Java 高并发之设计模式
作者:大道方圆
链接:cnblogs.com/xdecode/p/9137793.html
本文主要讲解几种常见并行模式, 具体目录结构如下图.
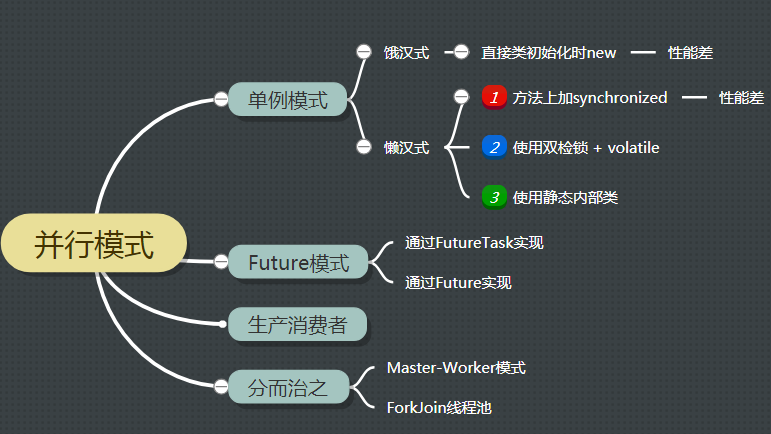
单例
单例是最常见的一种设计模式, 一般用于全局对象管理, 比如xml配置读写之类的.
一般分为懒汉式, 饿汉式.
我公众号 Java 相关的文章整理成了 PDF ,关注微信公众号 Java后端 回复 666 下载。
懒汉式: 方法上加synchronized
1 public static synchronized Singleton getInstance() {
2 if (single == null) {
3 single = new Singleton();
4 }
5 return single;
6 }这种方式, 由于每次获取示例都要获取锁, 不推荐使用, 性能较差
懒汉式: 使用双检锁 + volatile
1 private volatile Singleton singleton = null;
2 public static Singleton getInstance() {
3 if (singleton == null) {
4 synchronized (Singleton.class) {
5 if (singleton == null) {
6 singleton = new Singleton();
7 }
8 }
9 }
10 return singleton;
11 }本方式是对直接在方法上加锁的一个优化, 好处在于只有第一次初始化获取了锁.
后续调用getInstance已经是无锁状态. 只是写法上稍微繁琐点.
至于为什么要volatile关键字, 主要涉及到jdk指令重排, 详见之前的博文: Java内存模型与指令重排
懒汉式: 使用静态内部类
1 public class Singleton {
2 private static class LazyHolder {
3 private static final Singleton INSTANCE = new Singleton();
4 }
5 private Singleton (){}
6 public static final Singleton getInstance() {
7 return LazyHolder.INSTANCE;
8 }
9 }该方式既解决了同步问题, 也解决了写法繁琐问题. 推荐使用改写法.
缺点在于无法响应事件来重新初始化INSTANCE.
饿汉式
1 public class Singleton1 {
2 private Singleton1() {}
3 private static final Singleton1 single = new Singleton1();
4 public static Singleton1 getInstance() {
5 return single;
6 }
7 }缺点在于对象在一开始就直接初始化了.
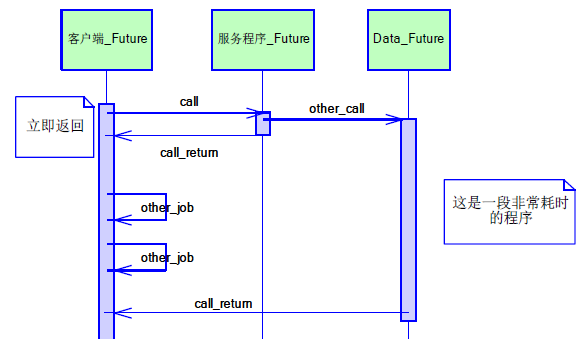
Future模式
该模式的核心思想是异步调用. 有点类似于异步的ajax请求.
当调用某个方法时, 可能该方法耗时较久, 而在主函数中也不急于立刻获取结果.
因此可以让调用者立刻返回一个凭证, 该方法放到另外线程执行,
后续主函数拿凭证再去获取方法的执行结果即可, 其结构图如下
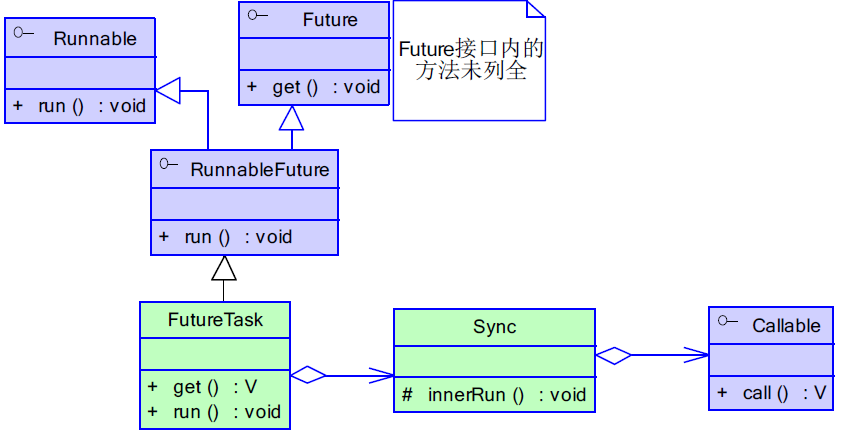
 jdk中内置了Future模式的支持, 其接口如下:
jdk中内置了Future模式的支持, 其接口如下:
通过FutureTask实现
注意其中两个耗时操作.
如果doOtherThing耗时2s, 则整个函数耗时2s左右.
如果doOtherThing耗时0.2s, 则整个函数耗时取决于RealData.costTime, 即1s左右结束.
1 public class FutureDemo1 {
2
3 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
4 FutureTask
future =
new FutureTask
(
new Callable
() {
5
@Override
6
public String call() throws Exception {
7
return
new RealData().costTime();
8 }
9 });
10 ExecutorService service = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
11 service.submit(future);
12
13 System.out.println(
"RealData方法调用完毕");
14
// 模拟主函数中其他耗时操作
15 doOtherThing();
16
// 获取RealData方法的结果
17 System.out.println(future.get());
18 }
19
20
private static void doOtherThing() throws InterruptedException {
21 Thread.sleep(
2000L);
22 }
23 }
24
25
class RealData {
26
27
public String costTime() {
28
try {
29
// 模拟RealData耗时操作
30 Thread.sleep(
1000L);
31
return
"result";
32 }
catch (InterruptedException e) {
33 e.printStackTrace();
34 }
35
return
"exception";
36 }
37
38 }
通过Future实现
与上述FutureTask不同的是, RealData需要实现Callable接口
1 public class FutureDemo2 {
2
3 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
4 ExecutorService service = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
5 Future
future = service.submit(
new RealData2());
6
7 System.out.println(
"RealData2方法调用完毕");
8
// 模拟主函数中其他耗时操作
9 doOtherThing();
10
// 获取RealData2方法的结果
11 System.out.println(future.get());
12 }
13
14
private static void doOtherThing() throws InterruptedException {
15 Thread.sleep(
2000L);
16 }
17 }
18
19
class RealData2 implements Callable<String>{
20
21
public String costTime() {
22
try {
23
// 模拟RealData耗时操作
24 Thread.sleep(
1000L);
25
return
"result";
26 }
catch (InterruptedException e) {
27 e.printStackTrace();
28 }
29
return
"exception";
30 }
31
32
@Override
33
public String call() throws Exception {
34
return costTime();
35 }
36 }
另外Future本身还提供了一些额外的简单控制功能, 其API如下
1 // 取消任务
2 boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning);
3 // 是否已经取消
4 boolean isCancelled();
5 // 是否已经完成
6 boolean isDone();
7 // 取得返回对象
8 V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;
9 // 取得返回对象, 并可以设置超时时间
10 V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
11 throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException;生产消费者模式
生产者-消费者模式是一个经典的多线程设计模式. 它为多线程间的协作提供了良好的解决方案。
在生产者-消费者模式中,通常由两类线程,即若干个生产者线程和若干个消费者线程。
生产者线程负责提交用户请求,消费者线程则负责具体处理生产者提交的任务。
生产者和消费者之间则通过共享内存缓冲区进行通信, 其结构图如下
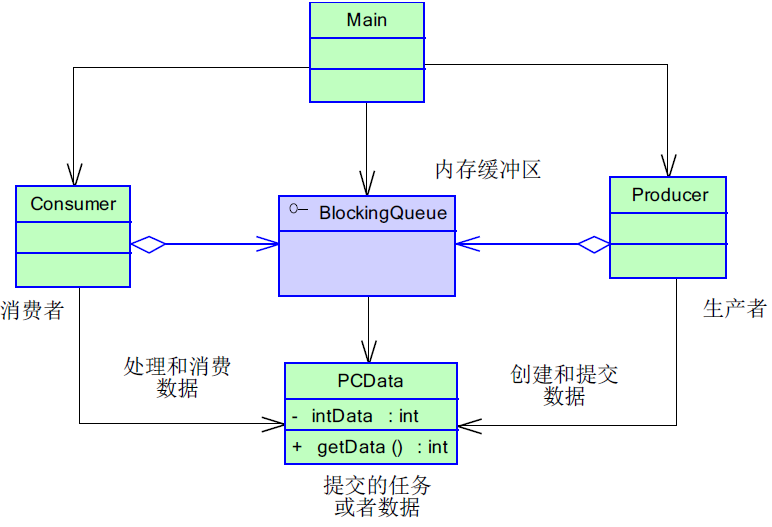
PCData为我们需要处理的元数据模型, 生产者构建PCData, 并放入缓冲队列.
消费者从缓冲队列中获取数据, 并执行计算.
生产者核心代码
1 while(isRunning) {
2 Thread.sleep(r.nextInt(SLEEP_TIME));
3 data = new PCData(count.incrementAndGet);
4 // 构造任务数据
5 System.out.println(data + " is put into queue");
6 if (!queue.offer(data, 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
7 // 将数据放入队列缓冲区中
8 System.out.println("faild to put data : " + data);
9 }
10 }消费者核心代码
1 while (true) {
2 PCData data = queue.take();
3 // 提取任务
4 if (data != null) {
5 // 获取数据, 执行计算操作
6 int re = data.getData() * 10;
7 System.out.println("after cal, value is : " + re);
8 Thread.sleep(r.nextInt(SLEEP_TIME));
9 }
10 }生产消费者模式可以有效对数据解耦, 优化系统结构.
降低生产者和消费者线程相互之间的依赖与性能要求.
一般使用BlockingQueue作为数据缓冲队列, 他是通过锁和阻塞来实现数据之间的同步,
如果对缓冲队列有性能要求, 则可以使用基于CAS无锁设计的ConcurrentLinkedQueue.
分而治之
严格来讲, 分而治之不算一种模式, 而是一种思想.
它可以将一个大任务拆解为若干个小任务并行执行, 提高系统吞吐量.
我们主要讲两个场景, Master-Worker模式, ForkJoin线程池.
Master-Worker模式
该模式核心思想是系统由两类进行协助工作: Master进程, Worker进程.
Master负责接收与分配任务, Worker负责处理任务. 当各个Worker处理完成后,
将结果返回给Master进行归纳与总结.
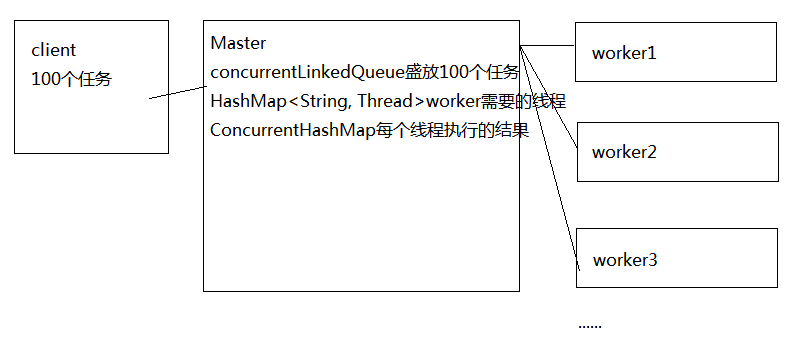
假设一个场景, 需要计算100个任务, 并对结果求和, Master持有10个子进程.
Master代码
1 public class MasterDemo {
2 // 盛装任务的集合
3 private ConcurrentLinkedQueue
workQueue =
new ConcurrentLinkedQueue
();
4
// 所有worker
5
private HashMap
workers =
new HashMap<>();
6
// 每一个worker并行执行任务的结果
7
private ConcurrentHashMap
resultMap =
new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
8
9
public MasterDemo(WorkerDemo worker, int workerCount) {
10
// 每个worker对象都需要持有queue的引用, 用于领任务与提交结果
11 worker.setResultMap(resultMap);
12 worker.setWorkQueue(workQueue);
13
for (
int i =
0; i < workerCount; i++) {
14 workers.put(
"子节点: " + i,
new Thread(worker));
15 }
16 }
17
18
// 提交任务
19
public void submit(TaskDemo task) {
20 workQueue.
add(task);
21 }
22
23
// 启动所有的子任务
24
public void execute(){
25
for (Map.Entry
entry : workers.entrySet()) {
26 entry.getValue().start();
27 }
28 }
29
30
// 判断所有的任务是否执行结束
31
public boolean isComplete() {
32
for (Map.Entry
entry : workers.entrySet()) {
33
if (entry.getValue().getState() != Thread.State.TERMINATED) {
34
return
false;
35 }
36 }
37
38
return
true;
39 }
40
41
// 获取最终汇总的结果
42
public int getResult() {
43
int result =
0;
44
for (Map.Entry
entry : resultMap.entrySet()) {
45 result += Integer.parseInt(entry.getValue().toString());
46 }
47
48
return result;
49 }
50
51 }
Worker代码
1 public class WorkerDemo implements Runnable{
2
3 private ConcurrentLinkedQueue
workQueue;
4
private ConcurrentHashMap
resultMap;
5
6
@Override
7
public void run() {
8
while (
true) {
9 TaskDemo input =
this.workQueue.poll();
10
// 所有任务已经执行完毕
11
if (input ==
null) {
12
break;
13 }
14
// 模拟对task进行处理, 返回结果
15
int result = input.getPrice();
16
this.resultMap.put(input.getId() +
"", result);
17 System.out.println(
"任务执行完毕, 当前线程: " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
18 }
19 }
20
21
public ConcurrentLinkedQueue
getWorkQueue
()
{
22
return workQueue;
23 }
24
25
public void setWorkQueue(ConcurrentLinkedQueue
workQueue)
26
this.workQueue = workQueue;
27 }
28
29
public ConcurrentHashMap
getResultMap
()
{
30
return resultMap;
31 }
32
33
public void setResultMap(ConcurrentHashMap
resultMap)
34
this.resultMap = resultMap;
35 }
36 }
1 public class TaskDemo {
2
3 private int id;
4 private String name;
5 private int price;
6
7 public int getId() {
8 return id;
9 }
10
11 public void setId(int id) {
12 this.id = id;
13 }
14
15 public String getName() {
16 return name;
17 }
18
19 public void setName(String name) {
20 this.name = name;
21 }
22
23 public int getPrice() {
24 return price;
25 }
26
27 public void setPrice(int price) {
28 this.price = price;
29 }
30 }主函数测试
1 MasterDemo master = new MasterDemo(new WorkerDemo(), 10);
2 for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
3 TaskDemo task = new TaskDemo();
4 task.setId(i);
5 task.setName("任务" + i);
6 task.setPrice(new Random().nextInt(10000));
7 master.submit(task);
8 }
9
10 master.execute();
11
12 while (true) {
13 if (master.isComplete()) {
14 System.out.println("执行的结果为: " + master.getResult());
15 break;
16 }
17 }ForkJoin线程池
该线程池是jdk7之后引入的一个并行执行任务的框架, 其核心思想也是将任务分割为子任务,
有可能子任务还是很大, 还需要进一步拆解, 最终得到足够小的任务.
将分割出来的子任务放入双端队列中, 然后几个启动线程从双端队列中获取任务执行.
子任务执行的结果放到一个队列里, 另起线程从队列中获取数据, 合并结果.
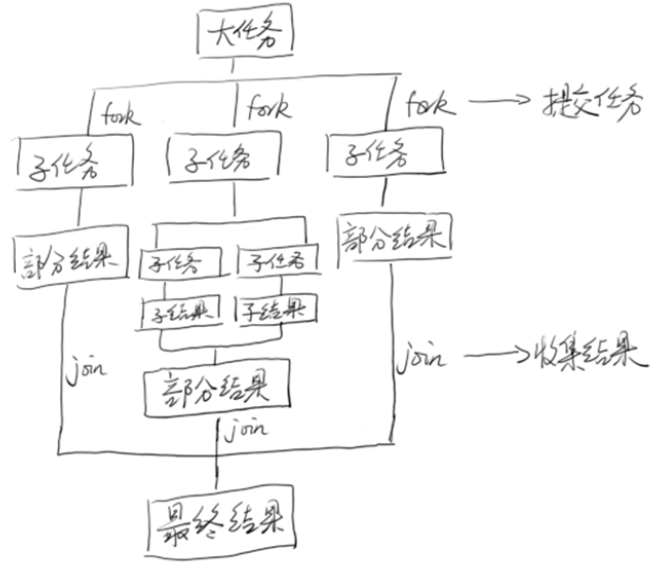
假设我们的场景需要计算从0到20000000L的累加求和. CountTask继承自RecursiveTask, 可以携带返回值.
每次分解大任务, 简单的将任务划分为100个等规模的小任务, 并使用fork()提交子任务.
在子任务中通过THRESHOLD设置子任务分解的阈值, 如果当前需要求和的总数大于THRESHOLD, 则子任务需要再次分解,
如果子任务可以直接执行, 则进行求和操作, 返回结果. 最终等待所有的子任务执行完毕, 对所有结果求和.
1 public class CountTask extends RecursiveTask<Long>{
2 // 任务分解的阈值
3 private static final int THRESHOLD = 10000;
4 private long start;
5 private long end;
6
7
8 public CountTask(long start, long end) {
9 this.start = start;
10 this.end = end;
11 }
12
13 public Long compute() {
14 long sum = 0;
15 boolean canCompute = (end - start) < THRESHOLD;
16 if (canCompute) {
17 for (long i = start; i <= end; i++) {
18 sum += i;
19 }
20 } else {
21 // 分成100个小任务
22 long step = (start + end) / 100;
23 ArrayList
subTasks =
new ArrayList
();
24
long pos = start;
25
for (
int i =
0; i <
100; i++) {
26
long lastOne = pos + step;
27
if (lastOne > end) {
28 lastOne = end;
29 }
30 CountTask subTask =
new CountTask(pos, lastOne);
31 pos += step +
1;
32
// 将子任务推向线程池
33 subTasks.add(subTask);
34 subTask.fork();
35 }
36
37
for (CountTask task : subTasks) {
38
// 对结果进行join
39 sum += task.join();
40 }
41 }
42
return sum;
43 }
44
45
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
46 ForkJoinPool pool =
new ForkJoinPool();
47
// 累加求和 0 -> 20000000L
48 CountTask task =
new CountTask(
0,
20000000L);
49 ForkJoinTask
result = pool.submit(task);
50 System.out.println(
"sum result : " + result.get());
51 }
52 }
ForkJoin线程池使用一个无锁的栈来管理空闲线程, 如果一个工作线程暂时取不到可用的任务, 则可能被挂起.
挂起的线程将被压入由线程池维护的栈中, 待将来有任务可用时, 再从栈中唤醒这些线程.

最后免费给大家分享50个Java项目实战资料,涵盖入门、进阶各个阶段学习内容,可以说非常全面了。大部分视频还附带源码,学起来还不费劲!
附上截图。(下面有下载方式)。




项目领取方式:
扫描下方公众号回复:50,
可获取下载链接
???
?长按上方二维码 2 秒
回复「50」即可获取资料
点赞是最大的支持 
评论
