剖析Netty之底层原理(三)
神秘北极圈 阿拉斯加的山巅
谁的脸出现海角的天边
忽然的瞬间在那遥远的地点
我看见恋人幸福的光点
灵魂在招唤唱着古老
陌生熟悉的歌谣 天空 在微笑
我的世界缤纷闪耀
前面浑浑噩噩的把服务端的实现底层源码来了个大致,感觉头有点大,这里用图例的方式来理下思绪。
一、EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
这是服务端的第一句代码,类似的还new了一个workGroup,工作线程组
这两句代码,Netty底层的各种初始化动作,前面也都说过了,这里做个总结:
底层逐步初始化调用程序如下图:
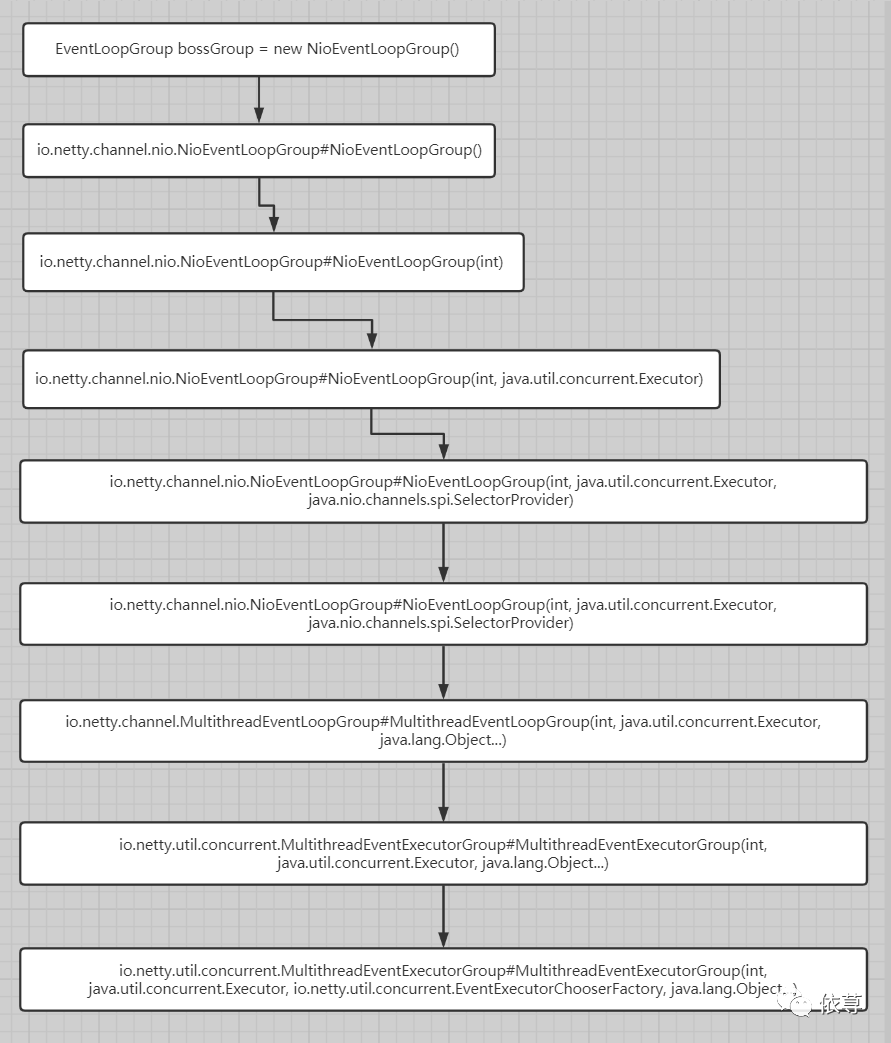
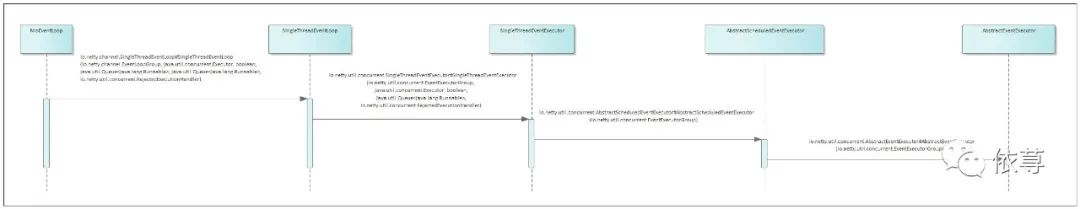
其类调用时序图如下所示
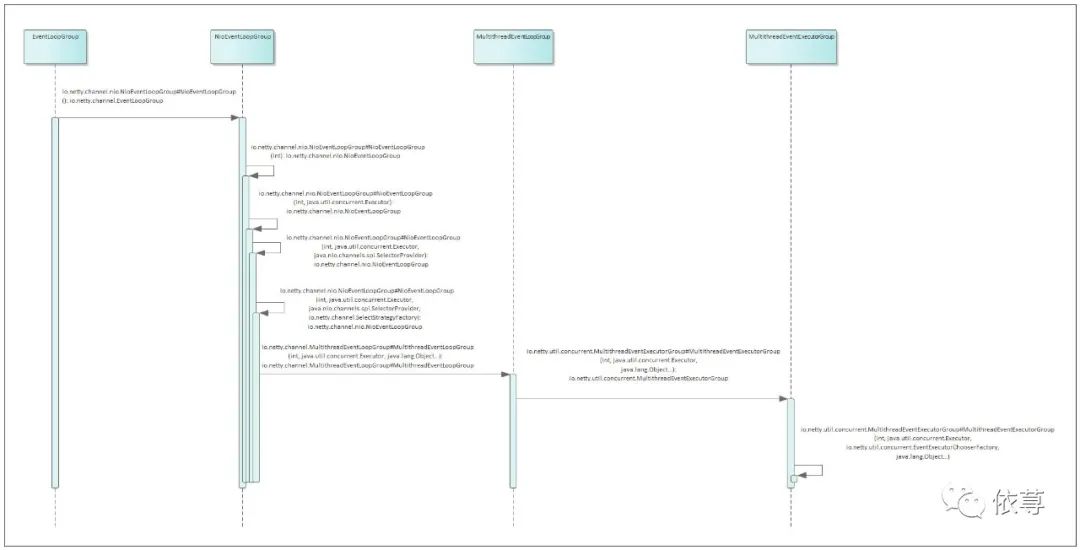
这里,需要重点看下
io.netty.util.concurrent.MultithreadEventExecutorGroup#MultithreadEventExecutorGroup
(int,
java.util.concurrent.Executor,
io.netty.util.concurrent.EventExecutorChooserFactory, java.lang.Object...
)方法
源码如下:
protected MultithreadEventExecutorGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor,EventExecutorChooserFactory chooserFactory, Object... args) {//当线程数没有的时候,抛出异常,根据前面分析,这里的线程数为服务器内核数量*2if (nThreads <= 0) {throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("nThreads: %d (expected: > 0)", nThreads));}//这里的Executor是null,所以初始化一个if (executor == null) {//初始化一个类型是io.netty.util.concurrent.ThreadPerTaskExecutor的线程池//线程池类型为io.netty.util.concurrent.DefaultThreadFactoryexecutor = new ThreadPerTaskExecutor(newDefaultThreadFactory());}// 设置事件驱动数组,大小根据设定或者默认的来children = new EventExecutor[nThreads];for (int i = 0; i < nThreads; i ++) {boolean success = false;try {//设定每个事件驱动数组为io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop//这里调用的newChild,下面会有详细解释children[i] = newChild(executor, args);success = true;} catch (Exception e) {// TODO: Think about if this is a good exception typethrow new IllegalStateException("failed to create a child event loop", e);} finally {if (!success) {for (int j = 0; j < i; j ++) {//如果添加失败,则关闭每一个io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopchildren[j].shutdownGracefully();}for (int j = 0; j < i; j ++) {EventExecutor e = children[j];try {while (!e.isTerminated()) {e.awaitTermination(Integer.MAX_VALUE, TimeUnit.SECONDS);}} catch (InterruptedException interrupted) {// Let the caller handle the interruption.Thread.currentThread().interrupt();break;}}}}}//初始化io.netty.util.concurrent.EventExecutorChooserFactory.EventExecutorChooser//其结果值为io.netty.util.concurrent.DefaultEventExecutorChooserFactory.PowerOfTwoEventExecutorChooser#PowerOfTwoEventExecutorChooser//或者io.netty.util.concurrent.DefaultEventExecutorChooserFactory.GenericEventExecutorChooser#GenericEventExecutorChooserchooser = chooserFactory.newChooser(children);final FutureListenerpublic void operationComplete(Futurefuture) throws Exception {if (terminatedChildren.incrementAndGet() == children.length) {terminationFuture.setSuccess(null);}}};for (EventExecutor e: children) {// 循环为每一个事件驱动器实例添加监听//这里的e.terminationFuture()实质调用//io.netty.util.concurrent.SingleThreadEventExecutor#terminationFuture//因为前面我们说到每一个children数组的实例是io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop//这里io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop继承自//io.netty.util.concurrent.SingleThreadEventExecutor#terminationFuturee.terminationFuture().addListener(terminationListener);}//这里将children复制出来一份给到readonlyChildren//Collections.unmodifiableSet返回的Set集合不可修改,即readonlySetchildrenSet = new LinkedHashSet (children.length); Collections.addAll(childrenSet, children);readonlyChildren = Collections.unmodifiableSet(childrenSet);}
如上所示为netty-all-4.1.50.final源码,其大致意义,在上面代码中也有添加注释,总结一下就是这里设定了事件驱动数组,并设定事件轮询线程组
上面的给每一个EventExecutor数组赋值的代码
这里可以发现
io.netty.util.concurrent.MultithreadEventExecutorGroup
类中,该方法是静态方法
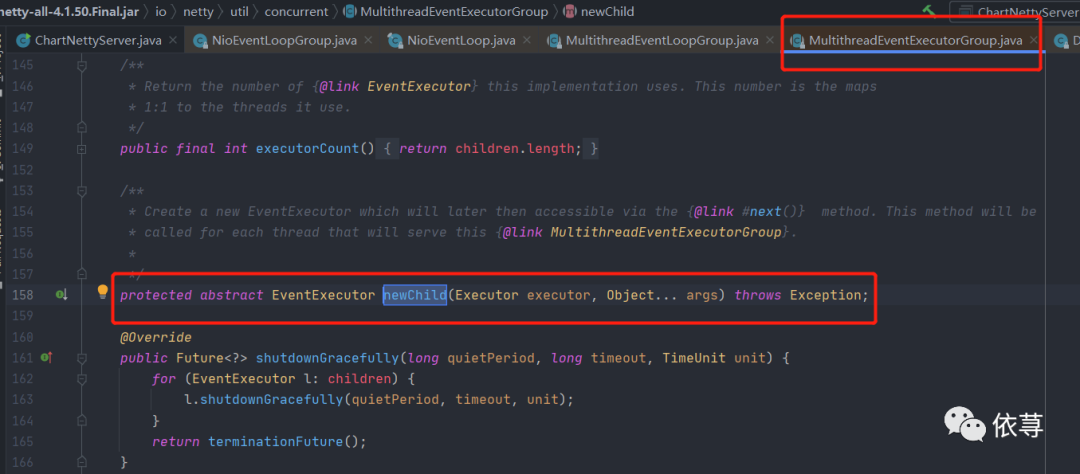
方法是由子类
io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup
调用而来,所以这里实质调用的是
io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup#newChild
源码如下:
protected EventLoop newChild(Executor executor, Object... args) throws Exception {EventLoopTaskQueueFactory queueFactory = args.length == 4 ? (EventLoopTaskQueueFactory) args[3] : null;return new NioEventLoop(this, executor, (SelectorProvider) args[0],((SelectStrategyFactory) args[1]).newSelectStrategy(), (RejectedExecutionHandler) args[2], queueFactory);}
这里的args数组,在根据以上配置的情况下,是3,第一个是选择器:
args[0] = SelectorProvider.provider()
即:
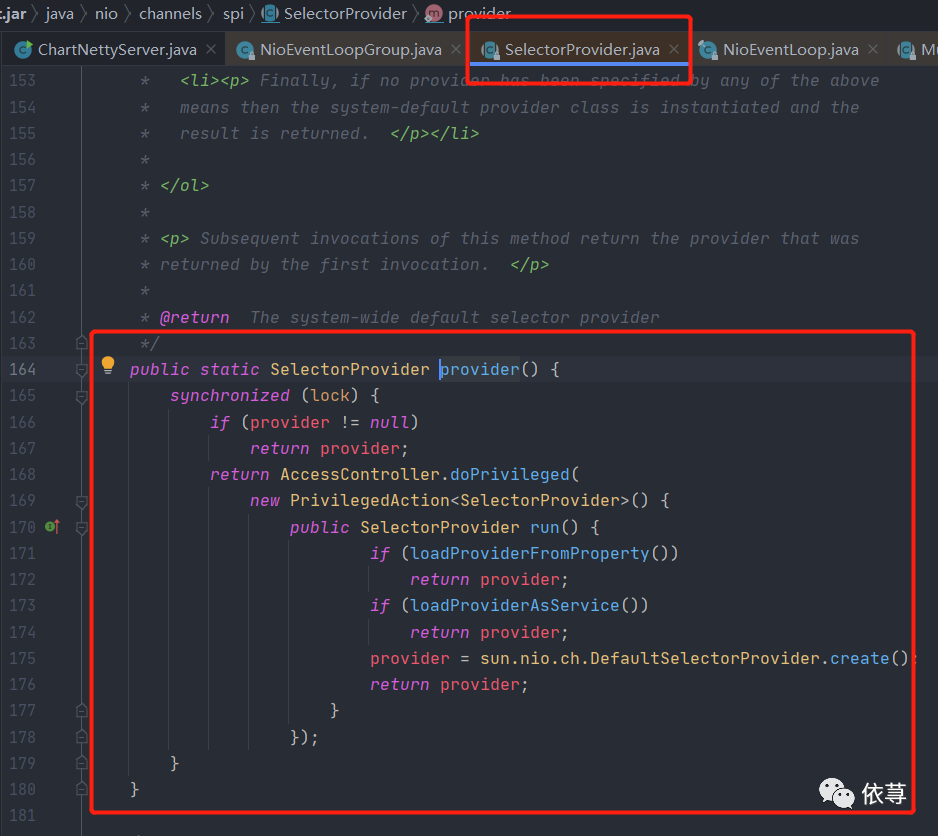
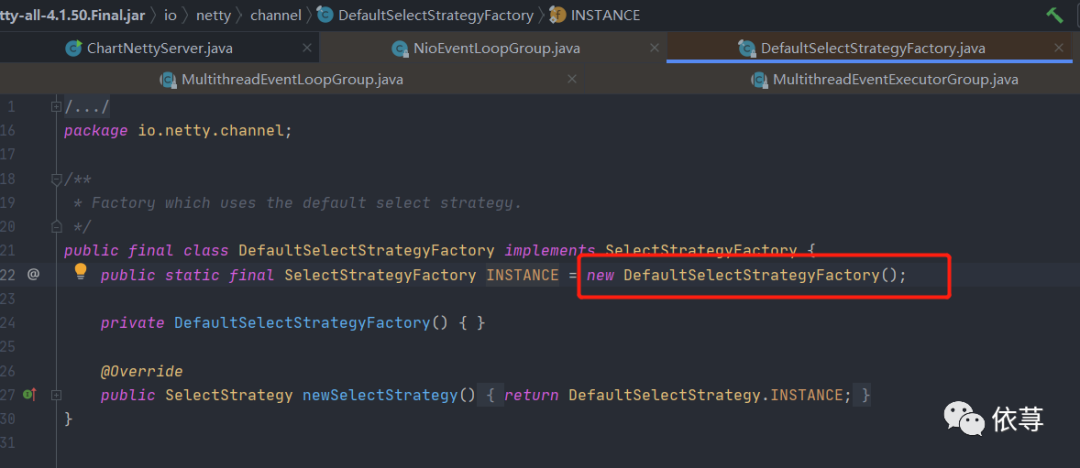
数组第二个元素是默认选择器策略
args[1] = DefaultSelectStrategyFactory.INSTANCE;
即:
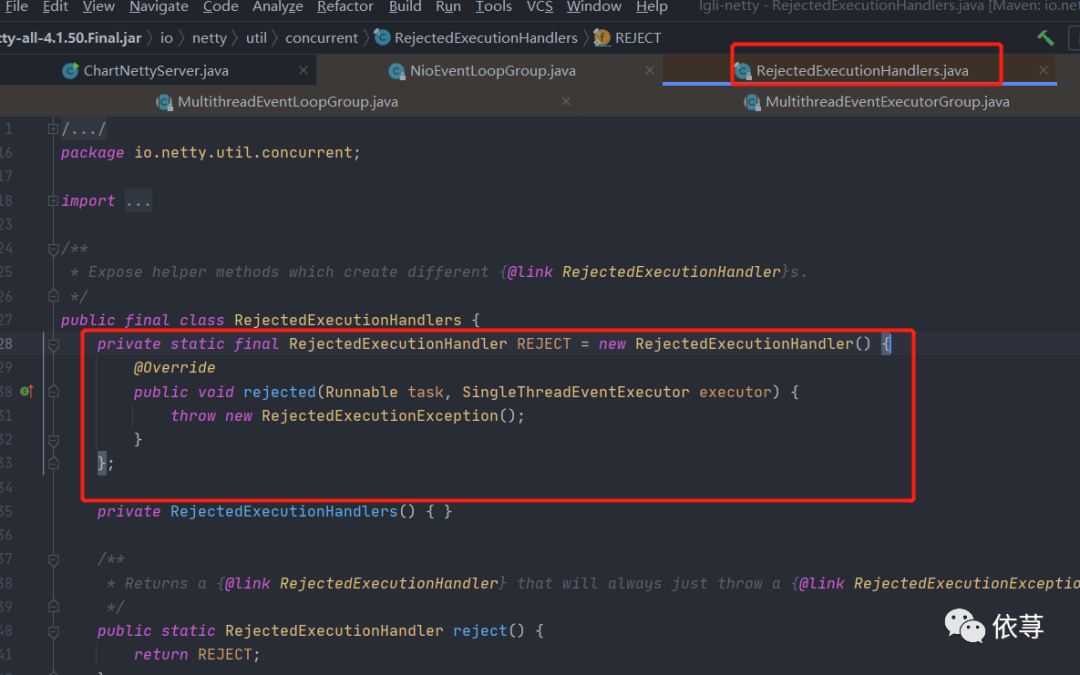
第三个是默认异常
args[2] = RejectedExecutionHandlers.reject();
下面主要看下
io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup#newChild
方法
该方法上面源代码已说明,返回了一个
io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop#NioEventLoop
对象
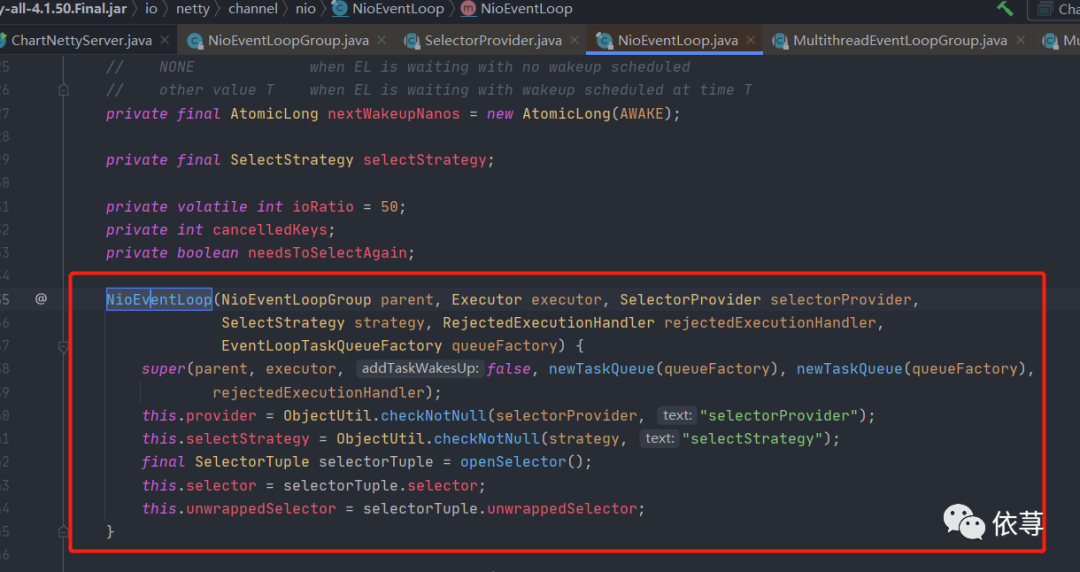
构造方法调用明细如下所示:
io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop
的构造方法,通过逐层super,为父级类参数赋值,同时创建了
NioEventLoop的多路复用选择器
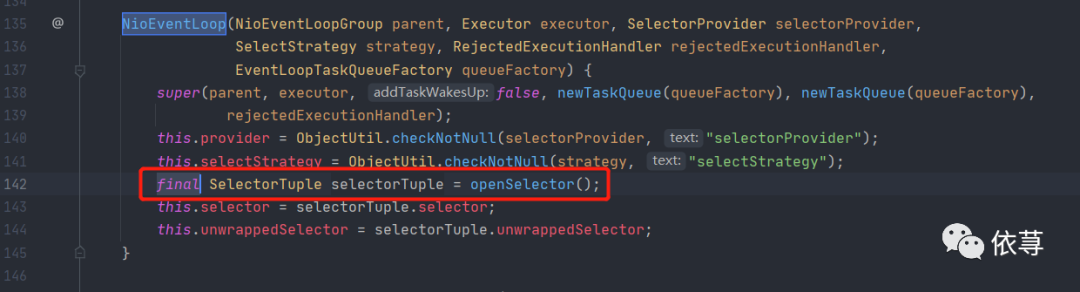
这里可以看下Netty的多路复用选择器是如何构建的:
源码如下:
private SelectorTuple openSelector() {final Selector unwrappedSelector;try {//首先直接打开选择器unwrappedSelector = provider.openSelector();} catch (IOException e) {throw new ChannelException("failed to open a new selector", e);}if (DISABLE_KEY_SET_OPTIMIZATION) {//这里选择是否不需要优化多路复用选择器的key//默认是false,即默认需要优化//可以通过properties文件中io.netty.noKeySetOptimization设定true或者falsereturn new SelectorTuple(unwrappedSelector);}//AccessController 是Java安全策略机制的一种方式,这里表示的是,//不管是否设定安全策略,这里临时扩大访问权限,强制执行方法//有需要了解更详细的,可以自行查阅资料Object maybeSelectorImplClass = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction() { public Object run() {try {//尝试返回sun.nio.ch.SelectorImpl实例,可能会抛出异常return Class.forName("sun.nio.ch.SelectorImpl",false,PlatformDependent.getSystemClassLoader());} catch (Throwable cause) {return cause;}}});if (!(maybeSelectorImplClass instanceof Class) ||// ensure the current selector implementation is what we can instrument.!((Class) maybeSelectorImplClass).isAssignableFrom(unwrappedSelector.getClass())) {if (maybeSelectorImplClass instanceof Throwable) {Throwable t = (Throwable) maybeSelectorImplClass;logger.trace("failed to instrument a special java.util.Set into: {}", unwrappedSelector, t);}//当尝试获取的sun.nio.ch.SelectorImpl实例是异常时候,则直接返回return new SelectorTuple(unwrappedSelector);}final Class selectorImplClass = (Class) maybeSelectorImplClass;final SelectedSelectionKeySet selectedKeySet = new SelectedSelectionKeySet();Object maybeException = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction() { public Object run() {try {//这里利用反射,获取到selectedKeys和publicSelectedKeysField selectedKeysField = selectorImplClass.getDeclaredField("selectedKeys");Field publicSelectedKeysField = selectorImplClass.getDeclaredField("publicSelectedKeys");//当java版本在9或者以上,并且sun.misc.Unsafe可以在classpath下找到//这里如果java版本在1.9及其以上,一般来说,都是可以的if (PlatformDependent.javaVersion() >= 9 && PlatformDependent.hasUnsafe()) {// Let us try to use sun.misc.Unsafe to replace the SelectionKeySet.// This allows us to also do this in Java9+ without any extra flags.//这里原始注释也比较好理解了:尝试用sun.misc.Unsafe替换SelectionKeySetlong selectedKeysFieldOffset = PlatformDependent.objectFieldOffset(selectedKeysField);long publicSelectedKeysFieldOffset =PlatformDependent.objectFieldOffset(publicSelectedKeysField);if (selectedKeysFieldOffset != -1 && publicSelectedKeysFieldOffset != -1) {PlatformDependent.putObject(unwrappedSelector, selectedKeysFieldOffset, selectedKeySet);PlatformDependent.putObject(unwrappedSelector, publicSelectedKeysFieldOffset, selectedKeySet);return null;}// We could not retrieve the offset, lets try reflection as last-resort.}Throwable cause = ReflectionUtil.trySetAccessible(selectedKeysField, true);if (cause != null) {return cause;}cause = ReflectionUtil.trySetAccessible(publicSelectedKeysField, true);if (cause != null) {return cause;}//给属性设置值selectedKeysField.set(unwrappedSelector, selectedKeySet);publicSelectedKeysField.set(unwrappedSelector, selectedKeySet);return null;} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {return e;} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {return e;}}});if (maybeException instanceof Exception) {selectedKeys = null;Exception e = (Exception) maybeException;logger.trace("failed to instrument a special java.util.Set into: {}", unwrappedSelector, e);return new SelectorTuple(unwrappedSelector);}selectedKeys = selectedKeySet;logger.trace("instrumented a special java.util.Set into: {}", unwrappedSelector);return new SelectorTuple(unwrappedSelector,new SelectedSelectionKeySetSelector(unwrappedSelector, selectedKeySet));}
上面代码,需要注意的地方:
各种赋值,打开的多路复用器

赋值到了
io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop.SelectorTuple
属性中
同时这个多路复用器的父级类
sun.nio.ch.SelectorImpl
属性被做出了优化,
即针对多路复用选择器实现类
sun.nio.ch.SelectorImpl
进行了优化
这里为何需要做这种优化呢?
首先需要知道,原本的sun.nio.ch.SelectorImpl
结构是什么样子的?
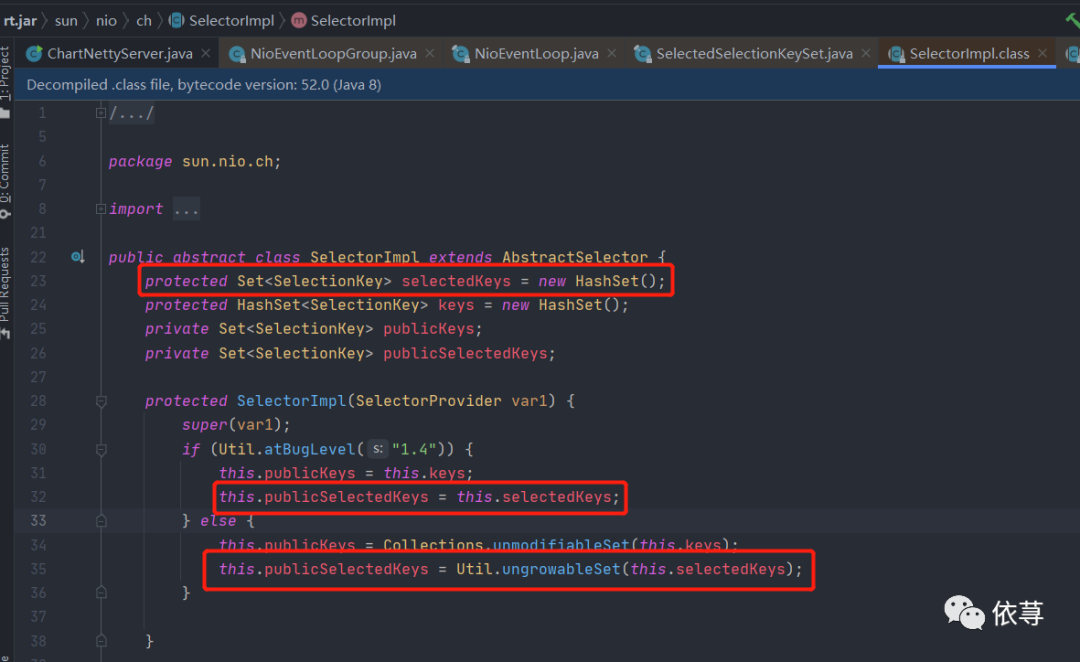
如上图所示,原本的
sun.nio.ch.SelectorImpl#selectedKeys
和
sun.nio.ch.SelectorImpl#publicSelectedKeys
属性是一个HashSet,而HashSet底层其实也就是一个HashMap,所以,其数据结构主要是由链表组成,链表就是一个不连续的内存存储,方便插入和删除,但是不利于查询
所以这里替换了一个
io.netty.channel.nio.SelectedSelectionKeySet
其构造方法为:
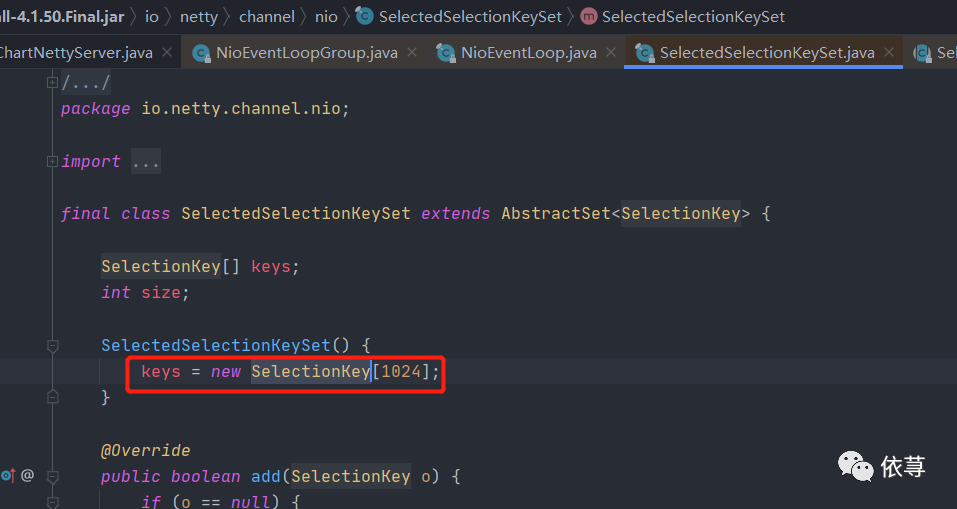
即是一个数组,我们知道数组在内存是一个连续的过程,有一个连续的内存地址,数组不利于新增和删除,但是利于查询
而这里
sun.nio.ch.SelectorImpl#selectedKeys
和
sun.nio.ch.SelectorImpl#publicSelectedKeys
主要存储的是和事件感兴趣的key值,即前面NIO中说到的可连接、可读、可写等状态:
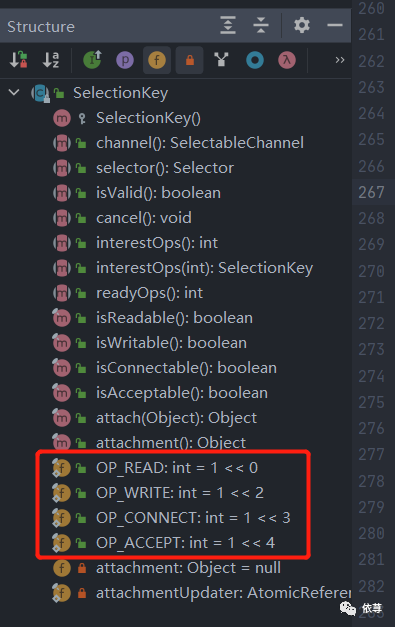
所以这里主要是在轮询的时候方便获取这种状态值,即快速查询,所以这里用数组替换链表
最终返回了一个优化后的
io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop.SelectorTuple
这里的
io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop.SelectorTuple
也是较之前NIO中所得到的
java.nio.channels.Selector
多路复用器不同,看下它的结构:
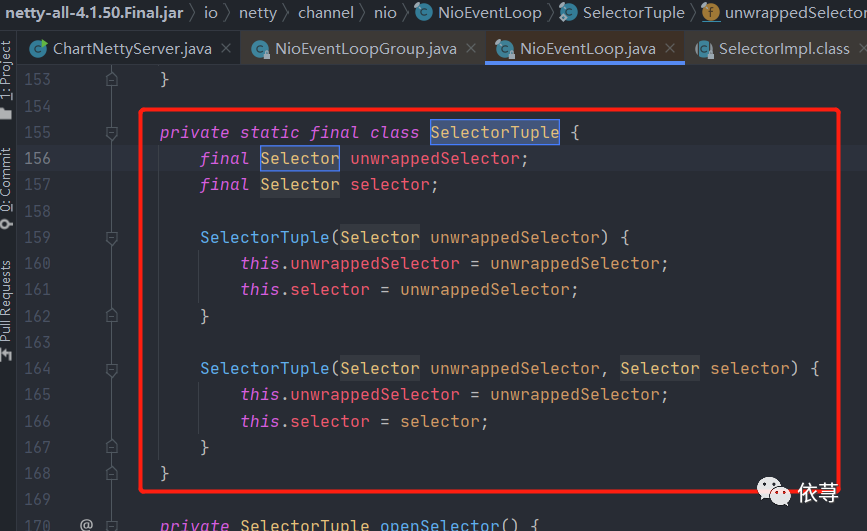
io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop.SelectorTuple
是
io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop的一个内部类,包含2个多路复用器,根据构造函数,这里返回的
io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop.SelectorTuple
属性值分别是:
io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop.SelectorTuple#unwrappedSelector
值为
java.nio.channels.Selector
io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop.SelectorTuple#selector
值为
io.netty.channel.nio.SelectedSelectionKeySetSelector#SelectedSelectionKeySetSelector
为此,在经历这一系列的关联调用之后(具体源码逻辑请见《剖析Netty之底层原理(一)》),其主要源码类的主要参数变化,这里总结了一张图表,
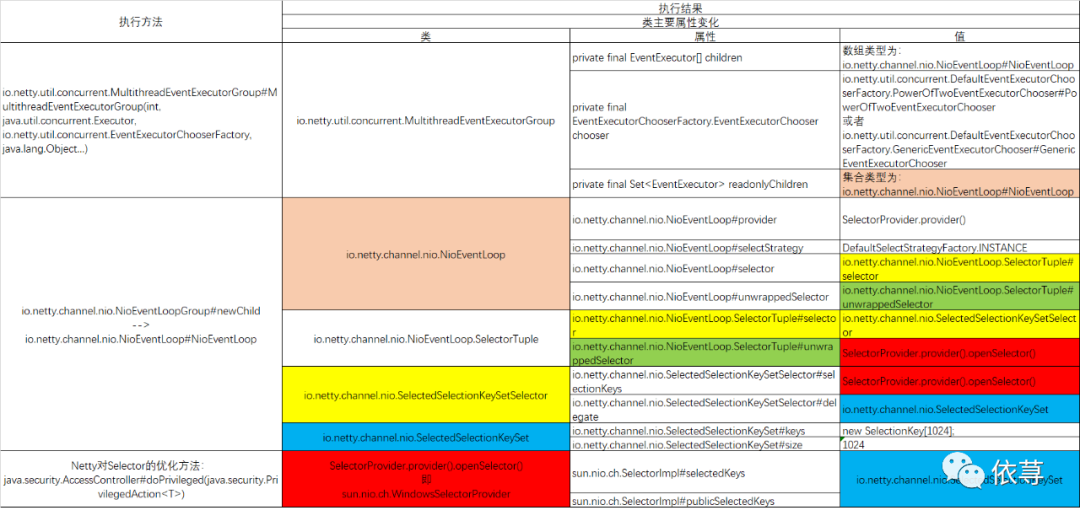
其中上图中,具有相似颜色的类,是同一个类,
针对此,可以初步了解完
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
和
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
方法所执行的所有逻辑<两者逻辑一样>
这里简单做出一个小结:
初始化NioEventLoopGroup的结果,实质是构建了一个EventExecutor数组,其数组类型是NioEventLoop。
由于篇幅已经够长了,所以,后续将接着分享,这里先简单告一段落。
有喜欢的,欢迎点赞关注,谢谢
麻烦给个再看呢!
