简简单单用OpenCV让一只小猫咪变成奶凶奶凶的科技猫
点击上方“AI算法与图像处理”,选择加"星标"或“置顶”
重磅干货,第一时间送达
导读
Hi,大家好,今天给各位读者分享一个比较酷炫的特效。
下面将会一步一步演示,并 详细分析内部的原因,会尽量用清晰直观的方式,让大家去理解,以收获更多的知识!
效果展示
首先看一下目标效果:
将一只可爱的小猫猫变成一只充满科技感奶凶的猫猫!
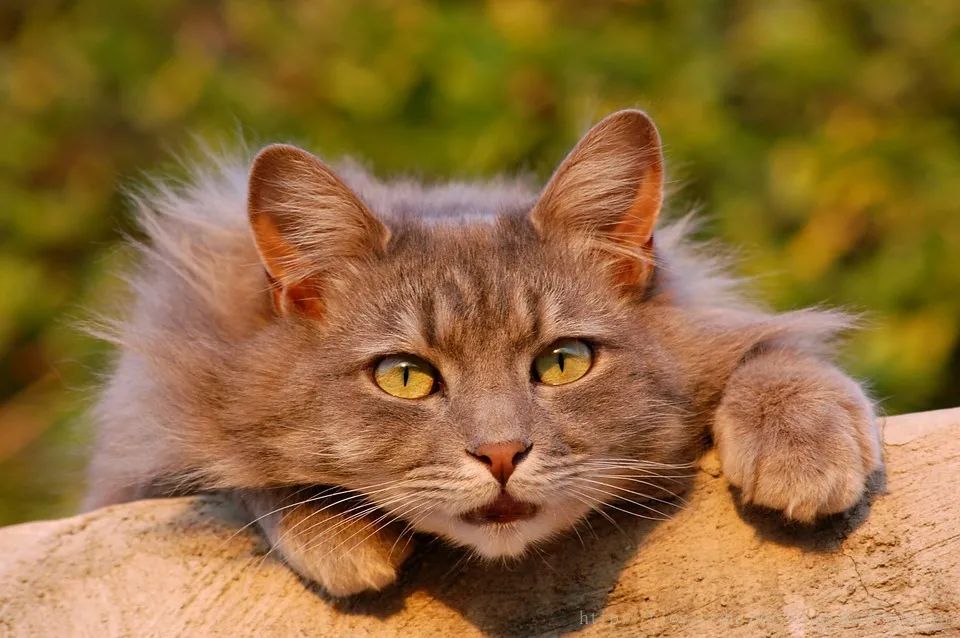

原图
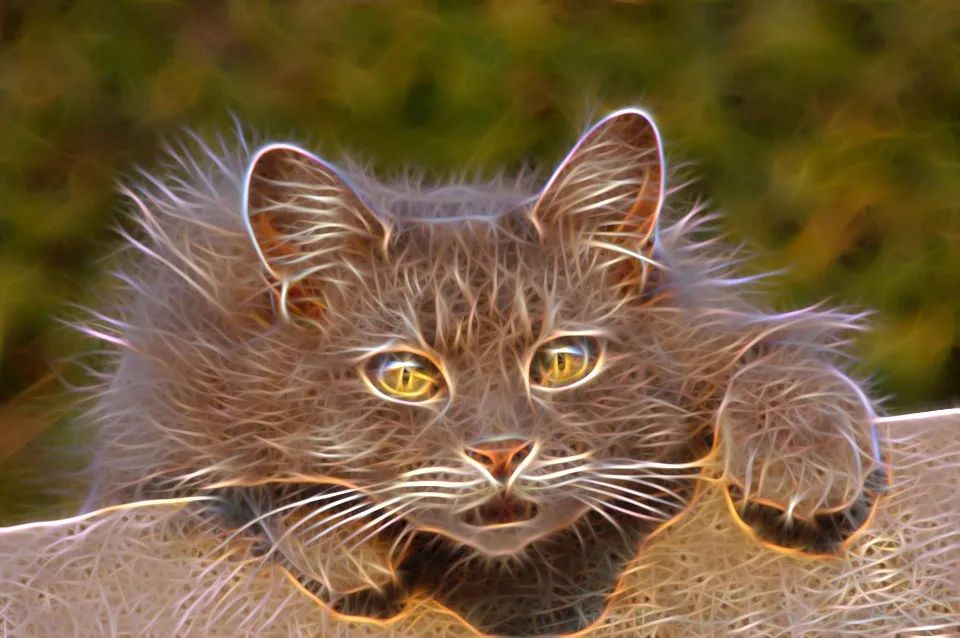

效果图
思路详解 & 代码实现
Gabor 滤波器特征检测
对特征信息进行重复赋值
使用滑动条调整参数
Gabor 变换是一种短时加窗Fourier变换(简单理解起来就是在特定时间窗内做Fourier变换),是短时傅里叶变换中窗函数取为高斯函数时的一种特殊情况。因此,Gabor滤波器可以在频域上不同尺度、不同方向上提取相关的特征。另外,Gabor函数与人眼的作用相仿,所以经常用作纹理识别上,并取得了较好的效果。
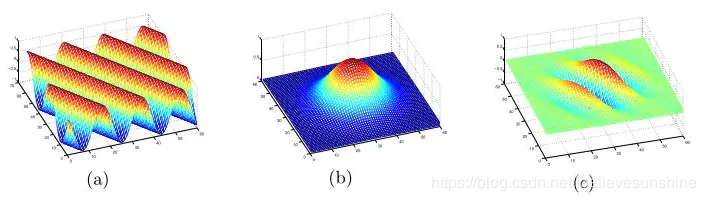
在二维空间中,使用一个三角函数(a)(如正弦函数)与一个高斯函数(b)叠加,我们得到了一个Gabor滤波器(c)。如下图所示:
原理参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/wojianxin/p/12574089.html

https://blog.csdn.net/lhanchao/article/details/55006663
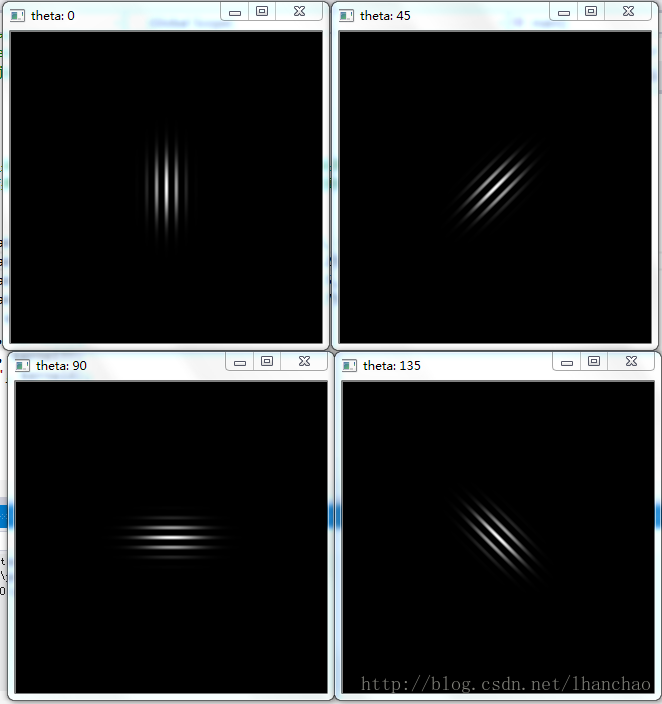
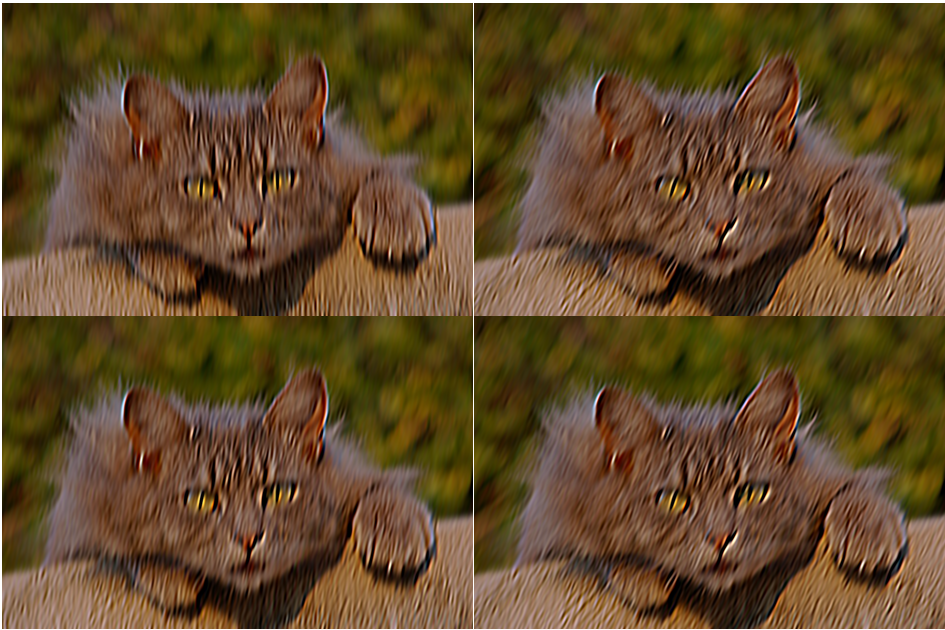
在本文中设置了 16 个不同的滤波器角度,分别检测不同角度
经过每个滤波器处理之后的效果(高能,把我看晕了):

# 创建滤波器(们)def build_filters(a=31):filters = []ksize = aprint(ksize)# 此处创建16个滤波器,只有getGaborKernel的第三个参数theta不同。for theta in np.arange(0, np.pi, np.pi / 16):kern = cv.getGaborKernel((ksize, ksize), 4.0, theta, 10.0, 0.5, 0, ktype=cv.CV_32F)kern /= 1.5*kern.sum()filters.append(kern)
import numpy as npa =[-5,-4,-3,-2,-1,0,1,2,3,4,5]np.maximum(a,0)# 输出 array([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
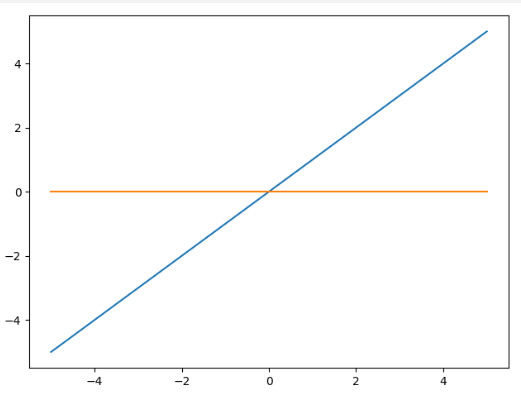
np.maximum 对参数中对应位置的值进行比较,输出较大的值作为最终的结果。
在曲线上表现形式如上图所示,那么对于一张图片又是如何呢?
曲线都是一维的情况,当我们这里处理的是图片时,此时numpy 处理的是三个通道的值,原理还是一样对应位置进行比较。
更加具体的来说,一张图片可以看成是 三通道的, RGB, 为了便于理解,我们假设取其中一个通道 例如 R 通道的值进行比较,那么最终的输出结果,一定是所有结果处理完(不同参数)之后 ,R 通道值最大的结果,同理可以对 G 通道和 B 通道也是 如此,因此最终的输出结果显示的颜色会比较鲜艳,比较亮。
# 重新赋值过程# 将不同滤波器处理的结果,经过 np.maximum 输出每个位置最亮的值def process(img, filters):# zeros_like:返回和输入大小相同,类型相同,用0填满的数组accum = np.zeros_like(img)for kern in filters:fimg = cv.filter2D(img, cv.CV_8UC3, kern)# maximum:逐位比较取其大np.maximum(accum, fimg, accum)return accum
知识点汇总和代码分享
本文简单介绍了 Gabor 滤波器,通过设置不同的滤波器参数来得到我们希望检测的特征,然后对特征进一步出来,展示出来较酷炫的效果。在代码中,我们还会用到 滑动条 以便更加轻松的调节参数。
具体的代码,在下面的内容中分享
后续会将代码和素材更新到项目中:https://github.com/DWCTOD/AI_study 主要需要下面两个代码
from __future__ import print_functionimport numpy as npimport cv2 as cvfrom multiprocessing.pool import ThreadPool# 创建滤波器(们)def build_filters(a=31):filters = []ksize = aprint(ksize)# 此处创建16个滤波器,只有getGaborKernel的第三个参数theta不同。for theta in np.arange(0, np.pi, np.pi / 16):kern = cv.getGaborKernel((ksize, ksize), 4.0, theta, 10.0, 0.5, 0, ktype=cv.CV_32F)kern /= 1.5*kern.sum()filters.append(kern)return filters# 单线程处理def process(img, filters):# zeros_like:返回和输入大小相同,类型相同,用0填满的数组accum = np.zeros_like(img)for kern in filters:fimg = cv.filter2D(img, cv.CV_8UC3, kern)#cv.imshow('fimg',fimg)#cv.waitKey(0)# maximum:逐位比较取其大np.maximum(accum, fimg, accum)return accum# 多线程处理,threadn = 8def process_threaded(img, filters, threadn = 8):accum = np.zeros_like(img)def f(kern):return cv.filter2D(img, cv.CV_8UC3, kern)pool = ThreadPool(processes=threadn)for fimg in pool.imap_unordered(f, filters):np.maximum(accum, fimg, accum)return accumdef nothing(x):passif __name__ == '__main__':import sysfrom common import Timer# 输出文件开头由''' '''包含的注释内容print(__doc__)try:img_fn = sys.argv[1]except:img_fn = 'cat1.jpg'img = cv.imread(img_fn)# 判断图片是否读取成功if img is None:print('Failed to load image file:', img_fn)sys.exit(1)# 增加滑动条cv.namedWindow('result')cv.createTrackbar('a', 'result', 0, 60, nothing)tmp =-1while True:a = cv.getTrackbarPos('a', 'result')print("a:",a)if a == tmp:cv.imshow('result', res2)if cv.waitKey(1) == 27:breakif cv.waitKey(1) == ord('s'):cv.imwrite(str(a)+'.jpg', res2)continuetmp = afilters = build_filters(a)with Timer('running single-threaded'):res1 = process(img, filters)with Timer('running multi-threaded'):res2 = process_threaded(img, filters)print('res1 == res2: ', (res1 == res2).all())# cv.imshow('img', img)cv.imshow('result', res2)if cv.waitKey(1) == 27:break# cv.destroyAllWindows()
还需要将下面的代码保存为 common.py
#!/usr/bin/env python'''This module contains some common routines used by other samples.'''# Python 2/3 compatibilityfrom __future__ import print_functionimport sysPY3 = sys.version_info[0] == 3if PY3:from functools import reduceimport numpy as npimport cv2 as cv# built-in modulesimport osimport itertools as itfrom contextlib import contextmanagerimage_extensions = ['.bmp', '.jpg', '.jpeg', '.png', '.tif', '.tiff', '.pbm', '.pgm', '.ppm']class Bunch(object):def __init__(self, **kw):self.__dict__.update(kw)def __str__(self):return str(self.__dict__)def splitfn(fn):path, fn = os.path.split(fn)name, ext = os.path.splitext(fn)return path, name, extdef anorm2(a):return (a*a).sum(-1)def anorm(a):return np.sqrt( anorm2(a) )def homotrans(H, x, y):xs = H[0, 0]*x + H[0, 1]*y + H[0, 2]ys = H[1, 0]*x + H[1, 1]*y + H[1, 2]s = H[2, 0]*x + H[2, 1]*y + H[2, 2]return xs/s, ys/sdef to_rect(a):a = np.ravel(a)if len(a) == 2:a = (0, 0, a[0], a[1])return np.array(a, np.float64).reshape(2, 2)def rect2rect_mtx(src, dst):src, dst = to_rect(src), to_rect(dst)cx, cy = (dst[1] - dst[0]) / (src[1] - src[0])tx, ty = dst[0] - src[0] * (cx, cy)M = np.float64([[ cx, 0, tx],[ 0, cy, ty],[ 0, 0, 1]])return Mdef lookat(eye, target, up = (0, 0, 1)):fwd = np.asarray(target, np.float64) - eyefwd /= anorm(fwd)right = np.cross(fwd, up)right /= anorm(right)down = np.cross(fwd, right)R = np.float64([right, down, fwd])tvec = -np.dot(R, eye)return R, tvecdef mtx2rvec(R):w, u, vt = cv.SVDecomp(R - np.eye(3))p = vt[0] + u[:,0]*w[0] # same as np.dot(R, vt[0])c = np.dot(vt[0], p)s = np.dot(vt[1], p)axis = np.cross(vt[0], vt[1])return axis * np.arctan2(s, c)def draw_str(dst, target, s):x, y = targetcv.putText(dst, s, (x+1, y+1), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 1.0, (0, 0, 0), thickness = 2, lineType=cv.LINE_AA)cv.putText(dst, s, (x, y), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 1.0, (255, 255, 255), lineType=cv.LINE_AA)class Sketcher:def __init__(self, windowname, dests, colors_func):self.prev_pt = Noneself.windowname = windownameself.dests = destsself.colors_func = colors_funcself.dirty = Falseself.show()cv.setMouseCallback(self.windowname, self.on_mouse)def show(self):cv.imshow(self.windowname, self.dests[0])def on_mouse(self, event, x, y, flags, param):pt = (x, y)if event == cv.EVENT_LBUTTONDOWN:self.prev_pt = ptelif event == cv.EVENT_LBUTTONUP:self.prev_pt = Noneif self.prev_pt and flags & cv.EVENT_FLAG_LBUTTON:for dst, color in zip(self.dests, self.colors_func()):cv.line(dst, self.prev_pt, pt, color, 5)self.dirty = Trueself.prev_pt = ptself.show()# palette data from matplotlib/_cm.py_jet_data = {'red': ((0., 0, 0), (0.35, 0, 0), (0.66, 1, 1), (0.89,1, 1),(1, 0.5, 0.5)),'green': ((0., 0, 0), (0.125,0, 0), (0.375,1, 1), (0.64,1, 1),(0.91,0,0), (1, 0, 0)),'blue': ((0., 0.5, 0.5), (0.11, 1, 1), (0.34, 1, 1), (0.65,0, 0),(1, 0, 0))}cmap_data = { 'jet' : _jet_data }def make_cmap(name, n=256):data = cmap_data[name]xs = np.linspace(0.0, 1.0, n)channels = []eps = 1e-6for ch_name in ['blue', 'green', 'red']:ch_data = data[ch_name]xp, yp = [], []for x, y1, y2 in ch_data:xp += [x, x+eps]yp += [y1, y2]ch = np.interp(xs, xp, yp)channels.append(ch)return np.uint8(np.array(channels).T*255)def nothing(*arg, **kw):passdef clock():return cv.getTickCount() / cv.getTickFrequency()def Timer(msg):print(msg, '...',)start = clock()try:yieldfinally:print("%.2f ms" % ((clock()-start)*1000))class StatValue:def __init__(self, smooth_coef = 0.5):self.value = Noneself.smooth_coef = smooth_coefdef update(self, v):if self.value is None:self.value = velse:c = self.smooth_coefself.value = c * self.value + (1.0-c) * vclass RectSelector:def __init__(self, win, callback):self.win = winself.callback = callbackcv.setMouseCallback(win, self.onmouse)self.drag_start = Noneself.drag_rect = Nonedef onmouse(self, event, x, y, flags, param):x, y = np.int16([x, y]) # BUGif event == cv.EVENT_LBUTTONDOWN:self.drag_start = (x, y)returnif self.drag_start:if flags & cv.EVENT_FLAG_LBUTTON:xo, yo = self.drag_startx0, y0 = np.minimum([xo, yo], [x, y])x1, y1 = np.maximum([xo, yo], [x, y])self.drag_rect = Noneif x1-x0 > 0 and y1-y0 > 0:self.drag_rect = (x0, y0, x1, y1)else:rect = self.drag_rectself.drag_start = Noneself.drag_rect = Noneif rect:self.callback(rect)def draw(self, vis):if not self.drag_rect:return Falsex0, y0, x1, y1 = self.drag_rectcv.rectangle(vis, (x0, y0), (x1, y1), (0, 255, 0), 2)return Truedef dragging(self):return self.drag_rect is not Nonedef grouper(n, iterable, fillvalue=None):'''grouper(3, 'ABCDEFG', 'x') --> ABC DEF Gxx'''args = [iter(iterable)] * nif PY3:output = it.zip_longest(fillvalue=fillvalue, *args)else:output = it.izip_longest(fillvalue=fillvalue, *args)return outputdef mosaic(w, imgs):'''Make a grid from images.w -- number of grid columnsimgs -- images (must have same size and format)'''imgs = iter(imgs)if PY3:img0 = next(imgs)else:img0 = imgs.next()pad = np.zeros_like(img0)imgs = it.chain([img0], imgs)rows = grouper(w, imgs, pad)return np.vstack(map(np.hstack, rows))def getsize(img):h, w = img.shape[:2]return w, hdef mdot(*args):return reduce(np.dot, args)def draw_keypoints(vis, keypoints, color = (0, 255, 255)):for kp in keypoints:x, y = kp.ptcv.circle(vis, (int(x), int(y)), 2, color)
最后
本文详细分析如何实现一直科技猫,同样可以用于你想要测试的图片素材上
感谢看到这里的小伙伴,希望能给个三连支持一下,周末还在努力的打工人!下期见
参考文献:
https://blog.csdn.net/lhanchao/article/details/55006663
http://www.aas.net.cn/fileZDHXB/journal/article/zdhxb/2007/5/PDF/070502.pdf
https://blog.csdn.net/lanchunhui/article/details/52700895
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/33311267
个人微信(如果没有备注不拉群!) 请注明:地区+学校/企业+研究方向+昵称
下载1:何恺明顶会分享
在「AI算法与图像处理」公众号后台回复:何恺明,即可下载。总共有6份PDF,涉及 ResNet、Mask RCNN等经典工作的总结分析
下载2:终身受益的编程指南:Google编程风格指南
在「AI算法与图像处理」公众号后台回复:c++,即可下载。历经十年考验,最权威的编程规范!
下载3 CVPR2020 在「AI算法与图像处理」公众号后台回复:CVPR2020,即可下载1467篇CVPR 2020论文
觉得不错就点亮在看吧