javascript算法学习打卡(第一周)

之前因为工作原因接触了很多有意思的算法知识,为了巩固大家的算法基础和编程能力,笔者将开展为期2个月的算法学习打卡, 每周3-5次算法训练, 并附有算法题的答案, 供大家学习参考. 接下来我们复盘第一周的算法打卡内容.
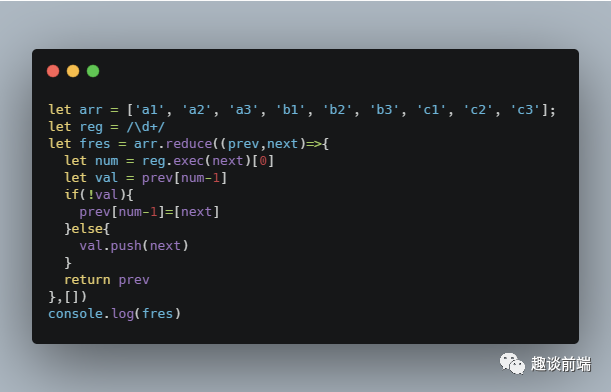
1.有一个数组arr = [a1, a2, a3, b1, b2, b3, c1, c2, c3...], 通过算法将数组进行拆分, 转化为如下格式的数组a1, b1, c1], [a2, b2, c2], [a3, b3, c3]并实现通用公式
/**
* arr 待排序数组
* result 计算的结果数组
*/
function rangeArr(arr = [], result = []) {
arr.forEach(item => {
let i = /\d*$/.exec(item)[0]
result[i] ? result[i].push(item) : (result[i] = [item])
})
return result.filter(Boolean)
}
网友优质答案:
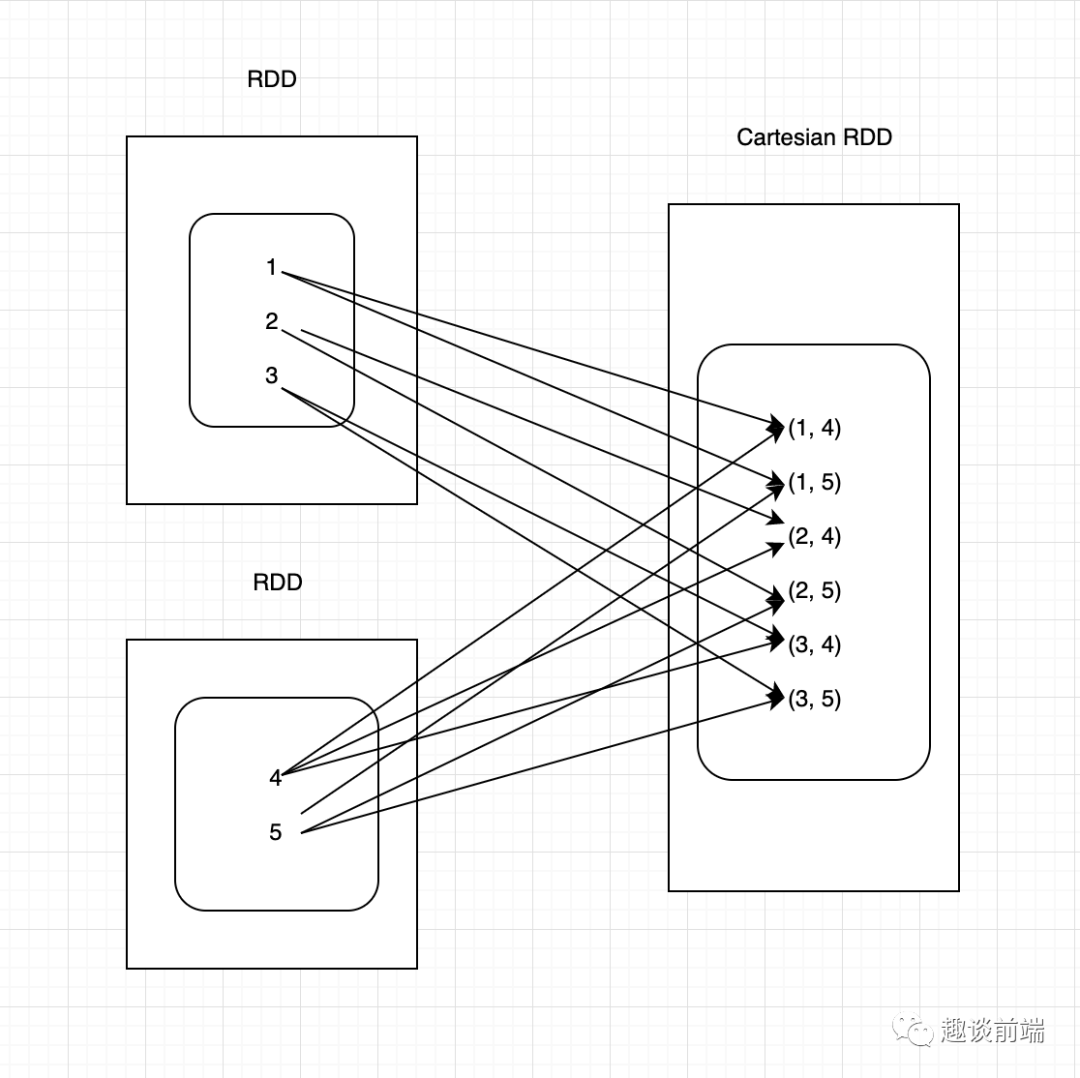
2.假设集合A={a, b},集合B={0, 1, 2},则两个集合的笛卡尔积为{(a, 0), (a, 1), (a, 2), (b, 0), (b, 1), (b, 2)}。求当A={a, b, ..., n}, B={0, 1, 2, ..., n}时的笛卡尔积.
笛卡尔乘积是指在数学中,两个集合X和Y的笛卡尓积,又称直积,表示为X × Y,第一个对象是X的成员而第二个对象是Y的所有可能有序对的其中一个成员 。
/*
* @Author: Mr Jiang.Xu
* @Date: 2019-08-31 00:05:33
* @Last Modified by: Mr Jiang.Xu
* @Last Modified time: 2019-08-31 00:05:33
*/
function cartesian(arr) {
if (arr.length < 2) return arr[0] || [];
return [].reduce.call(arr, function (col, set) {
let res = [];
col.forEach(c => {
set.forEach(s => {
let t = [].concat(Array.isArray(c) ? c : [c]);
t.push(s);
res.push(t);
})
});
return res;
});
}
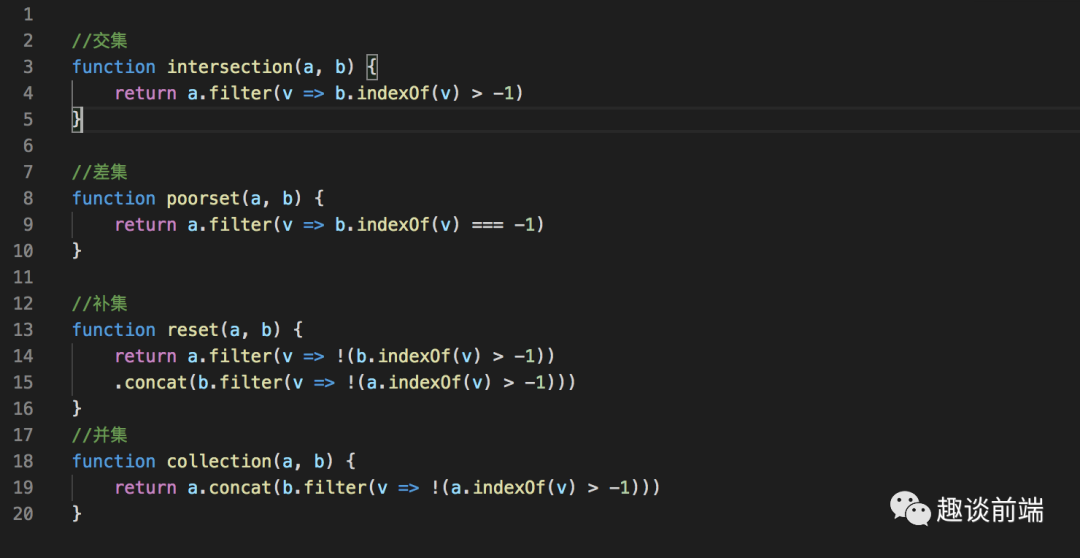
3.原生js实现一个Set数据类型, 并实现集合的差集, 并集, 补集, 交集
// 创建集合,并实现交集,差集,补集,并集function MySet() {let items = {}// 判断值是否存在this.has = function(val) {return val in items}// 添加this.add = function(val) {if(!this.has(val)) {items[val] = valreturn true}return false}// 移除this.remove = function(val) {if(this.has(val)) {delete items[val]return true}return false}// 清空this.clear = function() {items = {}}// 大小this.size = function() {return Object.keys(items).length}// 取值this.values = function() {return Object.keys(items)}// 并集this.union = function(otherSet) {let unionSet = new Set()let values = this.values()for(let i=0; i < values.length; i++) {unionSet.add(values[i])}values = otherSet.values()for(let i=0; i < values.length; i++) {unionSet.add(values[i])}return unionSet}// 交集this.intersection = function(otherSet) {let intersectionSet = new Set()let values = this.values()for(let i=0; i<values.length; i++) {if(otherSet.has(values[i])) {intersectionSet.add(values[i])}}return intersectionSet}// 差集this.difference = function(otherSet) {let differenceSet = new Set()let values = this.values()for(let i = 0; i < values.length; i++) {if(!otherSet.has(values[i])) {differenceSet.add(values[i])}}return differenceSet}// 子集this.subset = function(otherSet) {if(this.size() > otherSet.size()) {return false}else {let values = this.values()for(let i=0; i<values.length; i++) {if(!otherSet.has(values[i])) {return false}}return true}}}
评论
