大厂高频手撕算法题
目前互联网行业目前正在处于内卷状态,各个大厂不断提高招人门槛,前端工程师找工作也越发艰难,为了助力各位老铁能够在面试过程中脱颖而出,我结合自己的面试经验,准备了这三十六道面试过程中的手撕算法题,与各位共享。
一、冒泡排序
冒泡排序的思路:遍历数组,然后将最大数沉到最底部;
时间复杂度:O(N^2);
空间复杂度:O(1)
function BubbleSort(arr) {
if(arr == null || arr.length <= 0){
return [];
}
var len = arr.length;
for(var end = len - 1; end > 0; end--){
for(var i = 0; i < end; i++) {
if(arr[i] > arr[i + 1]){
swap(arr, i, i + 1);
}
}
}
return arr;
}
function swap(arr, i, j){
// var temp = arr[i];
// arr[i] = arr[j];
// arr[j] = temp;
//交换也可以用异或运算符
arr[i] = arr[i] ^ arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[i] ^ arr[j];
arr[i] = arr[i] ^ arr[j];
}
二、选择排序
选择排序的实现思路:遍历数组,把最小数放在头部;
时间复杂度:O(N^2);
空间复杂度:O(1)
function SelectionSort(arr) {
if(arr == null || arr.length < 0) {
return [];
}
for(var i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {
var minIndex = i;
for(var j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) {
minIndex = arr[j] < arr[minIndex] ? j : minIndex;
}
swap(arr, i, minIndex);
}
return arr;
}
function swap(arr, i, j) {
arr[i] = arr[i] ^ arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[i] ^ arr[j];
arr[i] = arr[i] ^ arr[j];
}
三、插入排序
插入排序实现思路:将一个新的数,和前面的比较,只要当前数小于前一个则和前一个交换位置,否则终止;
时间复杂度:O(N^2);
空间复杂度:O(1)
function insertSort(arr) {
if(arr == null || arr.length <= 0){
return [];
}
var len = arr.length;
for(var i = 1; i < len; i++) {
for(var j = i - 1; j >= 0 && arr[j] > arr[j + 1]; j--) {
swap(arr, j, j + 1);
}
}
return arr;
}
function swap(arr, i, j){
var temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
四、归并排序
归并排序的思路:
1.先左侧部分排好序
2.再右侧部分排好序
3.再准备一个辅助数组,用外排的方式,小的开始填,直到有个动到末尾,将另一个数组剩余部分拷贝到末尾
4.再将辅助数组拷贝回原数组
时间复杂度:O(N * logN)
空间复杂度:O(N)
// 递归实现
function mergeSort(arr){
if(arr == null || arr.length <= 0){
return [];
}
sortProcess(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
return arr;
}
function sortProcess(arr, L, R){
//递归的终止条件,就是左右边界索引一样
if(L == R){
return;
}
var middle = L + ((R - L) >> 1);//找出中间值
sortProcess(arr, L, middle);//对左侧部分进行递归
sortProcess(arr, middle + 1, R);//对右侧部分进行递归
merge(arr, L, middle, R);//然后利用外排方式进行结合
}
function merge(arr, L, middle, R){
var help = [];
var l = L;
var r = middle + 1;
var index = 0;
//利用外排方式进行
while(l <= middle && r <= R){
help[index++] = arr[l] < arr[r] ? arr[l++] : arr[r++];
}
while(l <= middle){
help.push(arr[l++]);
}
while(r <= R){
help.push(arr[r++]);
}
for(var i = 0; i < help.length; i++) {
arr[L + i] = help[i];
}
//arr.splice(L, help.length, ...help);//这个利用了ES6的语法
}
// 循环实现
function mergeSort(arr){
if(arr ==null || arr.length <= 0){
return [];
}
var len = arr.length;
//i每次乘2,是因为每次合并以后小组元素就变成两倍个了
for(var i = 1; i < len; i *= 2){
var index = 0;//第一组的起始索引
while( 2 * i + index <= len){
index += 2 * i;
merge(arr, index - 2 * i, index - i, index);
}
//说明剩余两个小组,但其中一个小组数据的数量已经不足2的幂次方个
if(index + i < len){
merge(arr, index, index + i, len);
}
}
return arr;
}
//利用外排的方式进行结合
function merge(arr, start, mid, end){
//新建一个辅助数组
var help = [];
var l = start, r = mid;
var i = 0;
while(l < mid && r < end){
help[i++] = arr[l] < arr[r] ? arr[l++] : arr[r++];
}
while(l < mid){
help[i++] = arr[l++];
}
while(r < end){
help[i++] = arr[r++];
}
for(var j = 0; j < help.length; j++){
arr[start + j] = help[j];
}
}
五、快速排序
快速排序实现思路:随机取出一个值进行划分,大于该值放右边,小于该值放左边(该算法在经典快排的基础上经过荷兰国旗思想和随机思想进行了改造)
时间复杂度:O(N*logN)
空间复杂度:O(logN)
function quickSort(arr) {
if(arr == null || arr.length <= 0){
return [];
}
quick(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
}
function quick(arr, L, R){
//递归结束条件是L >= R
if(L < R){
//随机找一个值,然后和最后一个值进行交换,将经典排序变为快速排序
swap(arr, L + Math.floor(Math.random() * (R - L + 1)), R);
//利用荷兰国旗问题获得划分的边界,返回的值是小于区域的最大索引和大于区域的最小索引,在这利用荷兰国旗问题将等于区域部分就不用动了
var tempArr = partition(arr, L, R, arr[R]);
quick(arr, L, tempArr[0]);
quick(arr, tempArr[1], R);
}
}
//返回值是小于区域最后的索引和大于区域的第一个索引
function partition(arr, L, R, num){
var less = L - 1;
var more = R + 1;
var cur = L;
while(cur < more){
if(arr[cur] < num){
swap(arr, ++less, cur++);
}else if(arr[cur] > num) {
swap(arr, --more, cur);
}else{
cur++;
}
}
return [less, more];
}
function swap(arr, i, j){
var temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
六、堆排序
堆排序思路:
1.让数组变成大根堆
2.把最后一个位置和堆顶做交换
3.则最大值在最后,则剩下部分做heapify,则重新调整为大根堆,则堆顶位置和该部分最后位置做交换
4.重复进行,直到减完,则这样最后就调整完毕,整个数组排完序(为一个升序)
时间复杂度:O(N * logN)
空间复杂度:O(1)
function heapSort(arr) {
if(arr == null || arr.length <= 0) {
return [];
}
//首先是建立大顶堆的过程
for(var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
heapInsert(arr, i);
}
var size = arr.length;//这个值用来指定多少个数组成堆,当得到一个排序的值后这个值减一
//将堆顶和最后一个位置交换
/**
* 当大顶堆建立完成后,然后不断将最后一个位置和堆顶交换;
* 这样最大值就到了最后,则剩下部分做heapify,重新调整为大根堆,则堆顶位置和倒数第二个位置交换,重复进行,直到全部排序完毕*/
//由于前面已经是大顶堆,所以直接交换
swap(arr, 0, --size);
while(size > 0) {
//重新变成大顶堆
heapify(arr, 0, size);
//进行交换
swap(arr, 0, --size);
}
}
//加堆过程中
function heapInsert(arr, index) {
//比较当前位置和其父位置,若大于其父位置,则进行交换,并将索引移动到其父位置进行循环,否则跳过
//结束条件是比父位置小或者到达根节点处
while(arr[index] > arr[parseInt((index - 1) / 2)]){
//进行交换
swap(arr, index, parseInt((index - 1) / 2));
index = parseInt((index - 1) / 2);
}
}
//减堆过程
/**
* size指的是这个数组前多少个数构成一个堆
* 如果你想把堆顶弹出,则把堆顶和最后一个数交换,把size减1,然后从0位置经历一次heapify,调整一下,剩余部分变成大顶堆*/
function heapify(arr, index, size) {
var left = 2 * index + 1;
while(left < size) {
var largest = (left + 1 < size && arr[left] < arr[left + 1]) ? left + 1 : left;
largest = arr[index] > arr[largest] ? index : largest;
//如果最大值索引和传进来索引一样,则该值到达指定位置,直接结束循环
if(index == largest) {
break;
}
//进行交换,并改变索引和其左子节点
swap(arr, index, largest);
index = largest;
left = 2 * index + 1;
}
}
function swap(arr, i, j) {
var temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
七、桶排序
桶排序会经历三次遍历:准备一个数组、遍历一遍数组、重构一遍数组,是非基于比较的排序,下面以一个问题来阐述其思路。
问题:
给定一个数组,求如果排序之后,相邻两个数的最大差值,要求时间复杂度O(N),且要求不能用基于比较的排序
思路:
1.准备桶:数组中有N个数就准备N+1个桶
2.遍历一遍数组,找到最大值max和最小值min 。若min = max,则差值=0;若min≠max,则最小值放在0号桶,最大值放在N号桶,剩下的数属于哪个范围就进哪个桶
3.根据鸽笼原理,则肯定有一个桶为空桶,设计该桶的目的是为了否定最大值在一个桶中,则最大差值的两个数一定来自于两个桶,但空桶两侧并不一定是最大值
4.所以只记录所有进入该桶的最小值min和最大值max和一个布尔值表示该桶有没有值
5.然后遍历这个数组,如果桶是空的,则跳到下一个数,如果桶非空,则找前一个非空桶,则最大差值=当前桶min - 上一个非空桶max,用全局变量更新最大值
时间复杂度:O(N)
空间复杂度:O(N)
function maxGap(arr) {
if(arr == null || arr.length <= 0) {
return 0;
}
var len = arr.length;
var max = -Infinity, min = Infinity;
//遍历一遍数组,找到最大值max和最小值min
for(var i = 0; i < len; i++) {
max = max > arr[i] ? max : arr[i];
min = min > arr[i] ? arr[i] : min;
}
//若min = max,则差值为0;
if(min == max) {
return 0;
}
var hasNum = new Array(len + 1);
var mins = new Array(len + 1);
var maxs = new Array(len + 1);
var bid = 0;//指定桶的编号
for(var i = 0; i < len; i++) {
bid = bucket(arr[i], min, max, len);//获得该值是在哪个桶//由于有N+1个桶,所以间隔就是N个,所以此处除以的是len,然后通过这个函数得到应该放到哪个桶里
maxs[bid] = hasNum[bid] ? Math.max(arr[i], maxs[bid]) : arr[i];
mins[bid] = hasNum[bid] ? Math.min(arr[i], mins[bid]) : arr[i];
hasNum[bid] = true;
}
var res = 0;
var lastMax = maxs[0];
for(var i = 0; i < len + 1; i++) {
if(hasNum[i]) {
res = Math.max(mins[i] - lastMax, res);
lastMax = maxs[i];
}
}
return res;
}
//获得桶号
//这个函数用于判断在哪个桶中,参数分别为值、最小值、最大值、桶间隔
function bucket(value, min, max, len) {
return parseInt((value - min) / ((max - min) / len));
}
八、new

function New (Fn, ...arg) {
// 一个新的对象被创建
const result = {};
// 该对象的__proto__属性指向该构造函数的原型
if (Fn.prototype !== null) {
Object.setPrototypeOf(result, Fn.prototype);
}
// 将执行上下文(this)绑定到新创建的对象中
const returnResult = Fn.apply(result, arg);
// 如果构造函数有返回值,那么这个返回值将取代第一步中新创建的对象。否则返回该对象
if ((typeof returnResult === "object" || typeof returnResult === "function") && returnResult !== null) {
return returnResult;
}
return result;
}
九、instanceof

function Instanceof(left, right) {
let leftVal = Object.getPrototypeOf(left);
const rightVal = right.prototype;
while (leftVal !== null) {
if (leftVal === rightVal)
return true;
leftVal = Object.getPrototypeOf(leftVal);
}
return false;
}
十、 Object.create()
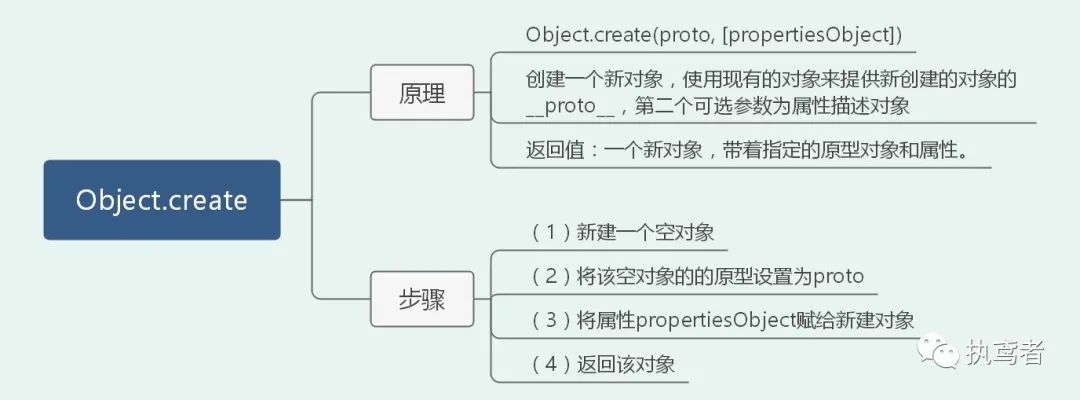
Object.ObjectCreate = (proto, propertiesObject)=> {
// 对输入进行检测
if (typeof proto !== 'object' && typeof proto !== 'function' && proto !== null) {
throw new Error(`Object prototype may only be an Object or null:${proto}`);
}
// 新建一个对象
const result = {};
// 将该对象的原型设置为proto
Object.setPrototypeOf(result, proto);
// 将属性赋值给该对象
Object.defineProperties(result, propertiesObject);
// 返回该对象
return result;
}
十一、 Object assign()
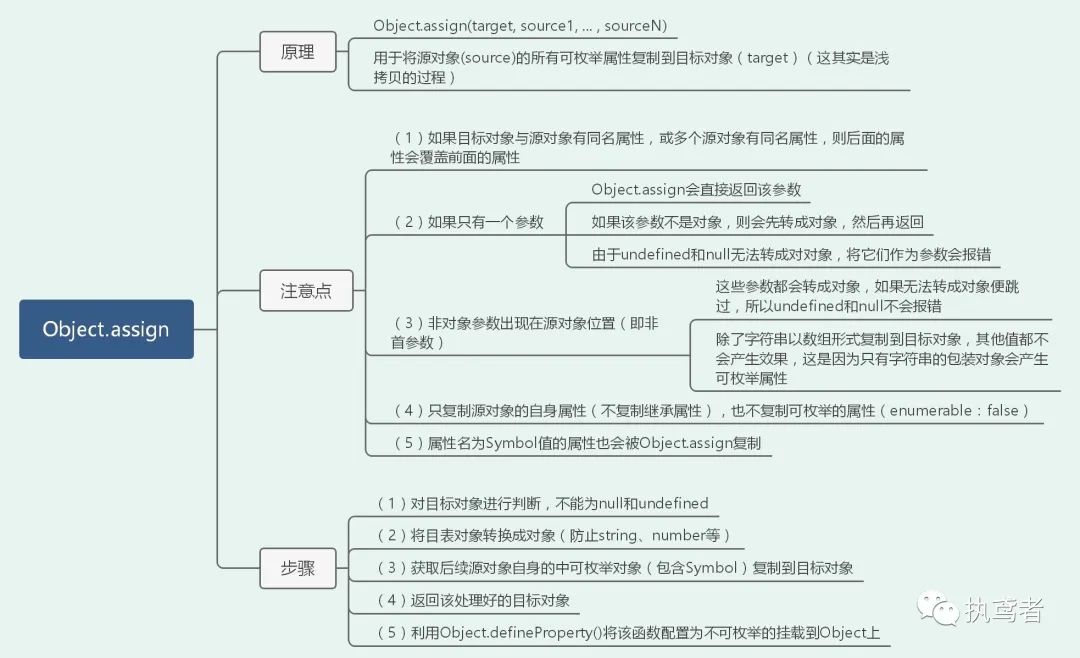
function ObjectAssign(target, ...sources) {
// 对第一个参数的判断,不能为undefined和null
if (target === undefined || target === null) {
throw new TypeError('cannot convert first argument to object');
}
// 将第一个参数转换为对象(不是对象转换为对象)
const targetObj = Object(target);
// 将源对象(source)自身的所有可枚举属性复制到目标对象(target)
for (let i = 0; i < sources.length; i++) {
let source = sources[i];
// 对于undefined和null在源角色中不会报错,会直接跳过
if (source !== undefined && source !== null) {
// 将源角色转换成对象
// 需要将源角色自身的可枚举属性(包含Symbol值的属性)进行复制
// Reflect.ownKeys(obj) 返回一个数组,包含对象自身的所有属性,不管属性名是Symbol还是字符串,也不管是否可枚举
const keysArray = Reflect.ownKeys(Object(source));
for (let nextIndex = 0; nextIndex < keysArray.length; nextIndex ++) {
const nextKey = keysArray[nextIndex];
// 去除不可枚举属性
const desc = Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(source, nextKey);
if (desc !== undefined && desc.enumerable) {
// 后面的属性会覆盖前面的属性
targetObj[nextKey] = source[nextKey];
}
}
}
}
return targetObj;
}
// 由于挂载到Object的assign是不可枚举的,直接挂载上去是可枚举的,所以采用这种方式
if (typeof Object.myAssign !== 'function') {
Object.defineProperty(Object, "myAssign", {
value : ObjectAssign,
writable: true,
enumerable: false,
configurable: true
});
}
十二、 map

Array.prototype.myMap = function(fn) {
// 判断输入的第一个参数是不是函数
if (typeof fn !== 'function') {
throw new TypeError(fn + 'is not a function');
}
// 获取需要处理的数组内容
const arr = this;
const len = arr.length;
// 新建一个空数组用于装载新的内容
const temp = new Array(len);
// 对数组中每个值进行处理
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
// 获取第二个参数,改变this指向
let result = fn.call(arguments[1], arr[i], i, arr);
temp[i] = result;
}
// 返回新的结果
return temp;
}
十三、 filter

Array.prototype.myFilter = function (fn) {
if (typeof fn !== 'function') {
throw new TypeError(`${fn} is not a function`);
}
// 获取该数组
const arr = this;
// 获取该数组长度
const len = this.length >>> 0;
// 新建一个新的数组用于放置该内容
const temp = [];
// 对数组中每个值进行处理
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
// 处理时注意this指向
const result = fn.call(arguments[1], arr[i], i, arr);
result && temp.push(arr[i]);
}
return temp;
}
十四、 reduce
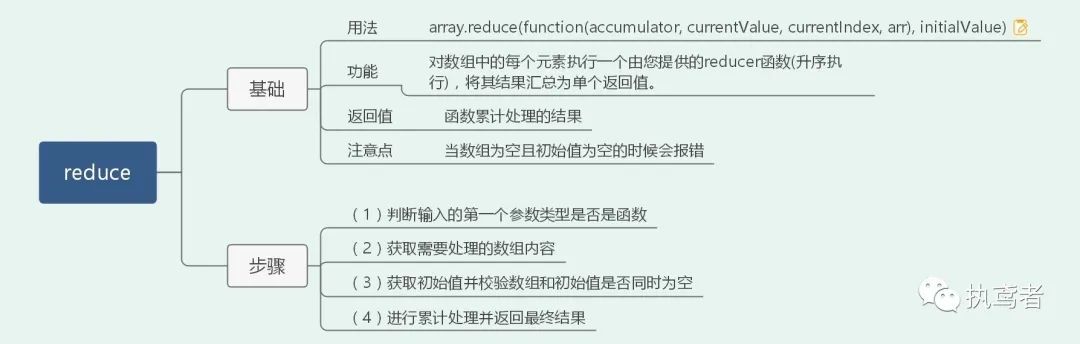
Array.prototype.myReduce = function(fn) {
if (typeof fn !== 'function') {
throw new TypeError(`${fn} is not a function`);
}
const arr = this;
const len = arr.length >>> 0;
let value;// 最终返回的值
let k = 0;// 当前索引
if (arguments.length >= 2) {
value = arguments[1];
} else {
// 当数组为稀疏数组时,判断数组当前是否有元素,如果没有索引加一
while (k < len && !( k in arr)) {
k++;
}
// 如果数组为空且初始值不存在则报错
if (k >= len) {
throw new TypeError('Reduce of empty array with no initial value');
}
value = arr[k++];
}
while (k < len) {
if (k in arr) {
value = fn(value, arr[k], k, arr);
}
k++;
}
return value;
}
十五、 flat
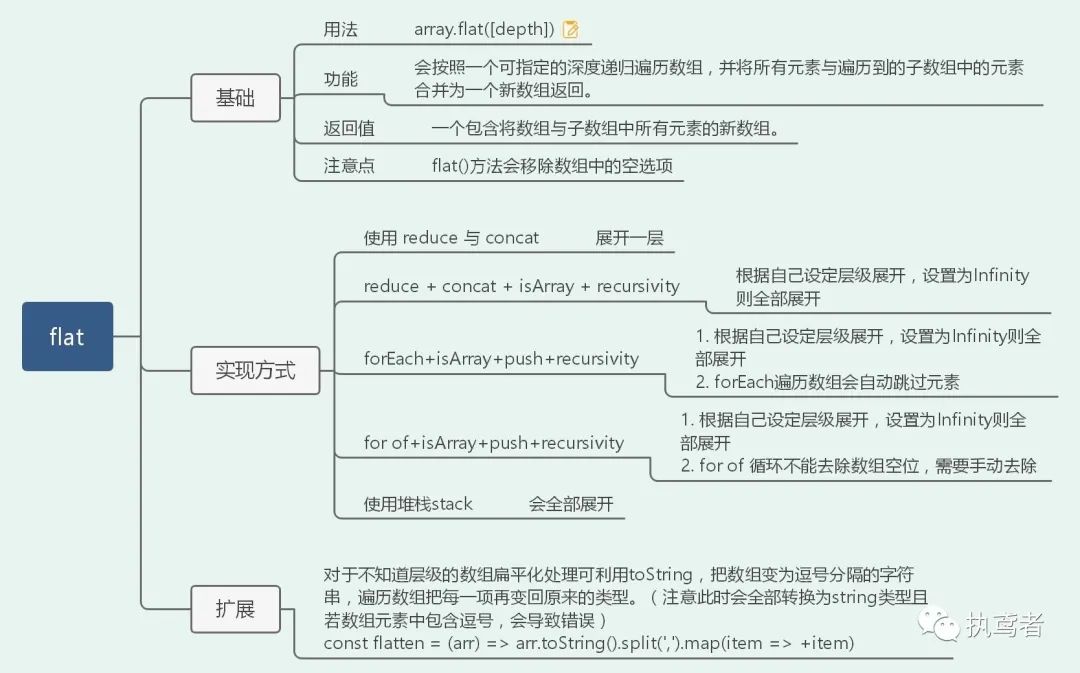
// 使用reduce和concat
Array.prototype.flat1 = function () {
return this.reduce((acc, val) => acc.concat(val), []);
}
// 使用reduce + concat + isArray +recursivity
Array.prototype.flat2 = function (deep = 1) {
const flatDeep = (arr, deep = 1) => {
// return arr.reduce((acc, val) => Array.isArray(val) && deep > 0 ? [...acc, ...flatDeep(val, deep - 1)] : [...acc, val], []);
return deep > 0 ? arr.reduce((acc, val) => acc.concat(Array.isArray(val) ? flatDeep(val, deep - 1) : val), []) : arr.slice();
}
return flatDeep(this, deep);
}
// 使用forEach + concat + isArray +recursivity
// forEach 遍历数组会自动跳过空元素
Array.prototype.flat3 = function (deep = 1) {
const result = [];
(function flat(arr, deep) {
arr.forEach((item) => {
if (Array.isArray(item) && deep > 0) {
flat(item, deep - 1);
} else {
result.push(item);
}
})
})(this, deep);
return result;
}
// 使用for of + concat + isArray +recursivity
// for of 遍历数组会自动跳过空元素
Array.prototype.flat4 = function (deep = 1) {
const result = [];
(function flat(arr, deep) {
for(let item of arr) {
if (Array.isArray(item) && deep > 0) {
flat(item, deep - 1);
} else {
// 去除空元素,因为void 表达式返回的都是undefined,不适用undefined是因为undefined在局部变量会被重写
item !== void 0 && result.push(item);
}
}
})(this, deep);
return result;
}
// 使用堆栈stack
Array.prototype.flat5 = function(deep = 1) {
const stack = [...this];
const result = [];
while (stack.length > 0) {
const next = stack.pop();
if (Array.isArray(next)) {
stack.push(...next);
} else {
result.push(next);
}
}
// 反转恢复原来顺序
return result.reverse();
}
十六、 call
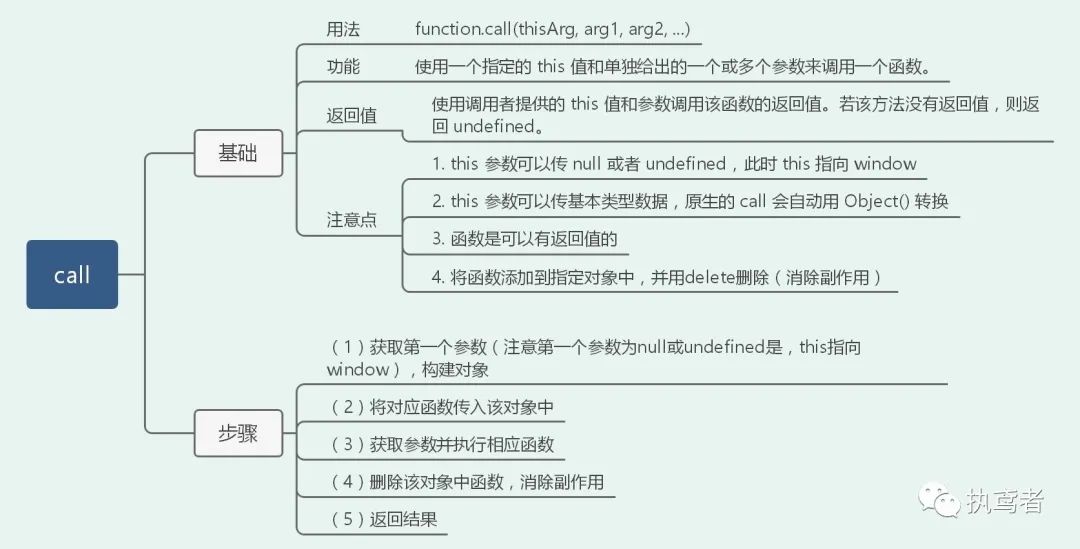
Function.prototype.call1 = function(context, ...args) {
// 获取第一个参数(注意第一个参数为null或undefined是,this指向window),构建对象
context = context ? Object(context) : window;
// 将对应函数传入该对象中
context.fn = this;
// 获取参数并执行相应函数
let result = context.fn(...args);
delete context.fn;
十七、 apply
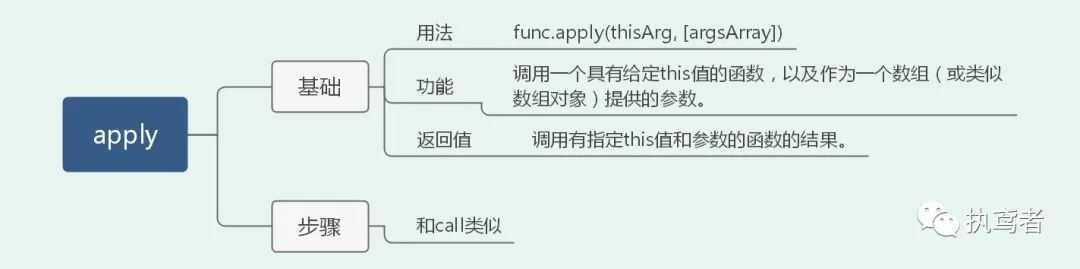
Function.prototype.apply1 = function(context, arr) {
context = context ? Object(context) : window;
context.fn = this;
let result = arr ? context.fn(...arr) : context.fn();
delete context.fn;
return result;
}
十八、 bind

Function.prototype.bind1 = function (context, ...args) {
if (typeof this !== 'function') {
throw new TypeError('The bound object needs to be a function');
}
const self = this;
const fNOP = function() {};
const fBound = function(...fBoundArgs) {
// 指定this
// 当作为构造函数时,this 指向实例,此时 this instanceof fBound 结果为 true
return self.apply(this instanceof fNOP ? this : context, [...args, ...fBoundArgs]);
}
// 修改返回函数的 prototype 为绑定函数的 prototype,为了避免直接修改this的原型,所以新建了一个fNOP函数作为中介
if (this.prototype) {
fNOP.prototype = this.prototype;
}
fBound.prototype = new fNOP();
return fBound;
}
十九、 防抖

function debounce(fn, wait, immediate) {
let timer = null;
return function(...args) {
// 立即执行的功能(timer为空表示首次触发)
if (immediate && !timer) {
fn.apply(this, args);
}
// 有新的触发,则把定时器清空
timer && clearTimeout(timer);
// 重新计时
timer = setTimeout(() => {
fn.apply(this, args);
}, wait)
}
}
二十、 节流

// 时间戳版本
function throttle(fn, wait) {
// 上一次执行时间
let previous = 0;
return function(...args) {
// 当前时间
let now = +new Date();
if (now - previous > wait) {
previous = now;
fn.apply(this, args);
}
}
}
// 定时器版本
function throttle(fn, wait) {
let timer = null;
return function(...args) {
if (!timer) {
timer = setTimeout(() => {
fn.apply(this, args);
timer = null;
}, wait)
}
}
}
二十一、深拷贝
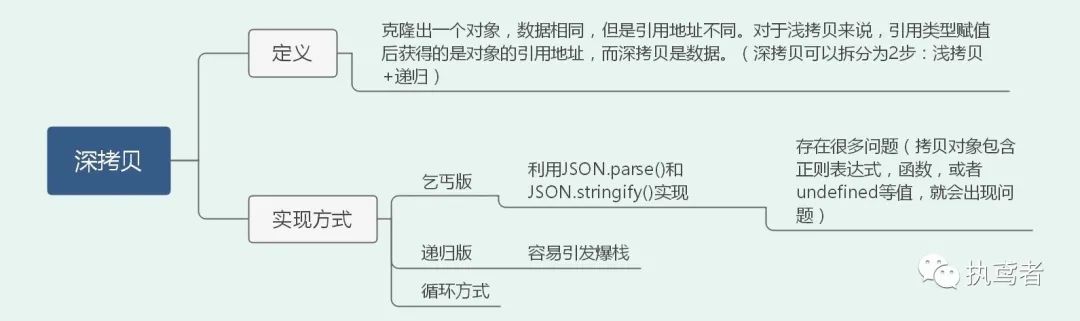
// 乞巧版
function cloneDeep1(source) {
return JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(source));
}
// 递归版
function cloneDeep2(source) {
// 如果输入的为基本类型,直接返回
if (!(typeof source === 'object' && source !== null)) {
return source;
}
// 判断输入的为数组函数对象,进行相应的构建
const target = Array.isArray(source) ? [] : {};
for (let key in source) {
// 判断是否是自身属性
if (Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(source, key)) {
if (typeof source === 'object' && source !== null) {
target[key] = cloneDeep2(source[key]);
} else {
target[key] = source[key];
}
}
}
return target;
}
// 循环方式
function cloneDeep3(source) {
if (!(typeof source === 'object' && source !== null)) {
return source;
}
const root = Array.isArray(source) ? [] : {};
// 定义一个栈
const loopList = [{
parent: root,
key: undefined,
data: source,
}];
while (loopList.length > 0) {
// 深度优先
const node = loopList.pop();
const parent = node.parent;
const key = node.key;
const data = node.data;
// 初始化赋值目标,key为undefined则拷贝到父元素,否则拷贝到子元素
let res = parent;
if (typeof key !== 'undefined') {
res = parent[key] = Array.isArray(data) ? [] : {};
}
for (let key in data) {
if (data.hasOwnProperty(key)) {
if (typeof data[key] === 'object' && data !== null) {
loopList.push({
parent: res,
key: key,
data: data[key],
});
} else {
res[key] = data[key];
}
}
}
}
return root;
}
二十二、 根据Promise/A+规范实现Promise
人家有相关标准,我们就要遵守,毕竟遵纪守法才是好公民,现在只能硬着头皮把这个标准过一遍。
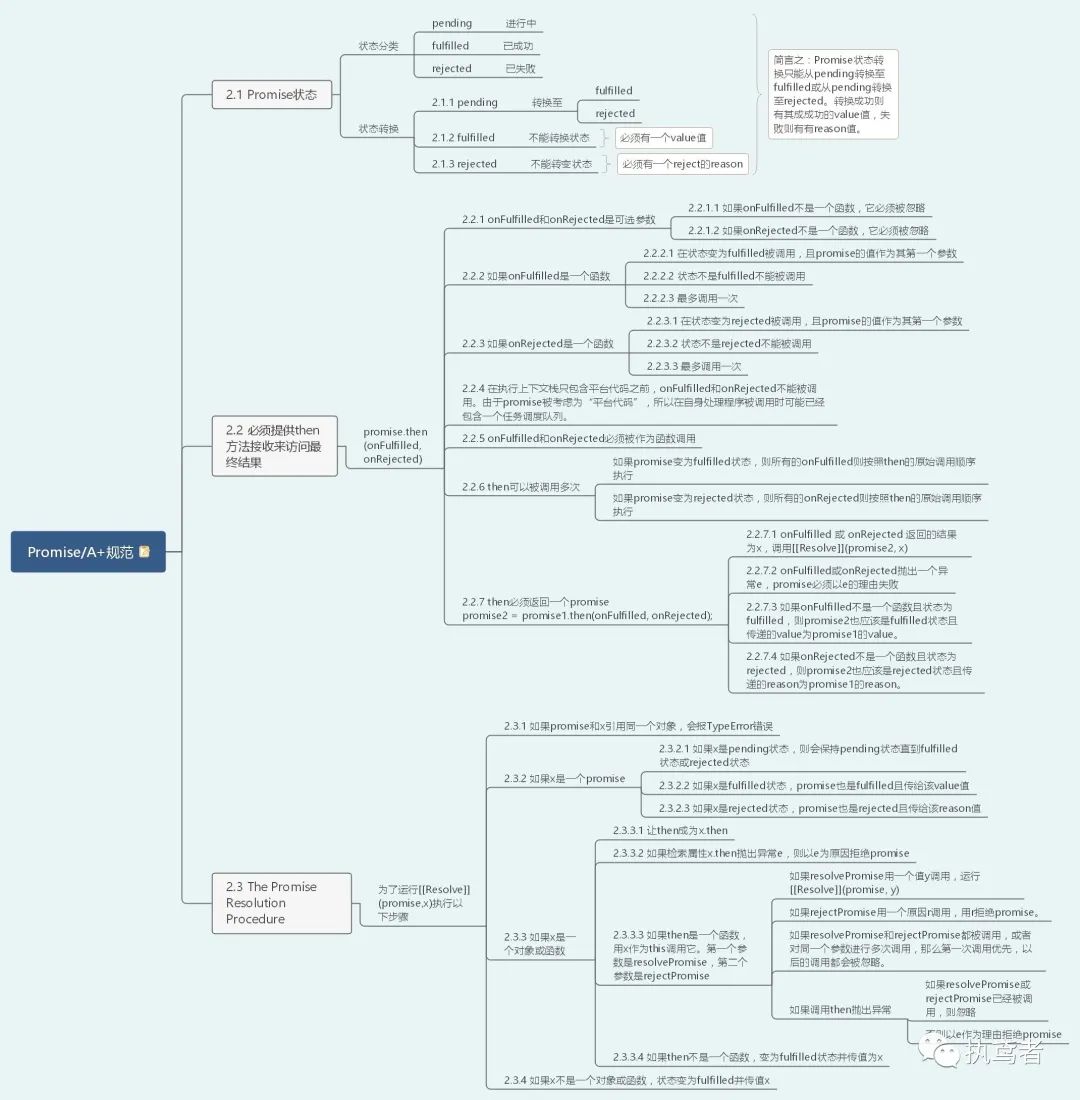
下面就是基于Promise/A+规范实现的代码,已经经过promises-aplus-tests库进行了验证。
const PENDING = 'pending';
const FULFILLED = 'fulfilled';
const REJECTED = 'rejected';
/**
* Promise构造函数
* excutor: 内部同步执行的函数
*/
class Promise {
constructor(excutor) {
const self = this;
self.status = PENDING;
self.onFulfilled = [];// 成功的回调
self.onRejected = [];// 失败的回调
// 异步处理成功调用的函数
// PromiseA+ 2.1 状态只能由Pending转为fulfilled或rejected;fulfilled状态必须有一个value值;rejected状态必须有一个reason值。
function resolve(value) {
if (self.status === PENDING) {
self.status = FULFILLED;
self.value = value;
// PromiseA+ 2.2.6.1 相同promise的then可以被调用多次,当promise变为fulfilled状态,全部的onFulfilled回调按照原始调用then的顺序执行
self.onFulfilled.forEach(fn => fn());
}
}
function reject(reason) {
if (self.status === PENDING) {
self.status = REJECTED;
self.reason = reason;
// PromiseA+ 2.2.6.2 相同promise的then可以被调用多次,当promise变为rejected状态,全部的onRejected回调按照原始调用then的顺序执行
self.onRejected.forEach(fn => fn());
}
}
try {
excutor(resolve, reject);
} catch (e) {
reject(e);
}
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
// PromiseA+ 2.2.1 onFulfilled和onRejected是可选参数
// PromiseA+ 2.2.5 onFulfilled和onRejected必须被作为函数调用
// PromiseA+ 2.2.7.3 如果onFulfilled不是函数且promise1状态是fulfilled,则promise2有相同的值且也是fulfilled状态
// PromiseA+ 2.2.7.4 如果onRejected不是函数且promise1状态是rejected,则promise2有相同的值且也是rejected状态
onFulfilled = typeof onFulfilled === 'function' ? onFulfilled : value => value;
onRejected = typeof onRejected === 'function' ? onRejected : reason => { throw reason };
const self = this;
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const handle = (callback, data) => {
// PromiseA+ 2.2.4 onFulfilled或者onRejected需要在自己的执行上下文栈里被调用,所以此处用setTimeout
setTimeout(() => {
try {
// PromiseA+ 2.2.2 如果onFulfilled是函数,则在fulfilled状态之后调用,第一个参数为value
// PromiseA+ 2.2.3 如果onRejected是函数,则在rejected状态之后调用,第一个参数为reason
const x = callback(data);
// PromiseA+ 2.2.7.1 如果onFulfilled或onRejected返回一个x值,运行这[[Resolve]](promise2, x)
resolvePromise(promise, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (e) {
// PromiseA+ 2.2.7.2 onFulfilled或onRejected抛出一个异常e,promise2必须以e的理由失败
reject(e);
}
})
}
if (self.status === PENDING) {
self.onFulfilled.push(() => {
handle(onFulfilled, self.value);
});
self.onRejected.push(() => {
handle(onRejected, self.reason);
})
} else if (self.status === FULFILLED) {
setTimeout(() => {
handle(onFulfilled, self.value);
})
} else if (self.status === REJECTED) {
setTimeout(() => {
handle(onRejected, self.reason);
})
}
})
return promise;
}
}
function resolvePromise(promise, x, resolve, reject) {
// PromiseA+ 2.3.1 如果promise和x引用同一对象,会以TypeError错误reject promise
if (promise === x) {
reject(new TypeError('Chaining Cycle'));
}
if (x && typeof x === 'object' || typeof x === 'function') {
// PromiseA+ 2.3.3.3.3 如果resolvePromise和rejectPromise都被调用,或者对同一个参数进行多次调用,那么第一次调用优先,以后的调用都会被忽略。
let used;
try {
// PromiseA+ 2.3.3.1 let then be x.then
// PromiseA+ 2.3.2 调用then方法已经包含了该条(该条是x是promise的处理)。
let then = x.then;
if (typeof then === 'function') {
// PromiseA+ 2.3.3.3如果then是一个函数,用x作为this调用它。第一个参数是resolvePromise,第二个参数是rejectPromise
// PromiseA+ 2.3.3.3.1 如果resolvePromise用一个值y调用,运行[[Resolve]](promise, y)
// PromiseA+ 2.3.3.3.2 如果rejectPromise用一个原因r调用,用r拒绝promise。
then.call(x, (y) => {
if (used) return;
used = true;
resolvePromise(promise, y, resolve, reject)
}, (r) => {
if (used) return;
used = true;
reject(r);
})
} else {
// PromiseA+ 如果then不是一个函数,变为fulfilled状态并传值为x
if (used) return;
used = true;
resolve(x);
}
} catch (e) {
// PromiseA+ 2.3.3.2 如果检索属性x.then抛出异常e,则以e为原因拒绝promise
// PromiseA+ 2.3.3.4 如果调用then抛出异常,但是resolvePromise或rejectPromise已经执行,则忽略它
if (used) return;
used = true;
reject(e);
}
} else {
// PromiseA+ 2.3.4 如果x不是一个对象或函数,状态变为fulfilled并传值x
resolve(x);
}
}
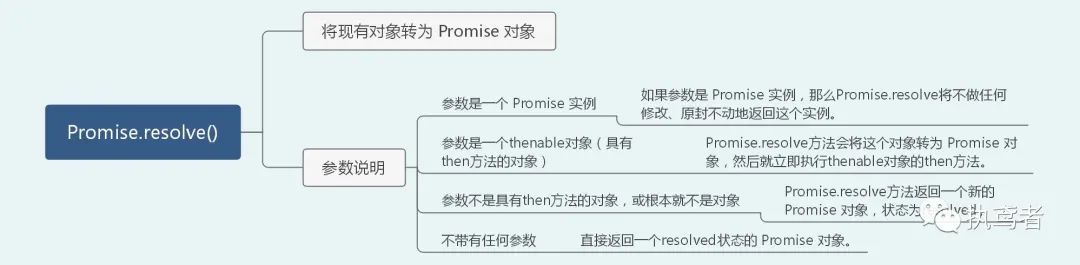
二十三、 Promise.resolve()
class Promise {
// ...
// 将现有对象转为 Promise 对象
static resolve(value) {
// 如果参数是 Promise 实例,那么Promise.resolve将不做任何修改、原封不动地返回这个实例。
if (value instanceof Promise) return value;
// 参数是一个thenable对象(具有then方法的对象),Promise.resolve方法会将这个对象转为 Promise 对象,然后就立即执行thenable对象的then方法。
if (typeof value === 'object' || typeof value === 'function') {
try {
let then = value.then;
if (typeof then === 'function') {
return new Promise(then.bind(value));
}
} catch (e) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
reject(e);
})
}
}
// 参数不是具有then方法的对象,或根本就不是对象,Promise.resolve方法返回一个新的 Promise 对象,状态为resolved。
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve(value);
})
}
}
二十四、 Promise.reject()

class Promise {
// ...
// 返回一个新的 Promise 实例,该实例的状态为rejected。
static reject(reason) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
reject(reason);
})
}
}
二十五、 Promise.all()

class Promise {
// ...
// 用于将多个 Promise 实例,包装成一个新的 Promise 实例。只有所有状态都变为fulfilled,p的状态才会是fulfilled
static all(promises) {
const values = [];
let resolvedCount = 0;
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
promises.forEach((p, index) => {
Promise.resolve(p).then(value => {
resolvedCount++;
values[index] = value;
if (resolvedCount === promises.length) {
resolve(values);
}
}, reason => {
reject(reason);
})
})
})
}
}
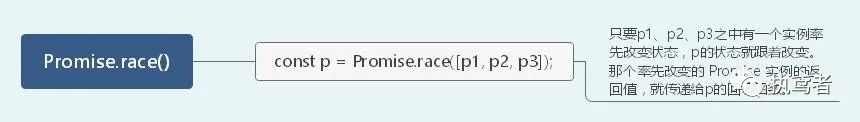
二十六、 Promise.race()
class Promise {
// ...
// 只要有一个实例率先改变状态,状态就跟着改变。那个率先改变的 Promise 实例的返回值,就传递给回调函数。
static race(promises) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
promises.forEach((p, index) => {
Promise.resolve(p).then(value => {
resolve(value);
}, reason => {
reject(reason);
})
})
})
}
}
二十七、 Promise.catch()

class Promise {
// ...
// 是.then(null, rejection)或.then(undefined, rejection)的别名,用于指定发生错误时的回调函数。
catch(onRejected) {
return this.then(undefined, onRejected);
}
}
二十八、 Promise.finally()

class Promise {
// ...
// 用于指定不管 Promise 对象最后状态如何,都会执行的操作。
finally(callback) {
return this.then(
value => Promise.resolve(callback()).then(() => value),
reason => Promise.resolve(callback()).then(() => { throw reason })
)
}
}
二十九、Async实现原理

这是Async的实现原理,即将Generator函数作为参数放入run函数中,最终实现自动执行并返回Promise对象。
function run(genF) {
// 返回值是Promise
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const gen = genF();
function step(nextF) {
let next;
try {
// 执行该函数,获取一个有着value和done两个属性的对象
next = nextF();
} catch (e) {
// 出现异常则将该Promise变为rejected状态
reject(e);
}
// 判断是否到达末尾,Generator函数到达末尾则将该Promise变为fulfilled状态
if (next.done) {
return resolve(next.value);
}
// 没到达末尾,则利用Promise封装该value,直到执行完毕,反复调用step函数,实现自动执行
Promise.resolve(next.value).then((v) => {
step(() => gen.next(v))
}, (e) => {
step(() => gen.throw(e))
})
}
step(() => gen.next(undefined));
})
}
三十、发布订阅模式

// 发布订阅(TypeScript版)
interface Publish {
registerObserver(eventType : string, subscribe : Subscribe) : void;
remove(eventType : string, subscribe ?: Subscribe) : void;
notifyObservers(eventType : string) : void;
}
interface SubscribesObject{
[key : string] : Array
}
class ConcretePublish implements Publish {
private subscribes : SubscribesObject;
constructor() {
this.subscribes = {};
}
registerObserver(eventType : string, subscribe : Subscribe) : void {
if (!this.subscribes[eventType]) {
this.subscribes[eventType] = [];
}
this.subscribes[eventType].push(subscribe);
}
remove(eventType : string, subscribe ?: Subscribe) : void {
const subscribeArray = this.subscribes[eventType];
if (subscribeArray) {
if (!subscribe) {
delete this.subscribes[eventType];
} else {
for (let i = 0; i < subscribeArray.length; i++) {
if (subscribe === subscribeArray[i]) {
subscribeArray.splice(i, 1);
}
}
}
}
}
notifyObservers(eventType : string, ...args : any[]) : void {
const subscribes = this.subscribes[eventType];
if (subscribes) {
subscribes.forEach(subscribe => subscribe.update(...args))
}
}
}
interface Subscribe {
update(...value : any[]) : void;
}
class ConcreteSubscribe1 implements Subscribe {
public update(...value : any[]) : void {
console.log('已经执行更新操作1,值为', ...value);
}
}
class ConcreteSubscribe2 implements Subscribe {
public update(...value : any[]) : void {
console.log('已经执行更新操作2,值为', ...value);
}
}
function main() {
const publish = new ConcretePublish();
const subscribe1 = new ConcreteSubscribe1();
const subscribe2 = new ConcreteSubscribe2();
publish.registerObserver('1', subscribe1);
publish.registerObserver('2', subscribe2);
publish.notifyObservers('2', '22222');
}
main();
三十一、懒加载
1)首先,不要将图片地址放到src属性中,而是放到其它属性(data-original)中。
2)页面加载完成后,根据scrollTop判断图片是否在用户的视野内,如果在,则将data-original属性中的值取出存放到src属性中。
3)在滚动事件中重复判断图片是否进入视野,如果进入,则将data-original属性中的值取出存放到src属性中。
elementNode.getAttribute(name):方法通过名称获取属性的值。
elementNode.setAttribute(name, value):方法创建或改变某个新属性。
elementNode.removeAttribute(name):方法通过名称删除属性的值。
//懒加载代码实现
var viewHeight = document.documentElement.clientHeight;//可视化区域的高度
function lazyload () {
//获取所有要进行懒加载的图片
let eles = document.querySelectorAll('img[data-original][lazyload]');//获取属性名中有data-original的
Array.prototype.forEach.call(eles, function(item, index) {
let rect;
if(item.dataset.original === '') {
return;
}
rect = item.getBoundingClientRect();
//图片一进入可视区,动态加载
if(rect.bottom >= 0 && rect.top < viewHeight) {
!function () {
let img = new Image();
img.src = item.dataset.original;
img.onload = function () {
item.src = img.src;
}
item.removeAttribute('data-original');
item.removeAttribute('lazyload');
}();
}
})
}
lazyload();
document.addEventListener('scroll', lazyload);
三十二、FileReader使用
function uploadMulFile(uploadFile) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
let fileLength = 0;
let reader = new FileReader();
reader.readAsText(uploadFile[fileLength]);
reader.onabort = function(e) {
console.log("文件读取异常");
}
reader.onerror = function(e) {
console.log("文件读取错误");
}
reader.onload = function(e){
if(e.target.result) {
fileLength++;
if(fileLength < uploadFile.length) {
reader.readAsText(uploadFile[fileLength]);
}else{
resolve({
carArr,
crossArr,
roadArr
})
}
}
}
})
}
三十三、Ajax使用(非Promise版)
function ajax(url) {
var XHR;
//进行性能检测
if(window.ActiveXObject) {
XHR = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");//兼容IE//IE浏览器中使用的请求的方法,需实例化
}else if(window.XMLHttpRequest) {
XHR = new XMLHttpRequest();//标准浏览器中的使用的请求方法,需实例化
}else{
XHR = null;
}
if(XHR) {
XHR.onreadystatechange = function() {
//readyState:Ajax请求服务的状态
if(XHR.readyState == 4) {
//status:页面的响应码
if(XHR.status == 200) {
//返回的数据以string的形式返回
console.log(XHR.responseText);
}
}
};
XHR.open("get", url);//open(‘method’,‘url’,boolean);参数1:请求方式;参数2:请求文件的地址;参数3:设置是否异步,true表示异步, 默认值为 true 所以可以不写。
XHR.send();
}
}
三十四、Ajax使用(Promise版)
//Promise形式
function ajaxPromise(method, url, data) {
var xhr = null;
if(window.ActiveXObject) {
xhr = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}else{
xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
}
return new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
xhr.onreadystatechange = function(){
if(xhr.readyState === 4 ) {
if(xhr.status === 200) {
resolve(JSON.parse(xhr.responseText));
}else{
reject(xhr.status);
}
}
};
if(method.toUpperCase() == "GET") {
var arr = [];
for(var key in data) {
arr.push(key + '=' + data[key]);
}
var getData = arr.join('&');
xhr.open("GET", url + "?" + getData, true);//true表示异步
xhr.send(null);
}else if(method.toUpperCase() == "POST") {
xhr.open("POST", url, true);
xhr.responseType = "json";
xhr.setRequestHeader('Content', 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=utf-8');
xhr.send(data);
}
})
}
三十五、JsonP
function jsonp(url, onsuccess, onerror, charset) {
var hash = Math.random().toString().slice(2);
window['jsonp' + hash] = function(data) {
if(onsuccess && typeof onsuccess == 'function') {
onsuccess(data);
}
}
var script = createScript(url + "?callback=jsonp" + hash, charset); // 动态产检一个script标签
//监听加载成功的事件,获取数据,这个位置用了两个事件onload和onreadystatechange是为了兼容IE,因为IE9之前不支持onload事件,只支持onreadystatechange事件
script.onload = script.onreadystatechange = function() {
//若不存在readyState事件则证明不是IE浏览器,可以直接执行,若是的话,必须等到状态变为loaded或complete才可以执行
if(!this.readyState || this.readyState == 'loaded' || this.readyState == 'complete') {
script.onload = script.onreadystatechange = null;
// 移除该script的DOM对象
if(script.parentNode) {
script.parentNode.removeChild(script);
}
//删除函数或变量
window['jsonp' + hash] = null;
}
}
script.onerror = function () {
if(onerror && typeof onerror == 'function') {
onerror();
}
}
document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0].appendChild(script);//往html中增加这个标签,目的是把请求发送出去
}
function createScript(url, charset) {
var script = document.createElement('script');
script.setAttribute('type', 'text/javascript');
charset && script.setAttribute('charset', charset);
script.setAttribute('src', url);
script.async = true;
}
三十六、将一个字符串转换为驼峰形式
//方式一:操作字符串数组
function transformStr2Hump1(str) {
if(str == null) {
return "";
}
var strArr = str.split('-');
for(var i = 1; i < strArr.length; i++) {
strArr[i] = strArr[i].charAt(0).toUpperCase() + strArr[i].substring(1);
}
return strArr.join('');
}
//方式二:操作字符数组
function transformStr2Hump2(str) {
if(str == null) {
return "";
}
var strArr =str.split('');
for(var i = 0; i < strArr.length; i++) {
if(strArr[i] == "-"){
//删除-
strArr.splice(i, 1);
//将该处改为大写
if(i < strArr.length) {
strArr[i] = strArr[i].toUpperCase();
}
}
}
return strArr.join("");
}
//方式三:利用正则
function transformStr2Hump3(str) {
if(str == null) {
return "";
}
var reg = /-(\w)/g;//匹配字母或数字或下划线或汉字
return str.replace(reg, function($0, $1) {
return $1.toUpperCase();
})
}