【手撕算法】PatchMatch图像修复算法
点击上方“AI算法与图像处理”,选择加"星标"或“置顶”
重磅干货,第一时间送达
PatchMatch: A Randomized Correspondence Algorithm for Structural Image Editing

首先是建立图像的下采样金字塔模型,代码中设定为五层,建立模型后
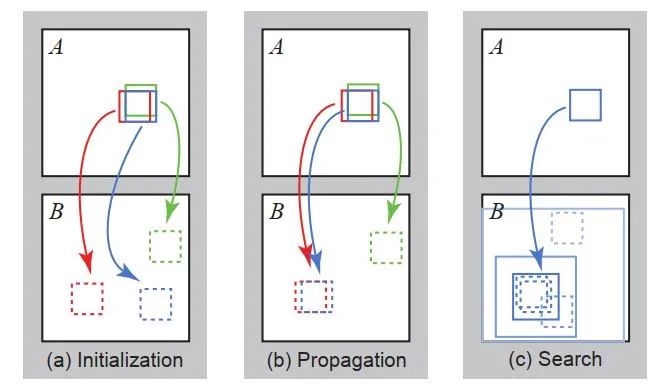
对A的待修复区域每个patch块随机在B已知区域中匹配一个patch块,即初始化偏置地图(上图a步骤)。
/*********************************函数声明:初始化偏置图像参数:NONE注释:NONE测试:NONE**********************************/void PatchMatch::InitOff(Mat Mask, Mat &Off){//为方便起见,将所有的都附上,要求不能赋值到非搜索区域//初始化格式Off = Mat(Mask.size(), CV_32FC2, Scalar::all(0));//2维无符号32位精度浮点数for (int i = 0; i < Mask.rows; i++){for (int j = 0; j < Mask.cols; j++){//不考虑search区域,没有破损,他们的最佳偏移向量当然是0,自己if (Mask.at<uchar>(i, j) == search){Off.at<Vec2f>(i, j)[0] = 0; //<Vec2f> 向量,2维,浮点数Off.at<Vec2f>(i, j)[1] = 0;}else//处理hole,采用随机偏置{//先初始化2个偏置数r_col,r_rowint r_col = rand() % Mask.cols; //rand()产生随机数,主要是产生一个偏置的初始值int r_row = rand() % Mask.rows;r_col = r_col + j < Mask.cols ? r_col : r_col - Mask.cols;//边界检测r_row = r_row + i < Mask.rows ? r_row : r_row - Mask.rows;//为什么要有这个循环?因为一次的随机赋值,很可能会出现偏置后的块跑到破损区域,或者是超出限定搜索框的边界while (!(Mask.at<uchar>(r_row + i, r_col + j) == search //这里加上I,j,是因为他是A投影到B中的搜索偏置&& abs(r_row) < searchrowratio*Mask.rows)) //searchrowratio=0.5,搜索的时候,确保r_row偏置不会太远,一定是在原图像的大小里{r_col = rand() % Mask.cols;r_row = rand() % Mask.rows;//边界检测r_col = r_col + j < Mask.cols ? r_col : r_col - Mask.cols;r_row = r_row + i < Mask.rows ? r_row : r_row - Mask.rows;}//赋偏置值Off.at<Vec2f>(i, j)[0] = r_row;Off.at<Vec2f>(i, j)[1] = r_col;}}}}
之后从低分辨率开始,对于每一层金字塔模型进行迭代:
每一次迭代都会遍历原图A待修复区域所有像素。当遍历到当前像素时,执行下面的步骤来进行修复:
步骤一:传播(图中b步骤)
传播会计算原图A当前像素块patch_A(蓝色)对应的B中的patch_B_1,patch_A上方(绿色)(奇数次迭代为下方)对应的B中的patch_B_2,patch_A左侧(红色)(奇数次迭代为右侧)对应的B中的patch_B_3这三个patch块中与patch_A相似度最高的patch块。
计算相似度函数为
//以块为单位,用所有像素点的相同颜色通道的差平方来简单判断相似度float PatchMatch::Distance(Mat Dst, Mat Src){float distance = 0;for (int i = 0; i < Dst.rows; i++){for (int j = 0; j < Dst.cols; j++){for (int k = 0; k < 3; k++)//K=3个颜色通道{int tem = Src.at < Vec3b >(i, j)[k] - Dst.at < Vec3b >(i, j)[k];distance += tem * tem;//差平方}}}return distance;}
传播函数:
//迭代第一步:传播//(now_row, now_col):patch里的像素//odd:当前迭代次void PatchMatch::Propagation(Mat Dst, Mat Src, Mat Mask, Mat &Off, int row, int col,int odd){Mat DstPatch = GetPatch(Dst, row, col);//获取长度为 patchsize = 3 的边界框, (row, col)代表的是中心像素点坐标if (odd % 2 == 0)//偶次迭代{//提取(row, col)的match块Mat SrcPatch = GetPatch(Src, row + Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col)[0],col + Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col)[1]);//提取(row, col-1)的match块Mat LSrcPatch = GetPatch(Src, row + Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col - 1)[0],col - 1 + Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col - 1)[1]);//提取(row-1, col)的match块Mat USrcPatch = GetPatch(Src,row - 1 + Off.at < Vec2f >(row - 1, col)[0],col + Off.at < Vec2f >(row - 1, col)[1]);//返回上面4个块最相似的块的代表数字,用于switch判断int location = GetMinPatch1(DstPatch, SrcPatch, LSrcPatch, USrcPatch);//利用上面的信息更新像素点的偏置地图switch (location){//若是1则不更新case 2:Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col)[0] = Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col - 1)[0];Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col)[1] = Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col - 1)[1] - 1;break;case 3:Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col)[0] = Off.at < Vec2f >(row - 1, col)[0] - 1;Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col)[1] = Off.at < Vec2f >(row - 1, col)[1];break;}}else//奇数次迭代{Mat SrcPatch = GetPatch(Src, row + Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col)[0],col + Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col)[1]);Mat RSrcPatch = GetPatch(Src, row + Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col + 1)[0],col + 1 + Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col + 1)[1]);Mat DSrcPatch = GetPatch(Src,row + 1 + Off.at < Vec2f >(row + 1, col)[0],col + Off.at < Vec2f >(row + 1, col)[1]);int location = GetMinPatch1(DstPatch, SrcPatch, RSrcPatch, DSrcPatch);switch (location){case 2:Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col)[0] = Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col + 1)[0];Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col)[1] = Off.at < Vec2f>(row, col + 1)[1] + 1;break;case 3:Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col)[0] = Off.at < Vec2f>(row + 1, col)[0] + 1;Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col)[1] = Off.at < Vec2f >(row + 1, col)[1];break;}}}
步骤二:随机扰动搜索(图中c步骤)
为了避免陷入局部极值,再额外再随机生成几个patch位置作为候选patch块,若小于当前patch,则更新。
随机扰动会在原图A中,以当前像素为中心点,初始半径区域为全图,在此区域内随机找寻patch块并与patch_A原本对应的B中的patch块对比,若更相似则更新对应关系offset,然后以新的patch_B为中心,半径缩小一倍,继续搜索,直到半径缩小为1,更新完毕。
//迭代第二步:随机搜索//(row,col)=(now_row, now_col):修复patch里的像素void PatchMatch::RandomSearch(Mat Dst, Mat Src, Mat Mask, Mat &Off, int row, int col){Mat DstPatch = GetPatch(Dst, row, col);//获取修复基准框,在框内操作//迭代指数int attenuate = 0;while (true){//获取随机参数,在 [-1;1] 间float divcol = rand() % 2000 / 1000.0f - 1.0f;float divrow = rand() % 2000 / 1000.0f - 1.0f;//减小框大小的公式,𝑢_𝑖=𝑣_0+𝑤*𝛼^𝑖*𝑅_𝑖//行列分别处理,MaxWindow:原始框宽度;divcol:随机系数;pow(A,B):A的B次方。随迭代次数而变小的缩小系数;RandomAttenuation=0.5;float veccol = MaxWindow * pow(RandomAttenuation, attenuate)* divcol;float vecrow = MaxWindow * pow(RandomAttenuation, attenuate)* divrow;float length = sqrt(veccol * veccol + vecrow * vecrow);//如果低于1个像素,没有意义,直接结束整个循环,对下一个像素处理if (length < 1)break;//x方向,前2项指向(row, col)的match块,后面是公式的后一项int nowrow = row + Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col)[0] + vecrow;//y方向int nowcol = col + Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col)[1] + veccol;//判断随机搜索的patch不越界,在search内if (nowcol >= 0 && nowcol <= Off.cols - 1 && nowrow >= 0&& nowrow <= Off.rows - 1&& Mask.at < uchar >(nowrow, nowcol) == search&& abs(nowrow - row) < searchrowratio * Mask.rows)//abs:绝对值{//取出原来的match块Mat SrcPatch1 = GetPatch(Src, Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col)[0] + row,Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col)[1] + col);//取出现在的随机match块Mat SrcPatch2 = GetPatch(Src, nowrow, nowcol);//对比相似性,找出最好的块int location = GetMinPatch2(DstPatch, SrcPatch1, SrcPatch2);//结合最好的相似块给像素新的偏置值switch (location){case 2:Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col)[1] = nowcol - col;Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col)[0] = nowrow - row;break;}}//迭代指数增加attenuate++;}}
经过该两个步骤,本次迭代完毕。
当最终迭代完成后,就完成了整个修复过程。

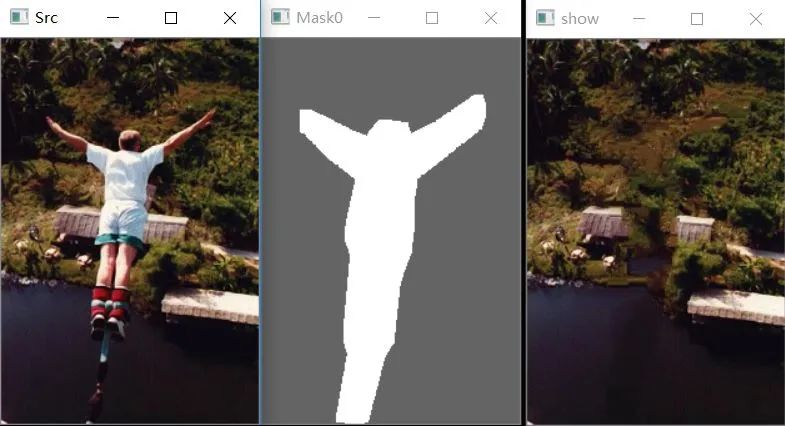
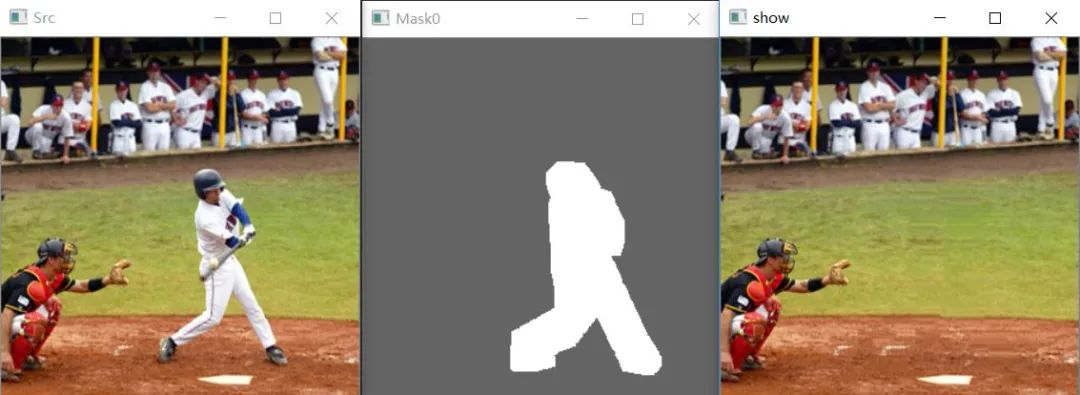
可以看到效果还是可以的,速度也比较快。
 End
End 
声明:部分内容来源于网络,仅供读者学术交流之目的。文章版权归原作者所有。如有不妥,请联系删除。
个人微信(如果没有备注不拉群!) 请注明:地区+学校/企业+研究方向+昵称
下载1:何恺明顶会分享
在「AI算法与图像处理」公众号后台回复:何恺明,即可下载。总共有6份PDF,涉及 ResNet、Mask RCNN等经典工作的总结分析
下载2:终身受益的编程指南:Google编程风格指南
在「AI算法与图像处理」公众号后台回复:c++,即可下载。历经十年考验,最权威的编程规范!
下载3 CVPR2021
在「AI算法与图像处理」公众号后台回复:CVPR,即可下载1467篇CVPR 2020论文 和 CVPR 2021 最新论文
点亮  ,告诉大家你也在看
,告诉大家你也在看
