风控策略的自动化生成-利用决策树分分钟生成上千条策略
一、数据说明及读取
1、数据集信息
2、数据属性信息
3、读取数据
#数据读取import pandas as pdimport numpy as nppd.set_option('display.max_columns', None)#显示所有的列path = '/Users/wuzhengxiang/Documents/DataSets/RizhaoGongJiJin/train.csv'train = pd.read_csv(path).fillna(-1)train.columnsIndex(['id', 'XINGBIE', 'CSNY', 'HYZK', 'ZHIYE', 'ZHICHEN', 'ZHIWU', 'XUELI','DWJJLX', 'DWSSHY', 'GRJCJS', 'GRZHZT', 'GRZHYE', 'GRZHSNJZYE','GRZHDNGJYE', 'GRYJCE', 'DWYJCE', 'DKFFE', 'DKYE', 'DKLL', 'label'],dtype='object')
train.head()#查看前面的数据id XINGBIE CSNY HYZK ZHIYE ZHICHEN ZHIWU XUELI DWJJLX \0 train_0 1 1038672000 90 90 999 0 99 1501 train_1 2 504892800 90 90 999 0 99 1102 train_2 1 736185600 90 90 999 0 99 1503 train_3 1 428515200 90 90 999 0 99 1504 train_4 2 544204800 90 90 999 0 99 900DWSSHY GRJCJS GRZHZT GRZHYE GRZHSNJZYE GRZHDNGJYE GRYJCE \0 12 1737.0 1 3223.515 801.310 837.000 312.001 0 4894.0 1 18055.195 53213.220 1065.200 795.842 9 10297.0 1 27426.600 13963.140 7230.020 1444.203 7 10071.5 1 111871.130 99701.265 2271.295 1417.144 14 2007.0 1 237.000 11028.875 35.780 325.50DWYJCE DKFFE DKYE DKLL label0 312.00 175237 154112.935 2.708 01 795.84 300237 298252.945 2.979 02 1444.20 150237 147339.130 2.708 03 1417.14 350237 300653.780 2.708 04 325.50 150237 145185.010 2.708 0#构建训练集X = train.loc[:,'XINGBIE':'DKLL']= train['label']
二、构建决策树
训练一个决策树,这里限制了最大深度和最小样本树 from sklearn import tree= tree.DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=3,min_samples_leaf=50)= clf.fit(X, Y)
三、决策树的可视化
1、plot_tree(太丑,不推荐)
#包里自带的,有点丑tree.plot_tree(clf)plt.show()

2、graphviz对决策树进行可视化
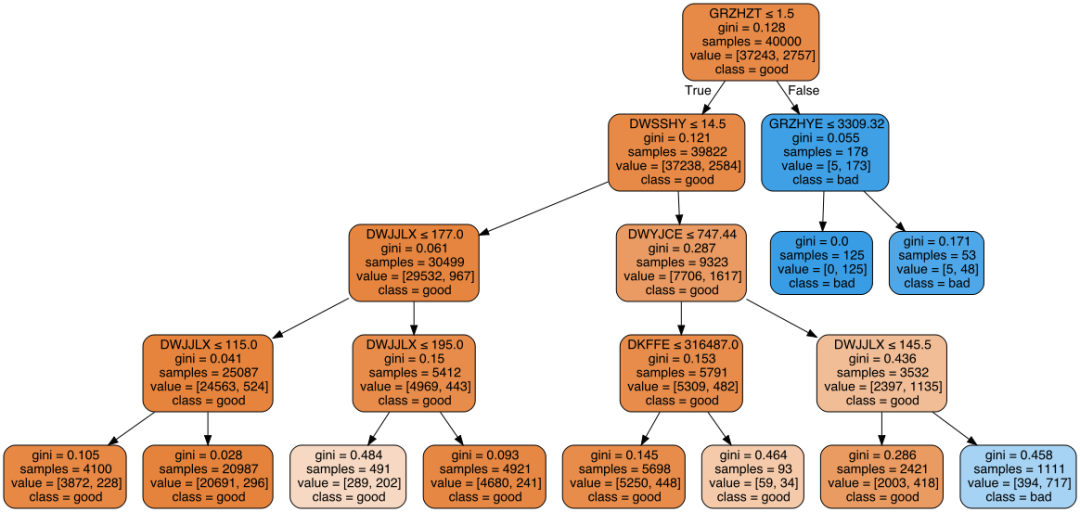
import graphviz= tree.export_graphviz(out_file=None,=X.columns,class_names=['good','bad'],filled=True, rounded=True,special_characters=True)= graphviz.Source(dot_data)graph
3、dtreeviz对决策树进行可视化
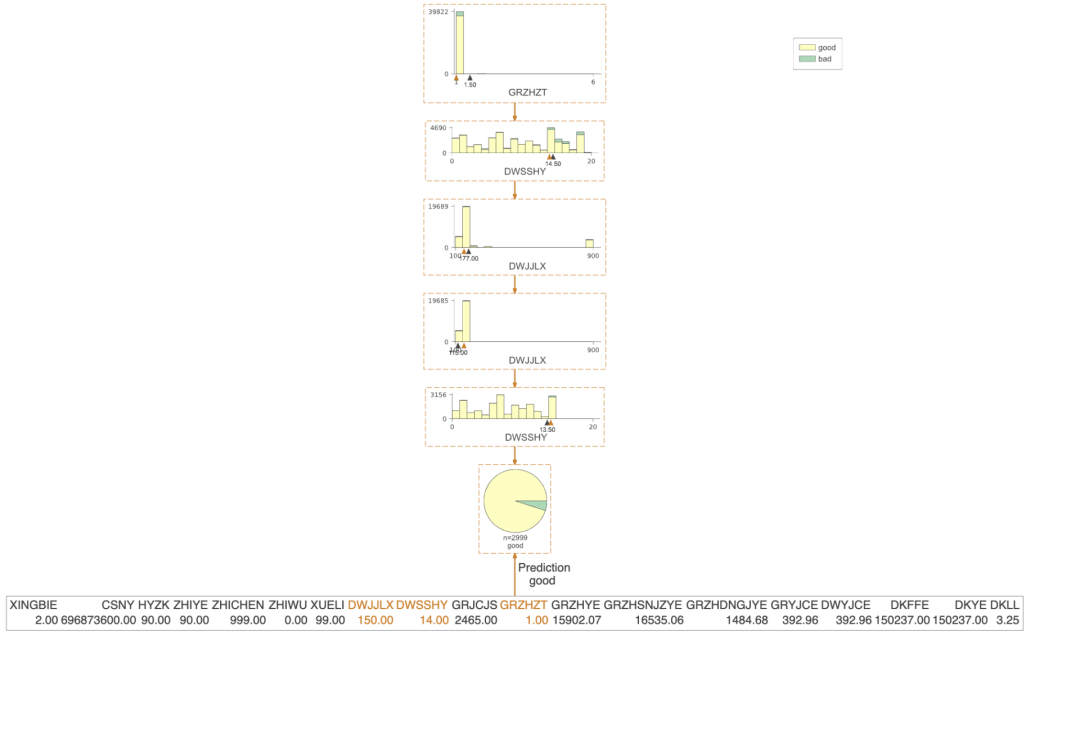
from dtreeviz.trees import dtreeviz= X.iloc[77,:]= dtreeviz(clf,X,Y,feature_names=np.array(X.columns),class_names={0:'good',1:'bad'},X = testX)viz.view()
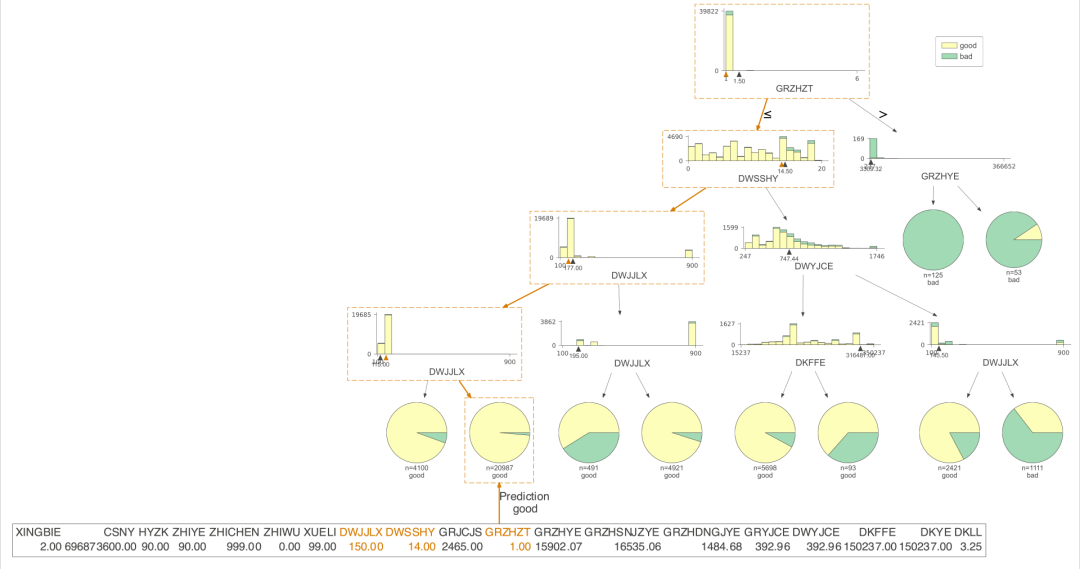
我们把树的深度再加深到5看看,树更复杂了 from sklearn import treeclf = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=5,min_samples_leaf=50)= clf.fit(X, Y)from dtreeviz.trees import dtreeviztestX = X.iloc[77,:]viz = dtreeviz(clf,X,Y,feature_names=np.array(X.columns),class_names={0:'good',1:'bad'},X = testX)viz.view()

viz = dtreeviz(clf,X,Y,orientation ='LR', # left-right orientationfeature_names=np.array(X.columns),class_names={0:'good',1:'bad'},X = testX)viz.view()#如果只想可视化预测路径,则需要设置参数 show_just_path=True
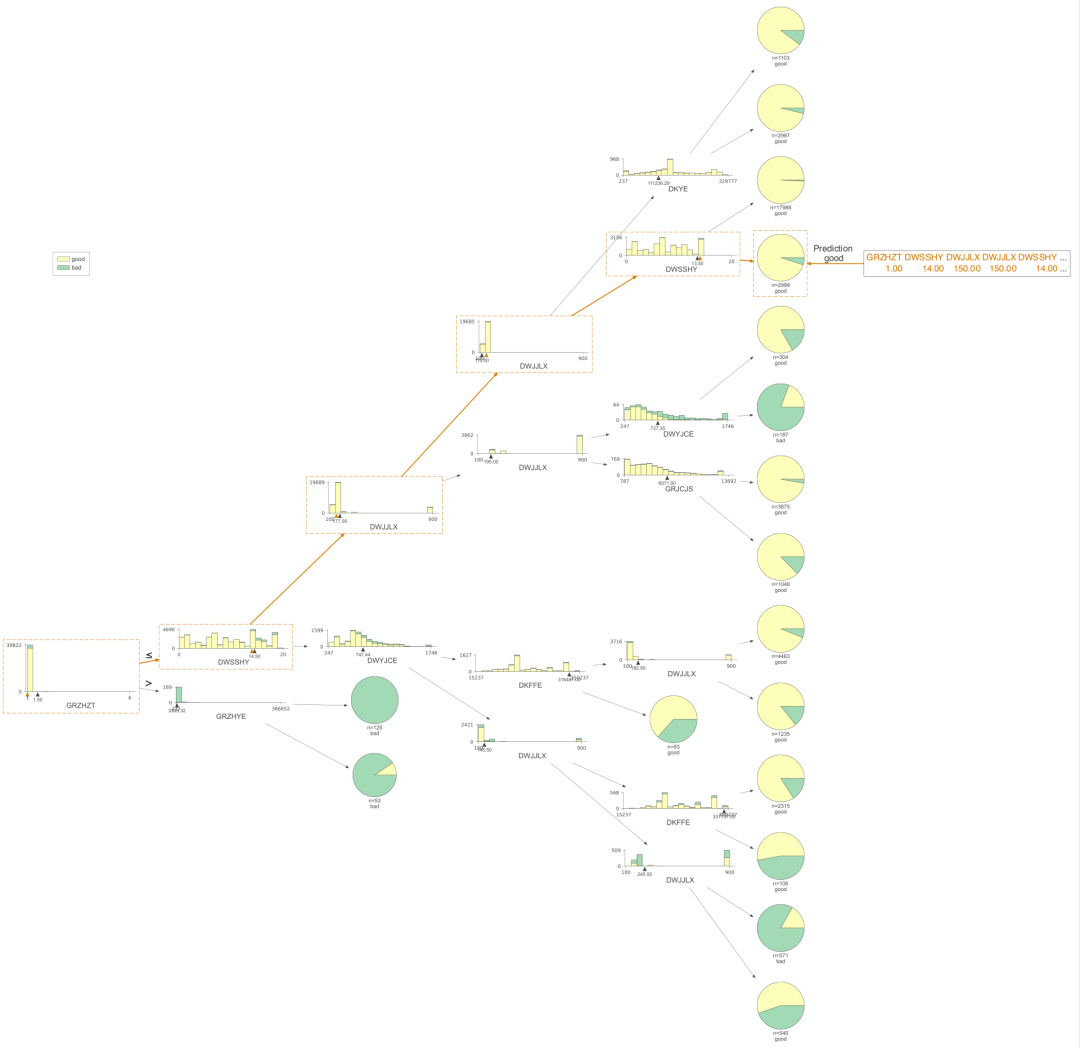
viz = dtreeviz(clf,X,Y,feature_names=np.array(X.columns),class_names={0:'good',1:'bad'},orientation ='LR', # left-right orientationshow_just_path=True,X = testX)viz.view()
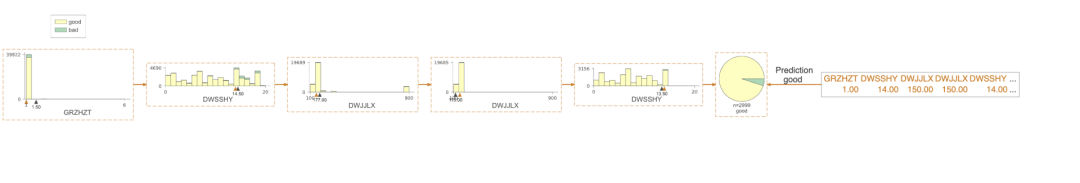
四、决策规则提取
1、决策树的生成的结构探索
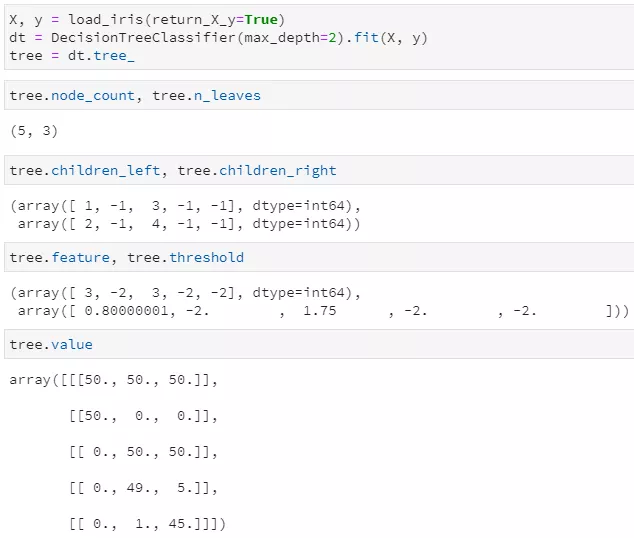
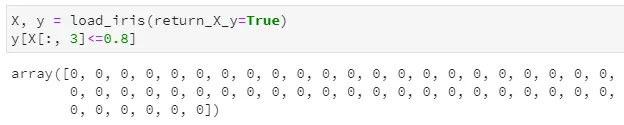
from sklearn.datasets import load_irisfrom sklearn import treeiris = load_iris()clf = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier()clf = clf.fit(iris.data, iris.target)clf.classes_[x for x in dir(clf) if not x.startswith('_')]
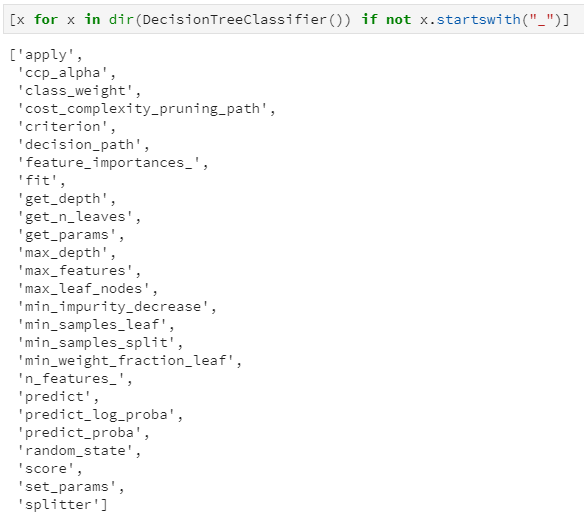

classes_:分类标签的取值,即y的唯一值集合 max_features_:最大特征数 n_classes_:类别数,如2分类或多分类等,即classes_属性中的长度 n_features_in_:输入特征数量,等价于老版sklearn中的n_features_,现已弃用,并推荐n_features_in_ n_outputs:多输出的个数,即决策树不仅可以用于实现单一的分类问题,还可同时实现多个分类问题,例如给定一组人物特征,用于同时判断其是男/女、胖/瘦和高矮,这是3个分类问题,即3输出(需要区别理解多分类和多输出任务) tree_:毫无疑问,这个tree_就是今天本文的重点,是在决策树训练之后新增的属性集,其中存储了决策树是如何存储的。

Array-based representation of a binary decision tree.
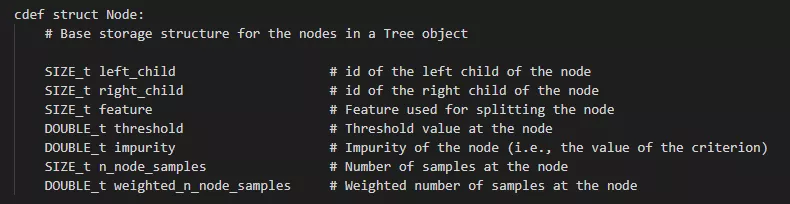
left_child:size类型(无符号整型),代表了当前节点的左子节点的索引 right_child:类似于left_child feature:size类型,代表了当前节点用于分裂的特征索引,即在训练集中用第几列特征进行分裂 threshold:double类型,代表了当前节点选用相应特征时的分裂阈值,一般是≤该阈值时进入左子节点,否则进入右子节点 n_node_samples:size类型,代表了训练时落入到该节点的样本总数。显然,父节点的n_node_samples将等于其左右子节点的n_node_samples之和。
# 决策树结构探索
dir(clf.tree_)['apply','capacity', 'children_left','children_right','compute_feature_importances','compute_partial_dependence','decision_path','feature','impurity','max_depth','max_n_classes','n_classes','n_features','n_leaves','n_node_samples','n_outputs','node_count','predict','threshold','value', 'weighted_n_node_samples']
clf.tree_.children_leftclf.tree_.children_rightclf.tree_.featureclf.tree_.capacityclf.tree_.thresholdclf.tree_.valueclf.tree_.impurityclf.tree_.decision_path
训练后的决策树共包含5个节点,其中3个叶子节点 通过children_left和children_right两个属性,可以知道第0个节点(也就是根节点)的左子节点索引为1,右子节点索引为2,;第1个节点的左右子节点均为-1,意味着该节点即为叶子节点;第2个节点的左右子节点分别为3和4,说明它是一个内部节点,并做了进一步分裂 通过feature和threshold两个属性,可以知道第0个节点(根节点)使用索引为3的特征(对应第4列特征)进行分裂,且其最优分割阈值为0.8;第1个节点因为是叶子节点,所以不再分裂,其对应feature和threshold字段均为-2 通过value属性,可以查看落入每个节点的各类样本数量,由于鸢尾花数据集是一个三分类问题,且该决策树共有5个节点,所以value的取值为一个5×3的二维数组,例如第一行代表落入根节点的样本计数为[50, 50, 50],第二行代表落入左子节点的样本计数为[50, 0, 0],由于已经是纯的了,所以不再继续分裂。 另外,tree中实际上并未直接标出各叶节点所对应的标签值,但完全可通过value属性来得到,即各叶子节点中落入样本最多的类别即为相应标签。甚至说,不仅可知道对应标签,还可通过计算数量之比得到相应的概率!

2、老方法提取决策树规则
数据读取 import pandas as pdimport numpy as nppd.set_option('display.max_columns', None)#显示所有的列path = '/Users/wuzhengxiang/Documents/DataSets/RizhaoGongJiJin/train.csv'train = pd.read_csv(path).fillna(-1)train.columns构建训练集 X = train.loc[:,'XINGBIE':'DKLL']Y = train['label']
训练一个决策树,这里限制了最大深度和最小样本树from sklearn import treeclf = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=3,min_samples_leaf=50)clf = clf.fit(X, Y)决策树规则提取-老方法
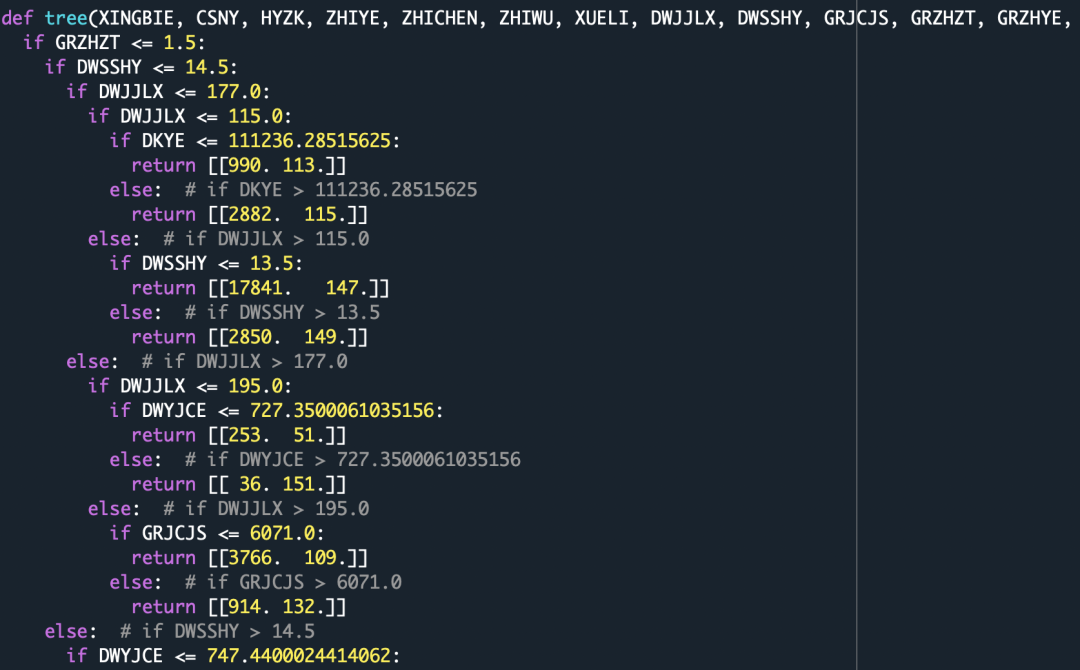
from sklearn.tree import _treedef tree_to_code(tree, feature_names):tree_ = tree.tree_feature_name = [feature_names[i] if i != _tree.TREE_UNDEFINED else "undefined!"for i in tree_.feature]print ("def tree({}):".format(", ".join(feature_names)))def recurse(node, depth):indent = " " * depthif tree_.feature[node] != _tree.TREE_UNDEFINED:name = feature_name[node]threshold = tree_.threshold[node]print("{}if {} <= {}:".format(indent, name, threshold))recurse(tree_.children_left[node], depth + 1)print("{}else: # if {} > {}".format(indent, name, threshold))recurse(tree_.children_right[node], depth + 1)else:print("{}return {}".format(indent, tree_.value[node]))recurse(0, 1)tree_to_code(clf,X.columns)return [[161. 0.]]
3、新方法提取决策树规则
def XiaoWuGe_Get_Rules(clf,X):n_nodes = clf.tree_.node_countchildren_left = clf.tree_.children_leftchildren_right = clf.tree_.children_rightfeature = clf.tree_.featurethreshold = clf.tree_.thresholdvalue = clf.tree_.valuenode_depth = np.zeros(shape=n_nodes, dtype=np.int64)is_leaves = np.zeros(shape=n_nodes, dtype=bool)stack = [(0, 0)]while len(stack) > 0:node_id, depth = stack.pop()node_depth[node_id] = depthis_split_node = children_left[node_id] != children_right[node_id]if is_split_node:stack.append((children_left[node_id], depth+1))stack.append((children_right[node_id], depth+1))else:is_leaves[node_id] = Truefeature_name = [X.columns[i] if i != _tree.TREE_UNDEFINED else "undefined!"for i in clf.tree_.feature]ways = []depth = []feat = []nodes = []rules = []for i in range(n_nodes):if is_leaves[i]:while depth[-1] >= node_depth[i]:depth.pop()ways.pop()feat.pop()nodes.pop()if children_left[i-1]==i:a='{f}<={th}'.format(f=feat[-1],th=round(threshold[nodes[-1]],4))ways[-1]=alast =' & '.join(ways)+':'+str(value[i][0][0])+':'+str(value[i][0][1])rules.append(last)else:a='{f}>{th}'.format(f=feat[-1],th=round(threshold[nodes[-1]],4))ways[-1]=alast = ' & '.join(ways)+':'+str(value[i][0][0])+':'+str(value[i][0][1])rules.append(last)else:if i==0:ways.append(round(threshold[i],4))depth.append(node_depth[i])feat.append(feature_name[i])nodes.append(i)else:while depth[-1] >= node_depth[i]:depth.pop()ways.pop()feat.pop()nodes.pop()if i==children_left[nodes[-1]]:w='{f}<={th}'.format(f=feat[-1],th=round(threshold[nodes[-1]],4))else:w='{f}>{th}'.format(f=feat[-1],th=round(threshold[nodes[-1]],4))ways[-1] = wways.append(round(threshold[i],4))depth.append(node_depth[i])feat.append(feature_name[i])nodes.append(i)return rules
4、利用函数对规则进行提取
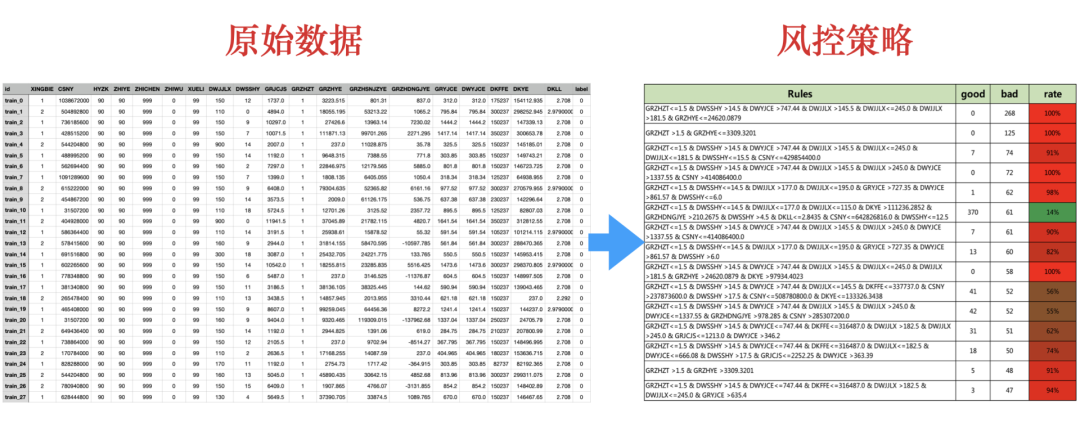
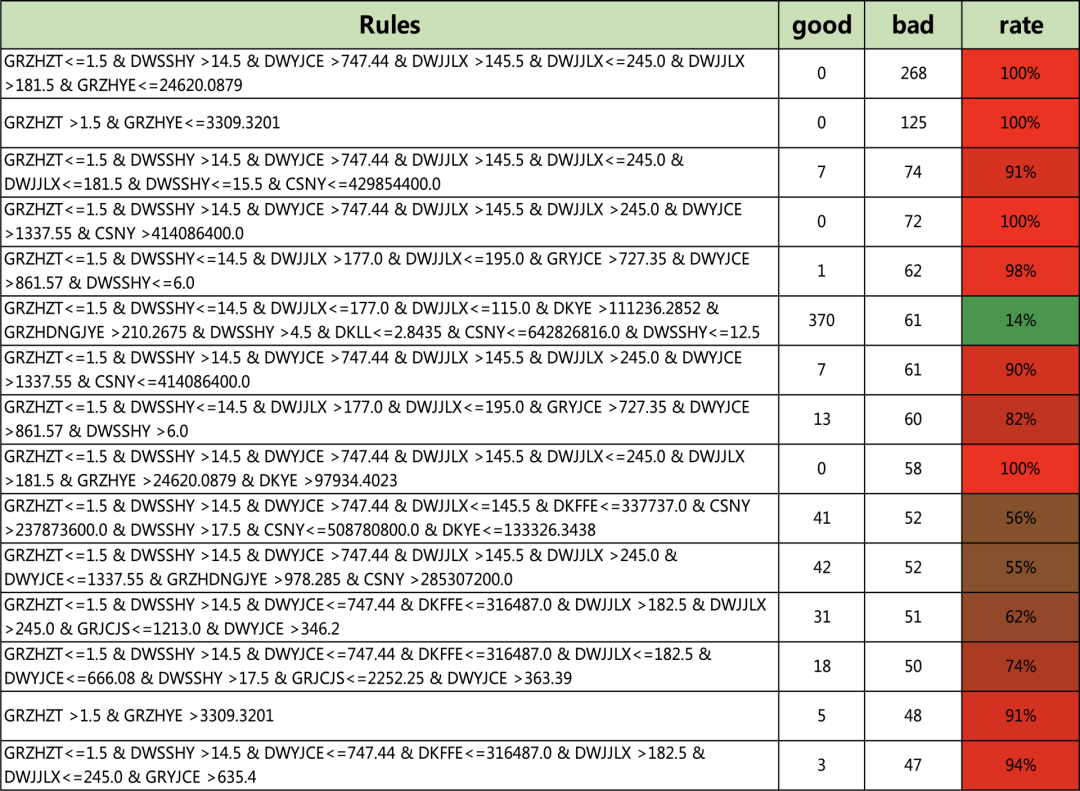
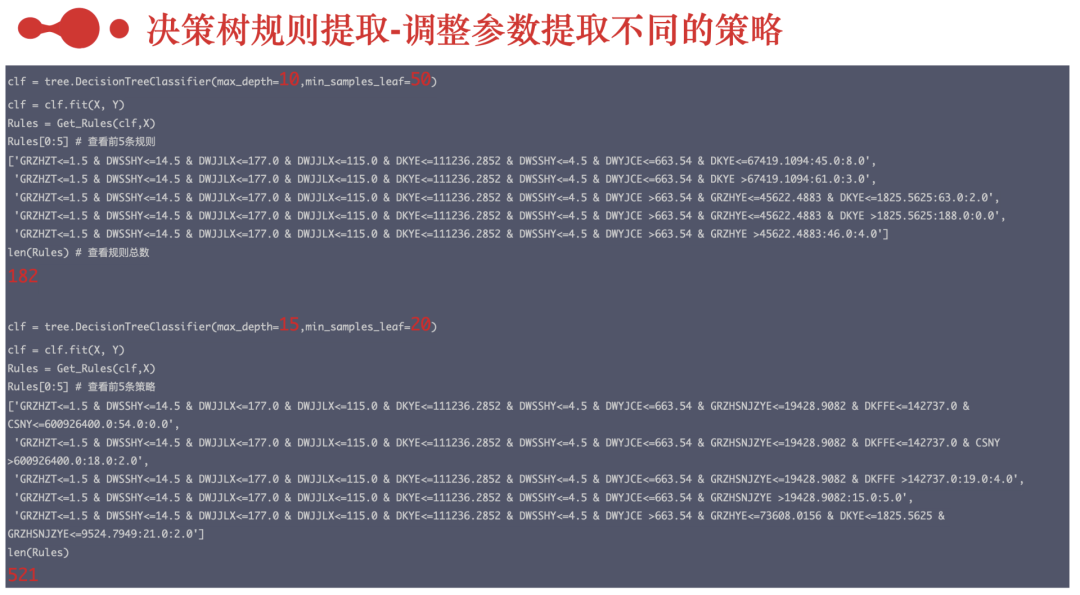
#训练一个决策树,对规则进行提取clf = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=10,min_samples_leaf=50)clf = clf.fit(X, Y)Rules = XiaoWuGe_Get_Rules(clf,X)Rules[0:5] # 查看前5条规则['GRZHZT<=1.5 & DWSSHY<=14.5 & DWJJLX<=177.0 & DWJJLX<=115.0 & DKYE<=111236.2852 & DWSSHY<=4.5 & DWYJCE<=663.54 & DKYE<=67419.1094:45.0:8.0','GRZHZT<=1.5 & DWSSHY<=14.5 & DWJJLX<=177.0 & DWJJLX<=115.0 & DKYE<=111236.2852 & DWSSHY<=4.5 & DWYJCE<=663.54 & DKYE >67419.1094:61.0:3.0','GRZHZT<=1.5 & DWSSHY<=14.5 & DWJJLX<=177.0 & DWJJLX<=115.0 & DKYE<=111236.2852 & DWSSHY<=4.5 & DWYJCE >663.54 & GRZHYE<=45622.4883 & DKYE<=1825.5625:63.0:2.0','GRZHZT<=1.5 & DWSSHY<=14.5 & DWJJLX<=177.0 & DWJJLX<=115.0 & DKYE<=111236.2852 & DWSSHY<=4.5 & DWYJCE >663.54 & GRZHYE<=45622.4883 & DKYE >1825.5625:188.0:0.0','GRZHZT<=1.5 & DWSSHY<=14.5 & DWJJLX<=177.0 & DWJJLX<=115.0 & DKYE<=111236.2852 & DWSSHY<=4.5 & DWYJCE >663.54 & GRZHYE >45622.4883:46.0:4.0']len(Rules) # 查看规则总数182
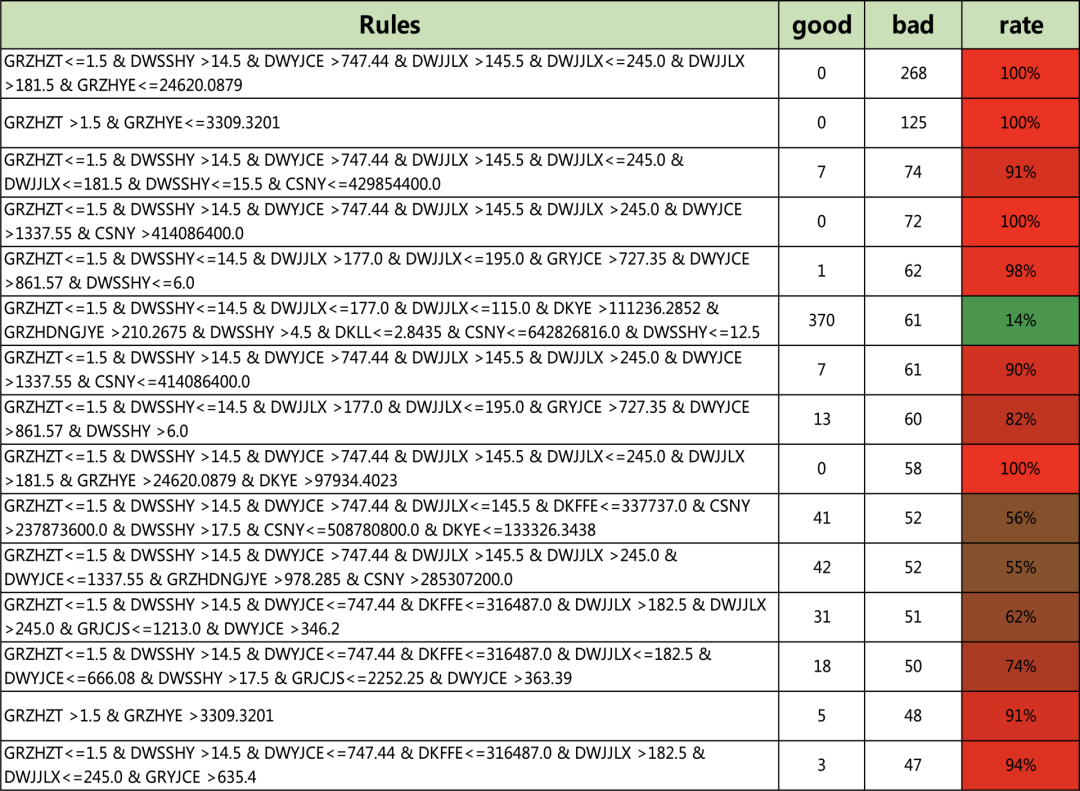
clf = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=15,min_samples_leaf=20)clf = clf.fit(X, Y)Rules = Get_Rules(clf,X)Rules[0:5]['GRZHZT<=1.5 & DWSSHY<=14.5 & DWJJLX<=177.0 & DWJJLX<=115.0 & DKYE<=111236.2852 & DWSSHY<=4.5 & DWYJCE<=663.54 & GRZHSNJZYE<=19428.9082 & DKFFE<=142737.0 & CSNY<=600926400.0:54.0:0.0','GRZHZT<=1.5 & DWSSHY<=14.5 & DWJJLX<=177.0 & DWJJLX<=115.0 & DKYE<=111236.2852 & DWSSHY<=4.5 & DWYJCE<=663.54 & GRZHSNJZYE<=19428.9082 & DKFFE<=142737.0 & CSNY >600926400.0:18.0:2.0','GRZHZT<=1.5 & DWSSHY<=14.5 & DWJJLX<=177.0 & DWJJLX<=115.0 & DKYE<=111236.2852 & DWSSHY<=4.5 & DWYJCE<=663.54 & GRZHSNJZYE<=19428.9082 & DKFFE >142737.0:19.0:4.0','GRZHZT<=1.5 & DWSSHY<=14.5 & DWJJLX<=177.0 & DWJJLX<=115.0 & DKYE<=111236.2852 & DWSSHY<=4.5 & DWYJCE<=663.54 & GRZHSNJZYE >19428.9082:15.0:5.0','GRZHZT<=1.5 & DWSSHY<=14.5 & DWJJLX<=177.0 & DWJJLX<=115.0 & DKYE<=111236.2852 & DWSSHY<=4.5 & DWYJCE >663.54 & GRZHYE<=73608.0156 & DKYE<=1825.5625 & GRZHSNJZYE<=9524.7949:21.0:2.0']len(Rules)521#可以遍历所有的规则for i in Rules:print(i)
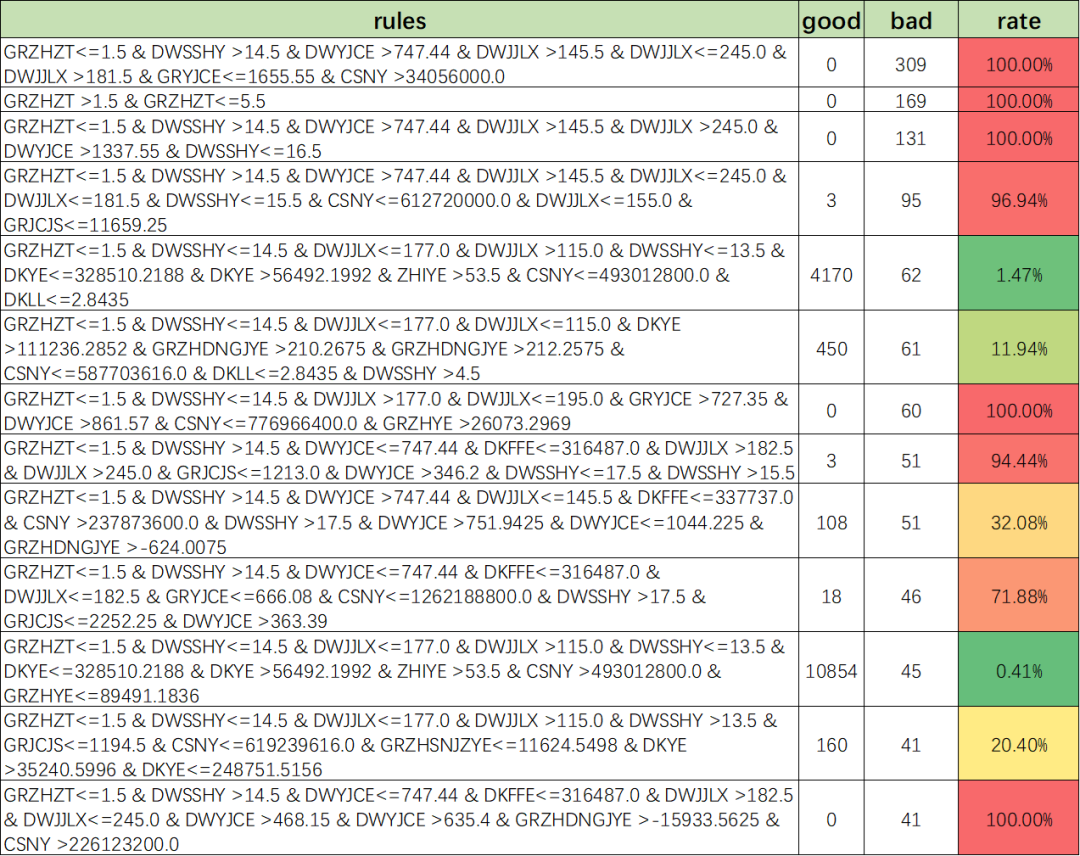
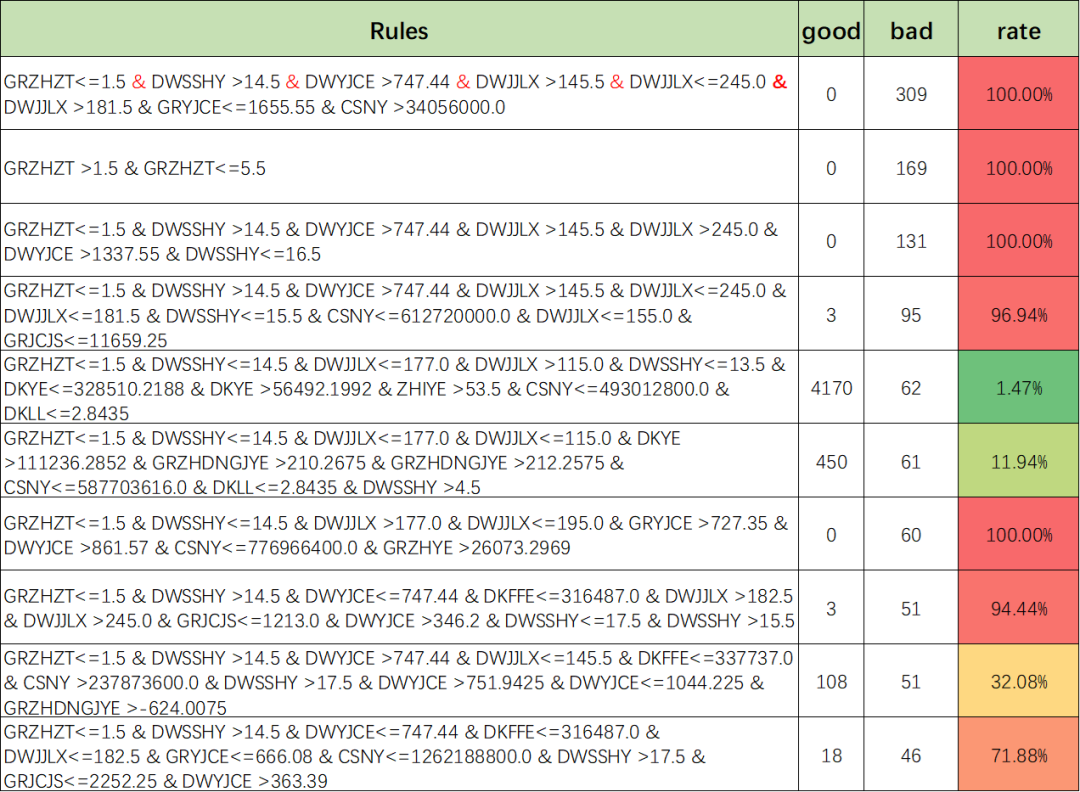
五、挖掘更多的风控策略
评论