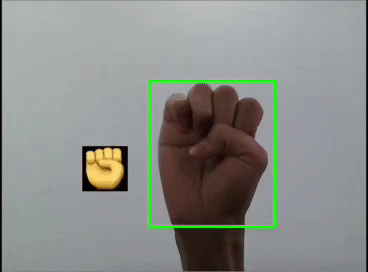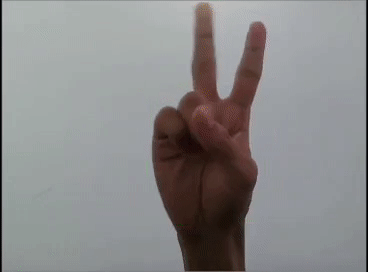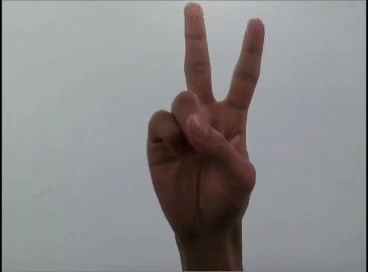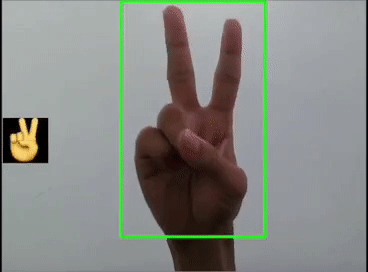
用YOLOv5模型识别出表情!
本文利用YOLOV5对手势进行训练识别,并识别显示出对应的emoji,如同下图:
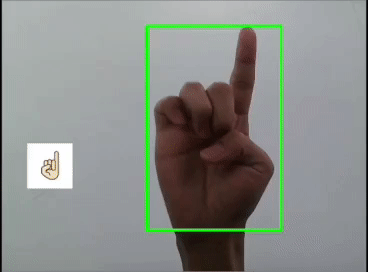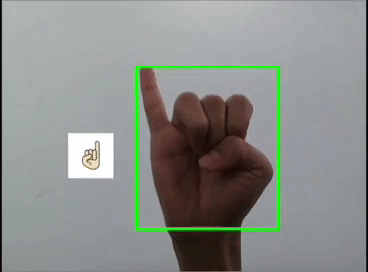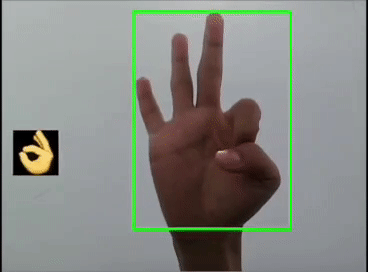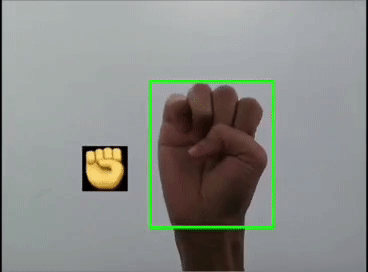
一 、YOLOV5训练数据集
1. 安装环境依赖
本教程所用环境:YOLOV5版本是V3.1。
通过git clone 将源码下载到本地,通过pip install -r requirements.txt 安装依赖包 (其中官方要求python>=3.8 and torch>=1.6)。
我的环境是:系统环境Ubuntu16.04;cuda版本10.2;cudnn版本7.6.5;torch版本1.6.0;python版本3.8
2. 准备手势识别数据集
其中手势数据集已上传至开源数据平台Graviti,包含了完整代码。
手势数据集地址:https://gas.graviti.cn/dataset/datawhale/HandPose?utm_medium=0831datawhale
2.1 数据集的采集以及标注
手势数据采集的代码:
import cv2
def main():
total_pics = 1000
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
pic_no = 0
flag_start_capturing = False
frames = 0
while True:
ret,frame = cap.read()
frame = cv2.flip(frame,1)
cv2.imwrite("hand_images/" +str(pic_no) +".jpg",frame)
cv2.imshow("Capturing gesture",frame)
cv2.waitKey(10)
pic_no += 1
if pic_no == total_pics:
break
main()
在yolov5目录下创建VOC2012文件夹(名字自己定义的),目录结构就是VOC数据集的,对应如下:
VOC2012 ../Annotations #这个是存放数据集图片对应的xml文件 ../images #这个存放图片的 ../ImageSets/Main #这个主要是存放train.txt,test.txt,val.txt和trainval.txt四个文件。里面的内容是训练集、测试集、验证集以及训练验证集的名字(不带扩展后缀名)。
示例:
VOC2012文件夹下内容:
Annotations文件中是xml文件(labelimg标注的):
images为VOC数据集格式中的JPRGImages:
ImageSets文件中Main子文件夹主要存放训练,测试验证集的划分txt。这个划分通过以下脚本代码生成:
# coding:utf-8
import os
import random
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
#xml文件的地址,根据自己的数据进行修改 xml一般存放在Annotations下
parser.add_argument('--xml_path', default='C:\\Users\\Lenovo\\Desktop\\hand_datasets\\VOC2012\\Annotations\\', type=str, help='input xml label path')
#数据集的划分,地址选择自己数据下的ImageSets/Main
parser.add_argument('--txt_path', default='C:\\Users\\Lenovo\\Desktop\\hand_datasets\\VOC2012\\ImageSets\\Main\\', type=str, help='output txt label path')
opt = parser.parse_args()
trainval_percent = 1.0
train_percent = 0.99
xmlfilepath = opt.xml_path
txtsavepath = opt.txt_path
total_xml = os.listdir(xmlfilepath)
if not os.path.exists(txtsavepath):
os.makedirs(txtsavepath)
num = len(total_xml)
list_index = range(num)
tv = int(num * trainval_percent)
tr = int(tv * train_percent)
trainval = random.sample(list_index, tv)
train = random.sample(trainval, tr)
file_trainval = open(txtsavepath + 'trainval.txt', 'w')
file_test = open(txtsavepath + 'test.txt', 'w')
file_train = open(txtsavepath + 'train.txt', 'w')
file_val = open(txtsavepath + 'val.txt', 'w')
for i in list_index:
name = total_xml[i][:-4] + '\n'
if i in trainval:
file_trainval.write(name)
if i in train:
file_train.write(name)
else:
file_val.write(name)
else:
file_test.write(name)
file_trainval.close()
file_train.close()
file_val.close()
file_test.close()
运行代码在Main文件下生成txt文档如下:

2.2 生成yolo训练格式labels
把xml标注信息转换成yolo的txt格式。其中yolo的txt标签格式信息:每个图像对应一个txt文件,文件每一行为一个目标信息,包括classx_center, y_center, width, height 格式。如下图所示:
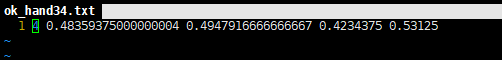
创建voc_label.py文件,将训练集,验证集以及测试集生成txt标签,代码如下:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import os
from os import getcwd
sets = ['train', 'val', 'test']
classes = ["four_fingers","hand_with_fingers_splayed","index_pointing_up","little_finger","ok_hand","raised_fist","raised_hand","sign_of_the_horns","three","thumbup","victory_hand"]
# 11 classes # 改成自己的类别
abs_path = os.getcwd()
print(abs_path)
def convert(size, box):
dw = 1. / (size[0])
dh = 1. / (size[1])
x = (box[0] + box[1]) / 2.0 - 1
y = (box[2] + box[3]) / 2.0 - 1
w = box[1] - box[0]
h = box[3] - box[2]
x = x * dw
w = w * dw
y = y * dh
h = h * dh
return x, y, w, h
def convert_annotation(image_id):
in_file = open('/home/yanyq/Ryan/yolov5/VOC2012/Annotations/%s.xml' % (image_id), encoding='UTF-8')
out_file = open('/home/yanyq/Ryan/yolov5/VOC2012/labels/%s.txt' % (image_id), 'w')
tree = ET.parse(in_file)
root = tree.getroot()
size = root.find('size')
w = int(size.find('width').text)
h = int(size.find('height').text)
for obj in root.iter('object'):
# difficult = obj.find('difficult').text
difficult = obj.find('difficult').text
cls = obj.find('name').text
if cls not in classes or int(difficult) == 1:
continue
cls_id = classes.index(cls)
xmlbox = obj.find('bndbox')
b = (float(xmlbox.find('xmin').text), float(xmlbox.find('xmax').text), float(xmlbox.find('ymin').text),
float(xmlbox.find('ymax').text))
b1, b2, b3, b4 = b
# 标注越界修正
if b2 > w:
b2 = w
if b4 > h:
b4 = h
b = (b1, b2, b3, b4)
bb = convert((w, h), b)
out_file.write(str(cls_id) + " " + " ".join([str(a) for a in bb]) + '\n')
wd = getcwd()
for image_set in sets:
if not os.path.exists('/home/yanyq/Ryan/yolov5/VOC2012/labels/'):
os.makedirs('/home/yanyq/Ryan/yolov5/VOC2012/labels/')
image_ids = open('/home/yanyq/Ryan/yolov5/VOC2012/ImageSets/Main/%s.txt' % (image_set)).read().strip().split()
list_file = open('%s.txt' % (image_set), 'w')
for image_id in image_ids:
list_file.write(abs_path + '/images/%s.jpg\n' % (image_id))
convert_annotation(image_id)
list_file.close()
运行上述脚本后会生成labels文件夹和三个包含数据集的txt文件,其中labels中为图像的yolo格式标注文件,train.txt,test.txt, val.txt文件为划分后图像所在位置的绝对路径。
三个txt文件内容:
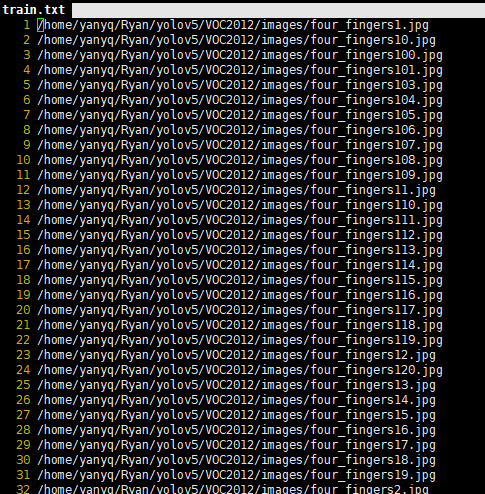
2.3 配置文件
1)数据集的配置
在yolov5目录的data文件夹新建一个Emoji.yaml文件(自己定义)。用来存放训练集验证集的划分文件train.txt和val.txt(其中这两个文件是voc_label.py生成的)。具体内容如下:
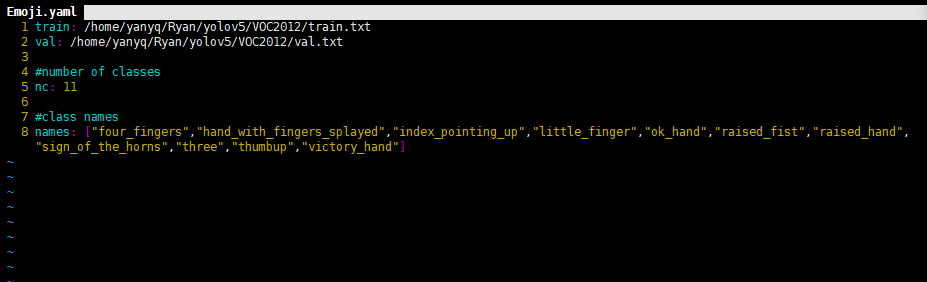
2)模型的配置文件
一般训练yolo模型的时候,是可以聚类自己标注的框作为先验框(这样可以保证标注样本最大化的利用)。我们这里就直接采用默认值了。
选择一个需要的模型,YOLOV5有提供s、m、l、x版本,其是逐渐增大的架构,也就是训练时间和推理时间都对应增加,我们这里选择s版本。在yolov5文件夹下的models文件夹中打开yolov5s.yaml文件,修改内容如下图(我们选择默认anchor,所以不做修改,只需要更改nc中的类别数,由于我们是11类,所以改成11就可以了):
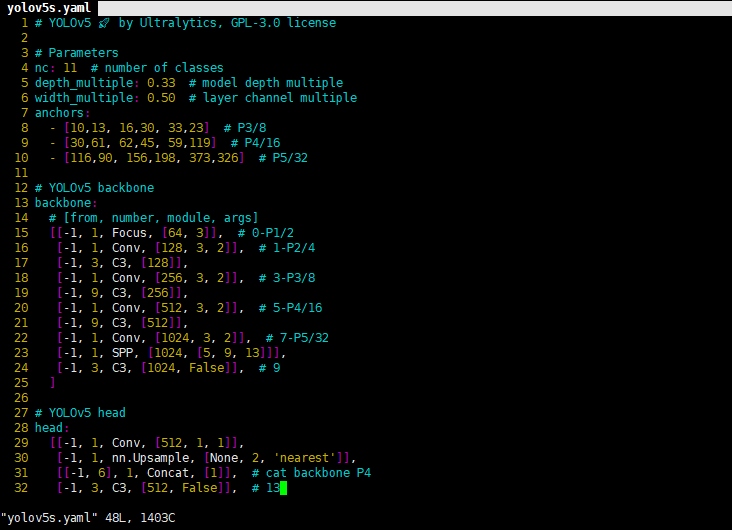
到这里我们的自定义数据集以及配置文件创建完毕,下面就是训练模型了。
3.模型训练
3.1、下载预训练模型
在源码yolov5目录下的weights文件夹下提供了下载smlx模型的脚本--download_weights.sh,执行这个脚本就可以下载这四个模型的预训练模型了。
3.2、训练模型
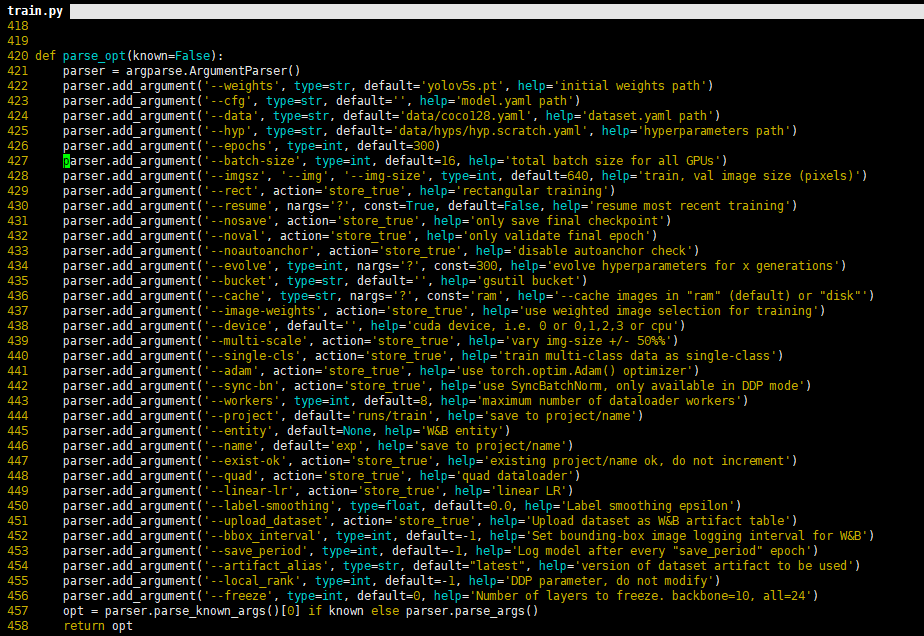
以上参数解释如下:epochs:指的就是训练过程中整个数据集将被迭代多少次,显卡不行你就调小点。batch-size:一次看完多少张图片才进行权重更新,梯度下降的mini-batch,显卡不行你就调小点。cfg:存储模型结构的配置文件。data:存储训练、测试数据的文件。img-size:输入图片宽高,显卡不行你就……。rect:进行矩形训练。resume:恢复最近保存的模型开始训练。nosave:仅保存最终checkpoint。notest:仅测试最后的epoch。evolve:进化超参数。bucket:gsutil bucket。 cache-images:缓存图像以加快训练速度。 weights:权重文件路径。name:重命名results.txt to results_name.txt。device:cuda device, i.e. 0 or 0,1,2,3 or cpu。adam:使用adam优化。multi-scale:多尺度训练,img-size +/- 50%。single-cls:单类别的训练集
训练只需要运行训练命令就可以了,如下:
$ python train.py --data Emoji.yaml --cfg yolov5s.yaml --weights weights/yolov5s.pt --batch-size 64 --device "0,1,2,3" --epochs 200 --img-size 640
其中device batch-size 等需要根据自己机器进行设置。
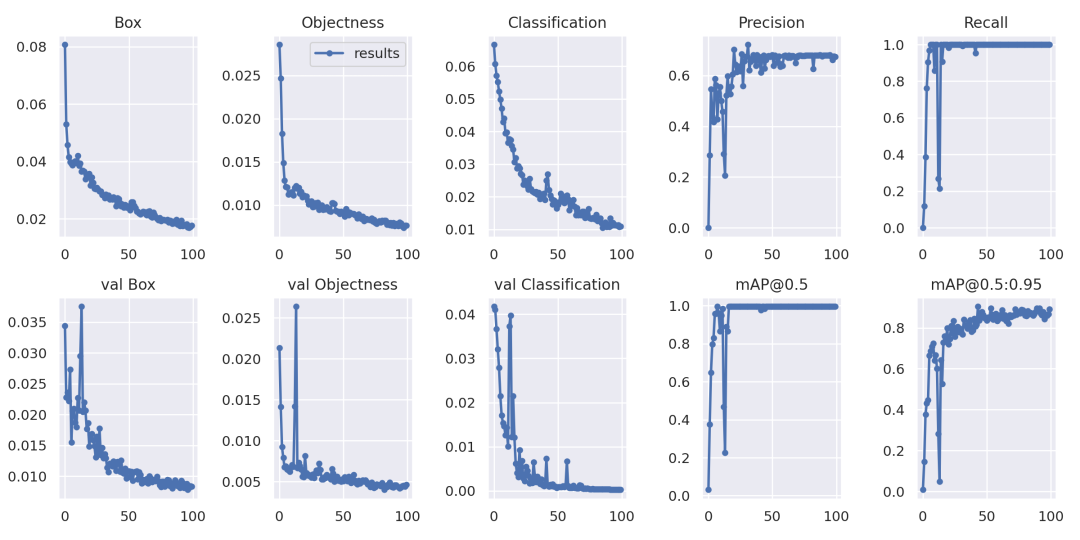
4.模型测试
评估模型好坏就是在有标注的测试集或验证集上进行模型效果的评估,在目标检测中最常使用的评估指标为mAP。yolov5文件下的test.py文件中指定了数据集的配置文件和训练结果模型如下:
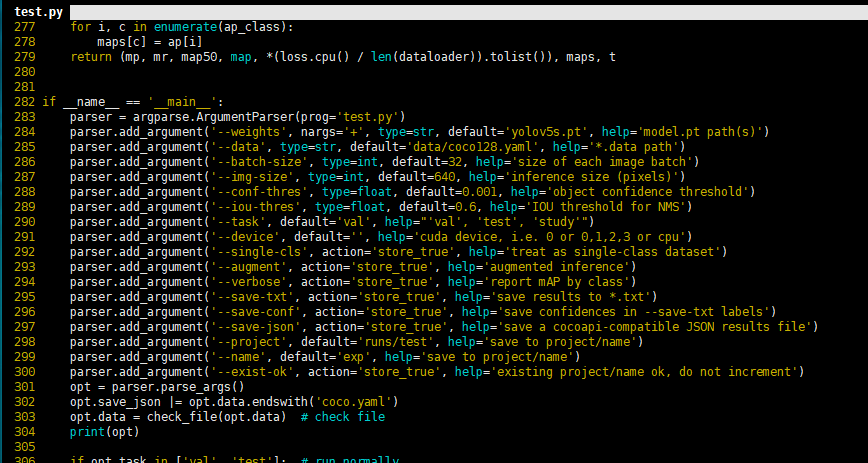
通过以下命令进行模型测试:
python test.py --data data/Emoji.yaml --weights runs/train/exp2/weights/best.pt --augment
模型测试效果:

测试结果图:

二、YOLOV5模型转换
1.安装依赖库
pip install onnx coremltools onnx-simplifier
2.导出ONNX模型
python models/export.py --weights runs/train/exp2/weights/best.pt --img 640 --batch 1
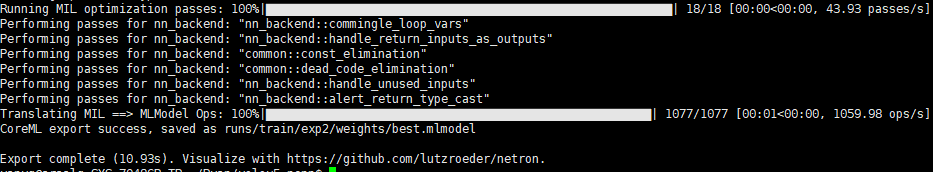
此时在best.pt同级目录下生成了best.mlmodel best.onnx best.torchscript.pt三个文件,我们只需best.onnx,这个文件可以直接用netron打开查看模型结构。
3.用onnx-simplifer简化模型
为什么要简化?
在训练完深度学习的pytorch或者tensorflow模型后,有时候需要把模型转成 onnx,但是很多时候,很多节点比如cast节点,Identity 这些节点可能都不需要,我们需要进行简化,这样会方便我们把模型转成ncnn或者mnn等这些端侧部署的模型格式或者通过tensorRT进行部署。
python -m onnxsim best.onnx yolov5-best-sim.onnx

完成后就生成了简化版本的模型yolov5-best-sim.onnx。
三、YOLOV5转换成ncnn模型
1、onnx转.param .bin
由上述生成了yolov5-best-sim.onnx这个模型,我们利用ncnn自带的工具onnx2ncnn.exe(这个工具是自己编译生成的,我这里是在windows下编译生成的,可以用linux下的可执行文件)生成yolov5s.param yolov5s.bin两个文件。
在windows平台下ctrl+r cmd命令行窗口输入:
onnx2ncnn.exe yolov5-best-sim.onnx yolov5s.param yolov5s.bin
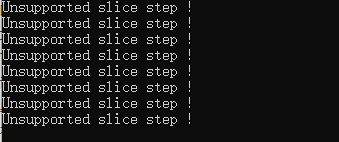
2、修改.param 参数去除不支持的网络层
去掉不支持的网络层,打开转换得到的yolov5s.param文件,前面几行需要删除的是标红部分。(注意我们训练yoloV5的版本是V3.1,这里不同的版本可能会不同。)
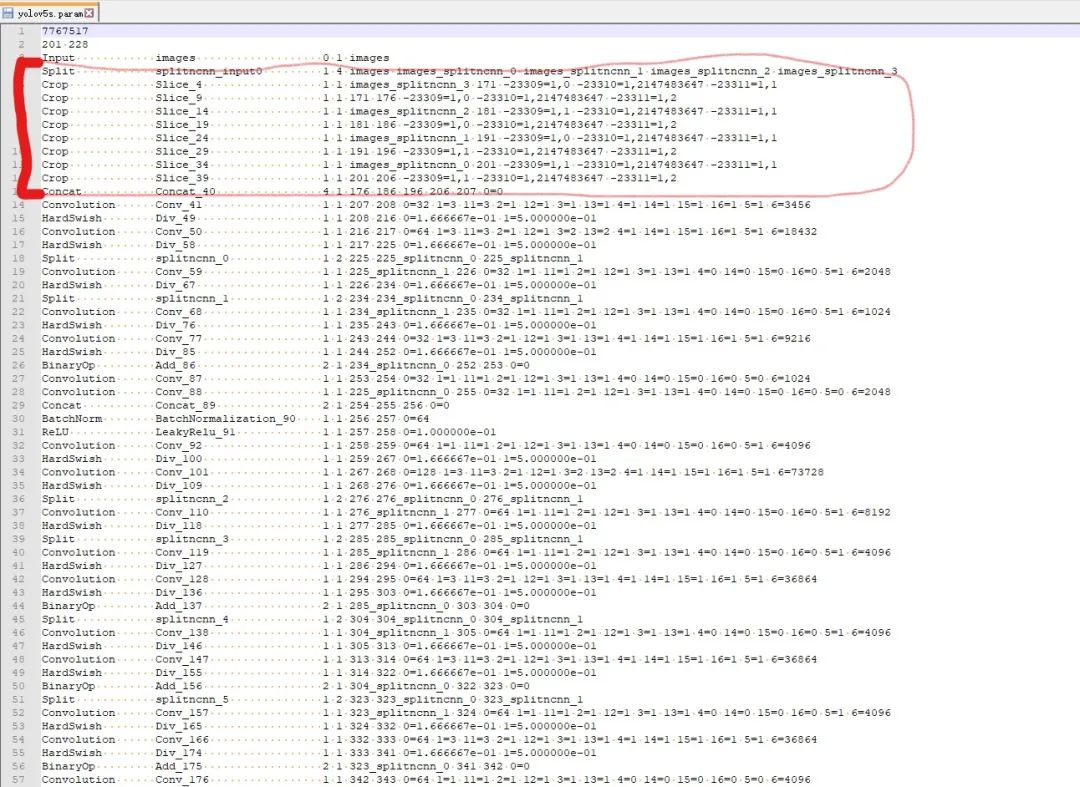
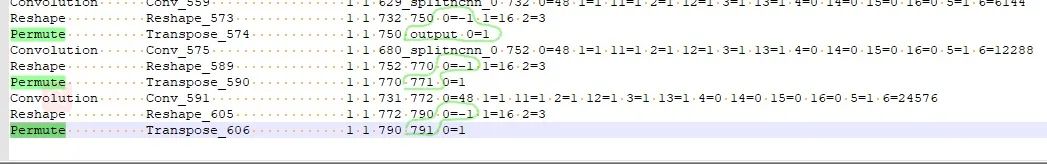
修改结果如下绿色框和红色框中的。因为去掉了10层所以变成191 228。并用YoloV5Focus网络层代替去掉的10层,而YoloV5Focus网络层中的images代表该层的输入,207代表的输出名,这个是根据下边一层的卷积层输入层数写的。
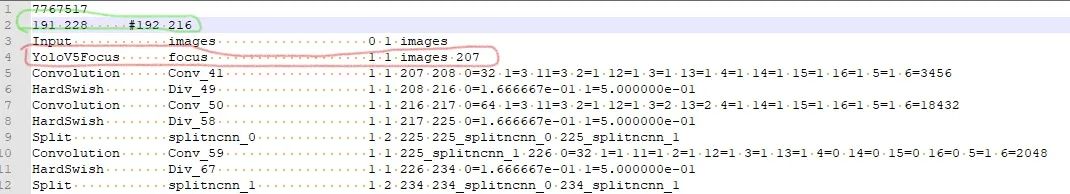
修改网路的输出shape:
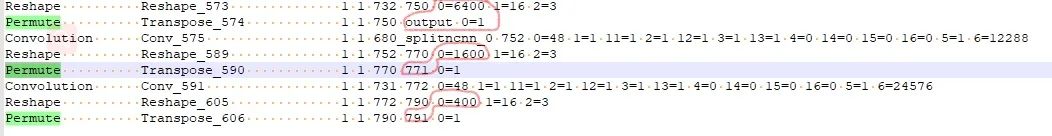
当基于修改后的网路使用ncnn/examples/yolov5测试时会发现出现图片中一堆乱框,这种情况需要修改网路的输出部分。在保证输出名一致的情况下,修改Reshape中的0=-1,使的最终的输出shape不固定。具体的修改地方以及修改之前和之后见下图。
3、ncnn的c++测试代码实现
以下是用C++实现的完整代码。建议一划到底,先看最后的整体思路
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include "iostream"
//#include <fstream>
//#include < ctime >
//#include <direct.h>
//#include <io.h>
// ncnn
#include "ncnn/layer.h"
#include "ncnn/net.h"
#include "ncnn/benchmark.h"
//#include "gpu.h"
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include <opencv2/imgproc.hpp>
#include "opencv2/opencv.hpp"
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
static ncnn::UnlockedPoolAllocator g_blob_pool_allocator;
static ncnn::PoolAllocator g_workspace_pool_allocator;
static ncnn::Net yolov5;
class YoloV5Focus : public ncnn::Layer
{
public:
YoloV5Focus()
{
one_blob_only = true;
}
virtual int forward(const ncnn::Mat& bottom_blob, ncnn::Mat& top_blob, const ncnn::Option& opt) const
{
int w = bottom_blob.w;
int h = bottom_blob.h;
int channels = bottom_blob.c;
int outw = w / 2;
int outh = h / 2;
int outc = channels * 4;
top_blob.create(outw, outh, outc, 4u, 1, opt.blob_allocator);
if (top_blob.empty())
return -100;
#pragma omp parallel for num_threads(opt.num_threads)
for (int p = 0; p < outc; p++)
{
const float* ptr = bottom_blob.channel(p % channels).row((p / channels) % 2) + ((p / channels) / 2);
float* outptr = top_blob.channel(p);
for (int i = 0; i < outh; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < outw; j++)
{
*outptr = *ptr;
outptr += 1;
ptr += 2;
}
ptr += w;
}
}
return 0;
}
};
DEFINE_LAYER_CREATOR(YoloV5Focus)
struct Object
{
float x;
float y;
float w;
float h;
int label;
float prob;
};
static inline float intersection_area(const Object& a, const Object& b)
{
if (a.x > b.x + b.w || a.x + a.w < b.x || a.y > b.y + b.h || a.y + a.h < b.y)
{
// no intersection
return 0.f;
}
float inter_width = std::min(a.x + a.w, b.x + b.w) - std::max(a.x, b.x);
float inter_height = std::min(a.y + a.h, b.y + b.h) - std::max(a.y, b.y);
return inter_width * inter_height;
}
static void qsort_descent_inplace(std::vector<Object>& faceobjects, int left, int right)
{
int i = left;
int j = right;
float p = faceobjects[(left + right) / 2].prob;
while (i <= j)
{
while (faceobjects[i].prob > p)
i++;
while (faceobjects[j].prob < p)
j--;
if (i <= j)
{
// swap
std::swap(faceobjects[i], faceobjects[j]);
i++;
j--;
}
}
#pragma omp parallel sections
{
#pragma omp section
{
if (left < j) qsort_descent_inplace(faceobjects, left, j);
}
#pragma omp section
{
if (i < right) qsort_descent_inplace(faceobjects, i, right);
}
}
}
static void qsort_descent_inplace(std::vector<Object>& faceobjects)
{
if (faceobjects.empty())
return;
qsort_descent_inplace(faceobjects, 0, faceobjects.size() - 1);
}
static void nms_sorted_bboxes(const std::vector<Object>& faceobjects, std::vector<int>& picked, float nms_threshold)
{
picked.clear();
const int n = faceobjects.size();
std::vector<float> areas(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
areas[i] = faceobjects[i].w * faceobjects[i].h;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
const Object& a = faceobjects[i];
int keep = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < (int)picked.size(); j++)
{
const Object& b = faceobjects[picked[j]];
// intersection over union
float inter_area = intersection_area(a, b);
float union_area = areas[i] + areas[picked[j]] - inter_area;
// float IoU = inter_area / union_area
if (inter_area / union_area > nms_threshold)
keep = 0;
}
if (keep)
picked.push_back(i);
}
}
static inline float sigmoid(float x)
{
return static_cast<float>(1.f / (1.f + exp(-x)));
}
static void generate_proposals(const ncnn::Mat& anchors, int stride, const ncnn::Mat& in_pad, const ncnn::Mat& feat_blob, float prob_threshold, std::vector<Object>& objects)
{
const int num_grid = feat_blob.h;
int num_grid_x;
int num_grid_y;
if (in_pad.w > in_pad.h)
{
num_grid_x = in_pad.w / stride;
num_grid_y = num_grid / num_grid_x;
}
else
{
num_grid_y = in_pad.h / stride;
num_grid_x = num_grid / num_grid_y;
}
const int num_class = feat_blob.w - 5;
const int num_anchors = anchors.w / 2;
for (int q = 0; q < num_anchors; q++)
{
const float anchor_w = anchors[q * 2];
const float anchor_h = anchors[q * 2 + 1];
const ncnn::Mat feat = feat_blob.channel(q);
for (int i = 0; i < num_grid_y; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < num_grid_x; j++)
{
const float* featptr = feat.row(i * num_grid_x + j);
// find class index with max class score
int class_index = 0;
float class_score = -FLT_MAX;
for (int k = 0; k < num_class; k++)
{
float score = featptr[5 + k];
if (score > class_score)
{
class_index = k;
class_score = score;
}
}
float box_score = featptr[4];
float confidence = sigmoid(box_score) * sigmoid(class_score);
if (confidence >= prob_threshold)
{
float dx = sigmoid(featptr[0]);
float dy = sigmoid(featptr[1]);
float dw = sigmoid(featptr[2]);
float dh = sigmoid(featptr[3]);
float pb_cx = (dx * 2.f - 0.5f + j) * stride;
float pb_cy = (dy * 2.f - 0.5f + i) * stride;
float pb_w = pow(dw * 2.f, 2) * anchor_w;
float pb_h = pow(dh * 2.f, 2) * anchor_h;
float x0 = pb_cx - pb_w * 0.5f;
float y0 = pb_cy - pb_h * 0.5f;
float x1 = pb_cx + pb_w * 0.5f;
float y1 = pb_cy + pb_h * 0.5f;
Object obj;
obj.x = x0;
obj.y = y0;
obj.w = x1 - x0;
obj.h = y1 - y0;
obj.label = class_index;
obj.prob = confidence;
objects.push_back(obj);
}
}
}
}
}
extern "C" {
void release()
{
fprintf(stderr, "YoloV5Ncnn finished!");
//ncnn::destroy_gpu_instance();
}
int init()
{
fprintf(stderr, "YoloV5Ncnn init!\n");
ncnn::Option opt;
opt.lightmode = true;
opt.num_threads = 4;
opt.blob_allocator = &g_blob_pool_allocator;
opt.workspace_allocator = &g_workspace_pool_allocator;
opt.use_packing_layout = true;
yolov5.opt = opt;
yolov5.register_custom_layer("YoloV5Focus", YoloV5Focus_layer_creator);
// init param
{
int ret = yolov5.load_param("yolov5s.param");
if (ret != 0)
{
std::cout << "ret= " << ret << std::endl;
fprintf(stderr, "YoloV5Ncnn, load_param failed");
return -301;
}
}
// init bin
{
int ret = yolov5.load_model("yolov5s.bin");
if (ret != 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "YoloV5Ncnn, load_model failed");
return -301;
}
}
return 0;
}
int detect(cv::Mat img, std::vector<Object> &objects)
{
double start_time = ncnn::get_current_time();
const int target_size = 320;
// letterbox pad to multiple of 32
const int width = img.cols;//1280
const int height = img.rows;//720
int w = img.cols;//1280
int h = img.rows;//720
float scale = 1.f;
if (w > h)
{
scale = (float)target_size / w;//640/1280
w = target_size;//640
h = h * scale;//360
}
else
{
scale = (float)target_size / h;
h = target_size;
w = w * scale;
}
cv::resize(img, img, cv::Size(w, h));
ncnn::Mat in = ncnn::Mat::from_pixels(img.data, ncnn::Mat::PIXEL_BGR2RGB, w, h);
// pad to target_size rectangle
// yolov5/utils/datasets.py letterbox
int wpad = (w + 31) / 32 * 32 - w;
int hpad = (h + 31) / 32 * 32 - h;
ncnn::Mat in_pad;
ncnn::copy_make_border(in, in_pad, hpad / 2, hpad - hpad / 2, wpad / 2, wpad - wpad / 2, ncnn::BORDER_CONSTANT, 114.f);
// yolov5
//std::vector<Object> objects;
{
const float prob_threshold = 0.4f;
const float nms_threshold = 0.51f;
const float norm_vals[3] = { 1 / 255.f, 1 / 255.f, 1 / 255.f };
in_pad.substract_mean_normalize(0, norm_vals);
ncnn::Extractor ex = yolov5.create_extractor();
//ex.set_vulkan_compute(use_gpu);
ex.input("images", in_pad);
std::vector<Object> proposals;
// anchor setting from yolov5/models/yolov5s.yaml
// stride 8
{
ncnn::Mat out;
ex.extract("output", out);
ncnn::Mat anchors(6);
anchors[0] = 10.f;
anchors[1] = 13.f;
anchors[2] = 16.f;
anchors[3] = 30.f;
anchors[4] = 33.f;
anchors[5] = 23.f;
std::vector<Object> objects8;
generate_proposals(anchors, 8, in_pad, out, prob_threshold, objects8);
proposals.insert(proposals.end(), objects8.begin(), objects8.end());
}
// stride 16
{
ncnn::Mat out;
ex.extract("771", out);
ncnn::Mat anchors(6);
anchors[0] = 30.f;
anchors[1] = 61.f;
anchors[2] = 62.f;
anchors[3] = 45.f;
anchors[4] = 59.f;
anchors[5] = 119.f;
std::vector<Object> objects16;
generate_proposals(anchors, 16, in_pad, out, prob_threshold, objects16);
proposals.insert(proposals.end(), objects16.begin(), objects16.end());
}
// stride 32
{
ncnn::Mat out;
ex.extract("791", out);
ncnn::Mat anchors(6);
anchors[0] = 116.f;
anchors[1] = 90.f;
anchors[2] = 156.f;
anchors[3] = 198.f;
anchors[4] = 373.f;
anchors[5] = 326.f;
std::vector<Object> objects32;
generate_proposals(anchors, 32, in_pad, out, prob_threshold, objects32);
proposals.insert(proposals.end(), objects32.begin(), objects32.end());
}
// sort all proposals by score from highest to lowest
qsort_descent_inplace(proposals);
// apply nms with nms_threshold
std::vector<int> picked;
nms_sorted_bboxes(proposals, picked, nms_threshold);
int count = picked.size();
objects.resize(count);
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
objects[i] = proposals[picked[i]];
// adjust offset to original unpadded
float x0 = (objects[i].x - (wpad / 2)) / scale;
float y0 = (objects[i].y - (hpad / 2)) / scale;
float x1 = (objects[i].x + objects[i].w - (wpad / 2)) / scale;
float y1 = (objects[i].y + objects[i].h - (hpad / 2)) / scale;
// clip
x0 = std::max(std::min(x0, (float)(width - 1)), 0.f);
y0 = std::max(std::min(y0, (float)(height - 1)), 0.f);
x1 = std::max(std::min(x1, (float)(width - 1)), 0.f);
y1 = std::max(std::min(y1, (float)(height - 1)), 0.f);
objects[i].x = x0;
objects[i].y = y0;
objects[i].w = x1;
objects[i].h = y1;
}
}
return 0;
}
}
static const char* class_names[] = {
"four_fingers","hand_with_fingers_splayed","index_pointing_up","little_finger",
"ok_hand","raised_fist","raised_hand","sign_of_the_horns","three","thumbup","victory_hand"
};
void draw_face_box(cv::Mat& bgr, std::vector<Object> object) //主要的emoji显示函数
{
for (int i = 0; i < object.size(); i++)
{
const auto obj = object[i];
cv::rectangle(bgr, cv::Point(obj.x, obj.y), cv::Point(obj.w, obj.h), cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0), 3, 8, 0);
std::cout << "label:" << class_names[obj.label] << std::endl;
string emoji_path = "emoji\\" + string(class_names[obj.label]) + ".png"; //这个是emoji图片的路径
cv::Mat logo = cv::imread(emoji_path);
if (logo.empty()) {
std::cout << "imread logo failed!!!" << std::endl;
return;
}
resize(logo, logo, cv::Size(80, 80));
cv::Mat imageROI = bgr(cv::Range(obj.x, obj.x + logo.rows), cv::Range(obj.y, obj.y + logo.cols)); //emoji的图片放在图中的位置,也就是手势框的旁边
logo.copyTo(imageROI); //把emoji放在原图中
}
}
int main()
{
Mat frame;
VideoCapture capture(0);
init();
while (true)
{
capture >> frame;
if (!frame.empty()) {
std::vector<Object> objects;
detect(frame, objects);
draw_face_box(frame, objects);
imshow("window", frame);
}
if (waitKey(20) == 'q')
break;
}
capture.release();
return 0;
}
这里是首先用yolov5s识别出手势,然后利用图像ROI融合,把相应的Emoji缩放到80x80大小显示在手势框的旁边,实现根据不同的手势显示相应的Emoji。
4、实现emoji和手势的映射
到这里,我们终于大功告成!达成了开头的效果。