poj 1049 Microprocessor Simulation
Microprocessor Simulation
Description
Consider a small microprocessor that has the following properties:
?Each word is four bits.
?Addresses are two words. The high word always comes first. That is, the high word of a two-word address will always occupy the lower word of memory.
?Memory is 256 words.
?There are two accumulators, A and B, each storing one word.
?There are nine instruction codes. Each instruction requires at least one word to store the code that specifies the instruction. Four instructions have arguments and require an additional two words.
Each 4 bit number can have the values from 0 to 15, inclusive, in base 10. We will write these using hexadecimal in the usual way, i.e. A means 10, B means 11, etc.
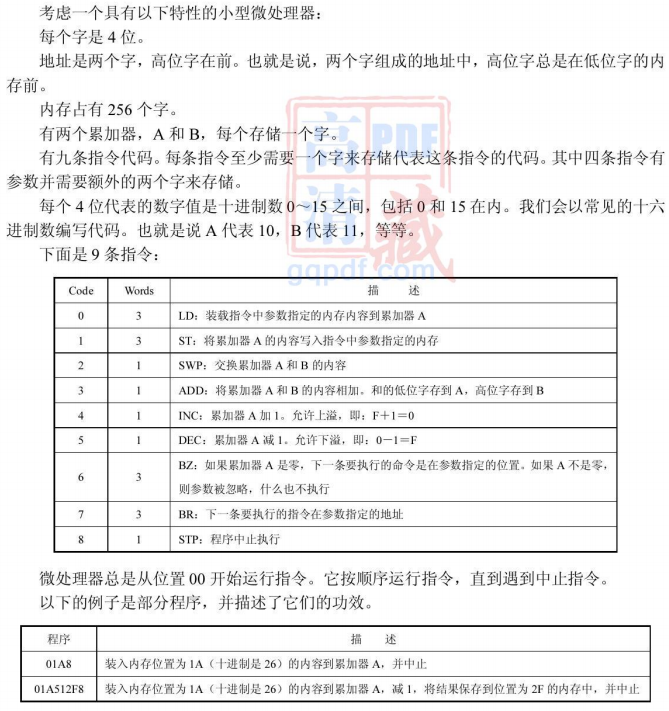
These are the nine instructions:
| Code | Words | Description |
| 0 | 3 | LD: Load accumulator A with the contents of memory at the specified argument. |
| 1 | 3 | ST: Write the contents of accumulator A to the memory location specified by the argumen |
| 2 | 1 | SWP: Swap the contents of accumulators A and B. |
| 3 | 1 | ADD: Add the contents of accumulators A and B. The low word of the sum is stored in A, and the high word in B |
| 4 | 1 | INC: Increment accumulator A. Overflow is allowed; that is, incrementing F yields 0. |
| 5 | 1 | DEC: Decrement accumulator A. Underflow is allowed; that is, decrementing 0 yields F. |
| 6 | 3 | BZ: If accumulator A is zero, the next command to be executed is at the location specified by the argument. If A is not zero, the argument is ignored and nothing happens. |
| 7 | 3 | BR: The next command to be executed is at the location specified by the argument. |
| 8 | 1 | STP: Stop execution of the program. |
The microprocessor always begins by executing the command at location 00. It executes the commands in sequence until it reaches the Stop command.
The examples below show partial programs and describe their affect.
| Program | Description |
| 01A8 | Load accumulator A with the contents of memory location 1A (26 in decimal) and stop. |
| 01A512F8 | Load accumulator A with the contents of memory location 1A (26 in decimal), decrement it, store the result to memory location 2F, then stop. |
Input
The input will consist of several lines of exactly 256 hex characters. Each line is the contents of memory, beginning with address 00 and ending with address FF. The end of the input is indicated by a memory state that has a stop instruction (an "8") at address 00. The input programs will never "fall of the end of memory" that is, you will never execute an instruction that is located between addresses F0 and FF, inclusive.
Output
For each memory state, you should simulate execution beginning with address 00. When the stop instruction is reached, you will dump the contents of memory to the output as a single string of 256 hex characters followed by a newline character.
Sample Input
0102011311321128FF0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Sample Output
0102011311321128FF1E00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000

代码:
#include
using namespace std;
char mem[257];
char A, B;
int pc;
int Hex2Dec(char c)
{
if (c >= '0' && c <= '9')
return c - '0';
else
return c - 'A' + 10;
}
int DHex2Dec(char a, char b)
{
return Hex2Dec(a) * 16 + Hex2Dec(b);
}
char Dec2Hex(int i)
{
if (i >= 10)
return 'A' + i - 10;
else
return i + '0';
}
int main()
{
while (scanf("%s", mem) && mem[0] != '8')
{
pc = 0;
char command;
char buf;
int buf1, buf2;
A = B = '0';
while ((command = mem[pc]) != '8')
{
switch (command)
{
case '0'://LD
A = mem[DHex2Dec(mem[pc + 1], mem[pc + 2])];
pc += 3;
break;
case '1'://ST
mem[DHex2Dec(mem[pc + 1], mem[pc + 2])] = A;
pc += 3;
break;
case '2'://SWP
buf = A;
A = B;
B = buf;
++pc;
break;
case '3'://ADD
buf1 = Hex2Dec(A);
buf2 = Hex2Dec(B);
B = Dec2Hex((buf1 + buf2) / 16);
A = Dec2Hex((buf1 + buf2) % 16);
++pc;
break;
case '4'://INC
if (A == 'F') A = '0';
else if (A == '9') A = 'A';
else ++A;
++pc;
break;
case '5'://DEC
if (A == '0') A = 'F';
else if (A == 'A') A = '9';
else --A;
++pc;
break;
case '6'://BZ
if (A == '0') pc = DHex2Dec(mem[pc + 1], mem[pc + 2]);
else pc += 3;
break;
case '7'://BR
pc = DHex2Dec(mem[pc + 1], mem[pc + 2]);
break;
}
}
printf("%s\n", mem);
}
return 0;
}
