OpenCV制作一个类“全能扫描王”的简易扫描软件
将证件轮廓找到
提取证件矩形轮廓四点进行透视变换
二值化
图像的信息区域的提取与矫正
图像的二值化
锐化和增强


正式实现
第一步,二值化+高斯滤波+膨胀+canny边缘提取
Mat src = imread("1.png");
imshow("src img", src);
Mat source = src.clone();
Mat bkup = src.clone();
Mat img = src.clone();
cvtColor(img, img, CV_RGB2GRAY); //二值化
imshow("gray", img);
//equalizeHist(img, img);
//imshow("equal", img);
GaussianBlur(img, img, Size(5, 5), 0, 0); //高斯滤波
//获取自定义核
Mat element = getStructuringElement(MORPH_RECT, Size(3, 3)); //第一个参数MORPH_RECT表示矩形的卷积核,当然还可以选择椭圆形的、交叉型的
//膨胀操作
dilate(img, img, element); //实现过程中发现,适当的膨胀很重要
imshow("dilate", img);
Canny(img, img, 30, 120, 3); //边缘提取
imshow("get contour", img);
}

第二步,轮廓查找并筛选
vector<vector<Point> > contours;
vector<vector<Point> > f_contours;
std::vector<cv::Point> approx2;
//注意第5个参数为CV_RETR_EXTERNAL,只检索外框
findContours(img, f_contours, CV_RETR_EXTERNAL, CV_CHAIN_APPROX_NONE); //找轮廓
//求出面积最大的轮廓
int max_area = 0;
int index;
for (int i = 0; i < f_contours.size(); i++)
{
double tmparea = fabs(contourArea(f_contours[i]));
if (tmparea > max_area)
{
index = i;
max_area = tmparea;
}
}
contours.push_back(f_contours[index]);
第三步,找出这个四边形轮廓的四个顶点
两两直线过于接近我们排除
两两直线没有交点我们排除
检测出来的直线数目不是4条我们排除
cv::Point2f computeIntersect(cv::Vec4i a, cv::Vec4i b)
{
int x1 = a[0], y1 = a[1], x2 = a[2], y2 = a[3];
int x3 = b[0], y3 = b[1], x4 = b[2], y4 = b[3];
if (float d = ((float)(x1 - x2) * (y3 - y4)) - ((y1 - y2) * (x3 - x4)))
{
cv::Point2f pt;
pt.x = ((x1*y2 - y1*x2) * (x3 - x4) - (x1 - x2) * (x3*y4 - y3*x4)) / d;
pt.y = ((x1*y2 - y1*x2) * (y3 - y4) - (y1 - y2) * (x3*y4 - y3*x4)) / d;
return pt;
}
else
return cv::Point2f(-1, -1);
}
如果两两定点的距离过近,我们排除
bool IsGoodPoints = true;
//保证点与点的距离足够大以排除错误点
for (int i = 0; i < corners.size(); i++)
{
for (int j = i + 1; j < corners.size(); j++)
{
int distance = sqrt((corners[i].x - corners[j].x)*(corners[i].x - corners[j].x) + (corners[i].y - corners[j].y)*(corners[i].y - corners[j].y));
if (distance < 5)
{
IsGoodPoints = false;
}
}
}
if (!IsGoodPoints) continue;
如果这四个点构成不了四边形我们排除
cv::approxPolyDP(cv::Mat(corners), approx, cv::arcLength(cv::Mat(corners), true) * 0.02, true);
if (lines.size() == 4 && corners.size() == 4 && approx.size() == 4)
{
flag = 1;
break;
}
bool x_sort(const Point2f & m1, const Point2f & m2)
{
return m1.x < m2.x;
}
//确定四个点的中心线
void sortCorners(std::vector<cv::Point2f>& corners,
cv::Point2f center)
{
std::vector<cv::Point2f> top, bot;
vector<Point2f> backup = corners;
sort(corners, x_sort); //注意先按x的大小给4个点排序
for (int i = 0; i < corners.size(); i++)
{
if (corners[i].y < center.y && top.size() < 2) //这里的小于2是为了避免三个顶点都在top的情况
top.push_back(corners[i]);
else
bot.push_back(corners[i]);
}
corners.clear();
if (top.size() == 2 && bot.size() == 2)
{
//cout << "log" << endl;
cv::Point2f tl = top[0].x > top[1].x ? top[1] : top[0];
cv::Point2f tr = top[0].x > top[1].x ? top[0] : top[1];
cv::Point2f bl = bot[0].x > bot[1].x ? bot[1] : bot[0];
cv::Point2f br = bot[0].x > bot[1].x ? bot[0] : bot[1];
corners.push_back(tl);
corners.push_back(tr);
corners.push_back(br);
corners.push_back(bl);
}
else
{
corners = backup;
}
}
第四步,四点法透射变换
int g_dst_hight; //最终图像的高度
int g_dst_width; //最终图像的宽度
void CalcDstSize(const vector<cv::Point2f>& corners)
{
int h1 = sqrt((corners[0].x - corners[3].x)*(corners[0].x - corners[3].x) + (corners[0].y - corners[3].y)*(corners[0].y - corners[3].y));
int h2 = sqrt((corners[1].x - corners[2].x)*(corners[1].x - corners[2].x) + (corners[1].y - corners[2].y)*(corners[1].y - corners[2].y));
g_dst_hight = MAX(h1, h2);
int w1 = sqrt((corners[0].x - corners[1].x)*(corners[0].x - corners[1].x) + (corners[0].y - corners[1].y)*(corners[0].y - corners[1].y));
int w2 = sqrt((corners[2].x - corners[3].x)*(corners[2].x - corners[3].x) + (corners[2].y - corners[3].y)*(corners[2].y - corners[3].y));
g_dst_width = MAX(w1, w2);
}
cv::Mat quad = cv::Mat::zeros(g_dst_hight, g_dst_width, CV_8UC3);
std::vector<cv::Point2f> quad_pts;
quad_pts.push_back(cv::Point2f(0, 0));
quad_pts.push_back(cv::Point2f(quad.cols, 0));
quad_pts.push_back(cv::Point2f(quad.cols, quad.rows));
quad_pts.push_back(cv::Point2f(0, quad.rows));
cv::Mat transmtx = cv::getPerspectiveTransform(corners, quad_pts);
cv::warpPerspective(source, quad, transmtx, quad.size());
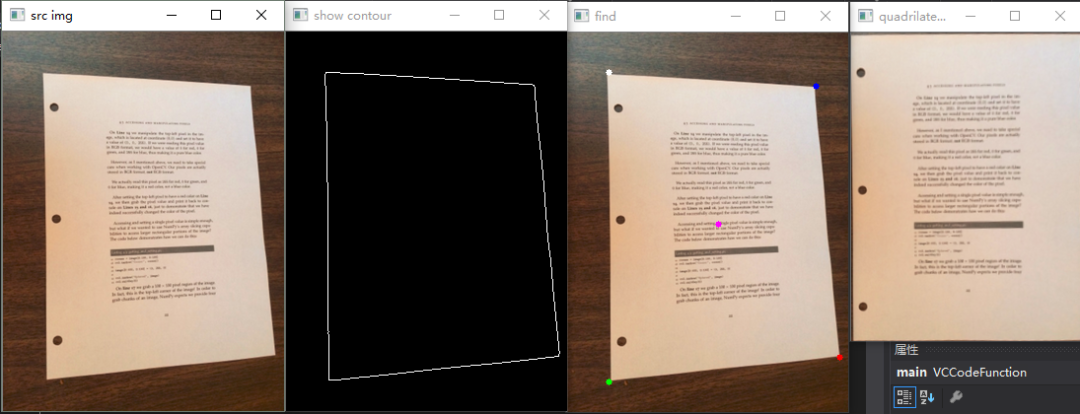
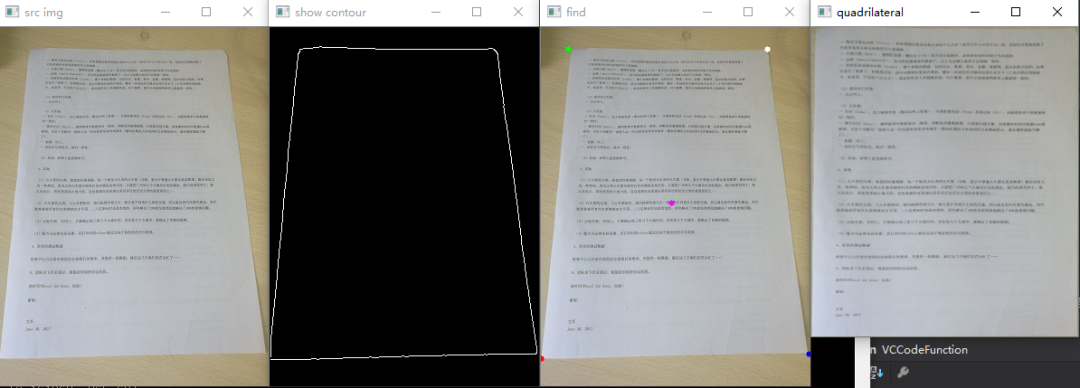
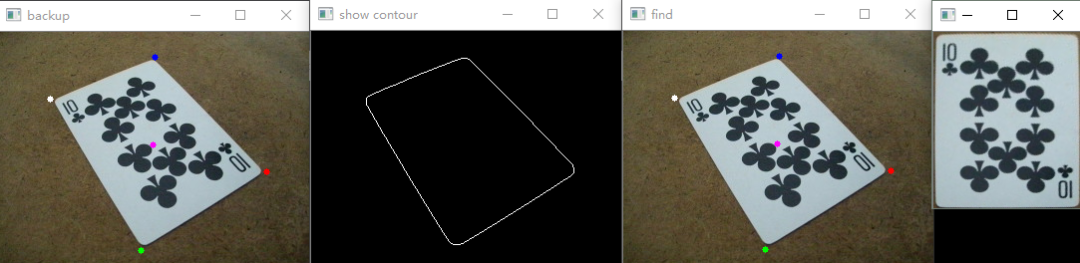
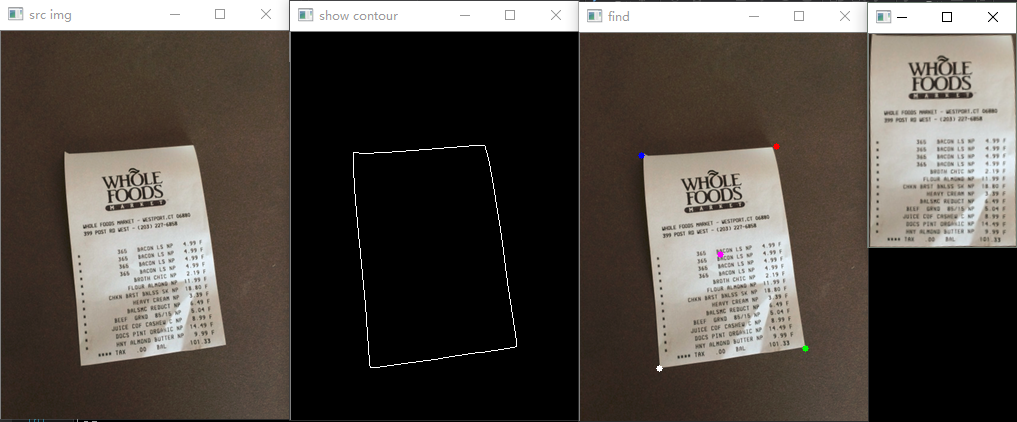
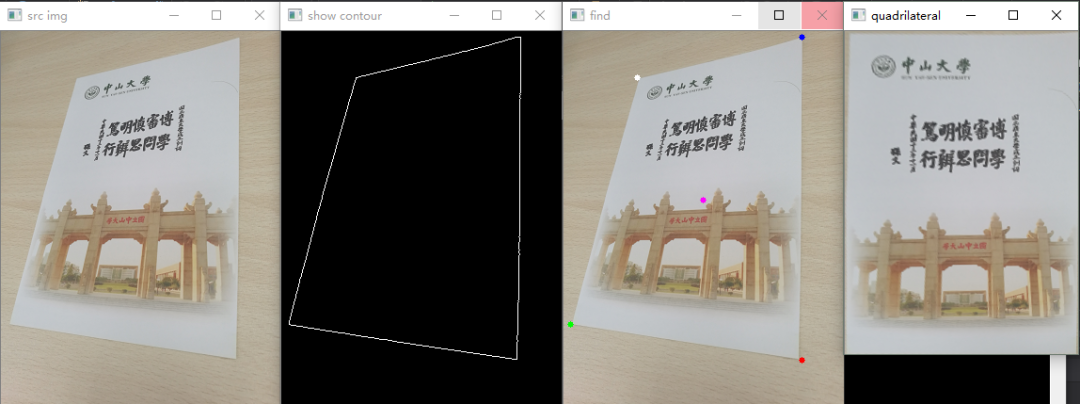
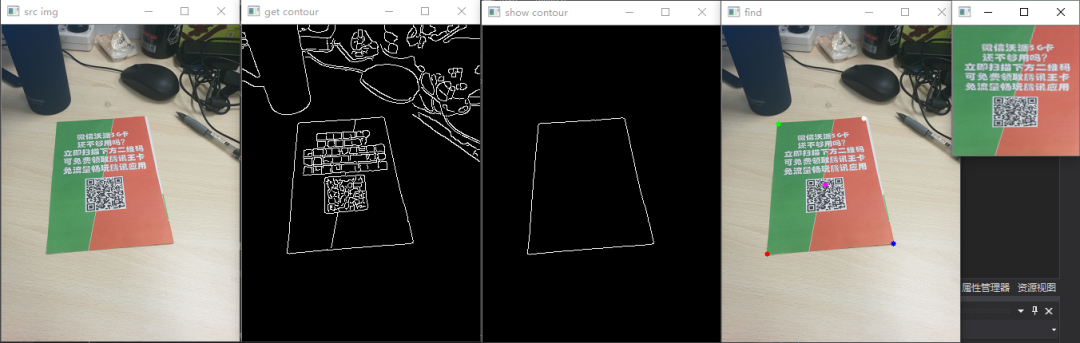
额外效果:二值化
Mat local,gray;
cvtColor(quad, gray, CV_RGB2GRAY);
int blockSize = 25;
int constValue = 10;
adaptiveThreshold(gray, local, 255, CV_ADAPTIVE_THRESH_MEAN_C, CV_THRESH_BINARY, blockSize, constValue);
imshow("二值化", local);


 End
End 
声明:部分内容来源于网络,仅供读者学术交流之目的。文章版权归原作者所有。如有不妥,请联系删除。
评论
