OpenCV双目标定操作完整版
点击上方“小白学视觉”,选择加"星标"或“置顶”
重磅干货,第一时间送达 
一、首先说明几个情况:
1、完成双目标定必须是自个拿棋盘图摆拍,网上涉及用opencv自带的标定图完成双目标定仅仅是提供个参考流程。我原来还以为用自带的图标定就行,但想不通的是咱们实际摆放的双目摄像头和人家当时摆放的肯定不一样,那用人家的标定图怎么能反应自己摄像头的实际情况;后来问了大神,才知道用opencv自带的标定图(或者说别人提供的图)进行标定,这是完全没有意义的。
2、进行双目标定必须是左右相机同时进行拍摄,再把图保存下来。这点我是看opencv自带的图发现的,左右相机对应的图摆拍的姿势是一模一样的,除了左右相机视角带来的影响。
3、我是先完成单目标定,再完成双目标定。记得把理论看看,要不然有些概念不清楚。
二、
1、先固定好左右相机,拿棋盘标定图摆拍并保存,我左右相机各15张,网上看的说是总共30~40张为宜,这个大家随意。
棋盘标定图在我另发的一个博客里免费下载,当时找了好久,下载的、程序生成的都或多或少有那么一些问题。知识是得有价,但棋盘图这种最最基本的工具,博客里基本都需要拿币下载,真是服。
程序:
// 同时调用两个摄像头,暂停并保存左右相机的标定棋盘图
#include
#include
#include
using namespace cv;
using namespace std; //开头我是从教程学的,一般不变,直接用
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
VideoCapture cap(0);
VideoCapture cap1(1); //打开两个摄像头
if(!cap.isOpened())
{
printf("Could not open camera0...\n");
return -1;
}
if (!cap1.isOpened())
{
printf("Could not open camera1...\n");
return -2;
} //判断还是加上为好,便于调程序
Mat frame, frame1;
bool stop = false;
while (!stop)
{
cap.read(frame);
cap1.read(frame1);
imshow("camera0", frame);
imshow("camera1", frame1);
int delay = 30;
if (delay >= 0 && waitKey(delay) >= 0)
{
waitKey(0); //实时拍摄暂停的程序
}
imwrite("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/11/left1.jpg", frame1);
imwrite("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/11/right1.jpg", frame); //给个位置保存图片,注意图片到底是左相机还是右相机的(用手在摄像头前晃晃),我用的笨方法,保存一下,再把(left1.jpg/right1.jpg)+1,接着保存
}
cap.release();
cap1.release(); //两个摄像头数据释放
return 0;
}
2、完成单目标定,程序我是借鉴网上的,修改的不多。
//左右单目相机分别标定
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include
#include "cv.h"
#include
#include
using namespace std;
using namespace cv; //人家这开头都长,遇到有红线标记的就删了,把你知道的开头加上,没问题
const int boardWidth = 9; //横向的角点数目
const int boardHeight = 6; //纵向的角点数据
const int boardCorner = boardWidth * boardHeight; //总的角点数据
const int frameNumber = 15; //相机标定时需要采用的图像帧数
const int squareSize = 25; //标定板黑白格子的大小 单位mm
const Size boardSize = Size(boardWidth, boardHeight); //总的内角点
Mat intrinsic; //相机内参数
Mat distortion_coeff; //相机畸变参数
vector
vector
vector<vector
vector<vector
vector
/*计算标定板上模块的实际物理坐标*/
void calRealPoint(vector<vector
{
vector
for (int rowIndex = 0; rowIndex < boardheight; rowIndex++)
{
for (int colIndex = 0; colIndex < boardwidth; colIndex++)
{
imgpoint.push_back(Point3f(rowIndex * squaresize, colIndex * squaresize, 0));
}
}
for (int imgIndex = 0; imgIndex < imgNumber; imgIndex++)
{
obj.push_back(imgpoint);
}
}
/*设置相机的初始参数 也可以不估计*/
void guessCameraParam(void)
{
/*分配内存*/
intrinsic.create(3, 3, CV_64FC1); //相机内参数
distortion_coeff.create(5, 1, CV_64FC1); //畸变参数
/*
fx 0 cx
0 fy cy
0 0 1 内参数
*/
intrinsic.at
intrinsic.at
intrinsic.at
intrinsic.at
intrinsic.at
intrinsic.at
intrinsic.at
intrinsic.at
intrinsic.at
/*
k1 k2 p1 p2 p3 畸变参数
*/
distortion_coeff.at
distortion_coeff.at
distortion_coeff.at
distortion_coeff.at
distortion_coeff.at
}
void outputCameraParam(void)
{
/*保存数据*/
//cvSave("cameraMatrix.xml", &intrinsic);
//cvSave("cameraDistoration.xml", &distortion_coeff);
//cvSave("rotatoVector.xml", &rvecs);
//cvSave("translationVector.xml", &tvecs);
/*输出数据*/
//cout << "fx :" << intrinsic.at
//cout << "cx :" << intrinsic.at
printf("fx:%lf...\n", intrinsic.at
printf("fy:%lf...\n", intrinsic.at
printf("cx:%lf...\n", intrinsic.at
printf("cy:%lf...\n", intrinsic.at
//cout << "k1 :" << distortion_coeff.at
//cout << "k2 :" << distortion_coeff.at
//cout << "p1 :" << distortion_coeff.at
//cout << "p2 :" << distortion_coeff.at
//cout << "p3 :" << distortion_coeff.at
printf("k1:%lf...\n", distortion_coeff.at
printf("k2:%lf...\n", distortion_coeff.at
printf("p1:%lf...\n", distortion_coeff.at
printf("p2:%lf...\n", distortion_coeff.at
printf("p3:%lf...\n", distortion_coeff.at
}
int main()
{
int imageHeight; //图像高度
int imageWidth; //图像宽度
int goodFrameCount = 0; //有效图像的数目
Mat rgbImage,grayImage;
Mat tImage = imread("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/11/right1.jpg");
if (tImage.empty())
{
printf("Could not load tImage...\n");
return -1;
}
imageHeight = tImage.rows;
imageWidth = tImage.cols;
grayImage = Mat::ones(tImage.size(), CV_8UC1);
while (goodFrameCount < frameNumber)
{
char filename[100];
sprintf_s(filename, "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/11/right%d.jpg", goodFrameCount + 1);
rgbImage = imread(filename);
if (rgbImage.empty())
{
printf("Could not load grayImage...\n");
return -2;
}
cvtColor(rgbImage, grayImage, CV_BGR2GRAY);
imshow("Camera", grayImage);
bool isFind = findChessboardCorners(rgbImage, boardSize, corner, CALIB_CB_ADAPTIVE_THRESH + CALIB_CB_NORMALIZE_IMAGE);
//bool isFind = findChessboardCorners( rgbImage, boardSize, corner,
//CV_CALIB_CB_ADAPTIVE_THRESH | CV_CALIB_CB_FAST_CHECK | CV_CALIB_CB_NORMALIZE_IMAGE);
if (isFind == true) //所有角点都被找到 说明这幅图像是可行的
{
//精确角点位置,亚像素角点检测
cornerSubPix(grayImage, corner, Size(5, 5), Size(-1, -1), TermCriteria(CV_TERMCRIT_EPS | CV_TERMCRIT_ITER, 20, 0.1));
//绘制角点
drawChessboardCorners(rgbImage, boardSize, corner, isFind);
imshow("chessboard", rgbImage);
corners.push_back(corner);
goodFrameCount++;
/*cout << "The image" << goodFrameCount << " is good" << endl;*/
printf("The image %d is good...\n", goodFrameCount);
}
else
{
printf("The image is bad please try again...\n");
}
if (waitKey(10) == 'q')
{
break;
}
}
/*
图像采集完毕 接下来开始摄像头的校正
calibrateCamera()
输入参数 objectPoints 角点的实际物理坐标
imagePoints 角点的图像坐标
imageSize 图像的大小
输出参数
cameraMatrix 相机的内参矩阵
distCoeffs 相机的畸变参数
rvecs 旋转矢量(外参数)
tvecs 平移矢量(外参数)
*/
/*设置实际初始参数 根据calibrateCamera来 如果flag = 0 也可以不进行设置*/
guessCameraParam();
printf("guess successful...\n");
/*计算实际的校正点的三维坐标*/
calRealPoint(objRealPoint, boardWidth, boardHeight, frameNumber, squareSize);
printf("calculate real successful...\n");
/*标定摄像头*/
calibrateCamera(objRealPoint, corners, Size(imageWidth, imageHeight), intrinsic, distortion_coeff, rvecs, tvecs, 0);
printf("calibration successful...\n");
/*保存并输出参数*/
outputCameraParam();
printf("output successful...\n");
/*显示畸变校正效果*/
Mat cImage;
undistort(rgbImage, cImage, intrinsic, distortion_coeff); //矫正相机镜头变形
imshow("Corret Image", cImage);
printf("Corret Image....\n");
printf("Wait for Key....\n");
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
注意:(1)把你得到的左右相机标定完的参数记下来,双目标定的时候会用;
(2)如果遇到cvtColor出问题,那就查一下构造一个新图像的Mat类使用方法;
(3)如果遇到结果一闪而过的问题,可以先用网上提供的两种方法试一下(一搜就有),但是我用这两种方法都没解决,最后才知道是frameNumber 的问题,我设的值比现有的图多一张。到时候具体问题具体分析吧,都是应该经历的过程。
3、完成双目标定,程序也是借鉴网上的,稍加修改。
// 双目相机标定
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "cv.h"
#include
using namespace std;
using namespace cv; //依旧很长的开头
const int imageWidth = 640; //摄像头的分辨率
const int imageHeight = 480;
const int boardWidth = 9; //横向的角点数目
const int boardHeight = 6; //纵向的角点数据
const int boardCorner = boardWidth * boardHeight; //总的角点数据
const int frameNumber = 15; //相机标定时需要采用的图像帧数
const int squareSize = 25; //标定板黑白格子的大小 单位mm
const Size boardSize = Size(boardWidth, boardHeight); //标定板的总内角点
Size imageSize = Size(imageWidth, imageHeight);
Mat R, T, E, F; //R 旋转矢量 T平移矢量 E本征矩阵 F基础矩阵
vector
vector
vector<vector
vector<vector
vector<vector
vector
vector
Mat rgbImageL, grayImageL;
Mat rgbImageR, grayImageR;
Mat Rl, Rr, Pl, Pr, Q; //校正旋转矩阵R,投影矩阵P 重投影矩阵Q (下面有具体的含义解释)
Mat mapLx, mapLy, mapRx, mapRy; //映射表
Rect validROIL, validROIR; //图像校正之后,会对图像进行裁剪,这里的validROI就是指裁剪之后的区域
/*
事先标定好的左相机的内参矩阵
fx 0 cx
0 fy cy
0 0 1
*/
Mat cameraMatrixL = (Mat_
0, 460.220741, 208.225803,
0, 0, 1); //这时候就需要你把左右相机单目标定的参数给写上
//获得的畸变参数
Mat distCoeffL = (Mat_
/*
事先标定好的右相机的内参矩阵
fx 0 cx
0 fy cy
0 0 1
*/
Mat cameraMatrixR = (Mat_
0, 462.203276, 256.100655,
0, 0, 1);
Mat distCoeffR = (Mat_
/*计算标定板上模块的实际物理坐标*/
void calRealPoint(vector<vector
{
vector
for (int rowIndex = 0; rowIndex < boardheight; rowIndex++)
{
for (int colIndex = 0; colIndex < boardwidth; colIndex++)
{
imgpoint.push_back(Point3f(rowIndex * squaresize, colIndex * squaresize, 0));
}
}
for (int imgIndex = 0; imgIndex < imgNumber; imgIndex++)
{
obj.push_back(imgpoint);
}
}
void outputCameraParam(void)
{
/*保存数据*/
/*输出数据*/
FileStorage fs("intrinsics.yml", FileStorage::WRITE); //文件存储器的初始化
if (fs.isOpened())
{
fs << "cameraMatrixL" << cameraMatrixL << "cameraDistcoeffL" << distCoeffL << "cameraMatrixR" << cameraMatrixR << "cameraDistcoeffR" << distCoeffR;
fs.release();
cout << "cameraMatrixL=:" << cameraMatrixL << endl << "cameraDistcoeffL=:" << distCoeffL << endl << "cameraMatrixR=:" << cameraMatrixR << endl << "cameraDistcoeffR=:" << distCoeffR << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Error: can not save the intrinsics!!!!!" << endl;
}
fs.open("extrinsics.yml", FileStorage::WRITE);
if (fs.isOpened())
{
fs << "R" << R << "T" << T << "Rl" << Rl << "Rr" << Rr << "Pl" << Pl << "Pr" << Pr << "Q" << Q;
cout << "R=" << R << endl << "T=" << T << endl << "Rl=" << Rl << endl << "Rr=" << Rr << endl << "Pl=" << Pl << endl << "Pr=" << Pr << endl << "Q=" << Q << endl;
fs.release();
}
else
cout << "Error: can not save the extrinsic parameters\n";
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
Mat img;
int goodFrameCount = 0;
while (goodFrameCount < frameNumber)
{
char filename[100];
/*读取左边的图像*/
sprintf_s(filename, "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/11/left%d.jpg", goodFrameCount + 1);
rgbImageL = imread(filename, CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR);
cvtColor(rgbImageL, grayImageL, CV_BGR2GRAY);
/*读取右边的图像*/
sprintf_s(filename, "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/11/right%d.jpg", goodFrameCount + 1);
rgbImageR = imread(filename, CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR);
cvtColor(rgbImageR, grayImageR, CV_BGR2GRAY);
bool isFindL, isFindR;
isFindL = findChessboardCorners(rgbImageL, boardSize, cornerL);
isFindR = findChessboardCorners(rgbImageR, boardSize, cornerR);
if (isFindL == true && isFindR == true) //如果两幅图像都找到了所有的角点 则说明这两幅图像是可行的
{
/*
Size(5,5) 搜索窗口的一半大小
Size(-1,-1) 死区的一半尺寸
TermCriteria(CV_TERMCRIT_EPS | CV_TERMCRIT_ITER, 20, 0.1)迭代终止条件
*/
cornerSubPix(grayImageL, cornerL, Size(5, 5), Size(-1, -1), TermCriteria(CV_TERMCRIT_EPS | CV_TERMCRIT_ITER, 20, 0.1));
drawChessboardCorners(rgbImageL, boardSize, cornerL, isFindL);
imshow("chessboardL", rgbImageL);
imagePointL.push_back(cornerL);
cornerSubPix(grayImageR, cornerR, Size(5, 5), Size(-1, -1), TermCriteria(CV_TERMCRIT_EPS | CV_TERMCRIT_ITER, 20, 0.1));
drawChessboardCorners(rgbImageR, boardSize, cornerR, isFindR);
imshow("chessboardR", rgbImageR);
imagePointR.push_back(cornerR);
//string filename = "res\\image\\calibration";
//filename += goodFrameCount + ".jpg";
//cvSaveImage(filename.c_str(), &IplImage(rgbImage)); //把合格的图片保存起来
goodFrameCount++;
cout << "The image" << goodFrameCount << " is good" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "The image is bad please try again" << endl;
}
if (waitKey(10) == 'q')
{
break;
}
}
/*
计算实际的校正点的三维坐标
根据实际标定格子的大小来设置
*/
calRealPoint(objRealPoint, boardWidth, boardHeight, frameNumber, squareSize);
cout << "cal real successful" << endl;
/*
标定摄像头
由于左右摄像机分别都经过了单目标定
所以在此处选择flag = CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS
*/
double rms = stereoCalibrate(objRealPoint, imagePointL, imagePointR,
cameraMatrixL, distCoeffL,
cameraMatrixR, distCoeffR,
Size(imageWidth, imageHeight),R, T,E, F, CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS,
TermCriteria(TermCriteria::COUNT + TermCriteria::EPS, 100, 1e-5)); //需要注意,应该是版本的原因,该函数最后两个参数,我是调换过来后才显示不出错的
cout << "Stereo Calibration done with RMS error = " << rms << endl;
/*
立体校正的时候需要两幅图像共面并且行对准 以使得立体匹配更加的可靠
使得两幅图像共面的方法就是把两个摄像头的图像投影到一个公共成像面上,这样每幅图像从本图像平面投影到公共图像平面都需要一个旋转矩阵R
stereoRectify 这个函数计算的就是从图像平面投影到公共成像平面的旋转矩阵Rl,Rr。Rl,Rr即为左右相机平面行对准的校正旋转矩阵。
左相机经过Rl旋转,右相机经过Rr旋转之后,两幅图像就已经共面并且行对准了。
其中Pl,Pr为两个相机的投影矩阵,其作用是将3D点的坐标转换到图像的2D点的坐标:P*[X Y Z 1]' =[x y w]
Q矩阵为重投影矩阵,即矩阵Q可以把2维平面(图像平面)上的点投影到3维空间的点:Q*[x y d 1] = [X Y Z W]。其中d为左右两幅图像的时差
*/
//对标定过的图像进行校正
stereoRectify(cameraMatrixL, distCoeffL, cameraMatrixR, distCoeffR, imageSize, R, T, Rl, Rr, Pl, Pr, Q,
CALIB_ZERO_DISPARITY, -1, imageSize, &validROIL, &validROIR);
/*
根据stereoRectify 计算出来的R 和 P 来计算图像的映射表 mapx,mapy
mapx,mapy这两个映射表接下来可以给remap()函数调用,来校正图像,使得两幅图像共面并且行对准
ininUndistortRectifyMap()的参数newCameraMatrix就是校正后的摄像机矩阵。在openCV里面,校正后的计算机矩阵Mrect是跟投影矩阵P一起返回的。
所以我们在这里传入投影矩阵P,此函数可以从投影矩阵P中读出校正后的摄像机矩阵
*/
//摄像机校正映射
initUndistortRectifyMap(cameraMatrixL, distCoeffL, Rl, Pr, imageSize, CV_32FC1, mapLx, mapLy);
initUndistortRectifyMap(cameraMatrixR, distCoeffR, Rr, Pr, imageSize, CV_32FC1, mapRx, mapRy);
Mat rectifyImageL, rectifyImageR;
cvtColor(grayImageL, rectifyImageL, CV_GRAY2BGR);
cvtColor(grayImageR, rectifyImageR, CV_GRAY2BGR);
imshow("Rectify Before", rectifyImageL);
cout << "按Q1退出 ..." << endl;
/*
经过remap之后,左右相机的图像已经共面并且行对准了
*/
Mat rectifyImageL2, rectifyImageR2;
remap(rectifyImageL, rectifyImageL2, mapLx, mapLy, INTER_LINEAR);
remap(rectifyImageR, rectifyImageR2, mapRx, mapRy, INTER_LINEAR);
cout << "按Q2退出 ..." << endl;
imshow("rectifyImageL", rectifyImageL2);
imshow("rectifyImageR", rectifyImageR2);
/*保存并输出数据*/
outputCameraParam();
/*
把校正结果显示出来
把左右两幅图像显示到同一个画面上
这里只显示了最后一副图像的校正结果。并没有把所有的图像都显示出来
*/
Mat canvas;
double sf;
int w, h;
sf = 600. / MAX(imageSize.width, imageSize.height);
w = cvRound(imageSize.width * sf);
h = cvRound(imageSize.height * sf);
canvas.create(h, w * 2, CV_8UC3);
/*左图像画到画布上*/
Mat canvasPart = canvas(Rect(w * 0, 0, w, h)); //得到画布的一部分
resize(rectifyImageL2, canvasPart, canvasPart.size(), 0, 0, INTER_AREA); //把图像缩放到跟canvasPart一样大小
Rect vroiL(cvRound(validROIL.x*sf), cvRound(validROIL.y*sf), //获得被截取的区域
cvRound(validROIL.width*sf), cvRound(validROIL.height*sf));
rectangle(canvasPart, vroiL, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 3, 8); //画上一个矩形
cout << "Painted ImageL" << endl;
/*右图像画到画布上*/
canvasPart = canvas(Rect(w, 0, w, h)); //获得画布的另一部分
resize(rectifyImageR2, canvasPart, canvasPart.size(), 0, 0, INTER_LINEAR);
Rect vroiR(cvRound(validROIR.x * sf), cvRound(validROIR.y*sf),
cvRound(validROIR.width * sf), cvRound(validROIR.height * sf));
rectangle(canvasPart, vroiR, Scalar(0, 255, 0), 3, 8);
cout << "Painted ImageR" << endl;
/*画上对应的线条*/
for (int i = 0; i < canvas.rows; i += 16)
line(canvas, Point(0, i), Point(canvas.cols, i), Scalar(0, 255, 0), 1, 8);
imshow("rectified", canvas);
cout << "wait key" << endl;
waitKey(0);
//system("pause");
return 0;
}
附上最后效果图:
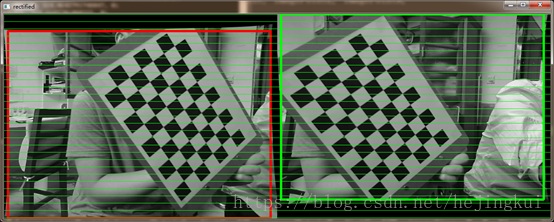
本文作者为CSDN博主「hejingkui」
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/hejingkui/java/article/details/80488763
下载1:OpenCV-Contrib扩展模块中文版教程
在「小白学视觉」公众号后台回复:扩展模块中文教程,即可下载全网第一份OpenCV扩展模块教程中文版,涵盖扩展模块安装、SFM算法、立体视觉、目标跟踪、生物视觉、超分辨率处理等二十多章内容。
下载2:Python视觉实战项目52讲 在「小白学视觉」公众号后台回复:Python视觉实战项目,即可下载包括图像分割、口罩检测、车道线检测、车辆计数、添加眼线、车牌识别、字符识别、情绪检测、文本内容提取、面部识别等31个视觉实战项目,助力快速学校计算机视觉。
下载3:OpenCV实战项目20讲 在「小白学视觉」公众号后台回复:OpenCV实战项目20讲,即可下载含有20个基于OpenCV实现20个实战项目,实现OpenCV学习进阶。
交流群
欢迎加入公众号读者群一起和同行交流,目前有SLAM、三维视觉、传感器、自动驾驶、计算摄影、检测、分割、识别、医学影像、GAN、算法竞赛等微信群(以后会逐渐细分),请扫描下面微信号加群,备注:”昵称+学校/公司+研究方向“,例如:”张三 + 上海交大 + 视觉SLAM“。请按照格式备注,否则不予通过。添加成功后会根据研究方向邀请进入相关微信群。请勿在群内发送广告,否则会请出群,谢谢理解~
