correction2)。
因为14式的缘故,要给分子除以 bias_correction1。
最后通过 p.addcdiv_(exp_avg, denom, value=-step_size) 更新梯度,相当于是上面的 3 式。
AdamW
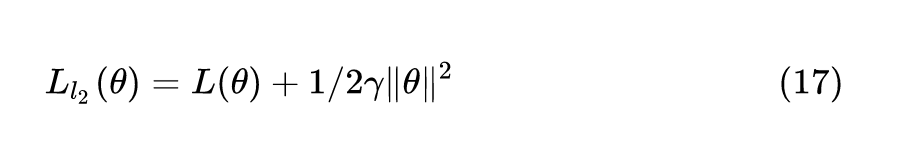
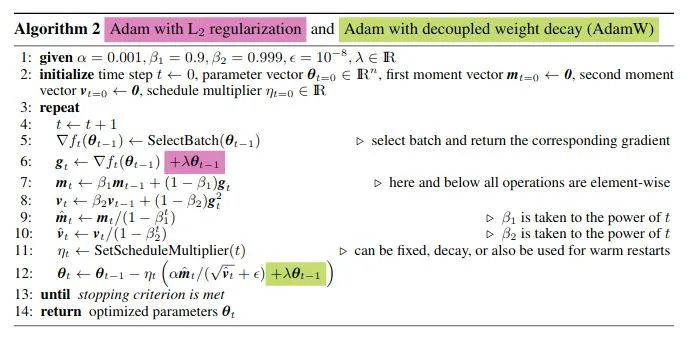
Just adding the square of the weights to the loss function is *not* the correct way of using L2 regularization/weight decay with Adam, since that will interact with the m and v parameters in strange ways. Instead we want to decay the weights in a manner that doesn't interact with the m/v parameters. This is equivalent to adding the square of the weights to the loss with plain (non-momentum) SGD. Add weight decay at the end (fixed version).
定义优化器:
CLASS torch.optim.AdamW(params, lr=0.001, betas=(0.9, 0.999), eps=1e-08, weight_decay=0.01, amsgrad=False)
参数:
params (iterable) – 优化器作用的模型参数。 lr (float) – learning rate – 相当于是统一框架中的 。 betas(Tuple[float,float],optional) – coefficients used for computing running averages of gradient and its square ((默认值:(0.9, 0.999)) weight_decay (float, optional) – 权重衰减系数 weight decay (L2 penalty) (默认值:0) eps(float,optional):防止分母为0的一个小数 (默认值:1e-10)
源码解读:
import math
import torch
from .optimizer import Optimizer
[docs]class AdamW(Optimizer):
r"""Implements AdamW algorithm.
The original Adam algorithm was proposed in `Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization`_.
The AdamW variant was proposed in `Decoupled Weight Decay Regularization`_.
Arguments:
params (iterable): iterable of parameters to optimize or dicts defining
parameter groups
lr (float, optional): learning rate (default: 1e-3)
betas (Tuple[float, float], optional): coefficients used for computing
running averages of gradient and its square (default: (0.9, 0.999))
eps (float, optional): term added to the denominator to improve
numerical stability (default: 1e-8)
weight_decay (float, optional): weight decay coefficient (default: 1e-2)
amsgrad (boolean, optional): whether to use the AMSGrad variant of this
algorithm from the paper `On the Convergence of Adam and Beyond`_
(default: False)
.. _Adam\: A Method for Stochastic Optimization:
https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6980
.. _Decoupled Weight Decay Regularization:
https://arxiv.org/abs/1711.05101
.. _On the Convergence of Adam and Beyond:
https://openreview.net/forum?id=ryQu7f-RZ
"""
def __init__(self, params, lr=1e-3, betas=(0.9, 0.999), eps=1e-8,
weight_decay=1e-2, amsgrad=False):
if not 0.0 <= lr:
raise ValueError("Invalid learning rate: {}".format(lr))
if not 0.0 <= eps:
raise ValueError("Invalid epsilon value: {}".format(eps))
if not 0.0 <= betas[0] < 1.0:
raise ValueError("Invalid beta parameter at index 0: {}".format(betas[0]))
if not 0.0 <= betas[1] < 1.0:
raise ValueError("Invalid beta parameter at index 1: {}".format(betas[1]))
if not 0.0 <= weight_decay:
raise ValueError("Invalid weight_decay value: {}".format(weight_decay))
defaults = dict(lr=lr, betas=betas, eps=eps,
weight_decay=weight_decay, amsgrad=amsgrad)
super(AdamW, self).__init__(params, defaults)
def __setstate__(self, state):
super(AdamW, self).__setstate__(state)
for group in self.param_groups:
group.setdefault('amsgrad', False)
[docs] @torch.no_grad()
def step(self, closure=None):
"""Performs a single optimization step.
Arguments:
closure (callable, optional): A closure that reevaluates the model
and returns the loss.
"""
loss = None
if closure is not None:
with torch.enable_grad():
loss = closure()
for group in self.param_groups:
for p in group['params']:
if p.grad is None:
continue
# Perform stepweight decay
p.mul_(1 - group['lr'] * group['weight_decay'])
# Perform optimization step
grad = p.grad
if grad.is_sparse:
raise RuntimeError('Adam does not support sparse gradients, please consider SparseAdam instead')
amsgrad = group['amsgrad']
state = self.state[p]
# State initialization
if len(state) == 0:
state['step'] = 0
# Exponential moving average of gradient values
state['exp_avg'] = torch.zeros_like(p, memory_format=torch.preserve_format)
# Exponential moving average of squared gradient values
state['exp_avg_sq'] = torch.zeros_like(p, memory_format=torch.preserve_format)
if amsgrad:
# Maintains max of all exp. moving avg. of sq. grad. values
state['max_exp_avg_sq'] = torch.zeros_like(p, memory_format=torch.preserve_format)
exp_avg, exp_avg_sq = state['exp_avg'], state['exp_avg_sq']
if amsgrad:
max_exp_avg_sq = state['max_exp_avg_sq']
beta1, beta2 = group['betas']
state['step'] += 1
bias_correction1 = 1 - beta1 ** state['step']
bias_correction2 = 1 - beta2 ** state['step']
# Decay the first and second moment running average coefficient
exp_avg.mul_(beta1).add_(grad, alpha=1 - beta1)
exp_avg_sq.mul_(beta2).addcmul_(grad, grad, value=1 - beta2)
if amsgrad:
# Maintains the maximum of all 2nd moment running avg. till now
torch.max(max_exp_avg_sq, exp_avg_sq, out=max_exp_avg_sq)
# Use the max. for normalizing running avg. of gradient
denom = (max_exp_avg_sq.sqrt() / math.sqrt(bias_correction2)).add_(group['eps'])
else:
denom = (exp_avg_sq.sqrt() / math.sqrt(bias_correction2)).add_(group['eps'])
step_size = group['lr'] / bias_correction1
p.addcdiv_(exp_avg, denom, value=-step_size)
return loss
与 Adam 不一样的地方是:
Adam 如果使用 weight_decay 的话,那么相当于目标函数加上 ,所以相当于是梯度相当于要再加上 ,故使用了 grad = grad.add(p, alpha=group['weight_decay'])。而 AdamW 是 p.mul_(1 - group['lr'] * group['weight_decay']) 直接让参数:
这样才能和绿色框一致。
猜您喜欢:
CVPR 2021 | GAN的说话人驱动、3D人脸论文汇总
附下载 |《TensorFlow 2.0 深度学习算法实战》
附下载 | 超100篇!CVPR 2020最全GAN论文梳理汇总!
评论
