Python实现敏感词过滤
作者 | 我被狗咬了
来源 | Python乱炖
在我们生活中的一些场合经常会有一些不该出现的敏感词,我们通常会使用*去屏蔽它,例如:尼玛 -> **,一些骂人的敏感词和一些政治敏感词都不应该出现在一些公共场合中,这个时候我们就需要一定的手段去屏蔽这些敏感词。下面我来介绍一些简单版本的敏感词屏蔽的方法。
(我已经尽量把脏话做成图片的形式了,要不然文章发不出去)



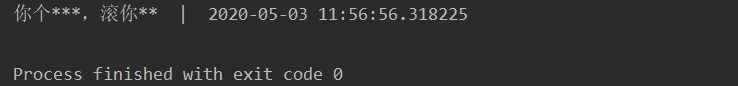
import datetime
now = datetime.datetime.now()
print(filter_sentence, " | ", now)
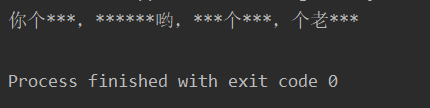
如果是多个敏感词可以用列表进行逐一替换


for i in dirty:
speak = speak.replace(i, '*')
print(speak, " | ", now)
方法二:正则表达式过滤

import re
def sentence_filter(keywords, text):
return re.sub("|".join(keywords), "***", text)
print(sentence_filter(dirty, speak))
方法三:DFA过滤算法
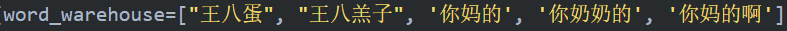
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# @Time:2020/4/15 11:40
# @Software:PyCharm
# article_add: https://www.cnblogs.com/JentZhang/p/12718092.html
__author__ = "JentZhang"
import json
MinMatchType = 1 # 最小匹配规则
MaxMatchType = 2 # 最大匹配规则
class DFAUtils(object):
"""
DFA算法
"""
def __init__(self, word_warehouse):
"""
算法初始化
:param word_warehouse:词库
"""
# 词库
self.root = dict()
# 无意义词库,在检测中需要跳过的(这种无意义的词最后有个专门的地方维护,保存到数据库或者其他存储介质中)
self.skip_root = [' ', '&', '!', '!', '@', '#', '$', '¥', '*', '^', '%', '?', '?', '<', '>', "《", '》']
# 初始化词库
for word in word_warehouse:
self.add_word(word)
def add_word(self, word):
"""
添加词库
:param word:
:return:
"""
now_node = self.root
word_count = len(word)
for i in range(word_count):
char_str = word[i]
if char_str in now_node.keys():
# 如果存在该key,直接赋值,用于下一个循环获取
now_node = now_node.get(word[i])
now_node['is_end'] = False
else:
# 不存在则构建一个dict
new_node = dict()
if i == word_count - 1: # 最后一个
new_node['is_end'] = True
else: # 不是最后一个
new_node['is_end'] = False
now_node[char_str] = new_node
now_node = new_node
def check_match_word(self, txt, begin_index, match_type=MinMatchType):
"""
检查文字中是否包含匹配的字符
:param txt:待检测的文本
:param begin_index: 调用getSensitiveWord时输入的参数,获取词语的上边界index
:param match_type:匹配规则 1:最小匹配规则,2:最大匹配规则
:return:如果存在,则返回匹配字符的长度,不存在返回0
"""
flag = False
match_flag_length = 0 # 匹配字符的长度
now_map = self.root
tmp_flag = 0 # 包括特殊字符的敏感词的长度
for i in range(begin_index, len(txt)):
word = txt[i]
# 检测是否是特殊字符"
if word in self.skip_root and len(now_map) < 100:
# len(nowMap)<100 保证已经找到这个词的开头之后出现的特殊字符
tmp_flag += 1
continue
# 获取指定key
now_map = now_map.get(word)
if now_map: # 存在,则判断是否为最后一个
# 找到相应key,匹配标识+1
match_flag_length += 1
tmp_flag += 1
# 如果为最后一个匹配规则,结束循环,返回匹配标识数
if now_map.get("is_end"):
# 结束标志位为true
flag = True
# 最小规则,直接返回,最大规则还需继续查找
if match_type == MinMatchType:
break
else: # 不存在,直接返回
break
if tmp_flag < 2 or not flag: # 长度必须大于等于1,为词
tmp_flag = 0
return tmp_flag
def get_match_word(self, txt, match_type=MinMatchType):
"""
获取匹配到的词语
:param txt:待检测的文本
:param match_type:匹配规则 1:最小匹配规则,2:最大匹配规则
:return:文字中的相匹配词
"""
matched_word_list = list()
for i in range(len(txt)): # 0---11
length = self.check_match_word(txt, i, match_type)
if length > 0:
word = txt[i:i + length]
matched_word_list.append(word)
# i = i + length - 1
return matched_word_list
def is_contain(self, txt, match_type=MinMatchType):
"""
判断文字是否包含敏感字符
:param txt:待检测的文本
:param match_type:匹配规则 1:最小匹配规则,2:最大匹配规则
:return:若包含返回true,否则返回false
"""
flag = False
for i in range(len(txt)):
match_flag = self.check_match_word(txt, i, match_type)
if match_flag > 0:
flag = True
return flag
def replace_match_word(self, txt, replace_char='*', match_type=MinMatchType):
"""
替换匹配字符
:param txt:待检测的文本
:param replace_char:用于替换的字符,匹配的敏感词以字符逐个替换,如"你是大王八",敏感词"王八",替换字符*,替换结果"你是大**"
:param match_type:匹配规则 1:最小匹配规则,2:最大匹配规则
:return:替换敏感字字符后的文本
"""
tuple_set = self.get_match_word(txt, match_type)
word_set = [i for i in tuple_set]
result_txt = ""
if len(word_set) > 0: # 如果检测出了敏感词,则返回替换后的文本
for word in word_set:
replace_string = len(word) * replace_char
txt = txt.replace(word, replace_string)
result_txt = txt
else: # 没有检测出敏感词,则返回原文本
result_txt = txt
return result_txt
if __name__ == '__main__':
dfa = DFAUtils(word_warehouse=word_warehouse)
print('词库结构:', json.dumps(dfa.root, ensure_ascii=False))
# 待检测的文本
msg = msg
print('是否包含:', dfa.is_contain(msg))
print('相匹配的词:', dfa.get_match_word(msg))
print('替换包含的词:', dfa.replace_match_word(msg))
方法四:AC自动机
ac自动机,就是在tire树的基础上,增加一个fail指针,如果当前点匹配失败,则将指针转移到fail指针指向的地方,这样就不用回溯,而可以路匹配下去了。
详细匹配机制我在这里不过多赘述,关于AC自动机可以参考一下这篇文章:
https://blog.csdn.net/bestsort/article/details/82947639
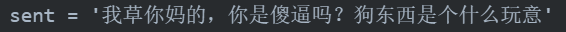
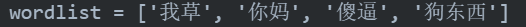
# python3 -m pip install pyahocorasick
import ahocorasick
def build_actree(wordlist):
actree = ahocorasick.Automaton()
for index, word in enumerate(wordlist):
actree.add_word(word, (index, word))
actree.make_automaton()
return actree
if __name__ == '__main__':
actree = build_actree(wordlist=wordlist)
sent_cp = sent
for i in actree.iter(sent):
sent_cp = sent_cp.replace(i[1][1], "**")
print("屏蔽词:",i[1][1])
print("屏蔽结果:",sent_cp)
class TrieNode(object):
__slots__ = ['value', 'next', 'fail', 'emit']
def __init__(self, value):
self.value = value
self.next = dict()
self.fail = None
self.emit = None
class AhoCorasic(object):
__slots__ = ['_root']
def __init__(self, words):
self._root = AhoCorasic._build_trie(words)
@staticmethod
def _build_trie(words):
assert isinstance(words, list) and words
root = TrieNode('root')
for word in words:
node = root
for c in word:
if c not in node.next:
node.next[c] = TrieNode(c)
node = node.next[c]
if not node.emit:
node.emit = {word}
else:
node.emit.add(word)
queue = []
queue.insert(0, (root, None))
while len(queue) > 0:
node_parent = queue.pop()
curr, parent = node_parent[0], node_parent[1]
for sub in curr.next.itervalues():
queue.insert(0, (sub, curr))
if parent is None:
continue
elif parent is root:
curr.fail = root
else:
fail = parent.fail
while fail and curr.value not in fail.next:
fail = fail.fail
if fail:
curr.fail = fail.next[curr.value]
else:
curr.fail = root
return root
def search(self, s):
seq_list = []
node = self._root
for i, c in enumerate(s):
matched = True
while c not in node.next:
if not node.fail:
matched = False
node = self._root
break
node = node.fail
if not matched:
continue
node = node.next[c]
if node.emit:
for _ in node.emit:
from_index = i + 1 - len(_)
match_info = (from_index, _)
seq_list.append(match_info)
node = self._root
return seq_list
if __name__ == '__main__':
aho = AhoCorasic(['foo', 'bar'])
print aho.search('barfoothefoobarman')
评论

