Python定时爬取 微博热搜 并动态展示
作者:叶庭云
来源:凹凸数据
本文介绍了可以实现定时执行任务的schedule模块,利用它实现定时爬取微博热搜数据,保存到CSV文件里。 讲解pyehcarts绘制基本时间轮播图,最后利用pyehcarts实现数据的动态图可视化。
schedule模块定时执行任务
# 安装
pip install schedule -i http://pypi.douban.com/simple --trusted-host pypi.douban.com
import schedule
import time
def run():
print("I'm doing something...")
schedule.every(10).minutes.do(run) # 每隔十分钟执行一次任务
schedule.every().hour.do(run) # 每隔一小时执行一次任务
schedule.every().day.at("10:30").do(run) # 每天的10:30执行一次任务
schedule.every().monday.do(run) # 每周一的这个时候执行一次任务
schedule.every().wednesday.at("13:15").do(run) # 每周三13:15执行一次任务
while True:
schedule.run_pending() # run_pending:运行所有可以运行的任务
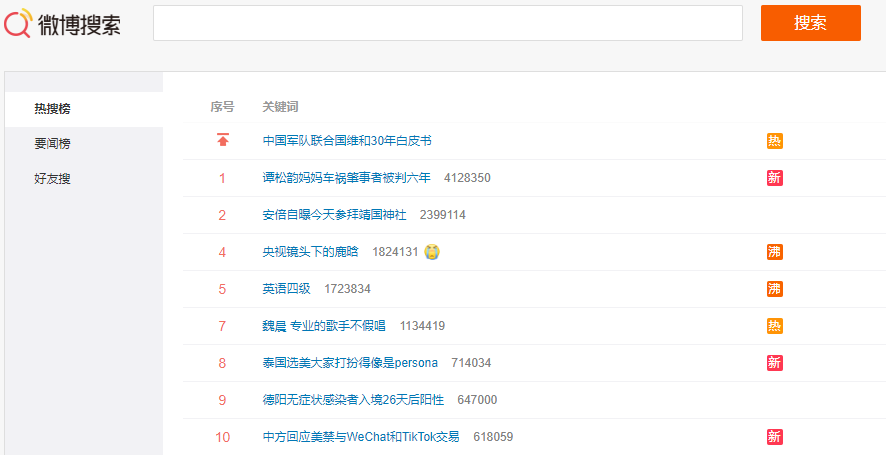
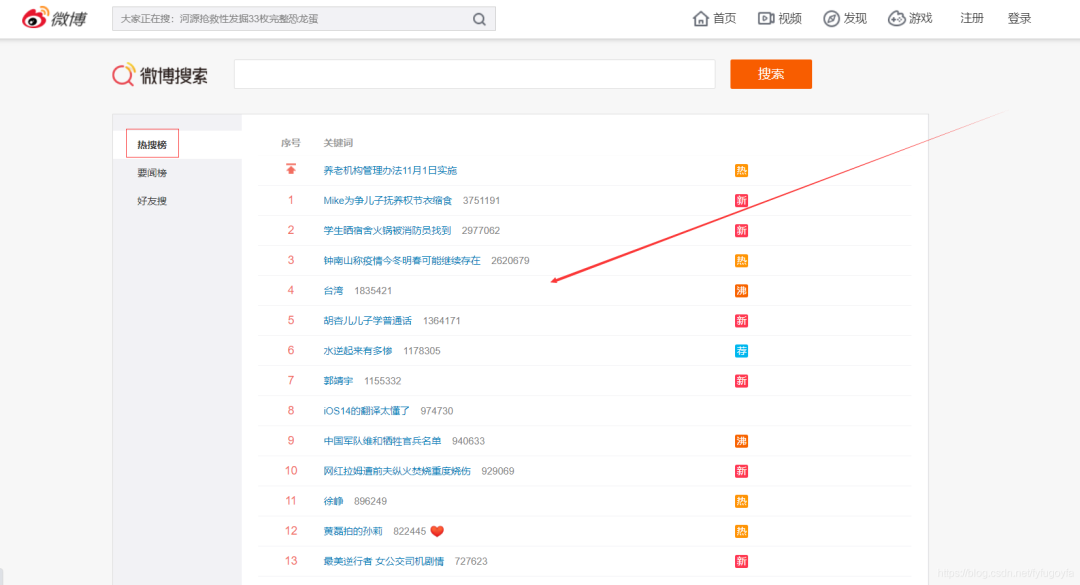
爬取微博热搜数据
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
"""
@File :微博热搜榜.py
@Author :叶庭云
@Date :2020/9/18 15:01
"""
import schedule
import pandas as pd
from datetime import datetime
import logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO, format='%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s: %(message)s')
count = 0
def get_content():
global count # 全局变量count
print('----------- 正在爬取数据 -------------')
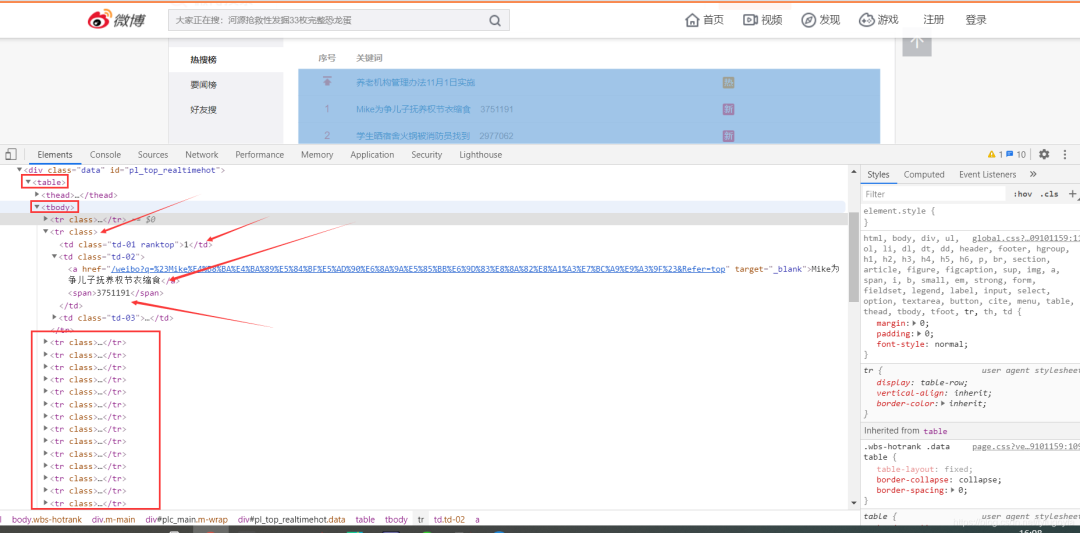
url = 'https://s.weibo.com/top/summary?cate=realtimehot&sudaref=s.weibo.com&display=0&retcode=6102'
df = pd.read_html(url)[0][1:11][['序号', '关键词']] # 获取热搜前10
time_ = datetime.now().strftime("%Y/%m/%d %H:%M") # 获取当前时间
df['序号'] = df['序号'].apply(int)
df['热度'] = df['关键词'].str.split(' ', expand=True)[1]
df['关键词'] = df['关键词'].str.split(' ', expand=True)[0]
df['时间'] = [time_] * len(df['序号'])
if count == 0:
df.to_csv('datas.csv', mode='a+', index=False)
count += 1
else:
df.to_csv('datas.csv', mode='a+', index=False, header=False)
# 定时爬虫
schedule.every(1).minutes.do(get_content)
while True:
schedule.run_pending()
pyehcarts动态图可视化
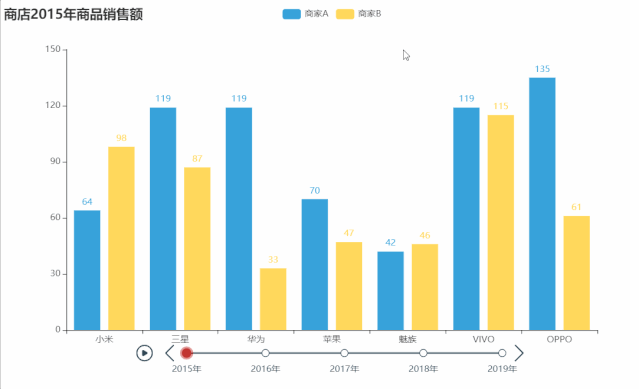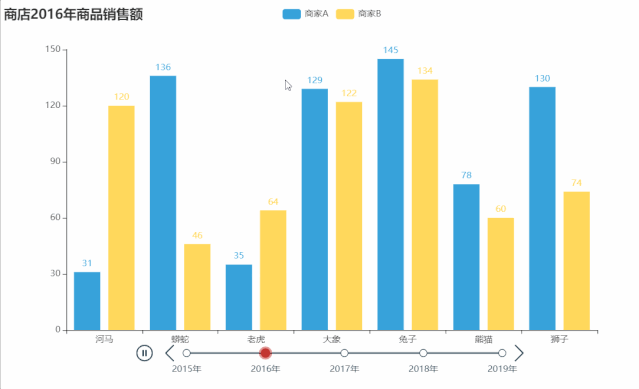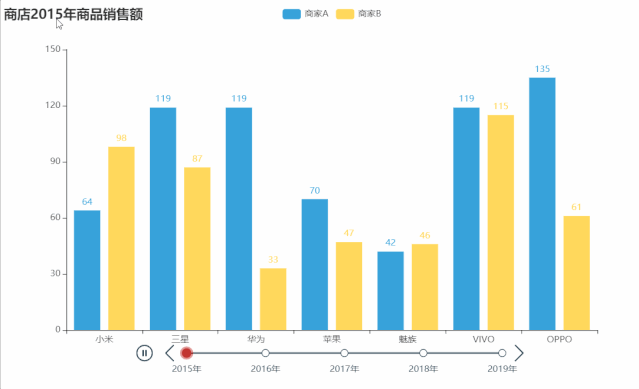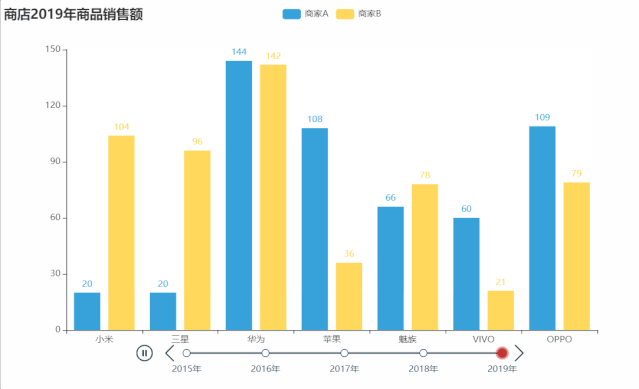
基本时间轮播图
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Bar, Timeline
from pyecharts.faker import Faker
from pyecharts.globals import CurrentConfig, ThemeType
CurrentConfig.ONLINE_HOST = 'D:/python/pyecharts-assets-master/assets/'
tl = Timeline(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(theme=ThemeType.LIGHT))
for i in range(2015, 2020):
bar = (
Bar()
.add_xaxis(Faker.choose())
.add_yaxis("商家A", Faker.values())
.add_yaxis("商家B", Faker.values())
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts("商店{}年商品销售额".format(i)))
)
tl.add(bar, "{}年".format(i))
tl.render("timeline_multi_axis.html")
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Bar, Timeline
from pyecharts.faker import Faker
from pyecharts.globals import ThemeType, CurrentConfig
CurrentConfig.ONLINE_HOST = 'D:/python/pyecharts-assets-master/assets/'
tl = Timeline(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(theme=ThemeType.DARK))
for i in range(2015, 2020):
bar = (
Bar()
.add_xaxis(Faker.choose())
.add_yaxis("商家A", Faker.values(), label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(position="right"))
.add_yaxis("商家B", Faker.values(), label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(position="right"))
.reversal_axis()
.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts("Timeline-Bar-Reversal (时间: {} 年)".format(i))
)
)
tl.add(bar, "{}年".format(i))
tl.render("timeline_bar_reversal.html")
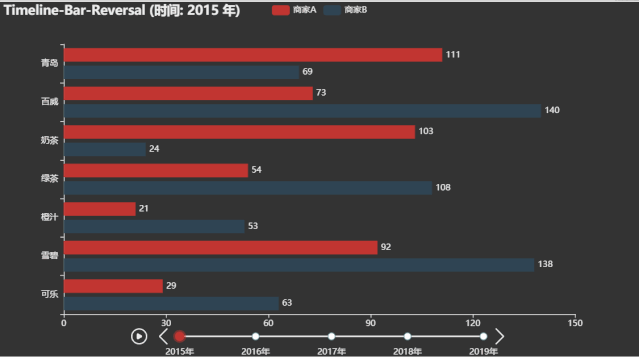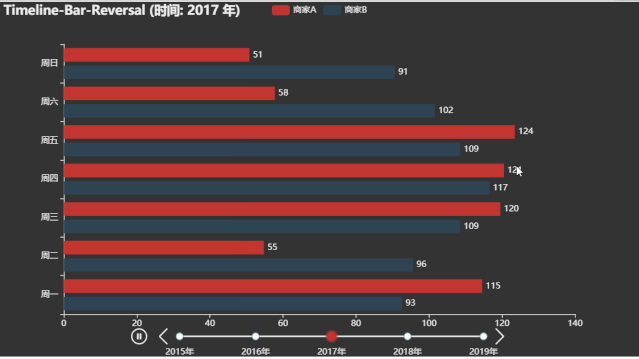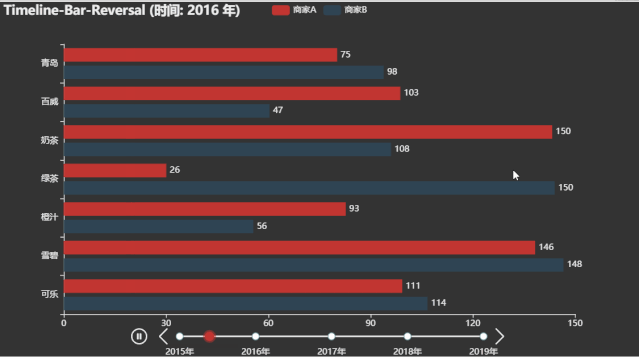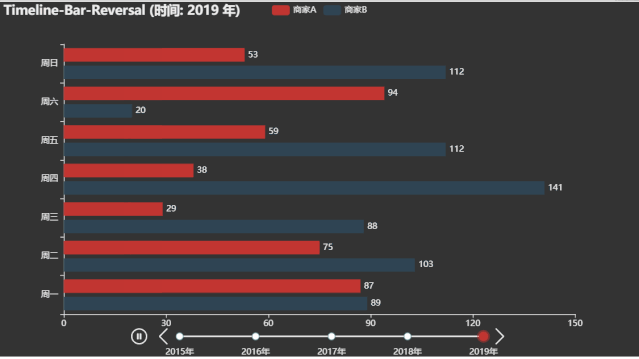
微博热搜动态图
import pandas as pd
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Bar, Timeline, Grid
from pyecharts.globals import ThemeType, CurrentConfig
CurrentConfig.ONLINE_HOST = 'D:/python/pyecharts-assets-master/assets/'
df = pd.read_csv('datas.csv')
# print(df.info())
t = Timeline(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(theme=ThemeType.MACARONS)) # 定制主题
for i in range(34):
bar = (
Bar()
.add_xaxis(list(df['关键词'][i*10: i*10+10][::-1])) # x轴数据
.add_yaxis('热度', list(df['热度'][i*10: i*10+10][::-1])) # y轴数据
.reversal_axis() # 翻转
.set_global_opts( # 全局配置项
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts( # 标题配置项
title=f"{list(df['时间'])[i*10]}",
pos_right="5%", pos_bottom="15%",
title_textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts(
font_family='KaiTi', font_size=24, color='#FF1493'
)
),
xaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts( # x轴配置项
splitline_opts=opts.SplitLineOpts(is_show=True),
),
yaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts( # y轴配置项
splitline_opts=opts.SplitLineOpts(is_show=True),
axislabel_opts=opts.LabelOpts(color='#DC143C')
)
)
.set_series_opts( # 系列配置项
label_opts=opts.LabelOpts( # 标签配置
position="right", color='#9400D3')
)
)
grid = (
Grid()
.add(bar, grid_opts=opts.GridOpts(pos_left="24%"))
)
t.add(grid, "")
t.add_schema(
play_interval=100, # 轮播速度
is_timeline_show=False, # 是否显示 timeline 组件
is_auto_play=True, # 是否自动播放
)
t.render('时间轮播图.html')
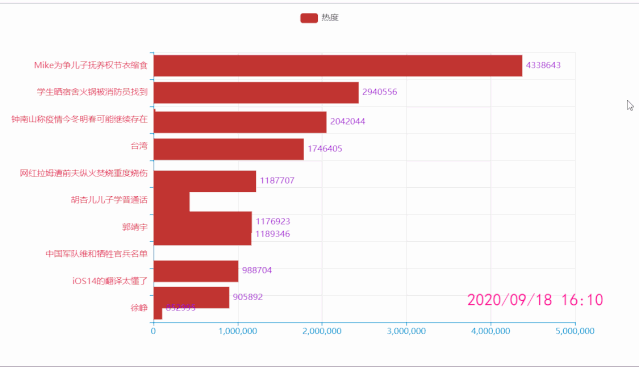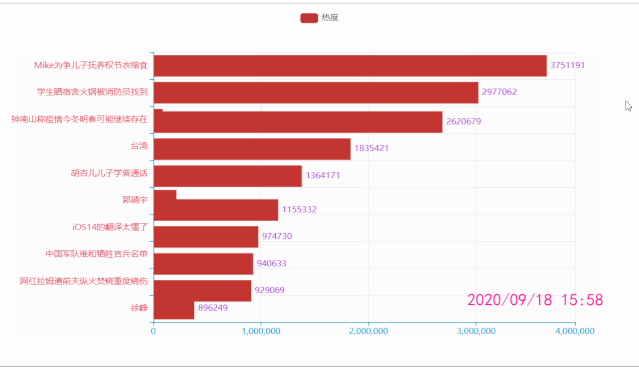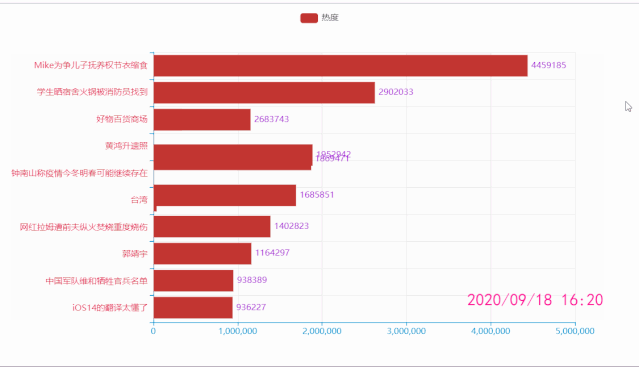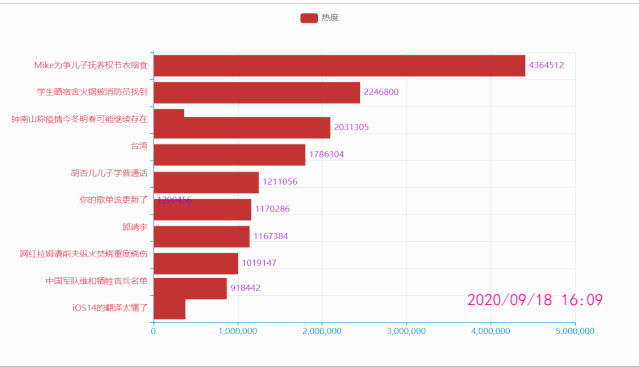
评论
