序列化与反序列化——作为Java开发,应该避开这些坑
点击上方蓝色字体,选择“标星公众号”
优质文章,第一时间送达
1.序列化与反序列化的概念
public class People {
private Long id;
public People(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "People{" +
"id=" + id +
'}';
}
}
import java.io.*;
// 屏蔽编译器的警告
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class Main {
/**
* 序列化和反序列化 People 对象
*/
private static void testSerializablePeople() throws Exception {
// 序列化的步骤
// 用于存储序列化的文件,这里的java_下划线仅仅为了说明是java序列化对象,没有任何其他含义
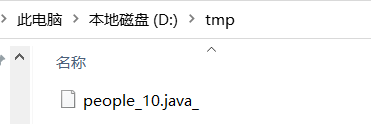
File file = new File("/tmp/people_10.java_");
if (!file.exists()) {
// 1,先得到文件的上级目录,并创建上级目录
file.getParentFile().mkdirs();
try {
// 2,再创建文件
file.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
People p = new People(10L);
// 创建一个输出流
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream(file)
);
// 输出可序列化对象
oos.writeObject(p);
// 关闭输出流
oos.close();
// 反序列化的步骤
// 创建一个输入流
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(
new FileInputStream(file)
);
// 得到反序列化的对象,这里可以强转为People类型
Object newPerson = ois.readObject();
// 关闭输入流
ois.close();
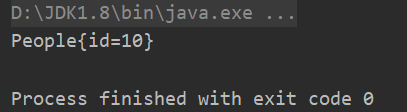
System.out.println(newPerson);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
testSerializablePeople();
}
}
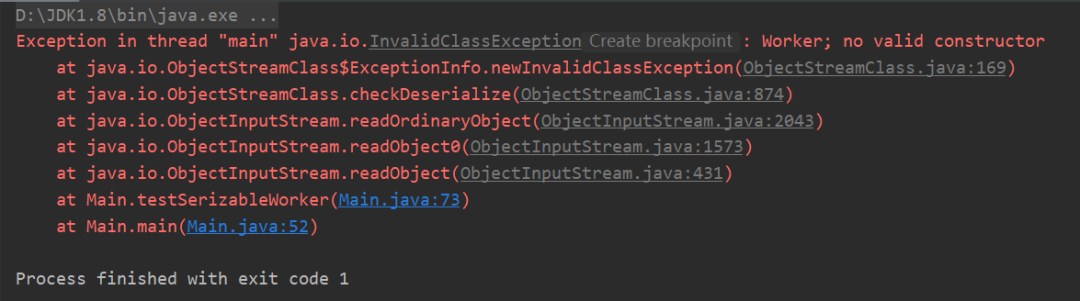
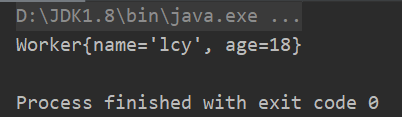
2.子类实现Serializable接口,父类没有实现,子类可以序列化吗?
public class Worker extends People implements Serializable {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public Worker(Long id, String name, Integer age) {
super(id);
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
testSerizableWorker();
}
/**
*子类实现序列化, 父类不实现序列化
* */
private static void testSerizableWorker() throws Exception {
File file = new File("/tmp/worker_10.java_");
if (!file.exists()) {
// 1,先得到文件的上级目录,并创建上级目录
file.getParentFile().mkdirs();
try {
// 2,再创建文件
file.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
Worker p = new Worker(10L, "lcy", 18);
// 创建一个输出流
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream(file)
);
// 输出可序列化对象
oos.writeObject(p);
// 关闭输出流
oos.close();
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));
Object newWorker = ois.readObject(); // 父类没有序列化的时候,需要调用父类的无参数构造方法
ois.close();
System.out.println(newWorker);
}
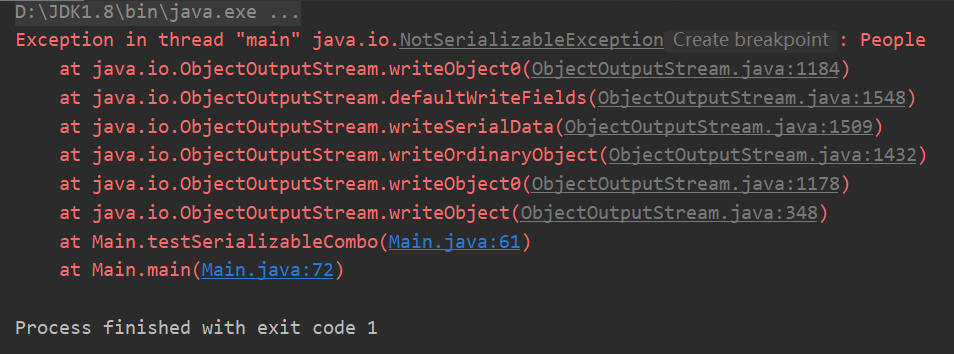
3.类中存在引用对象,这个类对象在什么情况下可以实现序列化?
public class Combo implements Serializable {
private int id;
private People people;
public Combo(int id, People people) {
this.id = id;
this.people = people;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public People getPeople() {
return people;
}
public void setPeople(People people) {
this.people = people;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Combo{" +
"id=" + id +
", people=" + people +
'}';
}
}
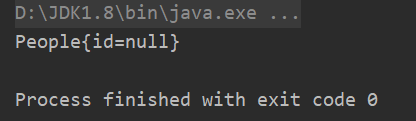
public class People {
private Long id;
public People() {
}
public People(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "People{" +
"id=" + id +
'}';
}
}
private static void testSerializableCombo() throws Exception {
File file = new File("/tmp/combo_10.java_");
if (!file.exists()) {
// 1,先得到文件的上级目录,并创建上级目录
file.getParentFile().mkdirs();
try {
// 2,再创建文件
file.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
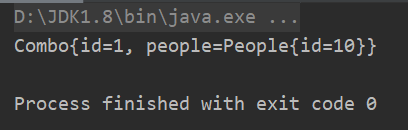
Combo p = new Combo(1, new People(10L));
// 创建一个输出流
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream(file)
);
// 输出可序列化对象
oos.writeObject(p);
// 关闭输出流
oos.close();
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));
Object newCombo = ois.readObject();
ois.close();
System.out.println(newCombo);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
testSerializableCombo();
}
4.同一个对象多次序列化之间有属性更新,前后的序列化有什么区别?
/**
* 同一个对象多次序列化的问题, 坑
* */
private static void sameObjectRepeatedSerialization() throws Exception {
File file = new File("/tmp/peopele_more.java_");
if (!file.exists()) {
// 1,先得到文件的上级目录,并创建上级目录
file.getParentFile().mkdirs();
try {
// 2,再创建文件
file.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
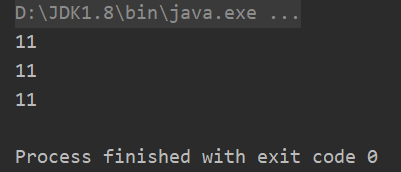
People p = new People(10L);
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(file));
// 未序列化,先修改属性
p.setId(11L);
oos.writeObject(p);
// 序列化一次后,再次修改属性
p.setId(15L);
oos.writeObject(p);
// 序列化两次后,再次修改属性
p.setId(20L);
oos.writeObject(p);
oos.close();
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));
Object people1 = ois.readObject();
Object people2 = ois.readObject();
Object people3 = ois.readObject();
ois.close();
System.out.println(((People) people1).getId());
System.out.println(((People) people2).getId());
System.out.println(((People) people3).getId());
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
sameObjectRepeatedSerialization();
}

作者 | 双子孤狼
来源 | csdn.net/qq_34115899/article/details/118463573/
加锋哥微信: java1239 围观锋哥朋友圈,每天推送Java干货!
评论

