poj 1032 Fence
Fence
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 10000K | |
| Total Submissions: 4236 | Accepted: 1493 |
Description
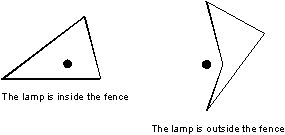
There is an area bounded by a fence on some flat field. The fence has the height h and in the plane projection it has a form of a closed polygonal line (without self-intersections), which is specified by Cartesian coordinates (Xi, Yi) of its N vertices. At the point with coordinates (0, 0) a lamp stands on the field. The lamp may be located either outside or inside the fence, but not on its side as it is shown in the following sample pictures (parts shown in a thin line are not illuminated by the lamp):
The fence is perfectly black, i.e. it is neither reflecting, nor diffusing, nor letting the light through. Research and experiments showed that the following law expresses the intensity of light falling on an arbitrary illuminated point of this fence:
where k is a known constant value not depending on the point in question, r is the distance between this point and the lamp in the plane projection. The illumination of an infinitesimal narrow vertical board with the width dl and the height h is
where I0 is the intensity of light on that board of the fence, α is the angle in the plane projection between the normal to the side of the fence at this point and the direction to the lamp.
You are to write a program that will find the total illumination of the fence that is defined as the sum of illuminations of all its illuminated boards.
Input
The first line of the input file contains the numbers k, h and N, separated by spaces. k and h are real constants. N (3 <= N <= 100) is the number of vertices of the fence. Then N lines follow, every line contains two real numbers Xi and Yi, separated by a space.
Output
Write to the output file the total illumination of the fence rounded to the second digit after the decimal point.
Sample Input
0.5 1.7 3
1.0 3.0
2.0 -1.0
-4.0 -1.0
Sample Output
5.34
栅栏
描述
在一些平坦的田野上有一个由栅栏围起来的区域。围栏的高度为 h,在平面投影中,它具有闭合折线的形式(无自相交),由其 N 个顶点的笛卡尔坐标 (Xi, Yi) 指定。在坐标为 (0, 0) 的点上,一盏灯矗立在场地上。灯可以位于围栏的外部或内部,但不能位于其侧面,如下面的示例图片所示(以细线显示的部分不被灯照亮)

栅栏是完全黑色的,即它既不反射也不漫射,也不让光线通过。研究和实验表明,以下定律表达了落在该围栏任意照明点上的光强:
其中 k 是一个已知的常数值,不取决于所讨论的点,r 是该点与平面投影中灯之间的距离。宽度为 dl,高度为 h 的无限小的窄垂直板的照度为
其中 I 0是栅栏那块板上的光强,α 是此时栅栏侧面的法线与灯的方向之间的平面投影角度。
您将编写一个程序,该程序将找到围栏的总照明度,该总照明度定义为其所有照明板的照明度之和。
输入
输入文件的第一行包含数字 k、h 和 N,用空格分隔。k 和 h 是实常数。N (3 <= N <= 100) 是围栏的顶点数。然后是N行,每行包含两个实数Xi和Yi,中间用空格隔开。
输出
将围栏的总照度四舍五入到小数点后的第二位写入输出文件。
样本输入
0.5 1.7 3
1.0 3.0
2.0 -1.0
-4.0 -1.0
样本输出
5.34
代码:
#include
#include
#define PI 3.14159265
using namespace std;
struct node
{
double x,y;
}p[1005];
int n;
double h,k;
double get(node a,node b)
{
double an1=atan2(a.y,a.x),an2=atan2(b.y,b.x);
if(an1-an2>PI) an2+=2*PI;
if(an2-an1>PI) an1+=2*PI;
return an1-an2;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%lf%lf%d",&k,&h,&n);
for(int i=0;i scanf("%lf%lf",&p[i].x,&p[i].y);
double mi=0,ma=0,sum=0;
p[n]=p[0];
for(int i=0;i {
sum+=get(p[i],p[i+1]);
ma=max(sum,ma);
mi=min(sum,mi);
if(ma-mi>2*PI)
{
ma=mi+2*PI;
break;
}
}
printf("%.2f\n",(ma-mi)*k*h);
}
