Linux社区关于链表的bug讨论我们要看一下
最近在Linux社区看到一个关于内核链表的讨论
原文讨论链接:
https://lwn.net/SubscriberLink/885941/01fdc39df2ecc25f/
先用例子说明怎么使用内核链表
list.h
/* SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-2.0 */
#ifndef LIST_H
#define LIST_H
/*
* Copied from include/linux/...
*/
#undef offsetof
#define offsetof(TYPE, MEMBER) ((size_t) &((TYPE *)0)->MEMBER)
/**
* container_of - cast a member of a structure out to the containing structure
* @ptr: the pointer to the member.
* @type: the type of the container struct this is embedded in.
* @member: the name of the member within the struct.
*
*/
#define container_of(ptr, type, member) ({ \
const typeof( ((type *)0)->member ) *__mptr = (ptr); \
(type *)( (char *)__mptr - offsetof(type,member) );})
struct list_head {
struct list_head *next, *prev;
};
#define LIST_HEAD_INIT(name) { &(name), &(name) }
#define LIST_HEAD(name) \
struct list_head name = LIST_HEAD_INIT(name)
/**
* list_entry - get the struct for this entry
* @ptr: the &struct list_head pointer.
* @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in.
* @member: the name of the list_head within the struct.
*/
#define list_entry(ptr, type, member) \
container_of(ptr, type, member)
/**
* list_for_each_entry - iterate over list of given type
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the list_head within the struct.
*/
#define list_for_each_entry(pos, head, member) \
for (pos = list_entry((head)->next, typeof(*pos), member); \
&pos->member != (head); \
pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member))
/**
* list_for_each_entry_safe - iterate over list of given type safe against removal of list entry
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @n: another type * to use as temporary storage
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the list_head within the struct.
*/
#define list_for_each_entry_safe(pos, n, head, member) \
for (pos = list_entry((head)->next, typeof(*pos), member), \
n = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member); \
&pos->member != (head); \
pos = n, n = list_entry(n->member.next, typeof(*n), member))
/**
* list_empty - tests whether a list is empty
* @head: the list to test.
*/
static inline int list_empty(const struct list_head *head)
{
return head->next == head;
}
/*
* Insert a new entry between two known consecutive entries.
*
* This is only for internal list manipulation where we know
* the prev/next entries already!
*/
static inline void __list_add(struct list_head *_new,
struct list_head *prev,
struct list_head *next)
{
next->prev = _new;
_new->next = next;
_new->prev = prev;
prev->next = _new;
}
/**
* list_add_tail - add a new entry
* @new: new entry to be added
* @head: list head to add it before
*
* Insert a new entry before the specified head.
* This is useful for implementing queues.
*/
static inline void list_add_tail(struct list_head *_new, struct list_head *head)
{
__list_add(_new, head->prev, head);
}
/*
* Delete a list entry by making the prev/next entries
* point to each other.
*
* This is only for internal list manipulation where we know
* the prev/next entries already!
*/
static inline void __list_del(struct list_head *prev, struct list_head *next)
{
next->prev = prev;
prev->next = next;
}
#define LIST_POISON1 ((void *) 0x00100100)
#define LIST_POISON2 ((void *) 0x00200200)
/**
* list_del - deletes entry from list.
* @entry: the element to delete from the list.
* Note: list_empty() on entry does not return true after this, the entry is
* in an undefined state.
*/
static inline void list_del(struct list_head *entry)
{
__list_del(entry->prev, entry->next);
entry->next = (struct list_head*)LIST_POISON1;
entry->prev = (struct list_head*)LIST_POISON2;
}
#endiftest.c
#include
#include
#include
#include "list.h"
struct stu_example {
struct list_head of_node;
int age;
};
static LIST_HEAD(stu_list_head);
#define LIST_LEN 10
int main( )
{
int i = 0;
/*初始化链表*/
struct stu_example stu_list[LIST_LEN];
struct stu_example *tmp = NULL;
for (i=0; i < LIST_LEN; i++) {
list_add_tail(&stu_list[i],&stu_list_head);
stu_list[i].age = i + 20;
}
/*遍历链表*/
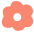
list_for_each_entry(tmp, &stu_list_head, of_node) {
printf("age=%d\n",tmp->age);
}
/*删除链表*/
list_del(&stu_list_head);
printf("Hello,world\n");
return 0;
}代码输出
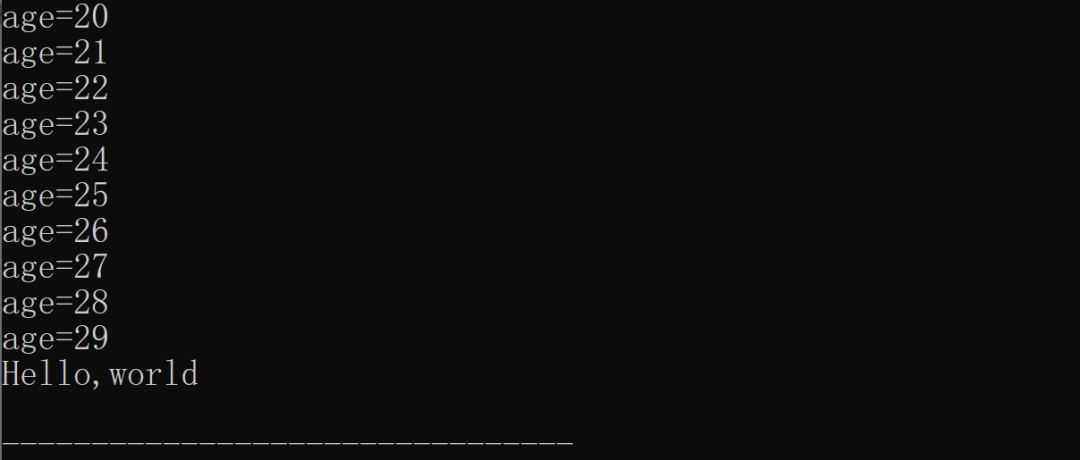

讨论的重点是?
如下图
因为Linux内核用的是C89标准,不能在for循环里面声明变量,所以导致tmp变量在使用之后的代码中还可以继续使用。
继续使用并不是大问题,大问题是因为继续使用导致了一个USB的BUG,当然,从代码的结构性上来说,我觉得也应该做好封装。


根据这个机制,有可能会被程序攻击到内核代码
具体可以查看这个网址
https://www.vusec.net/projects/kasper/
里面的描述和补丁说明差不多,都是因为没有遍历结束退出的原因。

修改后的部分补丁
+/* Override the default implementation from linux/nospec.h. */
+#define select_nospec(cond, exptrue, expfalse) \
+({ \
+ typeof(exptrue) _out = (exptrue); \
+ \
+ asm volatile("test %1, %1\n\t" \
+ "cmove %2, %0" \
+ : "+r" (_out) \
+ : "r" (cond), "r" (expfalse)); \
+ _out; \
+})
+
/* Prevent speculative execution past this barrier. */
#define barrier_nospec() alternative("", "lfence", X86_FEATURE_LFENCE_RDTSC)
diff --git a/include/linux/list.h b/include/linux/list.h
index dd6c2041d09c..1a1b39fdd122 100644
--- a/include/linux/list.h
+++ b/include/linux/list.h
@@ -636,7 +636,8 @@ static inline void list_splice_tail_init(struct list_head *list,
*/
#define list_for_each_entry(pos, head, member) \
for (pos = list_first_entry(head, typeof(*pos), member); \
- !list_entry_is_head(pos, head, member); \
+ ({ bool _cond = !list_entry_is_head(pos, head, member); \
+ pos = select_nospec(_cond, pos, NULL); _cond; }); \
pos = list_next_entry(pos, member))具体网址:
https://lwn.net/ml/linux-kernel/20220217184829.1991035-2-jakobkoschel@gmail.com/
评论
